





Preview text:
TOPIC 1. ATOMIC STRUCTURE PGS.TS. PHẠM CHIẾN THẮNG
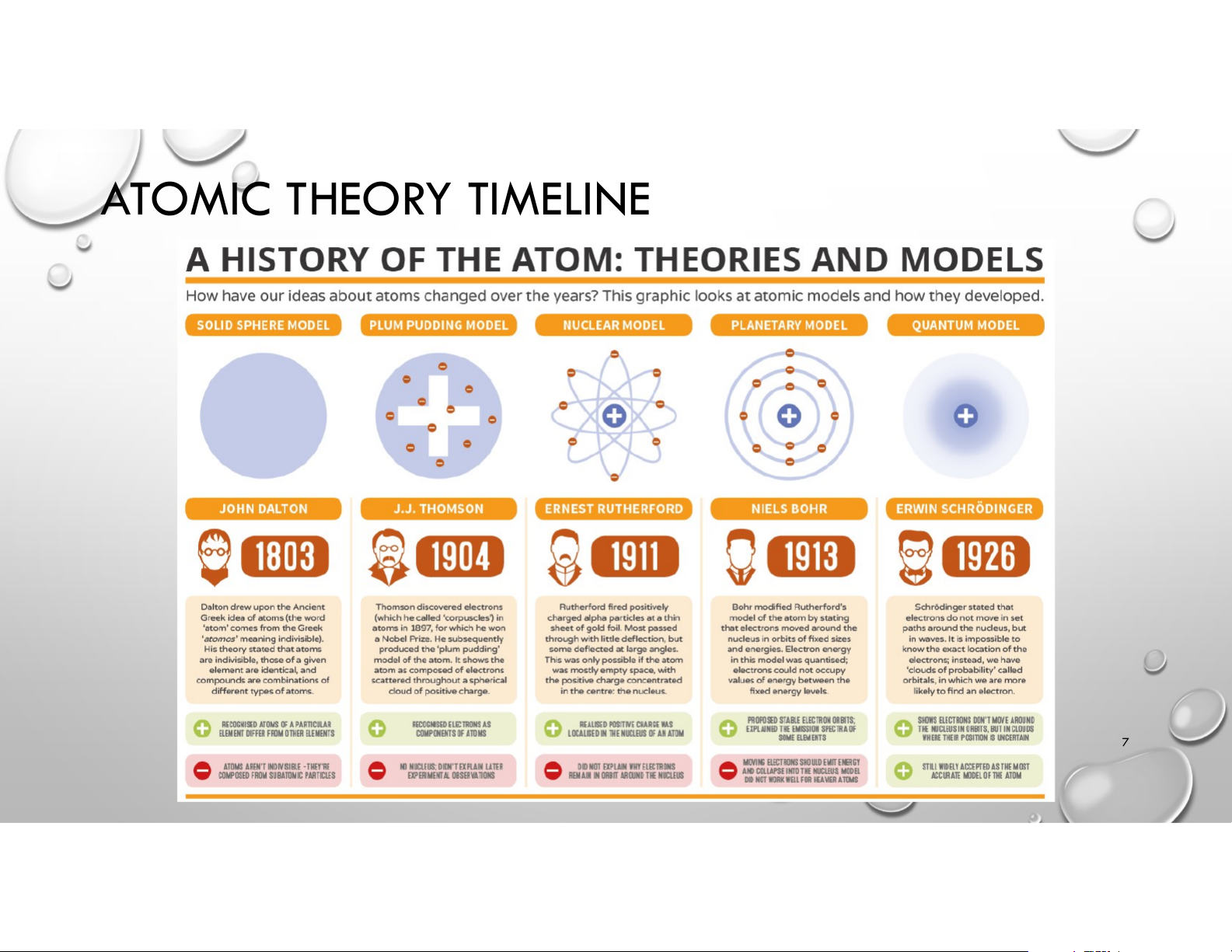
KHOA HÓA HỌC – HUS – VNU 1 OUTLINE • History of Atomic Theory • Modern Atomic Structure
• Electronic Structure of Atoms 2 WHAT IS ATOM?
• Greek philosopher Democritus
• Fundamental “stuff” atomos (460–370 BCE)
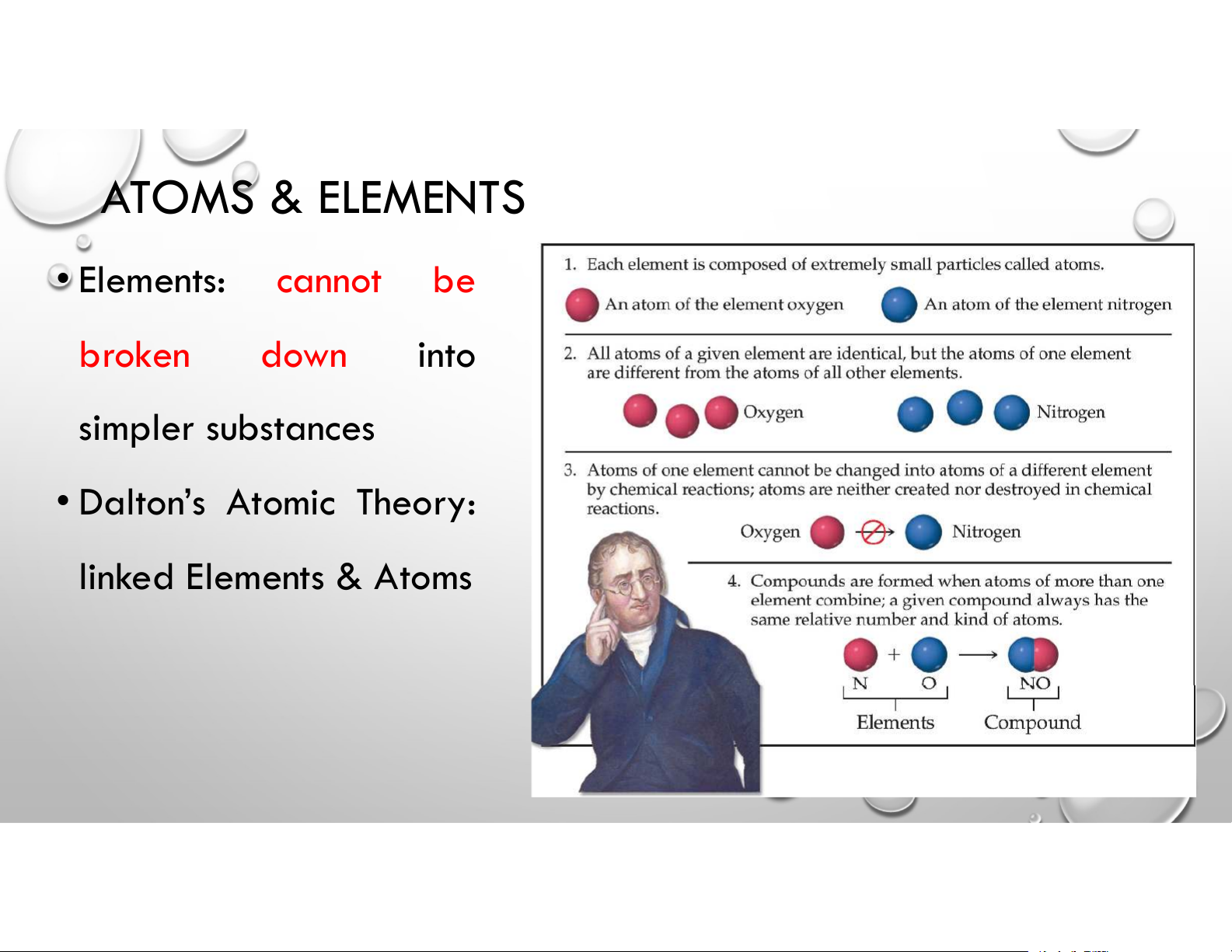
~ tiny “indivisible” particles 3 ATOMS & ELEMENTS • Elements: cannot be broken down into simpler substances • Dalton’s Atomic Theory: linked Elements & Atoms SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
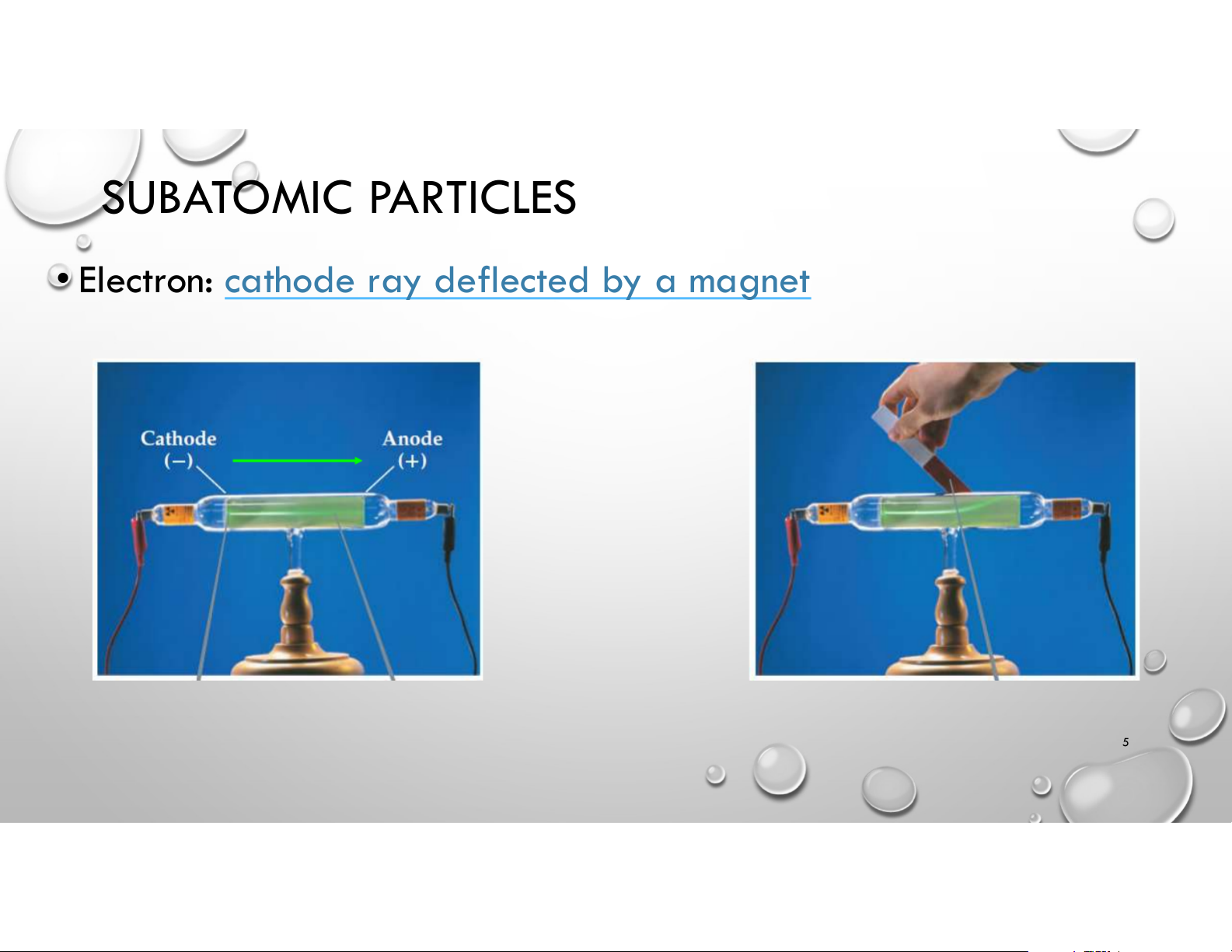
• Electron: cathode ray deflected by a magnet 5 SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
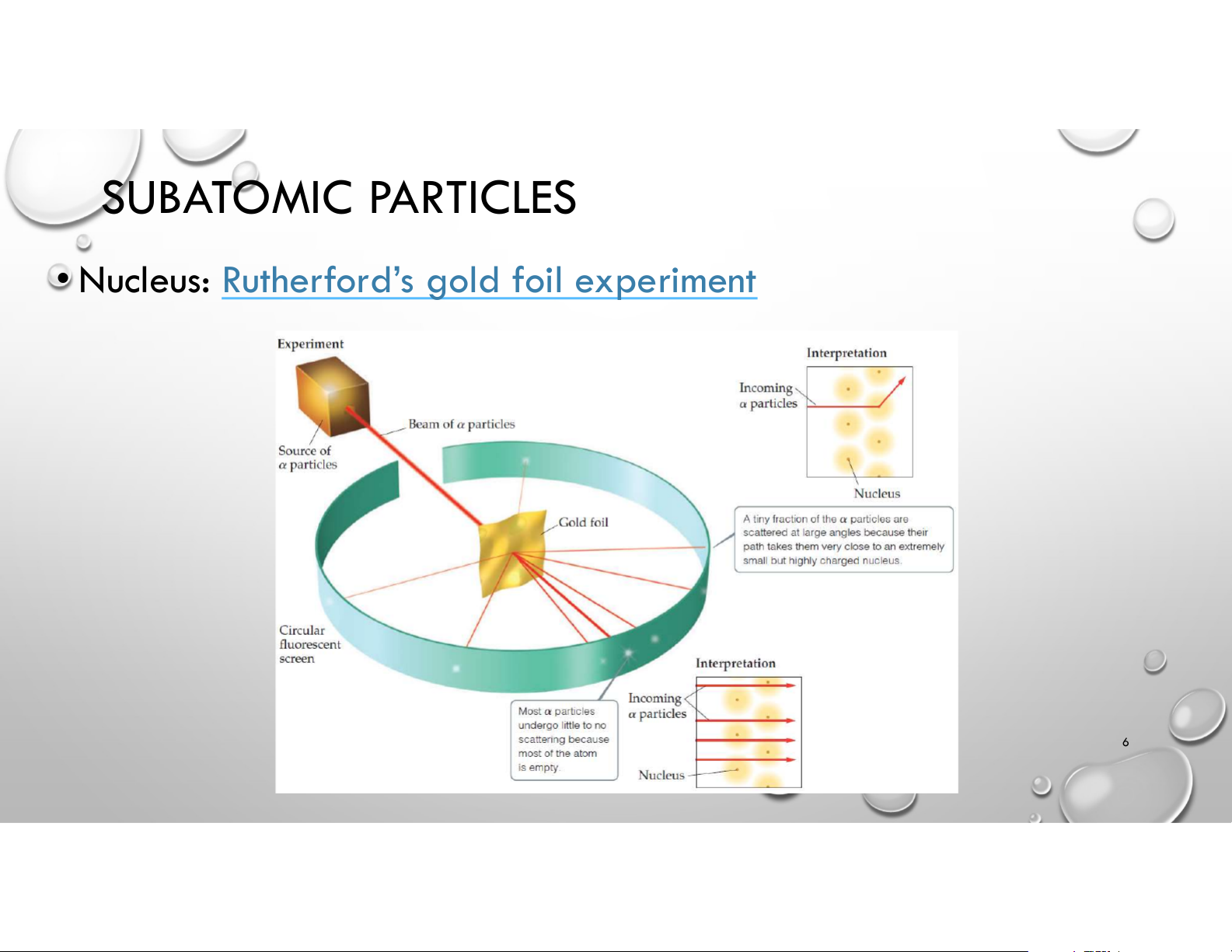
• Nucleus: Rutherford’s gold foil experiment 6 ATOMIC THEORY TIMELINE 7 OUTLINE • History of Atomic Theory • Modern Atomic Structure
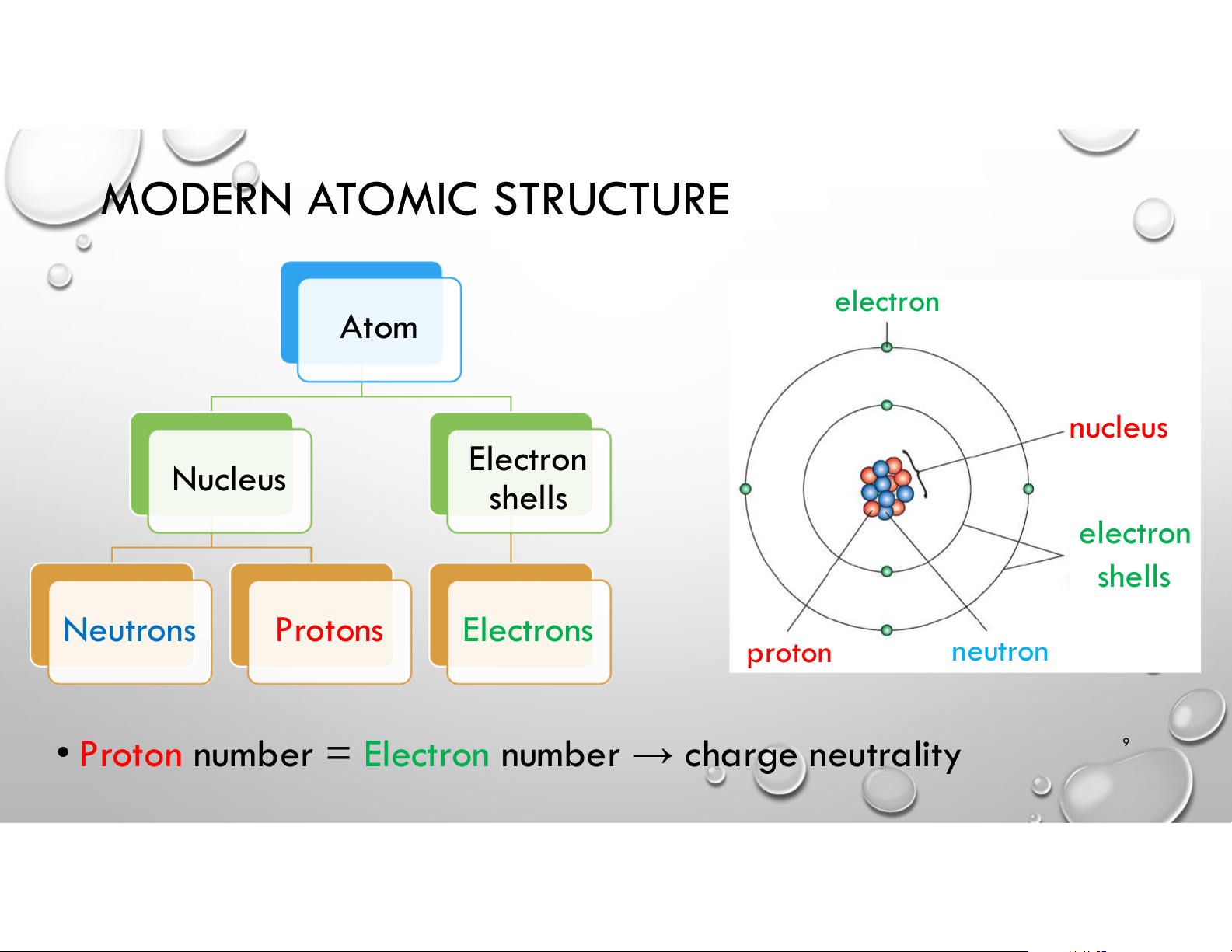
• Electronic Structure of Atoms 8 MODERN ATOMIC STRUCTURE electron Atom nucleus Electron Nucleus shells electron shells Neutrons Protons Electrons proton neutron
• Proton number = Electron number → charge neutrality 9 MODERN ATOMIC STRUCTURE
• Atom is tiny, but nucleus is far tinier → atom is almost empty!!! Atom Nucleus
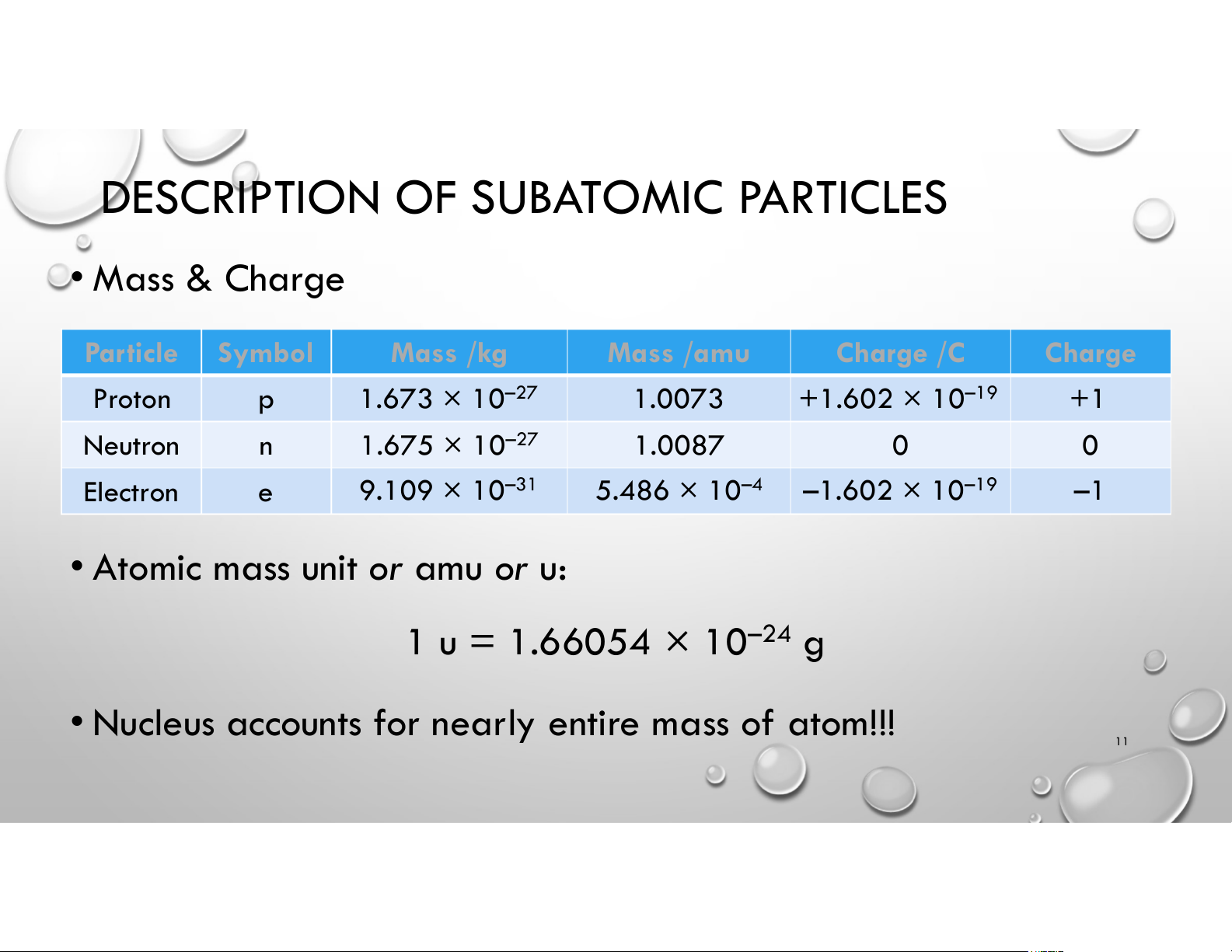
DESCRIPTION OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES • Mass & Charge Particle Symbol Mass /kg Mass /amu Charge /C Charge Proton 1.673 × 10–27 p +1.602 × 10–19 1.0073 +1 Neutron 1.675 × 10–27 n 1.0087 0 0 Electron –1.602 × 10–19 5.486 × 10–4 9.109 × 10–31 e –1
• Atomic mass unit or amu or u: 1 u = 1.66054 × 10–24 g
• Nucleus accounts for nearly entire mass of atom!! 11
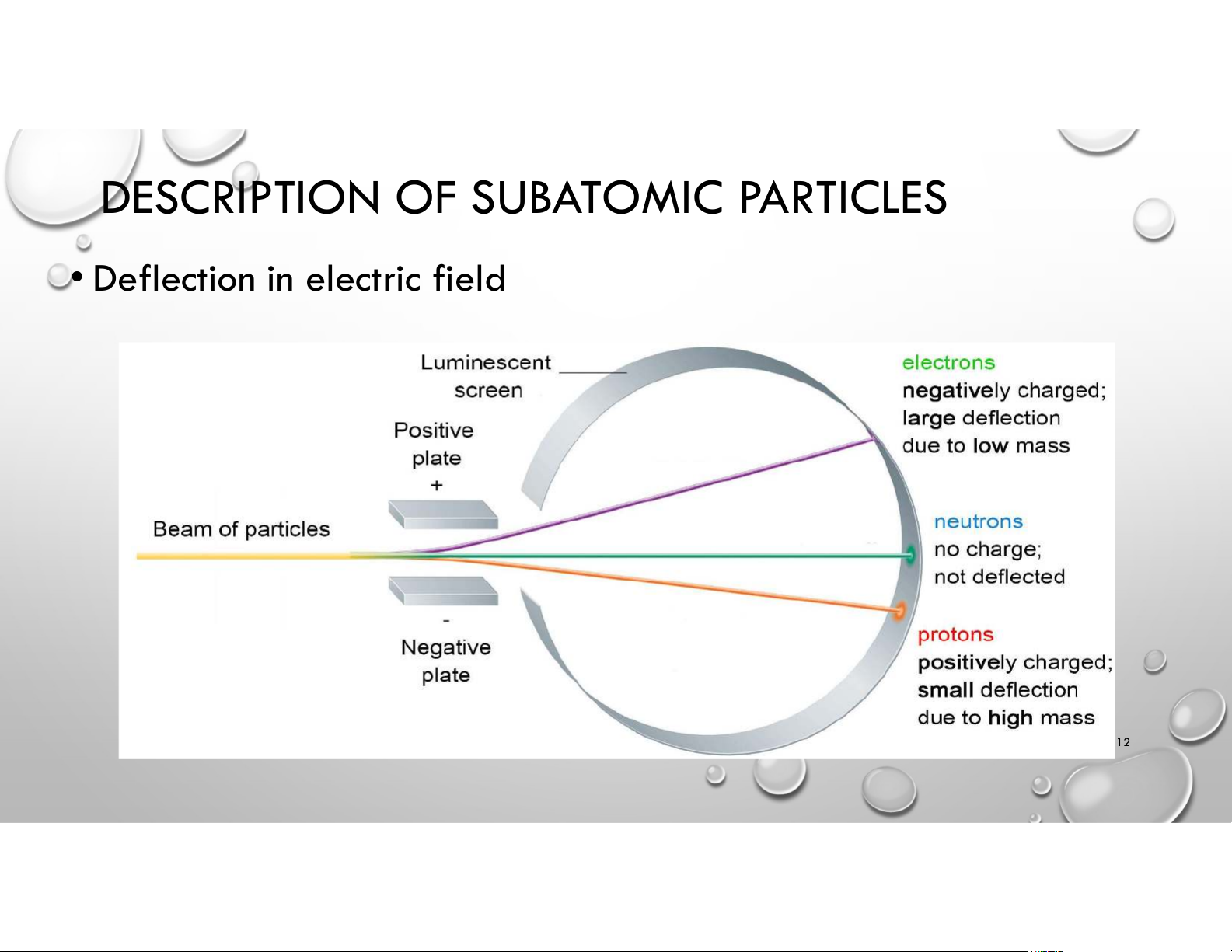
DESCRIPTION OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
• Deflection in electric field 12
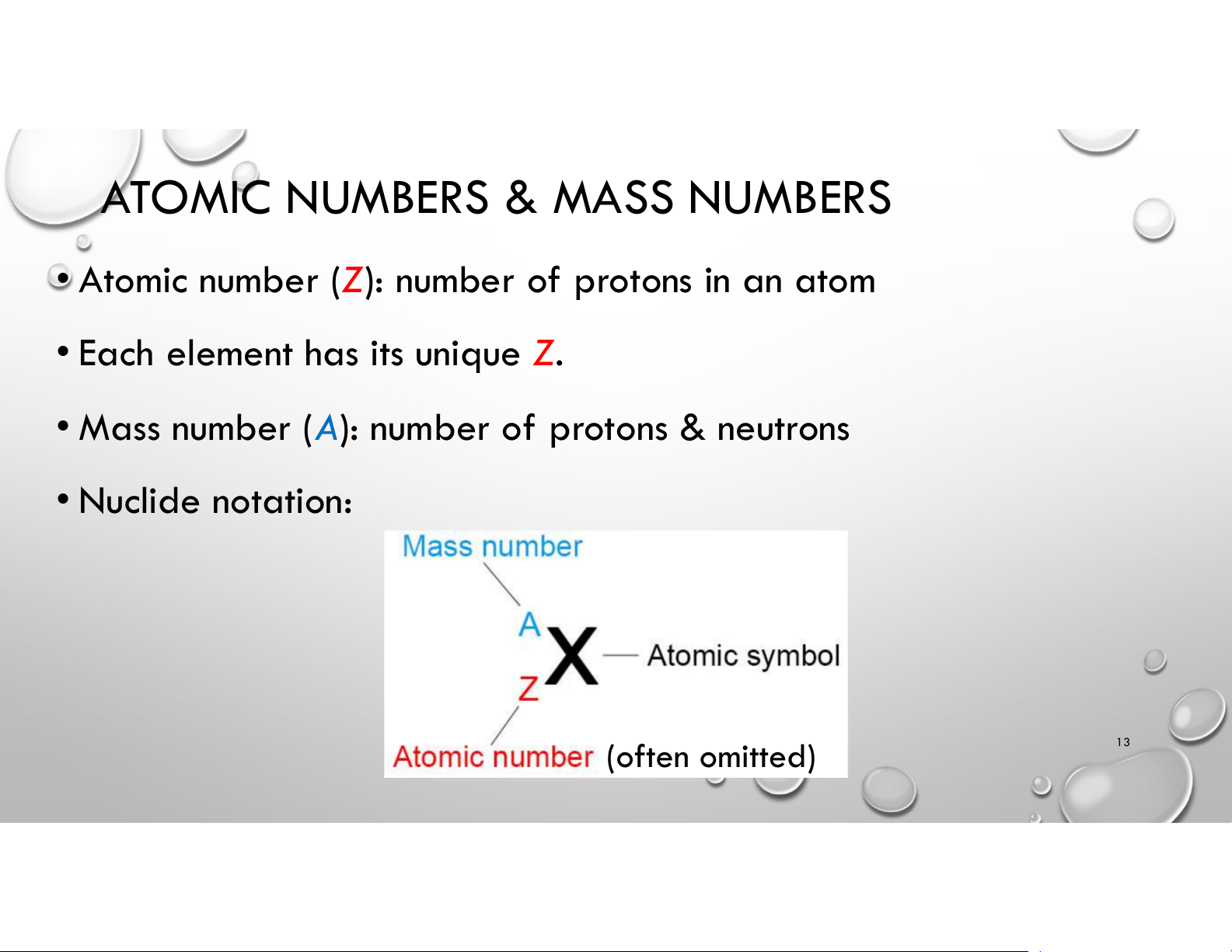
ATOMIC NUMBERS & MASS NUMBERS • Atomic number ( ): Z number of protons in an atom
• Each element has its unique Z.
• Mass number (A): number of protons & neutrons • Nuclide notation: 13 (often omitted) ISOTOPES
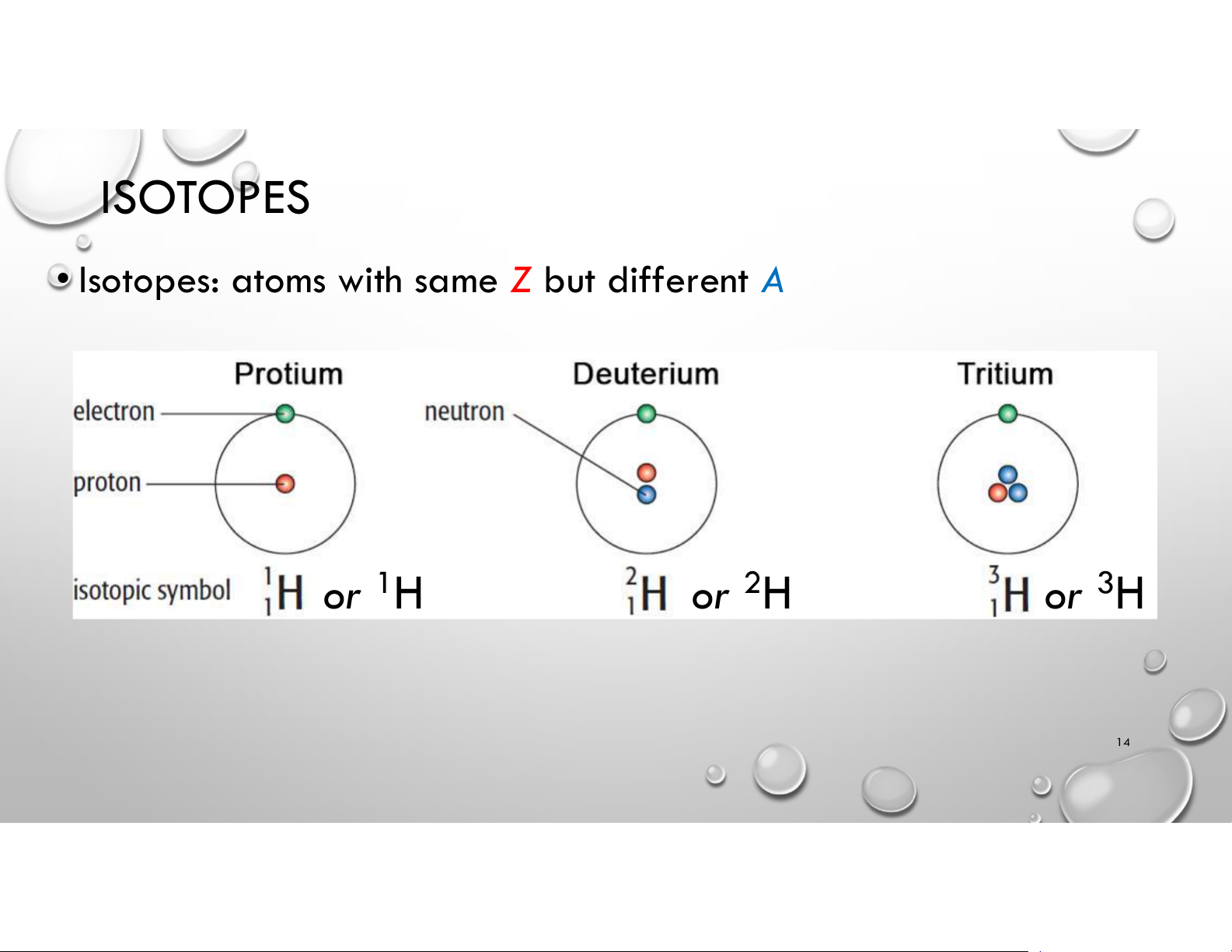
• Isotopes: atoms with same Z but different A or 1H or 2H or 3H 14 ISOTOPES
• Different physical properties
e.g., small differences in mass or in density
• Same chemical properties due to the same number of electrons 15 ISOTOPES
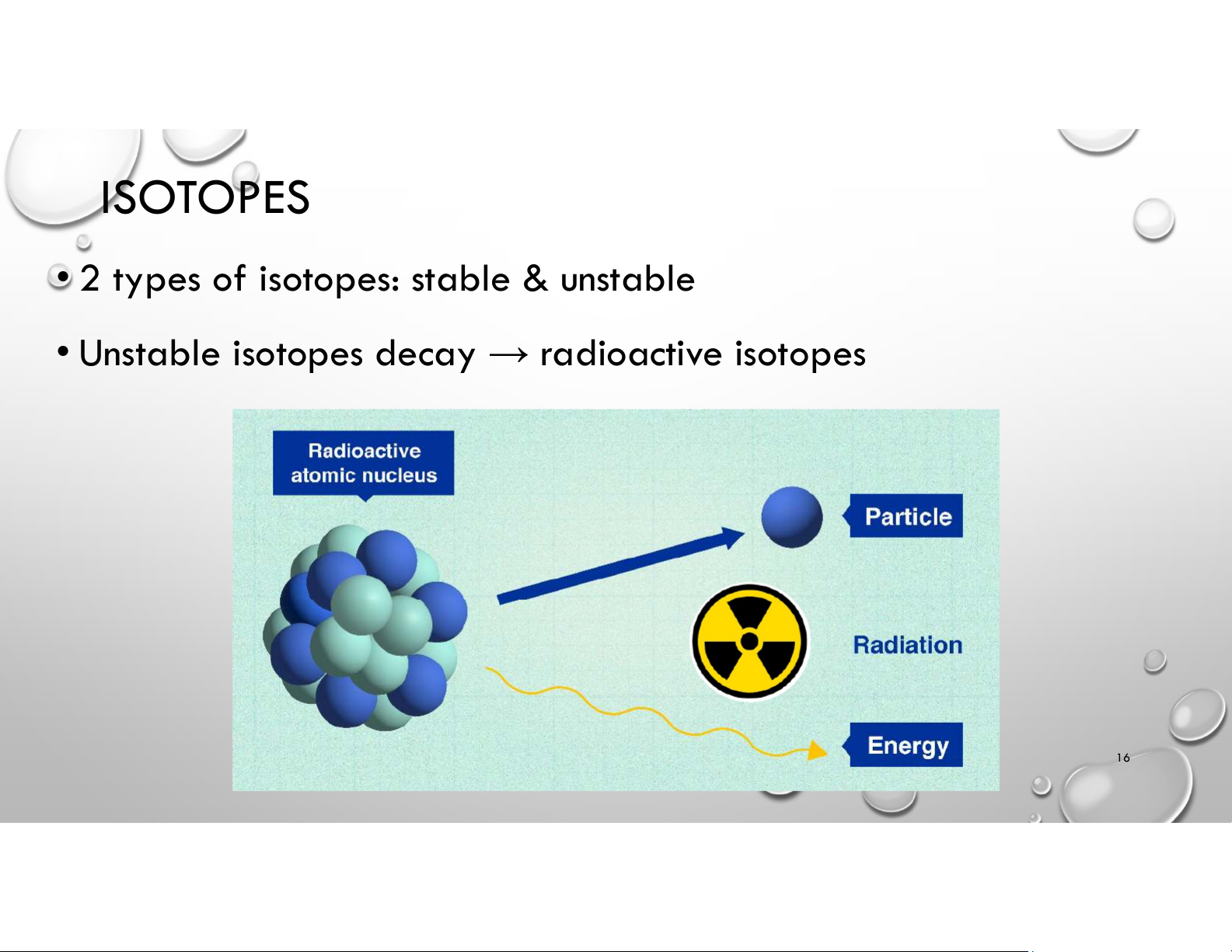
• 2 types of isotopes: stable & unstable
• Unstable isotopes decay → radioactive isotopes 16 ISOTOPES
• Application of radioactive isotopes: Nuclear power plant Radiometric dating Radiotherapy 17 ISOTOPES
• Different physical properties
e.g., small differences in mass or in density
• Same chemical properties due to the same number of electrons 18 MASS OF ATOMS
• Atoms of different elements have different masses.
• Mass of a single atom is too small → weigh a lot of atoms →
compare this mass with mass of same number of ‘standard’ atoms →
unified atomic mass unit (amu/ u)
• ‘Standard’ atoms: isotope of carbon-12 1 amu/ u = 1.66×10–27 kg MASS OF ATOMS
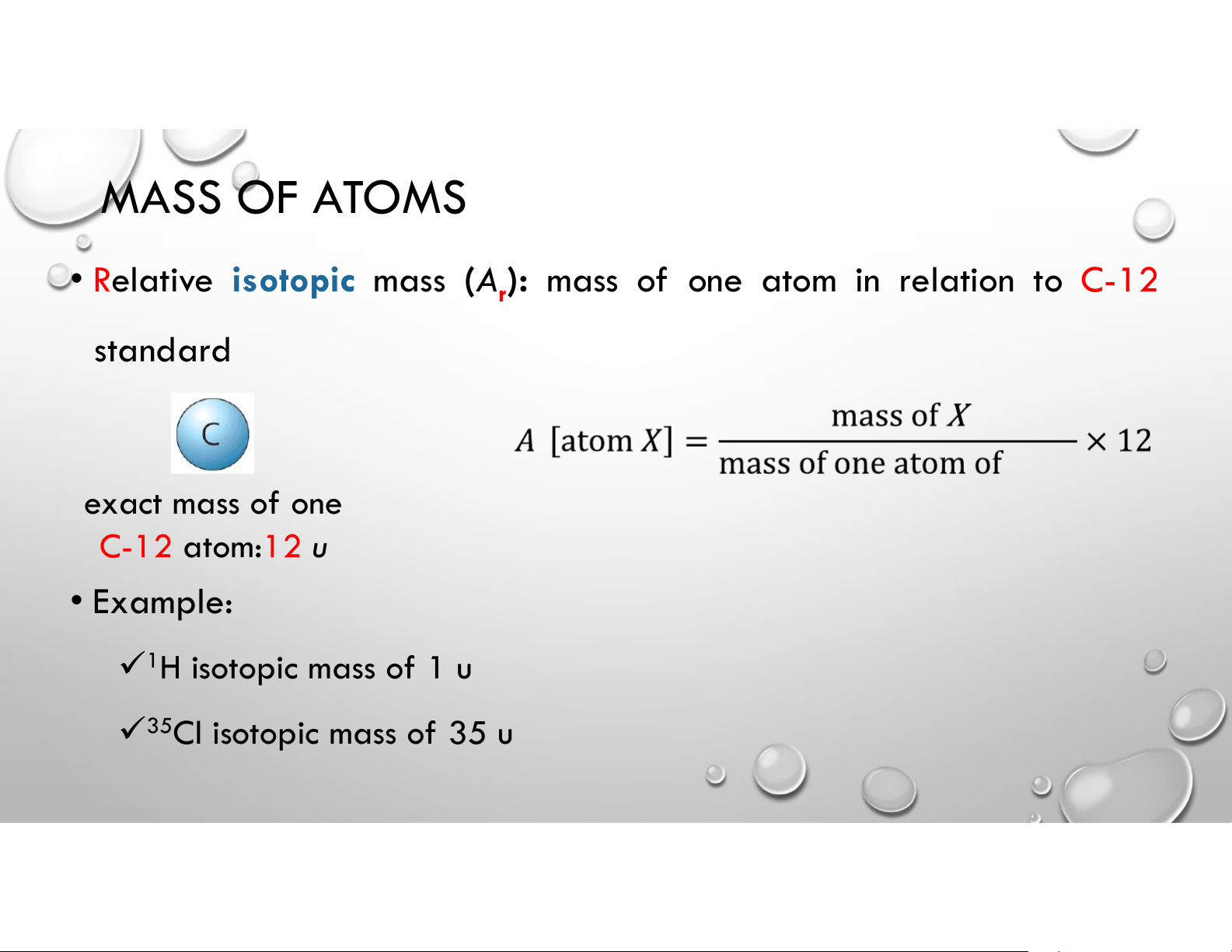
• Relative isotopic mass (A ): mass of one atom in relation to C-12 r standard exact mass of one C-12 atom:12 u • Example: 1H isotopic mass of 1 u 35Cl isotopic mass of 35 u




