




Preview text:
Vietnam National University – HCMC International University
SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS, FINANCE, AND ACCOUNTING COURSE SYLLABUS* BA054IU Corporate Finance
Note: The outline with specific venue and time, and updated learning materials for the current semester will
be provided to the enrolled students by the lecturer 1. COURSE STAFF
Lecturer: Assoc. Prof. Vo Thi Quy (PhD) Room: O1.305 E-mail: vtquy@hcmiu.edu.vn
Consultation Hours: Tuesday 8:30 a.m. – 10 a.m.
Teaching Assistant: N/A Room: Telephone: E-mail: Consultation Hours:
Should the students wish to meet the staff outside the consultation hours, they are advised
to make an appointment in advance. 2. COURSE INFORMATION
Prerequisite: Fundamentals of Financial Management – BA016IU
2.1 Teaching time and Location
Group 5: Tuesday 13:15 p.m. – 15:45 p.m. Room: L106 2.2 Units of Credit
This course is worth 3 credits.
2.3 Parallel teaching in the course
There is no parallel teaching involved in this course.
2.4 Relationship of this course to others
BA054IU–Corporate Finance is a continuation of BA016IU–Fundamentals of
Financial Management. Practical topics in corporate management, including capital
structure, dividend policy, raising capital, leasing, and merger and acquisition (M&A), are covered in this course. BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting
2.5 Approach to learning and teaching
Employing the interactive learning and case-based teaching approach, this course
emphasizes the interaction between lecturers and students. The course materials will be
uploaded on Blackboard to help students preview the materials and concentrate on listening
and critical thinking during the lecture. Students are encouraged to interact with the lecturer.
Students need to make presentations and discussions comprising of financial theories,
financial practice problems and some practical and conceptual questions, which help
students see how the concepts are applied in the real financial business context.
3. COURSE AIMS AND OUTCOMES 3.1 Course Aims
The objective of this course is to study the major decision-making areas of managerial
finance and some selected topics of financial theory. The course reviews the theory and
empirical evidence related to the investing and financing policies of the firm and attempts
to develop decision-making ability in these areas using both lectures and cases.
Some of the topics will be similar to the previous course-BA016IU, such as investment
decision, financing decision, and cost of capital. But they will be further elaborated and
discussed in-depth and more rigorously in this course. In addition to the above topics, this
course also covers other topics such as capital structure, dividend policy, raising capital, and M&A.
3.2 Course Learning Outcomes (CLO)
On the successful completion of the course, students should be able to:
1. understand different financial instruments in making financing decisions.
2. understand capital structure policy.
3. apply theories of capital structure in valuation and capital budgeting.
4. make dividend and payout decisions.
5. understand leasing and the process of raising capital.
6. analyze mergers and acquisitions (M&A) and divestitures; and
7. apply critical thinking and problem-solving skills to solve problems in finance.
In generic terms, students completing this course are likely to achieve the following attributes:
• In-depth knowledge of the field of study: A comprehensive and well-founded
knowledge of the field of study. All the course objectives lead to comprehensive
fundamentals and advances in the field of finance.
• Effective communication: The ability to collect, analyze, and organize information
and to convey information clearly and fluently, in both written and spoken forms. 3 BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting
• Critical argument and judgment: The ability to identify and debate critical issues /
problems, as well as to evaluate financial information, make decisions, and reflect
critically on the justification of decisions.
Mapping of Course Learning Outcomes to Program Learning Outcomes
Course Learning Outcome (CLO)
Program Learning Outcome (PLO) 1 1-5 2 1-5 3 1-5 4 1-5 5 1-5 6 1-5 7 4-7
Program Learning Outcomes (PLO): See Appendix 3.3 Teaching Strategies
The learning system in this course consists of lectures and scheduled
presentations/discussions. Lectures elaborate the appropriate theoretical content in the
textbook and readings. Classes provide a more detailed and refined analysis of both
concepts and applied materials. Classes are strongly oriented towards interactive discussion
of the text and cases. To gain the most from the lectures and class activities, the assigned
text/reading should be read before the lecture to participate in the discussions.
4. STUDENT RESPONSIBILITIES AND CONDUCT 4.1 Workload
Students are expected to spend at least 6 to 8 hours per week studying this course. This
time should be made up of reading, working on exercises, problems, group assignment,
and attending classes. Regular attendance is essential for successful performance and
learning in this course, particularly in view of the interactive teaching and learning approach adopted. 4.2 Attendance
Regular and punctual attendance at lectures is expected on this course. University
regulations indicate that if students attend less than 80% of the scheduled classes, they may
not be eligible for the final assessment. Exemptions may only be made on medical grounds or reasonable excuses. 4 BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting
4.3 General Conduct and Behavior
Students are expected to conduct themselves with consideration and respect for the needs
of fellow students and teaching staff. Conduct which unduly disrupts or interferes with the
class, such as ringing or talking on mobile phones, is not acceptable and students will be
asked to leave the class. More information on student conduct is available on the university webpage. 4.4 Keeping informed
Students should take note of all announcements made in class or on the course’s Blackboard.
From time to time, the university will send important announcements to students’
university e-mail addresses without providing a paper copy. Students will be deemed to
have received this information. 5. LEARNING ASSESSMENT 5.1 Formal Requirements
In order to pass this course, students must:
• achieve a composite mark of at least 50; and
• make a satisfactory attempt at all assessment tasks (see below). 5.2 Assessment Details
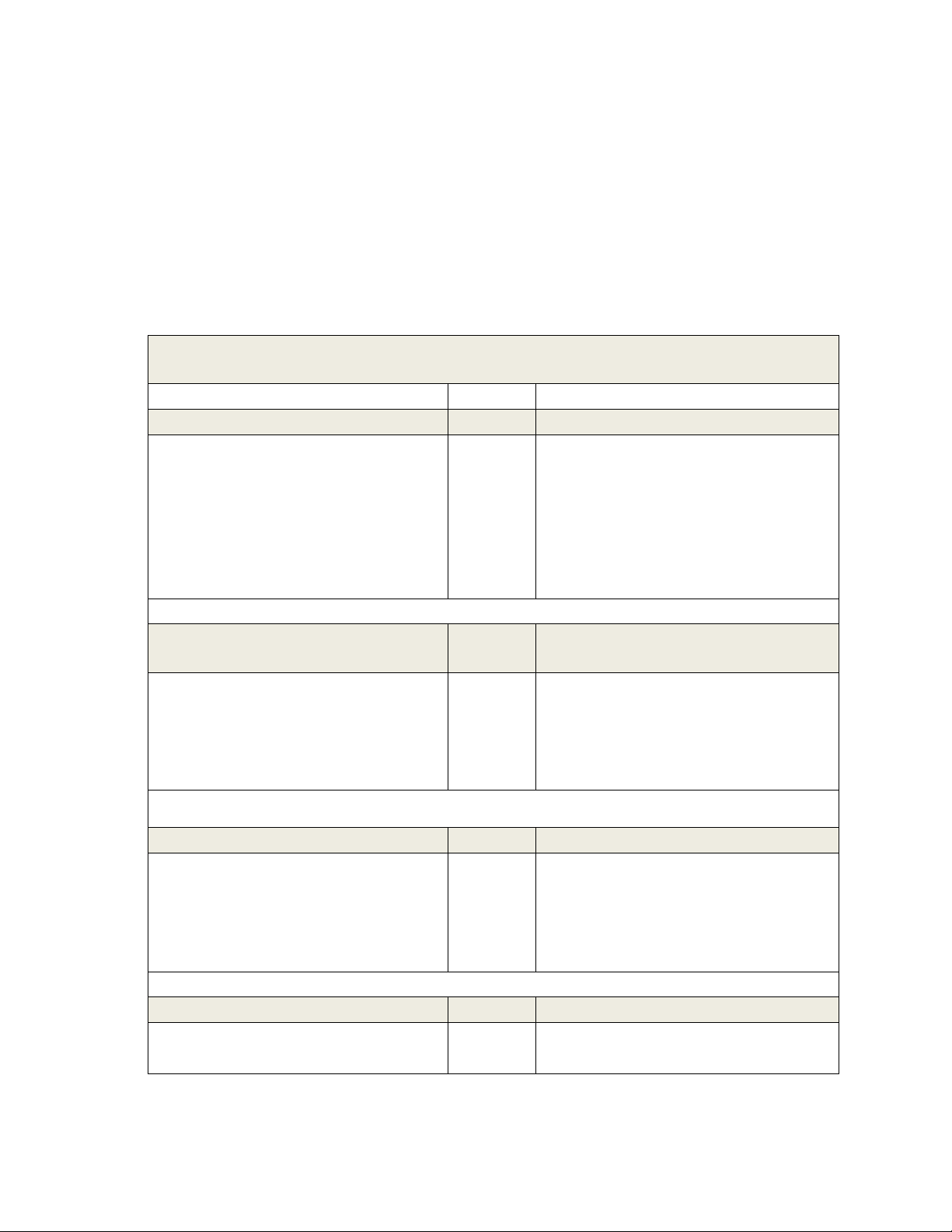
Assessment will be made as follows: Grading and Assessment Percentage of Course
Course Learning Outcome Tool Grade Assessed
Attendance, participation, and 10% 1-7 in-class exercises Group assignment 20% 1-3, 7 Midterm exam 30% 1-3, 7 Final exam 40% 4-7 In-class exercises
At the end of each chapter, there will be in-class questions and practice problems. If you
show your efforts in doing these assignments, you can get at least partial credit. Group assignment
You will work in groups of four to five students for the group assignment which includes
writing a report to analyze a case study. Please submit the names of your group’s members
by week 2. Details will be provided later. 5 BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting Exams
All exams are closed book and closed note. Students are not allowed to use any note sheet,
but formula sheet will be provided. Remember to bring calculators. Exams consist of
multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, and application problems.
You may not use a cell phone, computer, or similar electronic device during an exam. 5.3 Marking criteria MARKING CRITERIA Grading work Percent Learning Outcomes 1. Group assignment 20%
Ability to use and apply fundamental
concepts and skills of the course,
ability to identify and debate critical Case study written report
issues / problems logically, ability to give compelling arguments and
relevant evidences to support those arguments.
2. Participation and In-class 10% exercises
Ability to analyze and identify Participation
important information in the reading
Questions and practice problems on
material. Develop skills of critical designated chapters
reading, reasoning, and problem solving. 3. Midterm exam 30% Demonstrate awareness and - Long-term financing
understanding of deeper and subtler - Capital structure
aspect of the topics, ability to identify - Valuation and capital
critical problems, to think logically,
budgeting for the levered firm
and to solve non-routine problems. 4. Final exam 40% - Dividends and other payouts Demonstrate awareness and - Raising capital
understanding of deeper and subtler 6 BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting - Leasing
aspect of the topics, ability to identify - Mergers, acquisitions, and
critical problems, to think logically, divestitures
and to solve non-routine problems. 5.4 Special Consideration
Request for special consideration (for final examination only) must be made to the Office
of Academic Affairs within one week after the examination. General policy and
information on special consideration can be found at the Office of Academic Affairs.
6. ACADEMIC HONESTY AND PLAGIARISM
Plagiarism is the presentation of the thoughts or work of another as one’s own (definition
proposed by the University of Newcastle). Students are also reminded that careful time
management is an important part of study and one of the identified causes of plagiarism is
poor time management. Students should allow sufficient time for research, drafting, and
proper referencing of sources in preparing all assessment items. The university regards
plagiarism as a form of academic misconduct and has very strict rules regarding plagiarism. 7. STUDENT RESOURCES 7.1 Course Resources Textbook:
Ross, S.A., Westerfield, R.W. and Jaffe, J. (2013) Corporate Finance. 10th edition. McGraw-Hill Irwin. Reference books:
Brealey, R.A., Myers, S.C. and Marcus, A.J. (2007) Fundamentals of Corporate Finance.
5th edition. McGraw-Hill Education.
Berk, J. and DeMarzo, P. (2017) Corporate Finance. 4th edition. Pearson Series in Finance.
Bruner, R.F., Eades, K.M. and Schill, M.J. (2010) Case studies in Finance – Managing for
corporate value creation. 6th international edition. McGraw-Hill.
Additional materials provided on Blackboard
The lecturer will attempt to make lecture notes and additional reading available on
Blackboard. However, this is not an automatic entitlement for students doing this subject.
Note that this is not a distance-learning course, and you are expected to attend lectures and
take notes. This way, you will get the additional benefit of class interaction and demonstration.
Recommended internet sites 7 BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting Smart Money Quicken Business Week The Economist Fortune Forbes Recommended journals Harvard Business Review International Business Review Journal of Management Studies
Asia Pacific Journal of Management Journal of Corporate Finance
7.2 Other Resources, Support, and Information
Additional learning assistance is available for students in this course and will be made
available on Blackboard. Academic journal articles are available through connections via
the VNU - Central Library. Recommended articles will be duly informed to students.
8. COURSE SCHEDULE (TENTATIVE) Week Date Topic Required readings and activities 1 Course Syllabus
Syllabus. Form groups
Review of Financial Management Lecture notes
• Financial statements and cash flow from assets
• Capital budgeting decision and investment criteria 2
Long-term Financing: An Introduction Textbook, Chapter 15 Some features of common and
Complete forming 8 BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting preferred stocks groups • Corporate long-term debt
• Some different types of bonds • Bank loans • International bonds • Patterns of financing 3
Capital Structure: Basic Concepts Textbook, Chapter 16 • Pie theory
Case study (CPK) is
• Firm value vs. Stockholder interests released.
• M&M theory: proposition I 4
Capital Structure: Basic Concepts (Cont’) Textbook, Chapter 16
M&M theory: proposition II Effect of Taxes 5
Capital Structure: Limits to the use of Textbook, Chapter 17 Debt
• Financial distress, Cost of debt, Tax effects • Signaling • Agency cost 6
Capital Structure: Limits to the use of Textbook, Chapter 17 Debt (Cont’) • Pecking-order theory • Personal taxes
• How firms establish capital structure 7
Valuation and Capital Budgeting for the Textbook, Chapter 18 Levered Firm
• Adjusted-present-value approach (APV)
• Flow-to-equity approach (FTE) 8
Valuation and Capital Budgeting for the Textbook, Chapter 18 Levered Firm (Cont’)
• Weighted-average-cost-of-capital approach (WACC)
• A comparison of the APV, FTE, and WACC approaches 9&10 Midterm exam Chapters 15-18 9 BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting 11
Dividends and Other Payouts Textbook, Chapter 19 • Types of payouts
• Standard method of cash dividend payment
• Irrelevance of Dividend policy
• Stock repurchases, Dividends, and Taxes • The Clientele effect
• Stock dividends and Stock splits 12 Raising Capital Textbook, Chapter 20
• Early-stage financing and Venture capital • The public issue • Alternative issue methods • The cash offer
• The announcement of new equity and the value of the firm 13 Textbook, Chapter 20
Raising Capital (Cont’) • The cost of new issues • Rights
• The rights puzzle Dilution • Shelf registration • Issuing long-term debt 14 Leasing Textbook, Chapter 21 • Types of leases
Case study report due • Accounting and Leasing • Taxes and Leases • The cash flows of leasing
• A detour for discounting and Debt capacity with corporate taxes
• NPV analysis of the Lease-versusBuy decision
• Debt displacement and Lease valuation
• Does leasing ever pay? The base case • Reasons for leasing Some unanswered questions 15
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Divestitures Textbook, Chapter 29
• Basic forms of acquisitions • Synergy • Sources of synergy • NPV of a merger 10 BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting 16
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Divestitures Textbook, Chapter 29 (Cont’)
• Friendly vs. Hostile takeovers • Defensive tactics
• Going private and Leveraged buyouts • Divestitures 17 Review for Final exam Chapters 19-21, 29
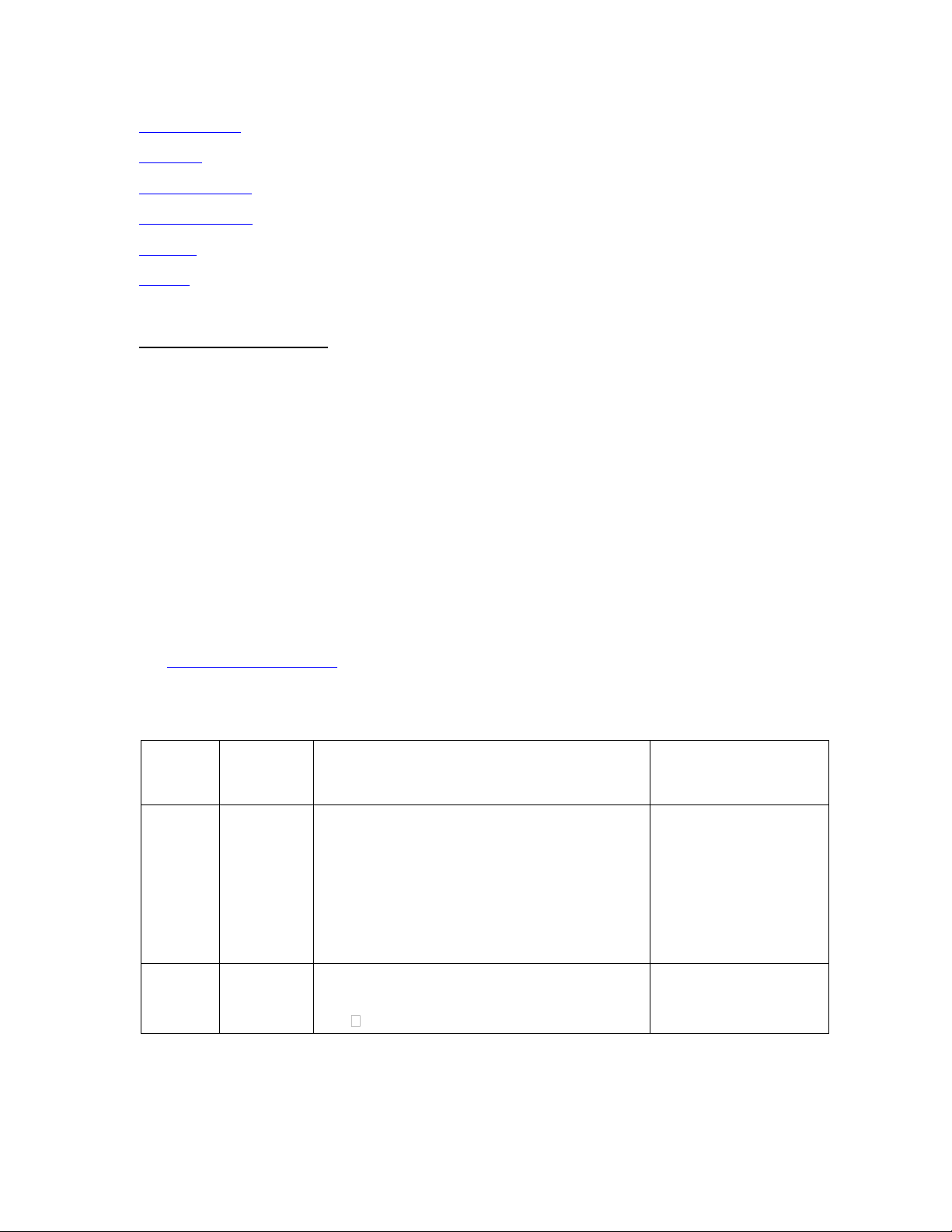
Appendix: Program Learning Outcomes (PLO)
No Business Knowledge .
a1. Students possess extended, updated knowledge about business management
which is based on the platform of the knowledge that has been taught at the
undergraduate level: knowledge of marketing management. statistics in business,
1. business finance, accounting, strategic management, international business
management, human resource management, supply chain management,
management information system, production and operation management,
economics and organizational behaviour.
a2. Students gain knowledge of scientific research methods to become capable
2. researchers in Business Administration field. With the acquired knowledge, they
can continue to learn Doctoral program in Business Administration.
a3. Students have deep knowledge about current economic issues in Vietnam as
well as in the world economy. They understand micro and macro environmental
3. factors that can affect company business performance and success. They know
about various models used to analyze strength, weakness, threats and opportunities a.
for strategic planning and forecasting purpose. Skills
b1. Students master up-to-date scientific research methods and tools in the field of
4. economics and management. They can recognize practical business problems, do
researches and propose measures to solve the problems. b.
b2. Students acquire skills of critical thinking, analyzing, researching, evaluating,
comparing, synthesizing, which they can use to find out and solve business
5. problems and make relevant business decisions. The students master
communication skills and social skills, which help them work successfully in an
international multicultural environment. Abilities
6. c1. Students are able to take management positions of all levels at domestic and
foreign companies in various sectors of an economy. They can perform well
management functions of planning, organizing, coordinating, motivating, leading,
and controlling. They are able to make appropriate decisions in fast changing
market conditions. They are able to design and develop strategic plans and policies c. for companies. d. Virtue 11 BA054IU
VNU – International University Corporate Finance
School of Economics, Finance, and Accounting
d1. Students possess professional ethics, moral, and proper understanding of
7. integrity, responsibility, accountability. Students are aware of unethical and illegal
behaviour and actions. They stand against bribery and corruption. e.
Language and computer skills
8. e1. Students master English skills that they use effectively in an international
working environment. They can work well with foreign partners and colleagues.
They can use English well in negotiation and networking, communication and reporting.
e2. Students have good computer skills they can use for their management purpose.
9. They can use some computer software to do research, process data and perform statistical analysis. 12
* The syllabus is prepared following the format provided by the School of Organization and Management, University of
New South Wales, with kind permission.



