



Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 50205883
Chương 3: Debt (fixed income) Market
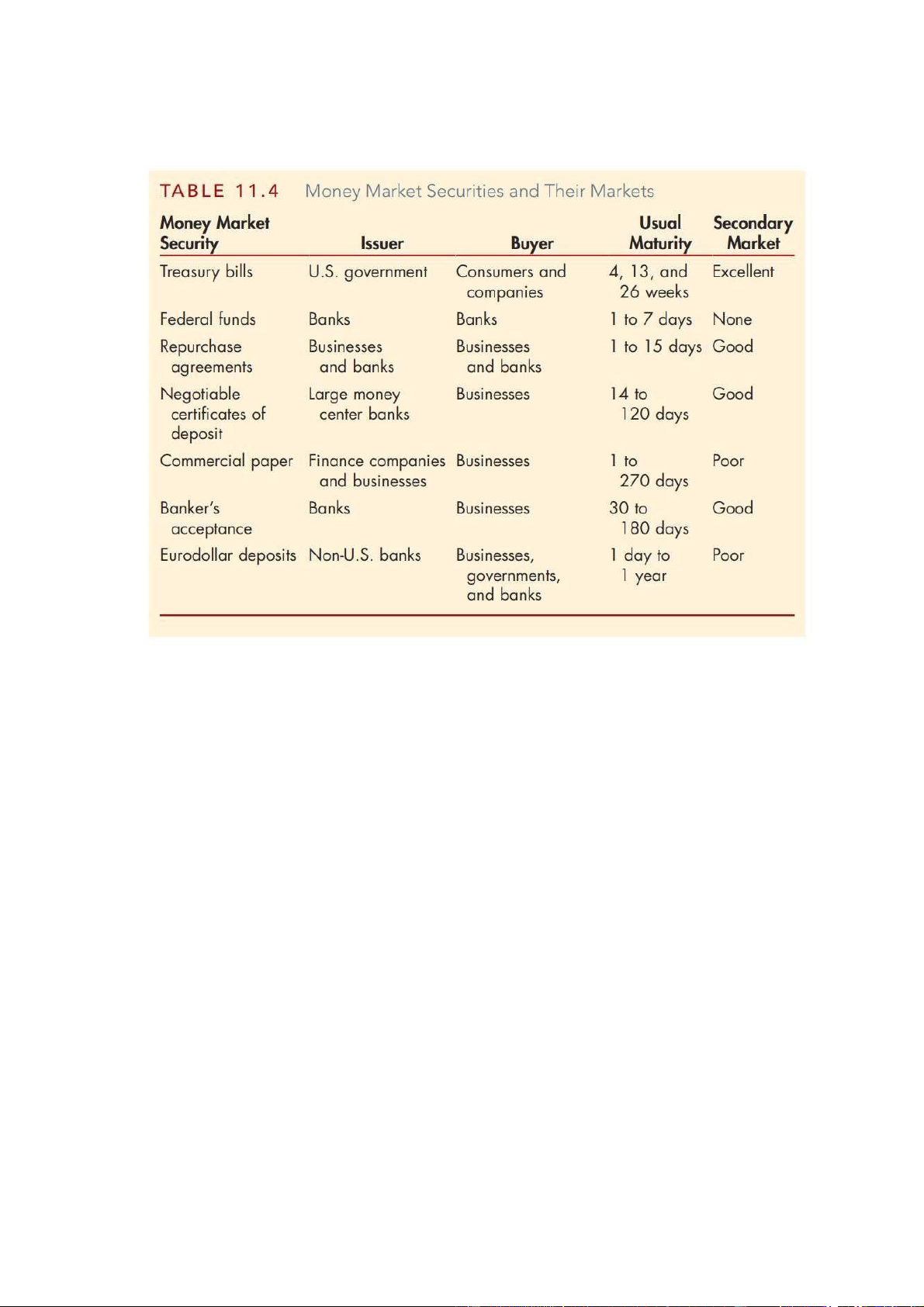
1. MONEY MARKET (SHORT TERM DEBT MARKET)
Three main characterictic of Money market: - Short term (<1year)
- Discount security: no interest (P- High liquidity (có secondary market)
- The wholesale market(bán buôn>< retail:bán lẻ): Bội số của facevalue luôn là 100K
*Currency market: chỉ là thị trường chuyển đổi cacsc loại tiền qua lại Purpose: - Raise the short term fund
- Apply monetary policy by OMO ( T-Bill)
Interest rate = Face value - Price 360: issuer 365: investor
Treasury bill: implement OMO
- Highest price (Interest rate giảm = Face value - Price tăng) - Highest liquidity
Money market instrument pricing
P=Face value/(1+1/360*n) n: Days to maturity Day
Yield (Holding period Yield)
Y= (Selling price – Purchasing price)/Purchasing price * 365/n (% năm)
n: from purchasing day to selling day
Meaning: If u invest 1 dollar in 1 year, u will receive Y dollar T- bill discount
T-bill discount = Face value – price/face value * 360/n
n: từ khi phát hành tới khi đáo hạn Example 11.1 page 262 lOMoARcPSD| 50205883
Homework: Quantiative problems page 277 (What would be ur annuealized discount rate
% and ủ annualized….) Dealine 9h tối chủ nhật
Commercial paper (CP) (lest liquidity) (lowest price)
Isseed only by famous, creaditworthy firm
CP just finacing or sponsor a firm’s investment in inventory and account recievable
( các khoản phải thu) (Không hỗ trợ cho đầu tư vào trang thiết bị)
Secondary market for CP is limited
Negotiable Certificates of deposit (NCDs)
Là loại duy nhất có trả lãi trên thị trường tiền tệ
Yncd= SP-PP+Interest/PP * 365/n
Repurchase agreement (Repo) (hợp đồng mua lại)
Cam kết mua lại với giá cao hơn khi bán ra Federal funds Banks is the issuer
Các ngân hang (depository institution) vay mượn lẫn nhau để đảm bảo tỷ lệ dự trữ bắt buộc
To maintain reserve requirement lOMoARcPSD| 50205883
In Vietnam, the money market just have T-Bill and federal fund: lãi suất liên ngân hang
2. BOND MARKET (LONGTERM DEBT MARKET)
- Convertible bond: (có khả năng chuyển đổi thành cổ phiếu)
+ Châp nhận lãi suất thấp hơn - Non – Convertible bond + Lãi suất cao hơn
- Floating/Variable bond (thả nổi)
+ Just depend on the reference interest rate (the market conditions)
+ Not depend on the performance of the corporation - Fixed Bond
- Call provision: the issuer can redeem the bond before the maturity dates
+ Just exercise the call provision when expect the interest rate in the market go down
+ Có lãi suất cao hơn so với loại k có call provision lOMoARcPSD| 50205883
- Collateral: (asset- backed): có tài sản để bào đảm cho việc phát hành
+ lãi suất thấp hơn loại trái phiếu k có
PV=C*[1-(1+i)-n/i]+Face value/(1+i)n
The investor in the bond market will get the benefit when the interest rate go
down: I giảm -> PV (giá bond) giảm
How can the investor decide to buy a bond in the secondary market or not?
Tính present value of the bond: trong đó tính C, n (từ lúc bắt đầu mua) So sánh PV và market value
Nếu market value > PV : k nên mua
Market valie < PV: Nên mua
Lãi suất thả nổi: theo quy định
Ví dụ: 3,7%/năm + lãi suất tham chiếu
Lãi suất tham chiếu: trung bình cộng lãi suất tiền gửi kỳ hạn 12 tháng của big4 bank
Loại trái phiếu nào người phát hành được quyền mua lại (redeem) trước hạn? A
callable bond is a debt security that can be redeemed early by the issuer before
its maturity at the issuer's discretion.
A callable bond allows companies to pay off their debt early and benefit from
favorable interest rate drops.
A callable bond benefits the issuer, and so investors of these bonds are
compensated with a more attractive interest rate than on otherwise similar noncallable bonds.
Most municipal bonds and some corporate bonds are callable. A
municipal bond has call features that may be exercised after a set period such as 10 years.
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/callablebond.asp
Thả nổi có phụ thuộc vào hoạt động kinh doanh của …?
What does the coupon rate of the floating bond depend on?
What does floating rate depend on? lOMoARcPSD| 50205883
The interest rate is determined by market conditions: The interest rate on floating
interest rate loans largely depends upon the market conditions, which can often get
unpredictable and dynamic. If the interest rate increases to a point where it becomes
difficult for one to pay the EMI, it can cause a lot of damage.



