




Preview text:
MINISTRY OF FINANCE
UNIVERSITY OF FINANCE – MARKETING FACULTY OF MARKETING
220525 – EXE 2 – GROUP 7
Course Code: 2521702074901
Instructor: PhD. Bao Trung Student Group Members
1. Nguyễn Huỳnh Ngọc Bích Student ID: 2221001512 2. Hà Trúc Linh Student ID: 2221001625 3. Hồ Thị Mỹ Ngân Student ID: 2221001668 4. Lương Minh Nhi Student ID: 2221001717 5. Phạm Thị Tuyết Trinh Student ID: 2221001862 MAJOR: MARKETING
SPECIALIZATION: MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS Ho Chi Minh City, 2025 MINISTRY OF FINANCE
UNIVERSITY OF FINANCE – MARKETING FACULTY OF MARKETING
220525 – EXE 2 – GROUP 7
Course Code: 2521702074901
Instructor: PhD. Bao Trung Student Group Members
1. Nguyễn Huỳnh Ngọc Bích Student ID: 2221001512 2. Hà Trúc Linh Student ID: 2221001625 3. Hồ Thị Mỹ Ngân Student ID: 2221001668 4. Lương Minh Nhi Student ID: 2221001717 5. Phạm Thị Tuyết Trinh Student ID: 2221001862 MAJOR: MARKETING
SPECIALIZATION: MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS Ho Chi Minh City, 2025
1. How does digital media differ from traditional media in terms of personalization and interactivity?
1.1. Definition of traditional media và digital media
1.1.1. Traditional Media
Traditional media is media that originated prior to the internet, including newspapers,
radio, and broadcast television (IGI Global, 2022).
Old media, often termed traditional media, encompasses the various information and
communication channels that were prevalent before the rise of the Internet and digital
technologies. Key examples include newspapers, television, radio, magazines, and books.
Unlike new media, which is characterized by interactivity and targeted content, traditional
media typically operates on a one-way communication model, delivering content from a
centralized source to a broad audience. Historically, the evolution of traditional media
began with written communication, gaining momentum with the invention of the printing
press in the 15th century, which significantly increased literacy and access to information.
By the 20th century, newspapers and radio had established themselves as primary sources
of news, later followed by the widespread adoption of television. However, the introduction
of the Internet and mobile technology in the late 20th and early 21st centuries has
dramatically shifted audience behavior, leading to a decline in traditional media
consumption. As digital platforms gained traction, many traditional outlets struggled with
dwindling circulation and viewership. Despite these challenges, traditional media
continues to play a notable role in the communications landscape, even as it adapts to a
more digital-centric world. (Sheposh and Richard, 2025) 1.1.2. Digital Media
At its most basic, digital media is any content, visual or audio, text or graphic, created with
technology and distributed through social media and website applications. Creators use
electronic devices and technology to design, update, and transmit digital media. Examples
include Social media posts, Websites and web pages, Electronic books and podcasts,
Digital audio such as streaming and mp3s, Email marketing and blogs, Mobile apps (Sessions College, 2025).
The term digital media is frequently used to refer to products and services that provide
information or entertainment in digital form, especially online via the Internet. Examples
of digital media include online news sources, video games, blogs, and social media. The
term may also be used to describe online content, especially content that is interactive; on-
demand media that is accessible through a range of devices; and media that is responded
to or shared in real time. It is sometimes used to refer to content that is created, published,
or distributed by individuals or non-traditional publishers, such as bloggers (Winston & Strawn, n.d).
1.2. Compare the differences between traditional and digital media in terms of
personalization and interactivity
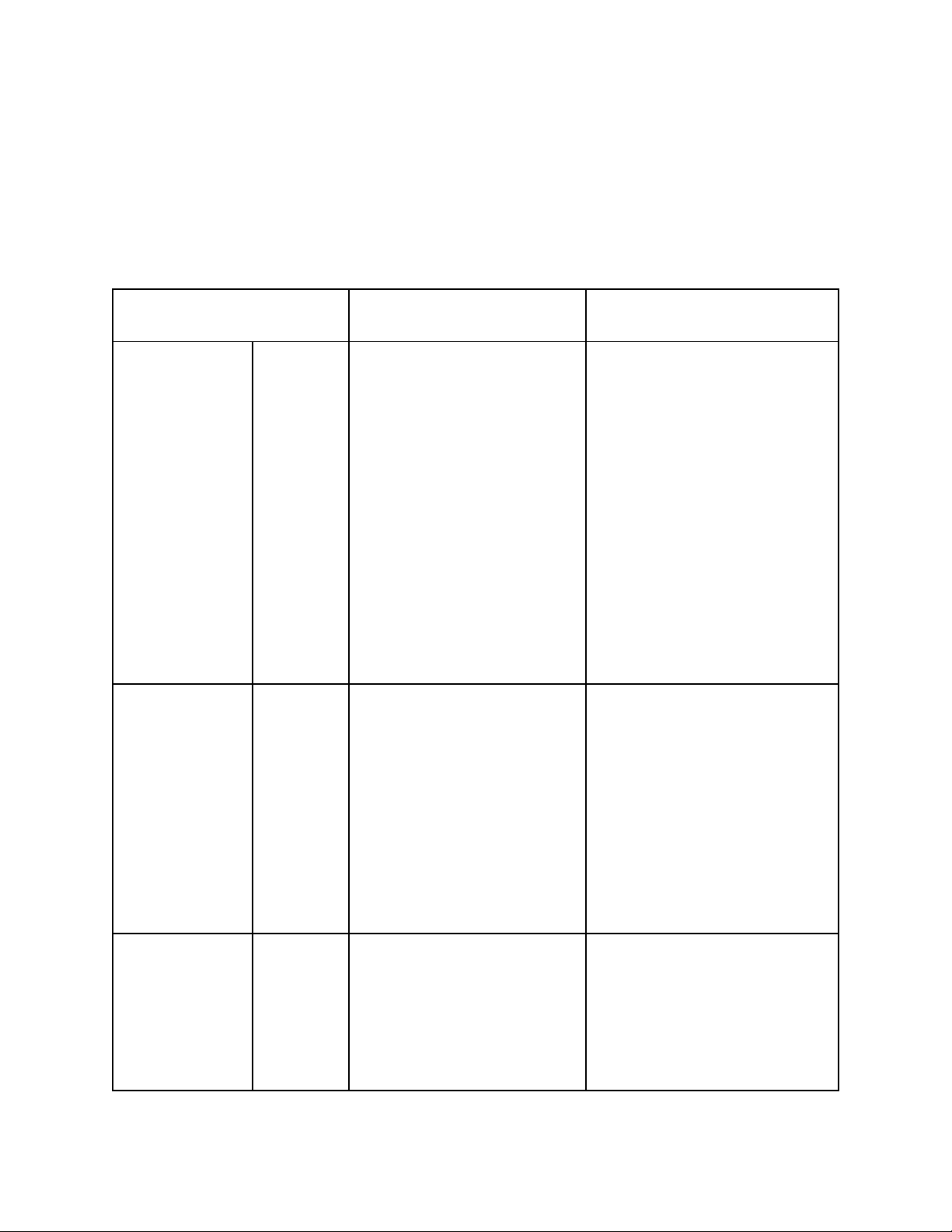
Table 1.1: Compare the differences between traditional and digital media Traditional Media Digital Media Personalization Level Low (almost none) Very high
- Content is designed for - Personal data (age, gender, the masses, generic. interests, browsing behavior,
- No ability to tailor purchase history,…) is used messages to individuals. to tailor content and
- No collection or use of advertising. specific consumer data. - Technologies such as AI,
- Often used for brand Machine Learning and Big awareness campaigns Data help create “right
rather than conversions person, right message, right
(Minh Duy Solution, 2023 time” experiences. & The7.vn, 2024). - Ads can be different for each user on the same platform (The7.vn, 2024).
Example - A printed flyer is - Running shoe ads only distributed
randomly show to people who have without distinction
of searched for sports, health. audience. - Netflix recommends movies - A TV or
print based on personal viewing
advertisement will be the history. same to everyone who sees it, regardless of age, gender, or consumer behavior. Effect
- Campaigns can easily - Higher efficiency because
waste budget because they the content is more relevant
do not target the right to each individual, increasing audience. conversion rates.
- It is difficult to evaluate - Easy A/B testing and actual
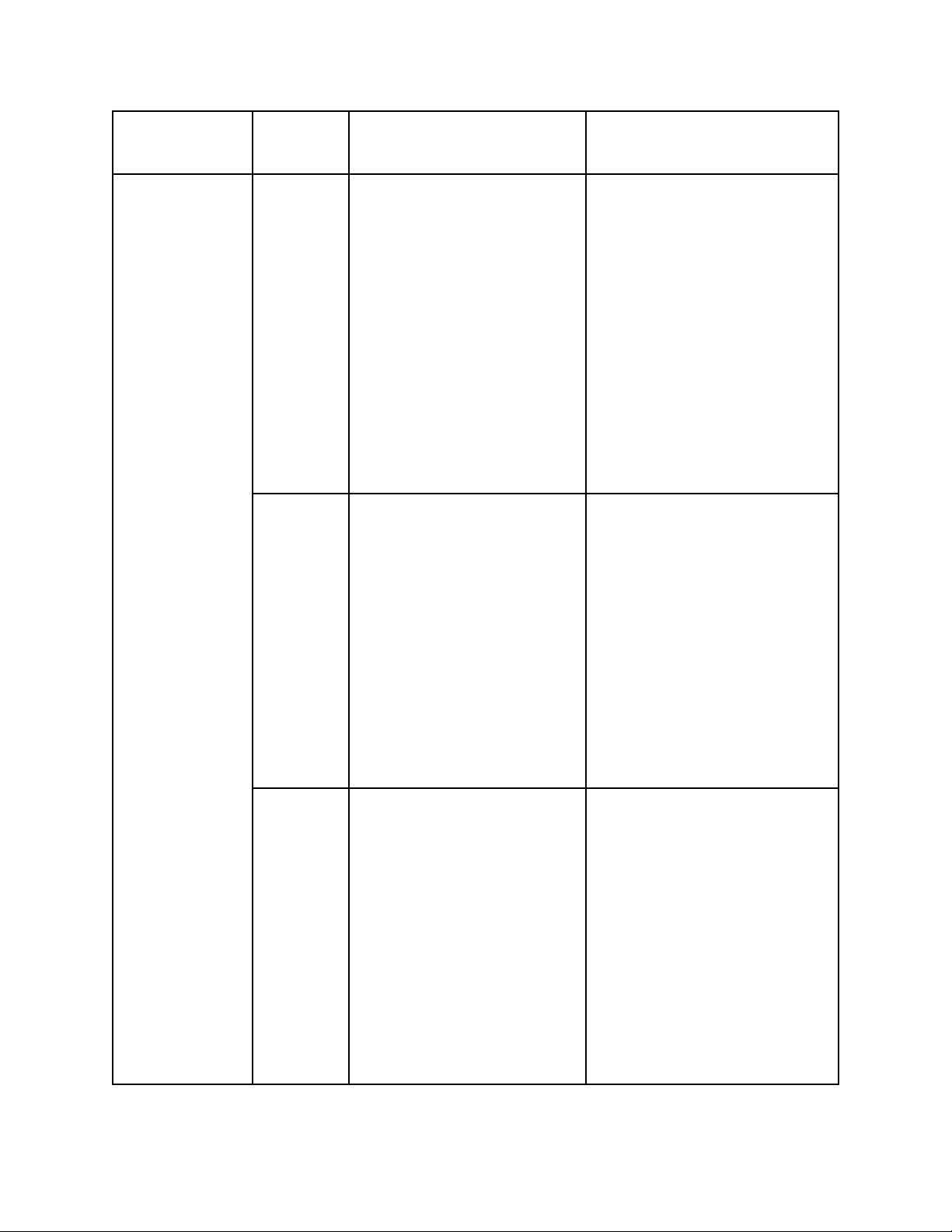
effectiveness continuous optimization. 2 because there is no detailed data for each individual. Interactivity Level One-way, passive Two-way, proactive - Users can only receive - Users can respond
information and cannot immediately via comments, respond immediately. messages, shares or
- Brand controls all content interactions with the chatbot. and timing of - Increases the feeling of transmission. being heard, thereby
- Slow interaction (via increasing satisfaction and mail, call center, loyalty. survey,…). - Brands and customers can have a continuous conversation, personalized to each response.
Example Advertising on TV, radio, - Users can chat directly with print,... viewers only the brand on Facebook or
receive information and through chatbots. cannot
respond - Consumers can comment, immediately. review products, share their opinions, and receive real- time feedback. - Livestream features on
social media allow for instant Q&A interactions. Effect
- Customers only receive - Customers can interact
information in a one-way proactively, increasing
manner, making it difficult engagement and feeling like
to build a deep relationship they are part of the brand. with the brand. - It can enhance customer
- Lack of connection makes loyalty and create a ripple
it challenging to develop (viral) effect for the brand. customer loyalty. - Performance can be
- Difficult to measure measured accurately: performance. tracking clicks, view time,
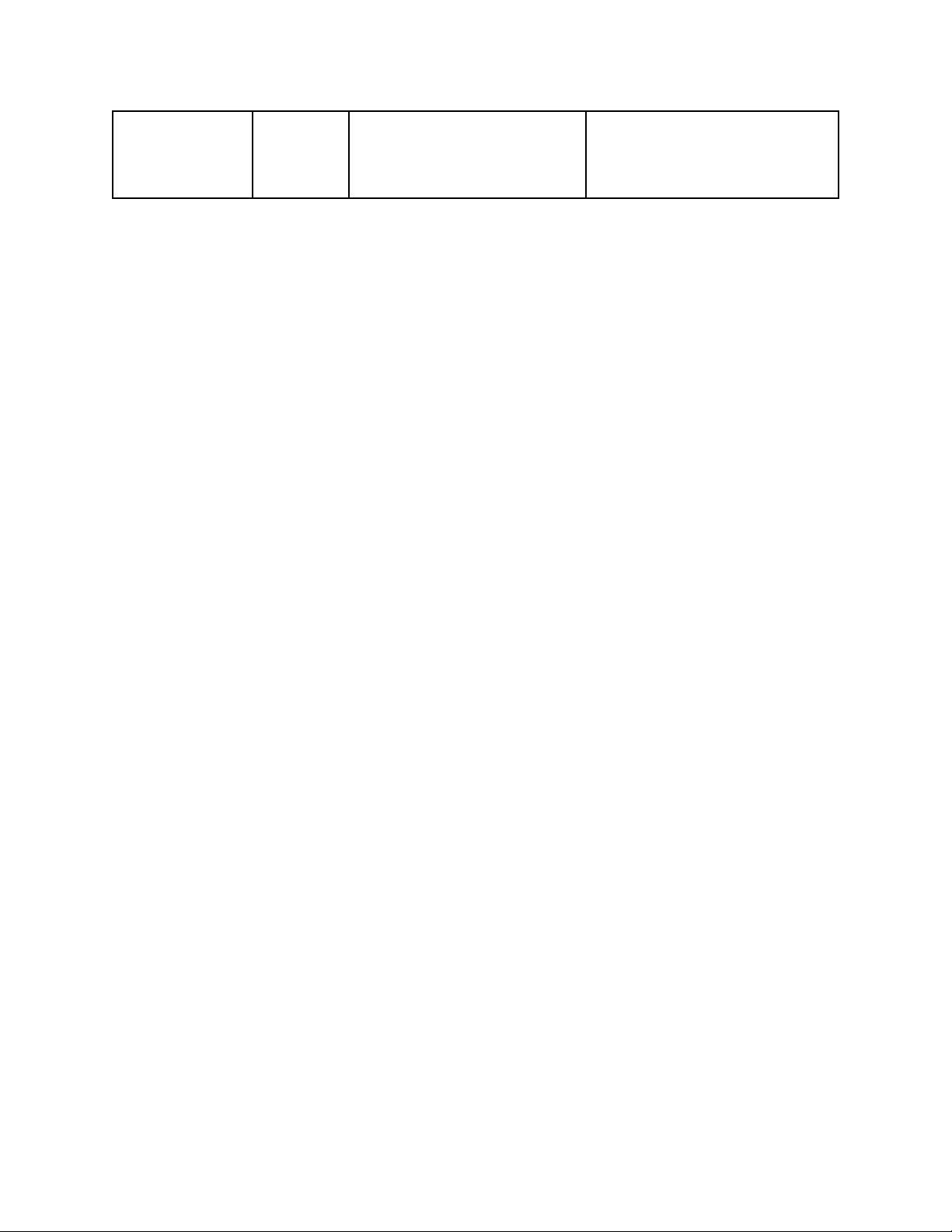
- Unable to track individual consumer behavior, etc. behavior, making campaign optimization - Automated reporting challenging. enables quick and continuous campaign optimization.
Source: Author’s Group
2. What is the role of digital media in brand building for businesses?
The role of digital media in brand building for businesses is immensely important in the
modern business landscape. As technology continues to evolve and consumer behavior
shifts toward digital platforms, brands must effectively leverage digital marketing
strategies to enhance visibility, engage audiences, and foster long-term relationships.
Digital media encompasses a wide range of techniques aimed at promoting brands through
digital channels such as search engines, social media, email, and websites. It has
revolutionized the way businesses connect with consumers.
According to the study “The Role of Digital Marketing in Brand Building” by
Venkateshaiah (2023), the core roles of digital media in brand building include:
Enhancing Brand Visibility and Awareness: In the digital age, consumers view
the Internet not just as a utility, but as an essential part of how they make purchasing
decisions and seek information. By optimizing content for search engines (SEO),
maintaining an active presence on social media, leveraging content marketing, and
using paid advertising (PPC), brands ensure they can be discovered by their target
audience. This approach not only attracts new customers but also reinforces brand
recall among existing ones. This heightened visibility is crucial for building brand awareness and recognition.
Driving Customer Engagement and Connection: Through digital media
platforms and email campaigns, brands can interact directly with consumers,
respond promptly to inquiries, and tailor messaging for specific audience segments.
Interactive content such as polls, quizzes, contests, and live streams also encourages
active participation from the audience. This helps build trust, foster loyalty, and
create a positive brand perception.
Establishing Credibility and Thought Leadership: By consistently creating and
sharing valuable content, participating in industry discussions, and showcasing their
insights and expertise, businesses not only affirm their position within the industry
but also build trust with customers. Additionally, by leveraging a variety of content
formats—such as articles, videos, images, and social media stories—brands can
effectively convey their message, share their journey, and express their identity and
core values in a dynamic way. This combination of high-quality content and 4
compelling storytelling helps brands stand out, foster strong relationships with the
public, and maintain a leading position in the market.
Enhancing Campaign Effectiveness: When a company limits its marketing
efforts to traditional media such as television or newspaper advertising, it
becomes difficult to make changes or add information when needed. There's also
a risk that the presented information may become outdated by the time it reaches
the audience. In contrast, digital media can often be edited or updated easily and
instantly, allowing for greater flexibility and responsiveness.
Delivers measurable results and insights: Analytics tools allow marketers to
track campaign performance, identify trends, and adjust strategies accordingly.
This data- driven approach ensures marketing efforts are optimized for maximum
effectiveness and ROI. Measurability provides valuable insights into consumer
behavior and campaign performance.
Building and Strengthening Customer Relationships: Through social media
platforms and digital marketing tools, businesses can interact directly and listen
to feedback. By creating dedicated groups, forums, or pages for their
products/services, brands can encourage like-minded individuals to connect and
share experiences, and address customer inquiries quickly. This builds trust,
loyalty, and sustainable relationships. Digital media facilitates direct
communication between brands and customers.
Differentiating Brands in a Competitive Market: Effective digital media
allows brands to highlight their unique values and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Fostering Loyalty and Brand Advocacy: Strategies such as loyalty programs,
personalized offers, and exclusive content reward existing customers and
encourage repeat purchases. Satisfied customers are more likely to become brand advocates.
Adapting to Changing Consumer Behaviors and Trends: Digital media
enables brands to be flexible and responsive to evolving consumer preferences,
technological advancements, and market trends.
Overall, digital media is not just a promotional tool but a foundation of modern
business strategy, allowing brands to navigate the complexities of the digital landscape
and achieve sustainable growth in a competitive market. It has democratized marketing
strategies, enabling businesses of all sizes to compete on a global scale. REFERENCES
EBSCO. (2025). Old media (traditional media). EBSCO Research Starters.
https://www.ebsco.com/research-starters/information-technology/old-media- traditional-media IGI Global. (2025.). What is Traditional Media. https://www.igi-
global.com/dictionary/improving-clinical-trial-diversity/47688
Minh Duy Solutions. (2023). Traditional media và new media khác nhau như thế nào?.
https://minhduy.vn/traditional-media-new-media.html
Sessions College. (2025). What is digital media?. Sessions College for Professional Design.
https://www.sessions.edu/notes-on-design/what-is-digital-media/ The7. (2022). Traditional marketing là gì?.
https://the7.vn/xu-huong-digital-
marketing/traditional-marketing-la-gi-17660/
Venkateshaiah, M. (2022). The role of digital marketing in brand building: A study. Govt.
First Grade College, Bangaluru.
Winston & Strawn LLP. (2025). Digital media. https://www.winston.com/en/legal- glossary/digital-media
Writer, R. C. (2021). Earned Media, Owned Media, Paid Media: The 3 Types of Digital
Media and How to Use Them. Rock Content. https://rockcontent.com/blog/types-of- digital-media/ 6




