






Preview text:
Study Question 1: What is motivation?
Planning Ahead — Chapter 14 Study Questions ØWhat is motivation? ØBasic motivational concepts Principles of Management
¡Motivation—the forces within the individual that
ØWhat are the different types of individual needs?
account for the level, direction, and persistence of effort expended at work.
ØWhat are the process theories of motivation?
¡Reward—a work outcome of positive value to the
ØWhat role does reinforcement play in motivation? individual
¡Extrinsic rewards—valued outcomes given to
ØWhat are the challenges of motivation in the new someone by another person. Schermerhorn workplace?
¡Intrinsic rewards—valued outcomes that occur
naturally as a person works on a task.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 2
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 3
Study Question 1: What is motivation?
Study Question 1: What is motivation?
Study Question 2: What are the different types of individual needs? ØTypes of motivation theories
ØTo achieve maximum motivational potential in ØNeeds ¡Content theories
linking rewards to performance,, we should:
lHuman needs and how people with different needs may
¡Unfulfilled physiological and psychological desires of an
respond to different work situations. individual.
¡Respect diversity and individual differences to best ¡Process theories
¡Explain workplace behavior and attitudes.
understand what people want from work.
lHow people give meaning to rewards and make decisions
on various work-related behaviors.
¡Create tensions that influence attitudes and behavior.
¡Allocate rewards to satisfy the interests of both ¡Reinforcement theory
¡Good managers and leaders facilitate employee need
individuals and the organization.
lHow people’s behavior is influenced by environmental consequences. satisfaction.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 4
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 5
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 6 1
Study Question 2: What are the different types of
Study Question 2: What are the different types of
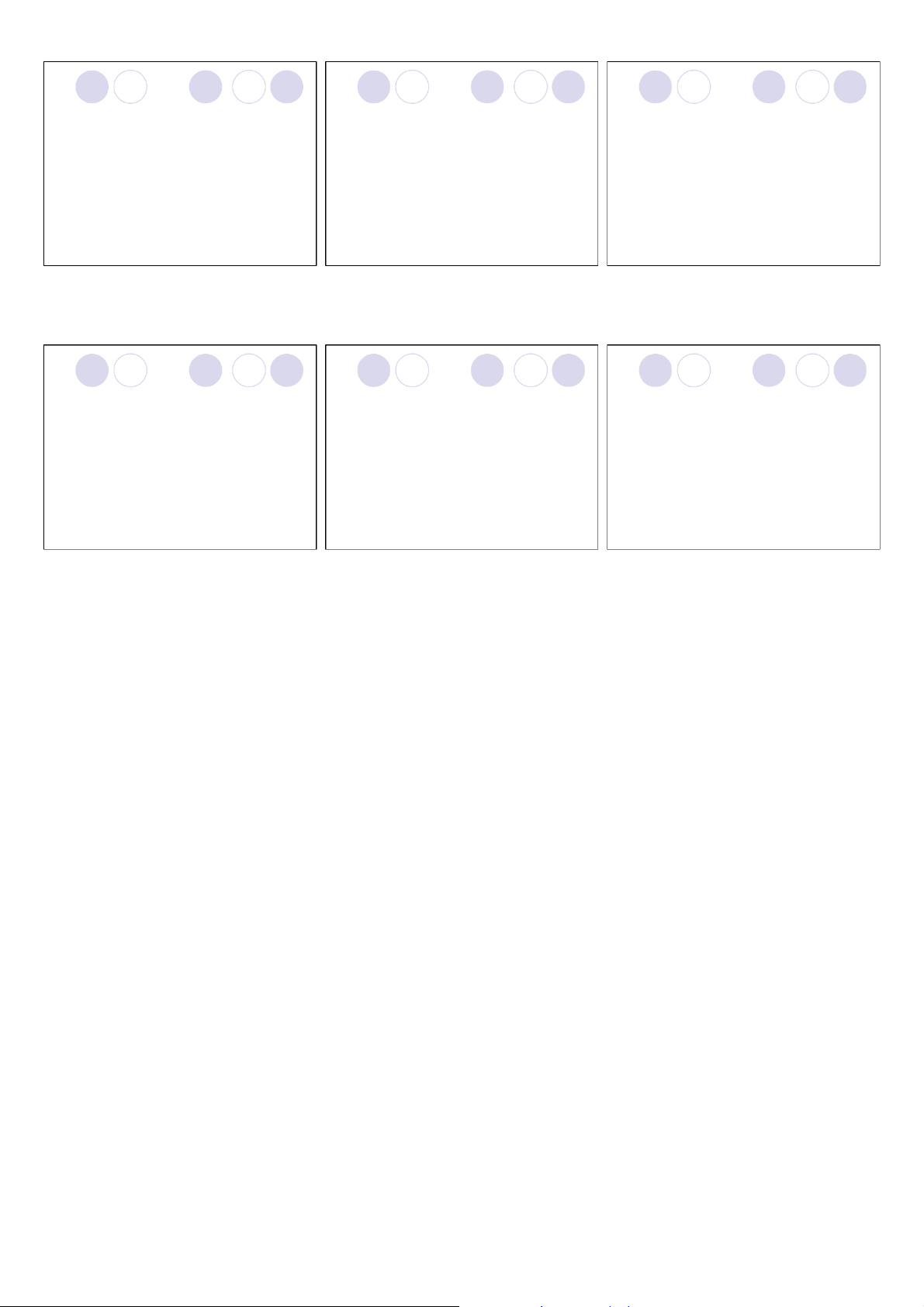
Study Question 2: What are the different types of individual needs? individual needs? individual needs? ØHierarchy of needs theory ØTypes of content theories: ØHierarchy of needs theory ¡Developed by Abraham Maslow.
¡Lower-order and higher-order needs affect workplace ¡Deficit principle lHierarchy of needs theory behavior and attitudes.
lA satisfied need is not a motivator of behavior. Need ¡Lower-order needs: lERG theory for which, a deficit exists.
lPhysiological, safety, and social needs.
lDesires for physical and social well being. ¡Progression principle lTwo-factor theory ¡Higher-order needs:
lA need at one level does not become activated until
lEsteem and self-actualization needs. lAcquired needs theory
the next lower-level need is satisfied.
lDesire for psychological growth and development.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 7
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 8
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 9
Figure 14.1 Opportunities for satisfaction in
Study Question 2: What are the different types of
Study Question 2: What are the different types of
Maslow’s hierarchy of human needs. individual needs? individual needs? ØERG theory ØERG theory
¡Developed by Clayton Alderfer. ¡Three need levels:
¡Any or all needs can influence behavior at one
lExistence needs — desires for physiological and time. material well-being.
lRelatedness needs — desires for satisfying
¡Frustration-regression principle. interpersonal relationships.
lAn already satisfied lower-level need becomes
lGrowth needs — desires for continued psychological
reactivated when a higher-level need is frustrated. growth and development.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 10
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 11
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 12 2
Study Question 2: What are the different types of
Study Question 2: What are the different types of individual needs?
Figure 14.2 Herzberg’s two-factor theory. individual needs? ØTwo-factor theory ØAcquired needs theory
¡Developed by Frederick Herzberg.
¡Developed by David McClelland. ¡Hygiene factors:
¡People acquire needs through their life lElements of the job context. experiences.
lSources of job dissatisfaction. ¡Needs that are acquired: ¡Satisfier factors: lNeed for Achievement (nAch) lElements of the job content. lNeed for Power (nPower)
lSources of job satisfaction and motivation. lNeed for Affiliation (nAff)
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 13
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 14
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 15
Study Question 2: What are the different types of
Study Question 2: What are the different types of
Study Question 2: What are the different types of individual needs? individual needs? individual needs? ØAcquired needs theory ØAcquired needs theory ØAcquired needs theory ¡Need for Achievement (nAch) ¡Need for Power (nPower) ¡Need for Affiliation (nAff)
lDesire to do something better or more efficiently, to
lDesire to control other persons, to influence their
behavior, or to be responsible for other people.
lDesire to establish and maintain friendly and warm
solve problems, or to master complex tasks.
lPersonal power versus social power. relations with other persons.
¡People high in (nAch) prefer work that:
¡People high in (nPower) prefer work that:
¡People high in (nAff) prefer work that:
lInvolves individual responsibility for results.
lInvolves control over other persons.
lInvolves interpersonal relationships.
lInvolves achievable but challenging goals.
lHas an impact on people and events. lProvides for companionship
lProvides feedback on performance.
lBrings public recognition and attention. lBrings social approval.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 16
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 17
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 18 3
Study Question 2: What are the different types of
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of individual needs?
Figure 14.3 Comparison of Maslow’s, Alderfer’s, Herzberg’s, and motivation?
McClelland’s motivation theories.
ØQuestions for summarizing the content
ØProcess theories of motivation … theories of motivation:
¡How people make choices to work hard or not. ¡Choices are based on:
¡How many different individual needs are there? lIndividual preferences. lAvailable rewards.
¡Can a work outcome or reward satisfy more lPossible work outcomes. than one need? ØTypes of process theories:
¡Is there a hierarchy of needs? ¡Equity theory.
¡How important are the various needs? ¡Expectancy theory. ¡Goal-setting theory.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 19
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 20
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 21
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of
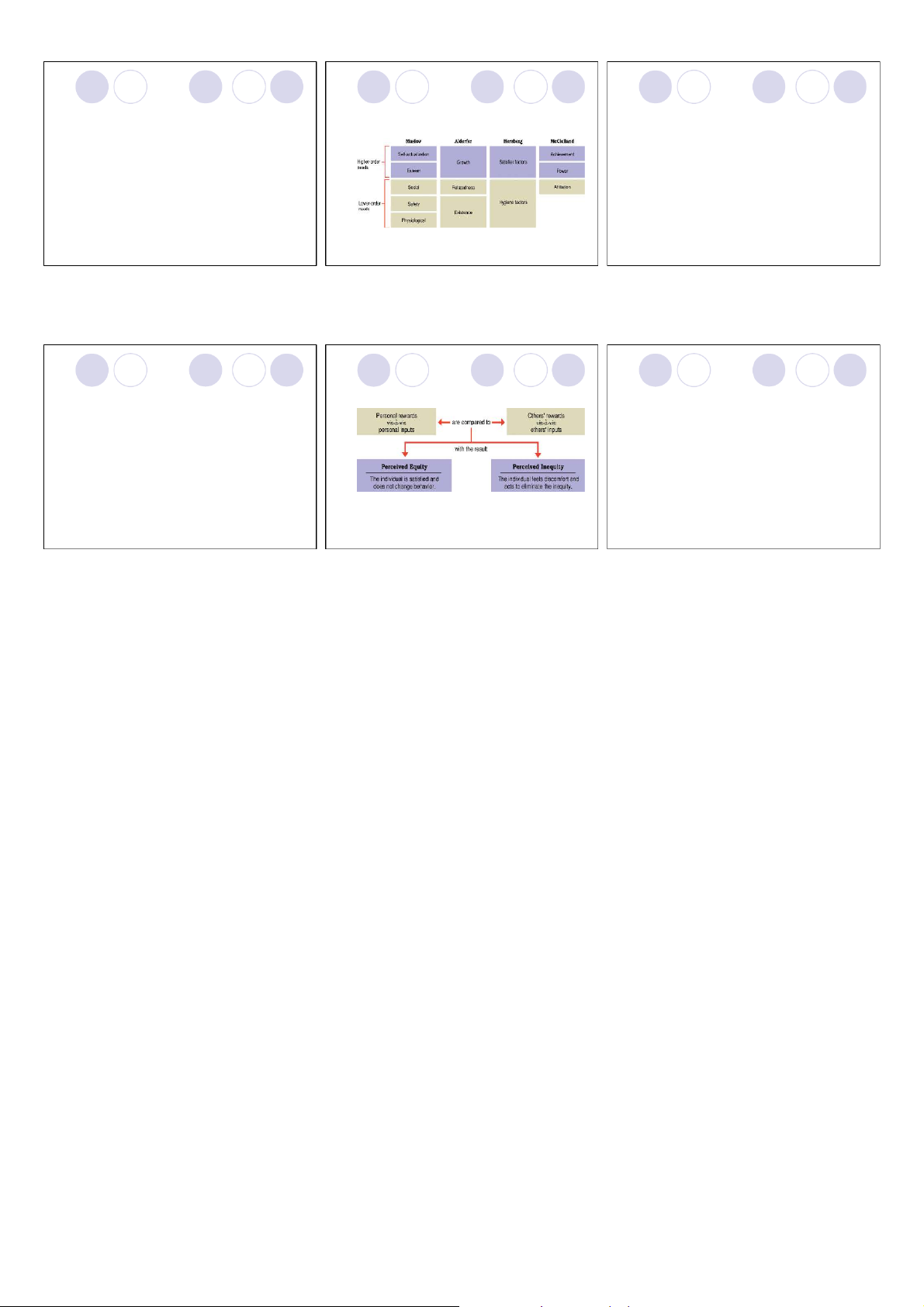
Figure 14.4 Equity theory and the role of social
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of motivation? comparison. motivation? ØEquity theory ØEquity theory ¡Developed by J. Stacy Adams.
¡People respond to perceived negative inequity
¡When people believe that they have been by changing …
treated unfairly in comparison to others, they try lWork inputs.
to eliminate the discomfort and restore a lRewards received.
perceived sense of equity to the situation. lComparison points. lPerceived inequity. lSituation. lPerceived equity.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 22
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 23
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 24 4
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of
Figure 14.5 Elements in the expectancy theory of motivation? motivation? motivation.
ØManagerial implications of equity theory— ØExpectancy theory
¡Underpaid people experience anger. ¡Developed by Victor Vroom.
¡Overpaid people experience guilt.
¡Perceptions of rewards determine motivational
¡Key expectancy theory variables: outcomes.
lExpectancy — belief that working hard will result in
¡Negative consequences of equity comparisons should desired level of performance.
be minimized, if not eliminated.
lInstrumentality — belief that successful performance
¡Do not underestimate the impact of pay as a source of will be followed by rewards.
equity controversies in the workplace.
lValence — value a person assigns to rewards and lGender equity. lComparable worth. other work related outcomes.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 25
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 26
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 27
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of motivation? motivation? motivation? ØExpectancy theory
ØManagerial implications of expectancy
ØManagerial implications of expectancy
¡Motivation (M), expectancy (E), instrumentality theory— theory—
(I), and valence (V) are related to one another
¡To maximize expectancy, managers should: in a multiplicative fashion:
¡To maximize instrumentality, managers should: lSelect workers with ability. M = E x I x V
lClarify psychological contracts. lTrain workers to use ability.
¡If either E, I, or V is low, motivation will
lCommunicate performance-outcome possibilities. lSupport work efforts. be low.
lIdentify rewards that are contingent on performance. lClarify performance goals.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 28
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 29
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 30 5
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of
Figure 14.6 Managerial implications of expectancy
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of motivation? theory. motivation?
ØManagerial implications of expectancy ØGoal-setting theory ¡Developed by Edwin Locke. theory—
¡Properly set and well-managed task goals can be highly
¡To maximize valence in a positive direction, motivating. managers should:
¡Motivational effects of task goals:
lProvide direction to people in their work. lIdentify individual needs.
lClarify performance expectations.
lAdjust rewards to match individual needs.
lEstablish a frame of reference for feedback.
lProvide a foundation for behavioral self-management.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 31
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 32
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 33
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of
Study Question 3: What are the process theories of
Study Question 4: What role does reinforcement play in motivation? motivation? motivation?
ØKey issues and principles in the goal- setting process: ØGoal-setting theory
ØFundamentals of reinforcement theory …
¡Reinforcement theory focuses on the impact of external ¡Set specific goals.
¡Participation in goal setting …
environmental consequences on behavior. ¡Set challenging goals.
lUnlocks the motivational potential of goal setting.
¡Law of effect — impact of type of consequence on future
¡Build goal acceptance and commitment.
behavior. Behavior that results in a pleasant outcome is
lManagement by objectives (MBO) promotes
likely to be repeated. Behavior that results in unpleasant ¡Clarify goal priorities. participation.
outcome is not likely to be repeated.
¡Provide feedback on goal accomplishment.
lWhen participation is not possible, workers will ¡Operant conditioning: ¡Reward goal accomplishment.
respond positively if supervisory trust and support lDeveloped by B.F. Skinner. exist.
lApplies law of effect to control behavior by manipulating its consequences.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 34
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 35
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 36 6
Study Question 4: What role does reinforcement play in
Study Question 4: What role does reinforcement play in
Study Question 4: What role does reinforcement play in motivation? motivation? motivation?
ØFour operant conditioning strategies:
ØOperant conditioning strategies:
ØSuccessful implementation of positive reinforcement is based on … ¡Positive reinforcement ¡Punishment
¡Law of contingent reinforcement —
lIncreases the frequency of a desirable behavior
lDecreases the frequency of a behavior through the
through the contingent presentation of a pleasant
contingent presentation of an unpleasant
lReward delivered only if desired behavior consequence. consequence. is exhibited. ¡Extinction ¡Negative reinforcement
¡Law of immediate reinforcement —
lDecreases the frequency of a behavior through the
lIncreases the frequency of a behavior through the
contingent removal of an pleasant consequence.
lMore immediate the delivery of a reward,
contingent removal of an unpleasant consequence.
the more reinforcement value it has.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 37
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 38
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 39
Study Question 4: What role does reinforcement play in
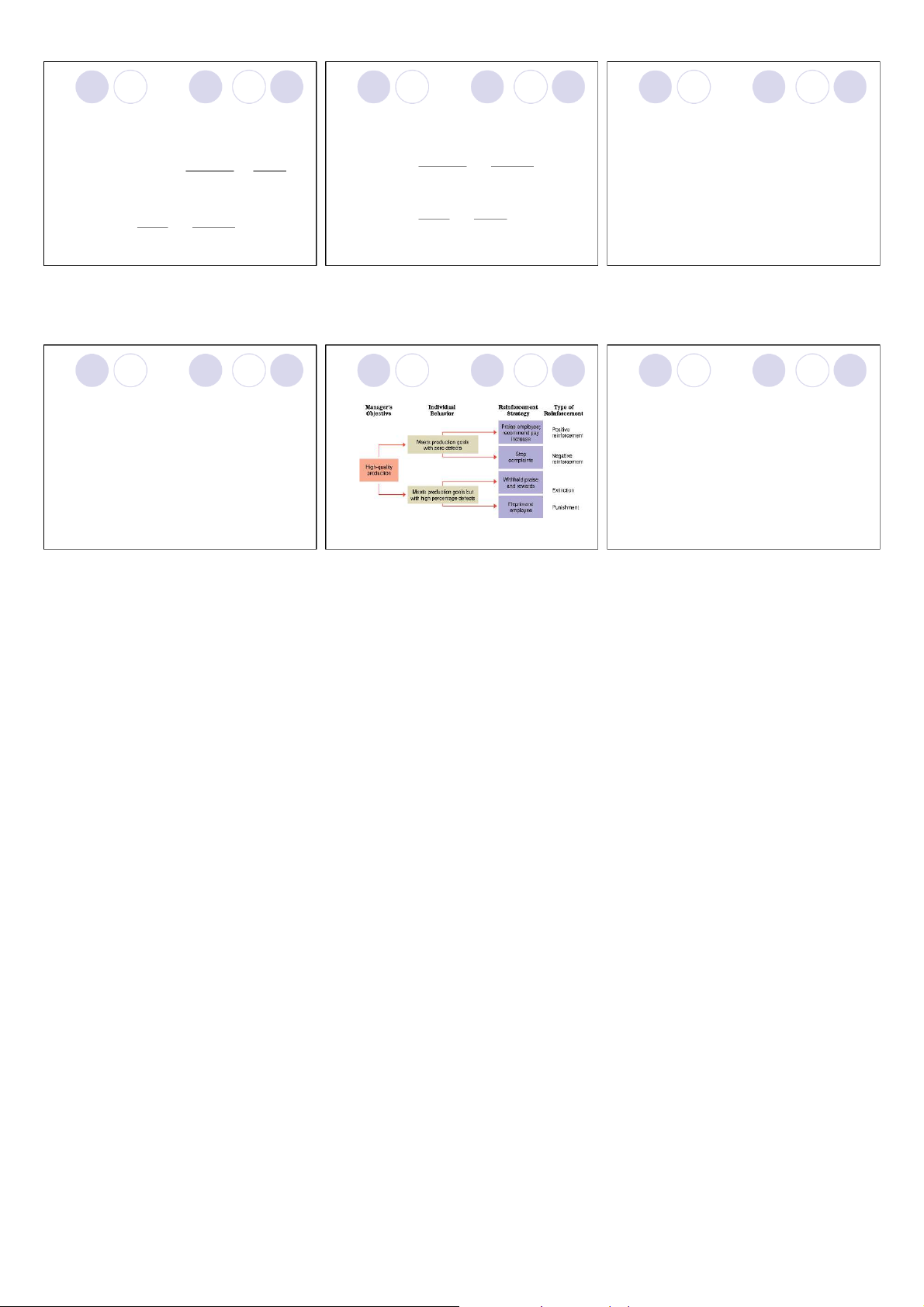
Figure 14.7 Applying reinforcement strategies:
Study Question 4: What role does reinforcement play in motivation?
case of total quality management. motivation?
ØGuidelines for using positive ØSchedules of reinforcement: reinforcement:
¡Continuous reinforcement administers a reward each
¡Clearly identify desired work behaviors.
time a desired behavior occurs.
¡Maintain a diverse inventory of rewards.
¡Intermittent reinforcement rewards behavior only
¡Inform everyone about what must be done to periodically. get rewards.
¡Acquisition of behavior is quicker with continuous
¡Recognize individual differences when reinforcement. allocating rewards.
¡Behavior acquired under an intermittent schedule is
¡Follow the laws of immediate and contingent more permanent. reinforcement.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 40
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 41
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 42 7
Study Question 4: What role does reinforcement play in
Study Question 4: What role does reinforcement play in
Study Question 5: What are the challenges of motivation motivation? motivation? in the new workplace?
ØGuidelines for using punishment:
ØEthical issues in reinforcement:
ØIntegrated model of motivation
¡Tell the person what is being done wrong. ¡Ignores individuality.
¡Motivation leads to work effort that, when combined with
appropriate individual abilities and organizational
¡Tell the person what is being done right. ¡Restricts freedom of choice.
support, leads to performance accomplishment.
¡Match the punishment to the behavior.
¡Ignores the possibility of other types of motivation.
¡The motivational impact of any rewards received for this
¡Administer punishment in private.
ØKey concern is whether it is ethical to not control
performance accomplishment depends on equity and reinforcement considerations.
¡Follow laws of immediate and contingent
behavior well enough to serve both individual
¡Ultimately, satisfaction with rewards should lead to reinforcement. and organizational goals.
increased motivation to work hard in the future.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 43
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 44
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 45
Figure 14.8 An integrated approach to motivational
Study Question 5: What are the challenges of motivation
Study Question 5: What are the challenges of motivation dynamics. in the new workplace? in the new workplace? ØPay for performance
ØIncentive compensation systems:
¡Paying people for performance is consistent with: ¡Skill-based pay. lEquity theory. lExpectancy theory.
lLinks pay to the number of job-relevant skills an lReinforcement theory. employee masters. ¡Merit pay ¡Bonus pay plans.
lAwards a pay increase in proportion to individual performance contributions.
lOne-time or lump-sum payments based on the
lProvides performance contingent reinforcement.
accomplishment of specific performance targets
lMay not succeed due to weakness in performance
or some extraordinary contribution.
appraisal system or lack of consistency in application.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 46
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 47
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 48 8
Study Question 5: What are the challenges of motivation in the new workplace? COPYRIGHT
ØIncentive compensation systems:
Copyright © 2007 John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd. All rights
reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that ¡Profit-sharing plans.
permitted by Access Copyright (The Canadian Copyright Licensing
Agency) is unlawful. Requests for further information should be
lSome or all employees receive a proportion of net
addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons
profits earned by the organization.
Canada, Ltd. The purchaser may make back-up copies for his or
her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The author and ¡Gain-sharing plans.
the publisher assume no responsibility for errors, omissions, or
lGroups of employees share in any savings realized
damages caused by the use of these programs or from the use of
the information contained herein.
through their efforts to reduce costs and increase productivity.
¡Employee stock ownership plans.
lEmployees own stock in the company that employs them.
Management Fundamentals - Chapter 14 49 9




