
Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 36490632 CORPORATE FINANCE
Chapter 13: Risk, Cost of Capital, and Valuation I.
The Cost of Equity Capital:
- CAPM: RS = RF + β(RM − RF )
- To estimate a firm’s cost of equity capital, we need to know three things:
1. The risk-free rate, R F
2. The market risk premium, RM − RF
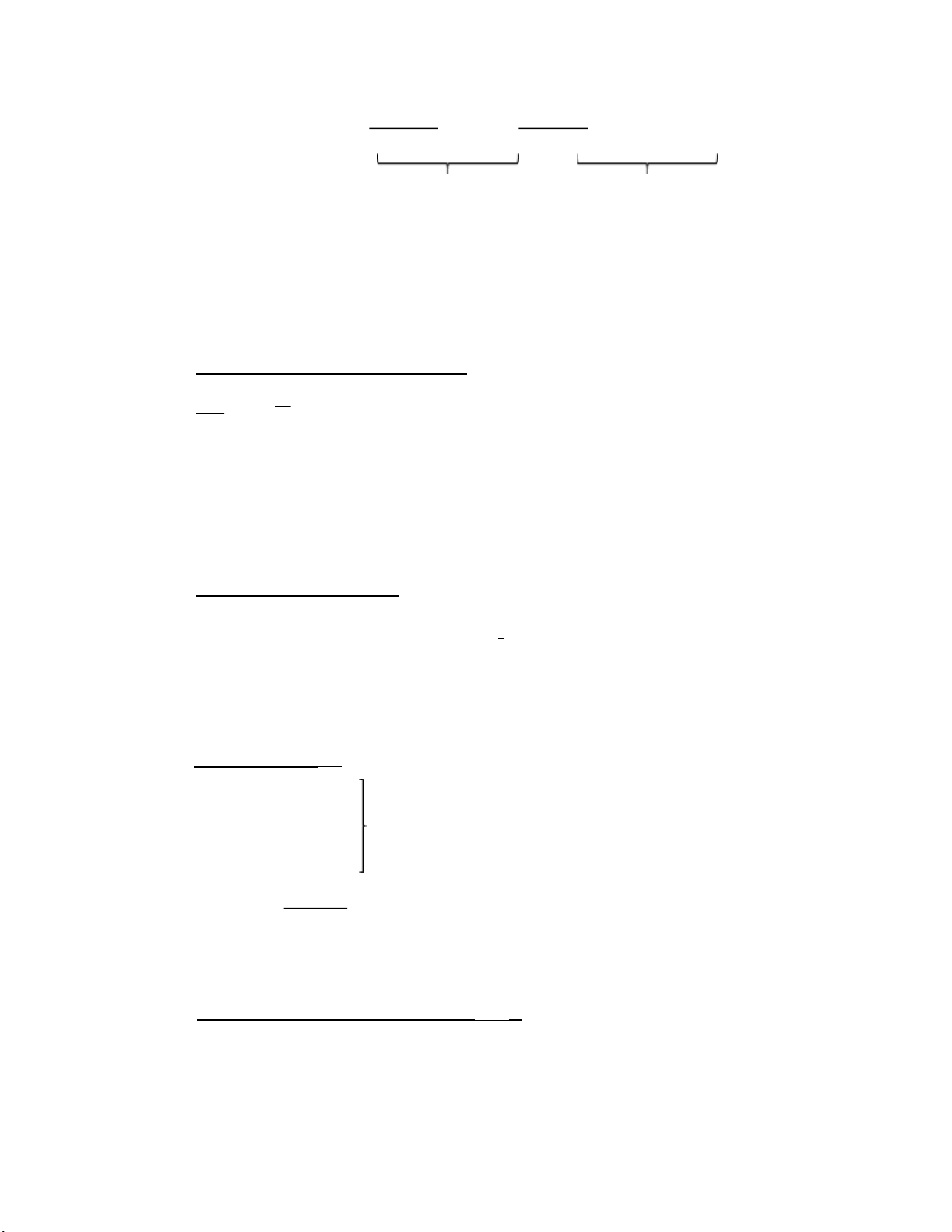
3. The company beta, βi = CovV ar(R(Ri,RMM) ) = σσiM,2M II. Determinants of beta: - Business risk + Cyclicality of Revenues:
● Highly cyclical stocks have higher betas.
● Note that cyclicality is not the same as variability—stocks with high
standard deviations need not have high betas. + Operating Leverage: Depreciation
● The degree of operating leverage measures how sensitive a firm (or project) is to its fixed costs.
● Operating leverage increases as fixed costs rise and variable costs fall.
● Operating leverage magnifies the effect of cyclicality on beta.
● The degree of operating leverage is given by:
DOL = ∆EBITEBIT x ∆SalesSales - Higher DOL → Higher β - Financial risk
+ Financial Leverage: interest expense lOMoAR cPSD| 36490632 βasset = Equity Debt x β Debt + Equity Debt Debt + Equity Equity + xβ Weight of debt Weight of Equity = 0 in most of cases -
βequity > βasset III.
Dividend Discount Model (DDM):
-RS = DP1 + g - P: market price
- The DDM is an alternative to the CAPM for calculating a firm’s cost of equity.
- The DDM and CAPM are internally consistent, but academics generally favor the
CAPM and companies seem to use the CAPM more consistently. IV.
Cost of Preferred Equity: RP = DP P - P: Market price
- DP : Preferred Dividend Ratio x FV ($100) V.
Cost of Debt (RB ): - Loan: RB Before tax - Bond: YTM 1−(1+ − R ) T B - P = C[ RB
] + (1+FVRB)T VI.
Weight Average Cost of Capital (RWACC ):
RWACC = ∑W iRi = W B x RB (1 − tc) + W RP P + W SRS lOMoAR cPSD| 36490632 WB : Weight of Debt
WP : Weight of preferred stock WS : Weight of common stock
MVB = Bond price x Number of Bonds
MVEP = PP x Number of Preferred Equity
MVEC = PC x Number of Common Equity W B = MV
B+MVMVEPB+MV EC MV EP
W P = MV B+MV EP +MV EC MV EC W S = MV
B+MV EP +MV EC
Document Outline
- CORPORATE FINANCE
- DOL = ∆EBITEBIT x ∆SalesSales
- RP = DPP
- - P = C[ RB ] + (1+FVRB)T
- W B = MV B+MVMVEPB+MV EC
- W S = MV




