














Preview text:
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC NGÂN HÀNG THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH INTERNATIONAL
FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT OF VIETNAM Group 7 Lecturer's name C lass Nguyê n Thị Hông Vinh DH38DD01 TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF MEMBERS 3 LIST OF FIGURES 4 INTRODUCTION 1
CHAPTER 1. OVERVIEW OF FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT (FDI) 1
1.1 CONCEPT OF FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT 1
1.2 CHARACTERISTICS OF FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT (FDI) 2
1.3. THE ROLE OF FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT (FDI) 2
1.3.1. THE ROLE OF FDI FOR COUNTRIES EXPORTING INVESTMENT CAPITAL 2
1.3.2. THE ROLE OF FDI FOR COUNTRIES RECEIVING INVESTMENT CAPITAL3
1.3.3. THE ROLE OF FDI FOR THE VIETNAMESE MARKET 3
1.4. FORMS OF FOREIGN INVESTMENT 4
1.4.1. ACCORDING TO THE INVESTOR'S PURPOSE 4 1.4.2. EQUITY-BASED 4
1.4.3. ACCORDING TO THE FORM AND INVESTMENT PROCESS 4
CHAPTER 2: VIETNAM'S FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT SITUATION 5
2.1. STATE PERSPECTIVE ON FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT IN VIETNAM. 5
2.2. FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT LEGAL SYSTEM IN VIETNAM 5
2.3. FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES IN VIETNAM 6
2.4.IMPACT OF FOREIGN INVESTMENT ON THE ECONOMY. 8
2.5. VIETNAM'S DIRECT INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES ABROAD 10
2.5.1. CURRENT STATUS OF VIETNAM'S DIRECT INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES ABROAD 10
2.5.2. SOME LESSONS LEARNED FROM THE SITUATION OF VIETNAM'S
DIRECT INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES ABROAD 13 1
CHAPTER 3: MEASURES TO IMPROVE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF
VIETNAM'S FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES 14 IN CONCLUSION 16 REFERENCES 17 2 LIST OF MEMBERS Name Student ID Mission Contributed Research the topic and learn about the concept of investment and investment Đặng Bảo An 120604220034 activities. 100% Create a quiz for everyone to participate. Phan Việt Hà
120604220043 Research on vietnam's foreign direct investment situation. 100% Research on overview of Huỳnh Thị Thanh Hằng 120604220007 foreign direct investment 100% (FDI) Research on Vietnam's direct investment activities abroad. Đoàn Thị Nhật Vy
120604220031 Propose solutions to at ract 100% more effective FDI 3
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE 1: FOREIGN INVESTMENT FIELDS IN 2023 (SOURCE: MINISTRY OF
PLANNING AND INVESTMENT) 7
FIGURE 2: TOP 10 LOCALITIES ATTRACTING THE MOST FDI CAPITAL IN
2023 (SOURCE: SENVANGDATA.COM ) 7
FIGURE 3: FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN 2023 BY PARTNER ( SOURCE:
GENERAL STATISTICS OFFICE) 8
FIGURE 4: TOTAL REALIZED INVESTMENT CAPITAL OF THE WHOLE
SOCIETY AT CURRENT PRICES IN 2019-2023 (SOURCE: GENERAL STATISTICS OFFICE) 9
FIGURE 5: VIETNAM'S FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT (FDI) ACTIVITIES
RECORDED STRONG DEVELOPMENT WITH TOTAL INVESTMENT CAPITAL
IN THE FIRST 11 MONTHS OF 2019. 11
FIGURE 6: VIETNAM'S FOREIGN INVESTMENT STRUCTURE BY COUNTRY (2024) 12 4 INTRODUCTI INTRODU ON
The world is standing on the threshold of globalization, promising many changes. The
increasingly widespread influence of multinational corporations along with the
development of science and technology has ended up pushing the whole society to race on the path of development.
The process of specialization and cooperation is increasingly specialized, contributing to
increasing the total product of the whole society. We are living in a period witnessing
rapid changes in the overal economy, engineering, technology, and other changes in politics and society.
To integrate with the world economy, we must also have changes so as not to be removed
from the cycle of development. In that context, the trend of opening the window,
economic cooperation with other countries is a prominent viewpoint of our Government.
Demonstrating this, on December 19, 1987, the National Assembly passed the Law on
Foreign Direct Investment, al owing foreign organizations and individuals to invest in
Vietnam. Next, the National Assembly passed the Investment Law 2005 (effective in July
2006) with additional provisions on foreign direct investment. In the context of an
underdeveloped economy and low integration capacity, increasing the mobilization of
foreign capital sources to supplement total development investment capital is very
important. Foreign investment is a source of additional capital for investment, a way to
transfer technology, a solution to create jobs and income for workers, generate revenue
for banks and ultimately accelerate the process of economic restructuring. The issue of
at racting foreign direct investment in the coming years is very important for economic
growth. In that context, our State must improve the organization and policies to at ract
foreign direct investment, meeting the need for effective use of foreign direct investment
in accordance with the important policy of our Party and State, which is to consider
internal strength as decisive and external strength as important; combining internal
strength and external strength into a combined strength in national construction.
So how should we properly perceive the role of FDI? And what should be done to
enhance the role of this important capital source to realize Vietnam's industrialization
and modernization goals in the context of deep integration into the world economy? 1
CHAPTER 1. OVERVIEW OF FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT (FDI)
1.1. Concept of foreign direct investment
FDI activities have become very popular today. The nature of this activity is the same
but there are many different interpretations depending on each aspect considered.
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), FDI is an investment activity
carried out to achieve long-term benefits in an enterprise operating in the territory of
an economy other than the investor's economy. , the investor's purpose is to gain real
management rights of the enterprise.
According to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD),
FDI is made to establish long-term economic relationships with a business, especial y
investments that bring the ability to influence the economy. Managing the above
mentioned enterprise by: (i) Establishing or expanding an enterprise or a branch under
the ful management of the investor; (i ) Acquiring al existing businesses; (i i)
Participate in a new business; and (iv) long-term credit (>5 years).
UNCTAD defines FDI as a long-term investment activity to gain long-term benefits
and control by an entity (foreign direct investor or parent enterprise) of a country in
the country. an enterprise (overseas branch) in another country. The purpose of the
direct investor is to have more influence in the management of businesses located in
that economy. This definition does not tel us exactly what an investment is.
The WTO believes that: “Foreign direct investment takes place when an investor from
one country (the investor country) acquires an asset in another country (the investment
recipient country) with the right to manage that asset. ”. This concept emphasizes that
FDI is an asset. The management aspect is what distinguishes FDI from other
financial instruments. In this case, the investor is often cal ed the “parent company”
and the assets are called “subsidiaries” or “company affiliates”.
The concepts of the above organizations are basical y consistent with each other
regarding the relationship, role and interests of investors and time in FDI activities.
The most widely accepted international definition of FDI today is given by the IMF
and UNCTAD based on the concept of balance of payments. 1
In short, FDI can be understood as a form of international investment in which an
investor from one country invests al or a large enough capital in a project in another
country to gain control or participate in making profits control that project.
2. Characteristics of foreign direct investment (FDI)
Investors must contribute a minimum amount of capital according to the
regulations of each country (according to Vietnam's regulations, the minimum is 30%).
The division of management rights depends on the level of capital contribution.
The profits of investors depend on the business performance and are divided
according to the capital contribution ratio.
FDI is implemented through the construction of new enterprises, the acquisition of
al or consulting part of operating enterprises or the merger of enterprises.
FDI is not only associated with capital movement but also with the transfer of
technology and management experience.
FDI is currently associated with the international business activities of multinational companies.
3. The role of foreign direct investment (FDI)
3.1. The role of FDI for countries exporting investment capital
There are a number of advantages to the function that FDI plays for nations that export investment capital:
Economic support: Investors can take ful advantage of the recipient countries,
thereby reducing production costs, while also possessing a stable supply of raw materials.
Increase competitiveness: Thanks to production in the new environment, investors
have the conditions to innovate production structures, apply new technologies and improve competitiveness.
Improve reputation: Help investor countries affirm their economic potential,
expand consumption markets and avoid countries' protective trade barriers.
There are various drawbacks to FDI for nations that export investment money. 2
Increasing unemployment: Moving production to another country causes the supply
of jobs to decline, thereby increasing the unemployment rate.
Difficulties in the new environment: Investing in less developed countries requires
investors to spend time, effort to correct and provide initial guidance.
3.2. The role of FDI for countries receiving investment capital
The role of FDI for countries receiving investment capital has several positive aspects:
Economic growth: Contribute to increasing income sources and creating conditions
to improve the state budget situation, creating a positive competitive environment.
Promoting transformation: FDI brings modern scientific technology, highly
specialized techniques, and advanced management levels.
Providing employment: FDI helps to solve socio-economic difficulties, typical y
unemployment among manual workers.
Improving the quality of manpower: Workers and line managers have the
opportunity to learn and improve their qualifications.
There are various drawbacks to FDI's involvement in nations that receive investment funds.
Financial disadvantage: capital contribution ratio in enterprises puts the receiving
country at a disadvantage in profit sharing, and high production costs also increase
the cost of domestic products.
Pol uting the environment: Because of policies to encourage investment, the long-
term issue of environmental protection is stil not strictly regulated, which wil
greatly affect the environment of the host country.
Political instability: The amount of capital poured into developing countries can
add to regional imbalances, adversely affect society such as changes in personality,
human outlook, the occurrence of evils…
3.3. The role of FDI for the Vietnamese market
Economy: Contribute to perfecting market economic institutions, improving economic
management and corporate governance capacity.
Markets: Providing capital resources, improving technological capabilities,
competitiveness of firms in the market, and opportunities to access international markets. 3
Structure: Contribute to changing economic structure, forming a number of key industries.
Human resources: Through cooperation with foreign businesses, workers can acquire
modern technical qualifications and management skil s, suitable for the current
environment. Improve labor productivity, support strategic industries of countries.
4. Forms of foreign investment
4.1. According to the investor's purpose
Horizontal Investment is a form of investment that only pours capital into foreign
companies in the same industry or produces similar products as in the investing company.
Vertical Investment is a form of investment made throughout the length of a
company's supply chain, which can be in one industry or many different industries. 4.2. Equity-based
Investment in establishing an economic organization is a form of direct investment in
which the investor as a legal economic organization puts his capital and assets into establishing a new business.
Private Investment is a form of investment in which the investor as a business
individual provides investment resources in another country.
4.3. According to the form and investment process
Joint Venture is a form that al ows partners from two or more countries to cooperate
in investing and sharing profits.
Mergers and Acquisition consists of the acquisition of part or al of the shares of a
business available in the recipient country.
Greenfield Investment is a form of investment from the beginning by building a new
business or expanding production in the receiving country. 4
CHAPTER 2: VIETNAM'S FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT SITUATION
2.1. State perspective on foreign direct investment in Vietnam.
The Government of Vietnam views foreign direct investment (FDI) as vital for economic
growth and modernization. Policies are in place to improve the investment environment,
protect investor rights, and prioritize high-tech and eco-friendly sectors. The government
also focuses on human resource development, technology transfer, and reducing regional
disparities. With a commitment to environmental protection, sustainable development,
and international cooperation, Vietnam has created an at ractive, stable, and transparent
investment environment, drawing increasing FDI inflows.
2.2. Foreign direct investment legal system in Vietnam
Vietnam is considered one of the most stable and safest countries in the world, which
significantly influences its at ractiveness for foreign direct investment (FDI). Political
stability creates a business environment based on trust and minimizes risks for
investors. According to the World Bank's 2005 World Development Report, Vietnam
is evaluated to have a good legal framework and a favorable investment environment,
contributing to diversified and multilateral economic relations with other countries.
The Foreign Investment Law in Vietnam was first enacted in 1987 and has undergone
multiple amendments and supplements, aligning with international standards and
practices. This law initiated the at raction and efficient utilization of FDI into
Vietnam, promoting economic diversification and multilateral economic relations.
Alongside the continuous enhancement of legal frameworks and bilateral/multilateral
agreements related to FDI, Vietnam has signed 51 investment encouragement and
protection agreements with various countries and territories.
In 2005, the National Assembly enacted the Investment Law effective from July 1,
2006, replacing the Foreign Investment Law and the Domestic Investment
Encouragement Law. This change reflects the Party and State's at ention to the FDI 5
sector, a crucial component of Vietnam's economy, adapting to general laws to timely
respond to objective changes in domestic and international economic developments.
Research on FDI activities in Vietnam over different periods has demonstrated that the
Investment Law has significantly contributed to positive transformations, facilitating
the at raction and effective utilization of FDI into Vietnam's economy. Improved
management mechanisms include strong decentralization to provincial People's
Commit ees and Management Boards of Industrial Parks, Export Processing Zones,
High-Tech Zones, and Economic Zones, enhancing policy-making, inspection,
supervision, and support for FDI activities at local levels. The "one-stop shop" and
"red carpet" approaches have widely applied, further enhancing the effectiveness of
at racting and utilizing FDI in Vietnam.
2.3. Foreign direct investment activities in Vietnam
Since implementing the Renovation Campaign in 1986, Vietnam has at racted
significant FDI inflows, emerging as a rising star in the global production supply
chain. While initial y most investments were directed towards low value-added sectors
such as textiles, apparel, and footwear, Vietnam quickly ascended the value chain,
developing into a crucial hub for electronics assembly. Despite fierce trade chal enges,
Vietnam continues to lead in at racting high-quality FDI. Investment in manufacturing
sectors now accounts for 85% of total new FDI.
In 2023, a notable highlight was the significant increase in new FDI flows into the
manufacturing sector, despite global economic chal enges and post-Covid-19
limitations. FDI remains a "favorable wind" for Vietnam amidst global supply chain
diversification. Despite existing chal enges related to the quality of the workforce,
Vietnam is stil recognized for its at ractive investment environment with numerous
competitive advantages and appealing foreign investment policies.
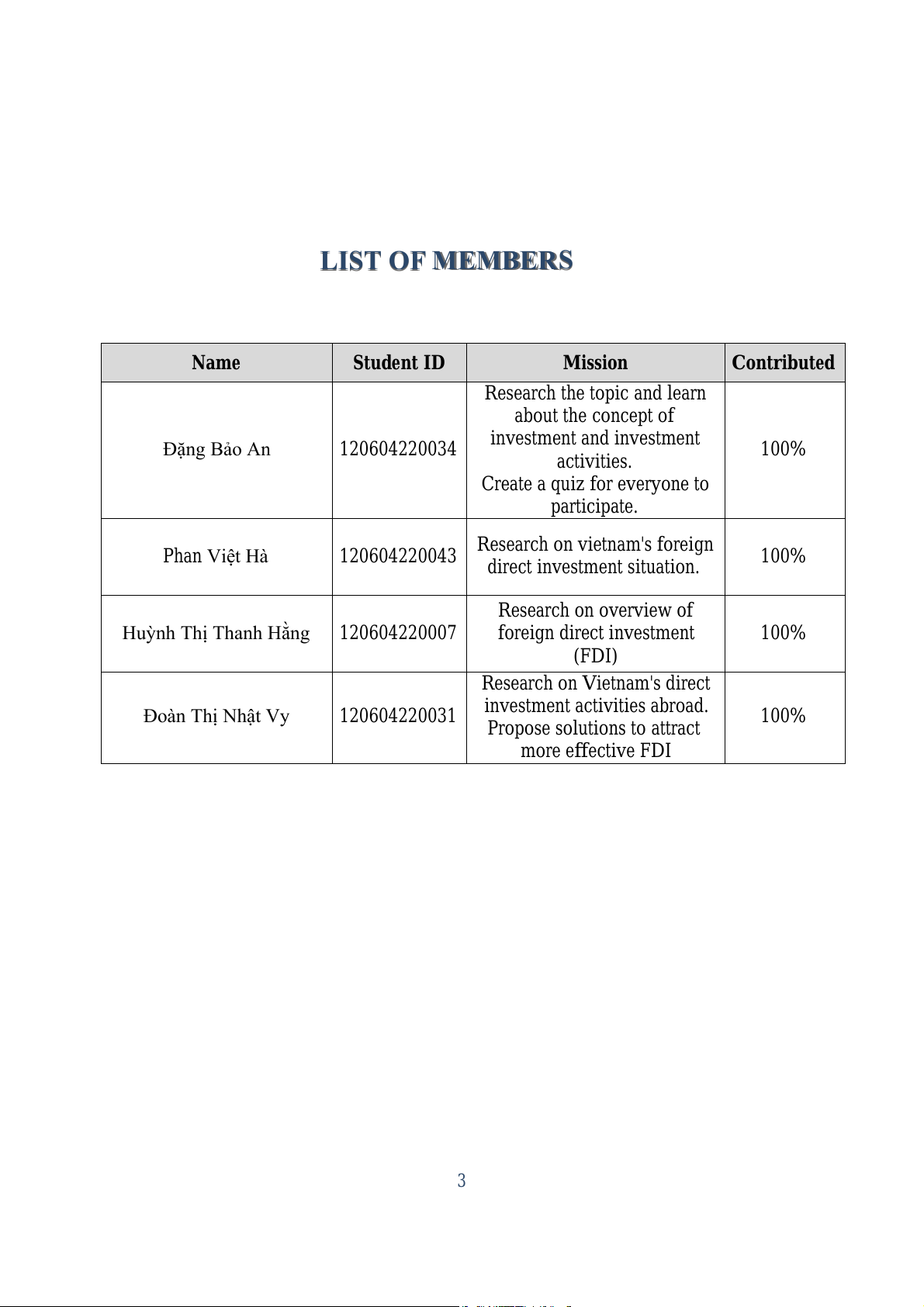
Foreign investors have entered 18 out of Vietnam's 21 economic sectors.
Manufacturing leads with over USD 23.5 bil ion, 64.2% of total investment, up
39.9%. Real estate fol ows with nearly USD 4.67 bil ion, 12.7% of total, up 4.8%. 6
Electricity, finance sectors rank next with over USD 2.37 bil ion (up 4.9%) and nearly
USD 1.56 bil ion (almost 27 times higher).
Figure 1: Foreign investment fields in 2023 (Source: Ministry of Planning and Investment)
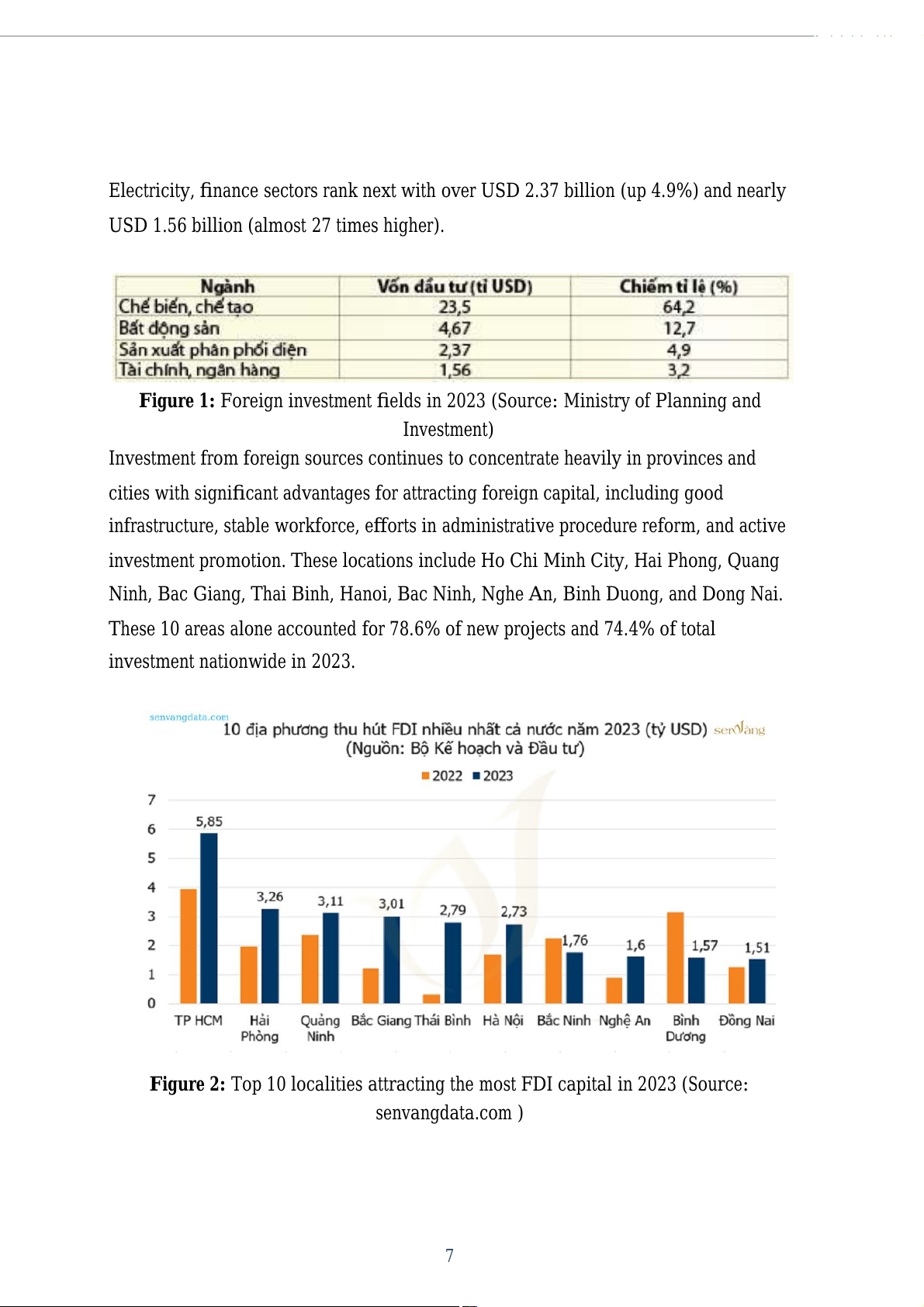
Investment from foreign sources continues to concentrate heavily in provinces and
cities with significant advantages for at racting foreign capital, including good
infrastructure, stable workforce, efforts in administrative procedure reform, and active
investment promotion. These locations include Ho Chi Minh City, Hai Phong, Quang
Ninh, Bac Giang, Thai Binh, Hanoi, Bac Ninh, Nghe An, Binh Duong, and Dong Nai.
These 10 areas alone accounted for 78.6% of new projects and 74.4% of total
investment nationwide in 2023.
Figure 2: Top 10 localities at racting the most FDI capital in 2023 (Source: senvangdata.com ) 7
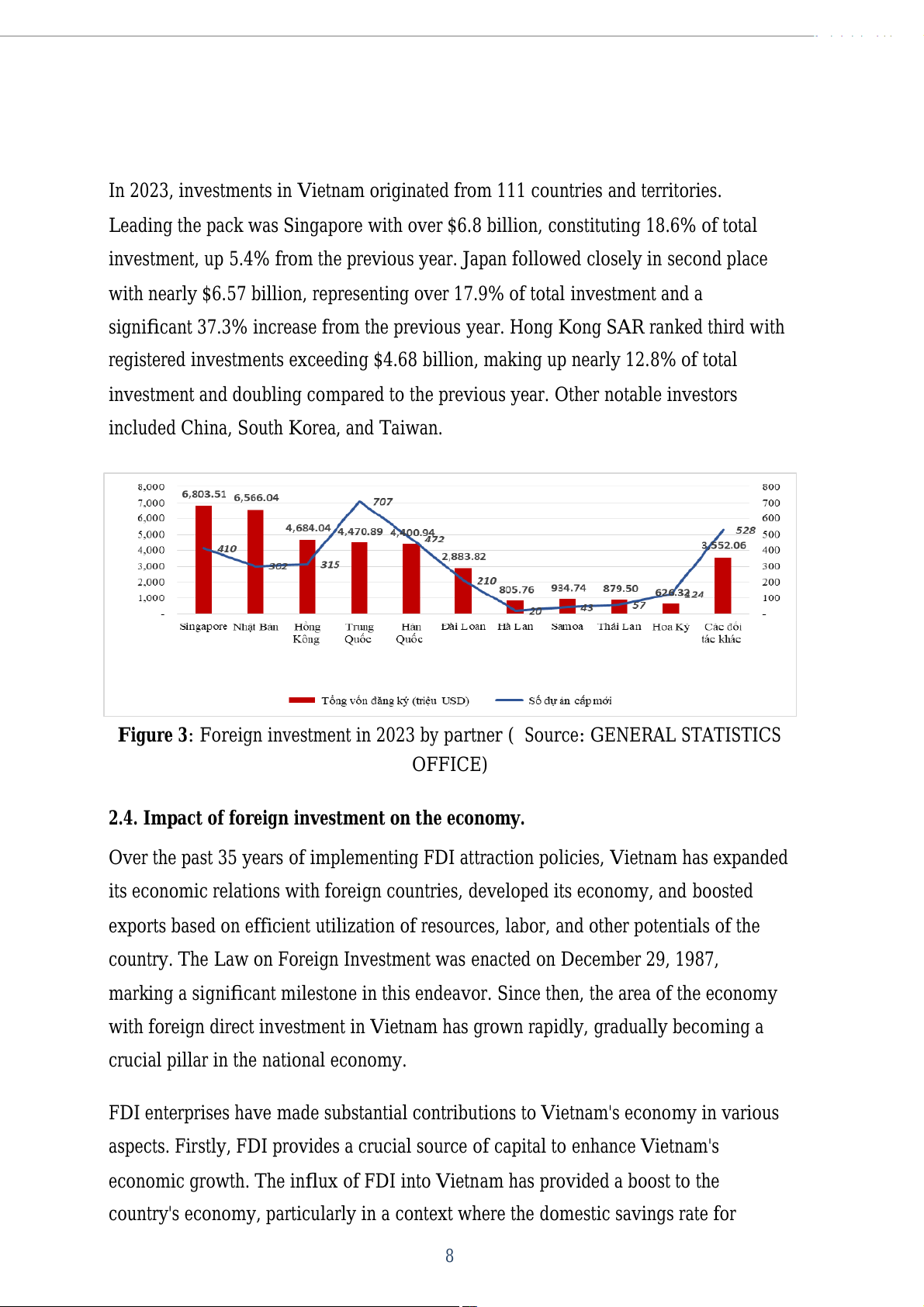
In 2023, investments in Vietnam originated from 111 countries and territories.
Leading the pack was Singapore with over $6.8 bil ion, constituting 18.6% of total
investment, up 5.4% from the previous year. Japan fol owed closely in second place
with nearly $6.57 bil ion, representing over 17.9% of total investment and a
significant 37.3% increase from the previous year. Hong Kong SAR ranked third with
registered investments exceeding $4.68 bil ion, making up nearly 12.8% of total
investment and doubling compared to the previous year. Other notable investors
included China, South Korea, and Taiwan.
Figure 3: Foreign investment in 2023 by partner ( Source: GENERAL STATISTICS OFFICE)
2.4. Impact of foreign investment on the economy.
Over the past 35 years of implementing FDI attraction policies, Vietnam has expanded
its economic relations with foreign countries, developed its economy, and boosted
exports based on efficient utilization of resources, labor, and other potentials of the
country. The Law on Foreign Investment was enacted on December 29, 1987,
marking a significant milestone in this endeavor. Since then, the area of the economy
with foreign direct investment in Vietnam has grown rapidly, gradual y becoming a
crucial pil ar in the national economy.
FDI enterprises have made substantial contributions to Vietnam's economy in various
aspects. Firstly, FDI provides a crucial source of capital to enhance Vietnam's
economic growth. The influx of FDI into Vietnam has provided a boost to the
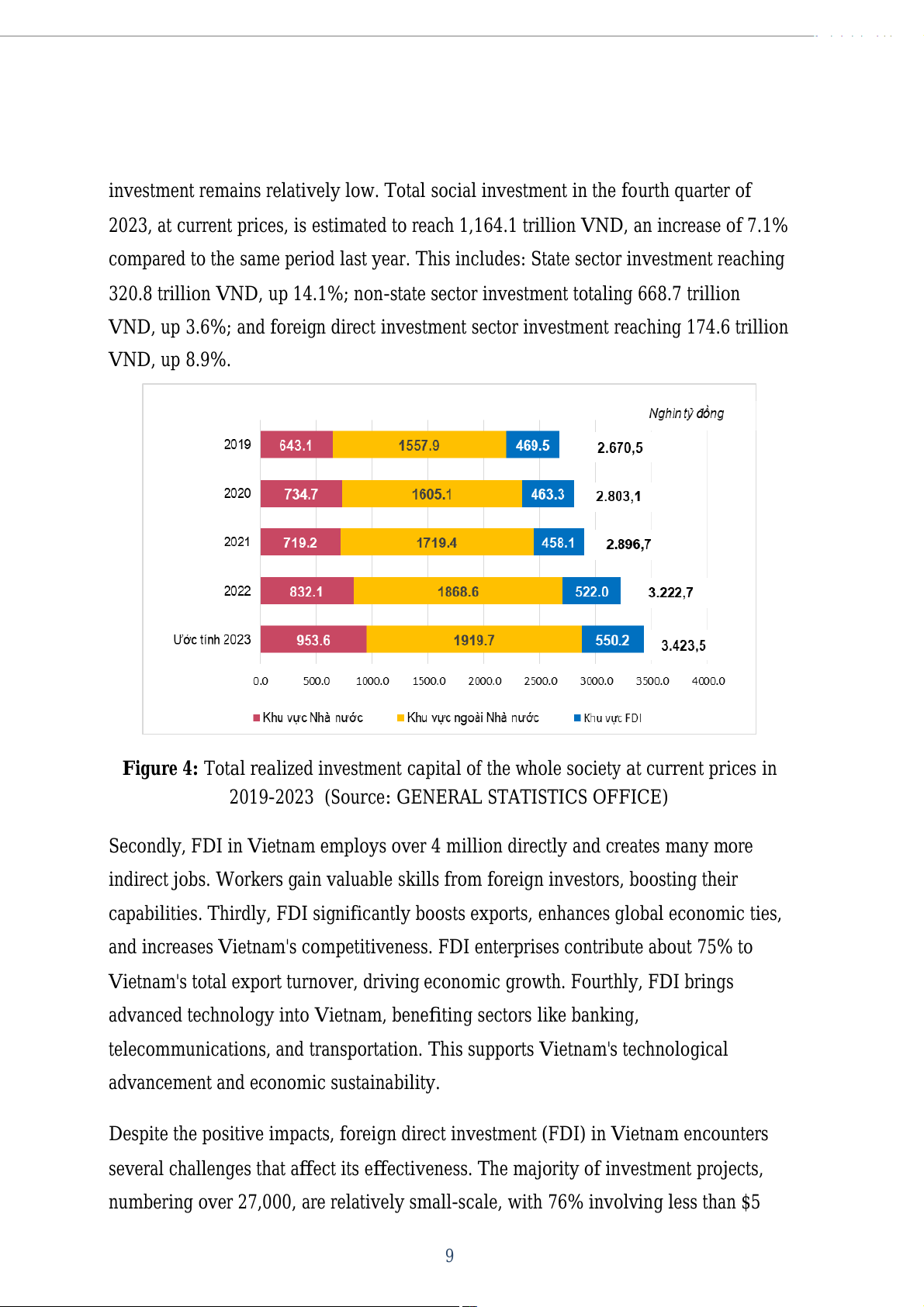
country's economy, particularly in a context where the domestic savings rate for 8
investment remains relatively low. Total social investment in the fourth quarter of
2023, at current prices, is estimated to reach 1,164.1 tril ion VND, an increase of 7.1%
compared to the same period last year. This includes: State sector investment reaching
320.8 tril ion VND, up 14.1%; non-state sector investment totaling 668.7 tril ion
VND, up 3.6%; and foreign direct investment sector investment reaching 174.6 tril ion VND, up 8.9%.
Figure 4: Total realized investment capital of the whole society at current prices in
2019-2023 (Source: GENERAL STATISTICS OFFICE)
Secondly, FDI in Vietnam employs over 4 mil ion directly and creates many more
indirect jobs. Workers gain valuable skil s from foreign investors, boosting their
capabilities. Thirdly, FDI significantly boosts exports, enhances global economic ties,
and increases Vietnam's competitiveness. FDI enterprises contribute about 75% to
Vietnam's total export turnover, driving economic growth. Fourthly, FDI brings
advanced technology into Vietnam, benefiting sectors like banking,
telecommunications, and transportation. This supports Vietnam's technological
advancement and economic sustainability.
Despite the positive impacts, foreign direct investment (FDI) in Vietnam encounters
several chal enges that affect its effectiveness. The majority of investment projects,
numbering over 27,000, are relatively smal -scale, with 76% involving less than $5 9
mil ion and 45% less than $1 mil ion, limiting their competitiveness in the global
business environment. Moreover, compliance issues with Vietnamese laws are
prevalent among FDI enterprises, particularly concerning environmental regulations,
labor practices, wage standards, and tax obligations. Many firms exploit legal
loopholes and lax enforcement, which adversely impacts Vietnam's environment and
social conditions. Additional y, FDI tends to introduce technologies that are not
cut ing-edge, focusing more on labor-intensive operations that do not significantly
contribute to enhancing local industry capabilities. Therefore, the localization rate of
FDI remains relatively low, posing ongoing chal enges to Vietnam's economic
integration and sustainable development goals.
2.5. Vietnam's direct investment activities abroad
Vietnam's direct investment activities abroad in recent years have achieved significant
developments, contributing to the process of international economic integration and
affirming Vietnam's position in the international market. . However, besides the
achievements, direct investment activities also reveal some limitations that need to be
recognized and have solutions to improve efficiency in the next period.
2.5.1. Current status of Vietnam's direct investment activities abroad
After more than 30 years of integration and development to date; Vietnam is not only
a leading investment receiving country in the region but also has risen to become a
country with many businesses investing abroad. Vietnam's overseas investment
activities are increasingly diverse and clearly demonstrated through markets,
investment industries, scale, investment forms and economic types in which businesses invest.
In the first 11 months of 2019, Vietnam's foreign direct investment (FDI) activities
recorded strong development with total investment capital (new and increased capital)
reaching 458.8 mil ion USD. Prominent in this vibrant investment picture are the fol owing areas:
Wholesale and retail, repair of cars, motorbikes, motorbikes and other motor vehicles:
At racted 118.2 mil ion USD, accounting for 25.8% of total investment capital,
showing the great potential of the consumer market used in neighboring countries. 10
Agriculture, forestry and fisheries: At racted capital of 65.6 mil ion USD,
equivalent to 14.3% of total investment capital, demonstrating the need for food
security and sustainable development in the region.
Professional, scientific and technological activities: Received 60 mil ion USD,
accounting for 13.1% of total investment capital, showing the potential for
cooperation in the field of artificial intel igence and innovation.
Real estate business activities: At racted 59.3 mil ion USD, equivalent to 12.9% of
total investment capital, showing the at ractiveness of the real estate market in
countries with developing economies.
Figure 5 : Vietnam's foreign direct investment (FDI) activities recorded strong
development with total investment capital in the first 11 months of 2019.
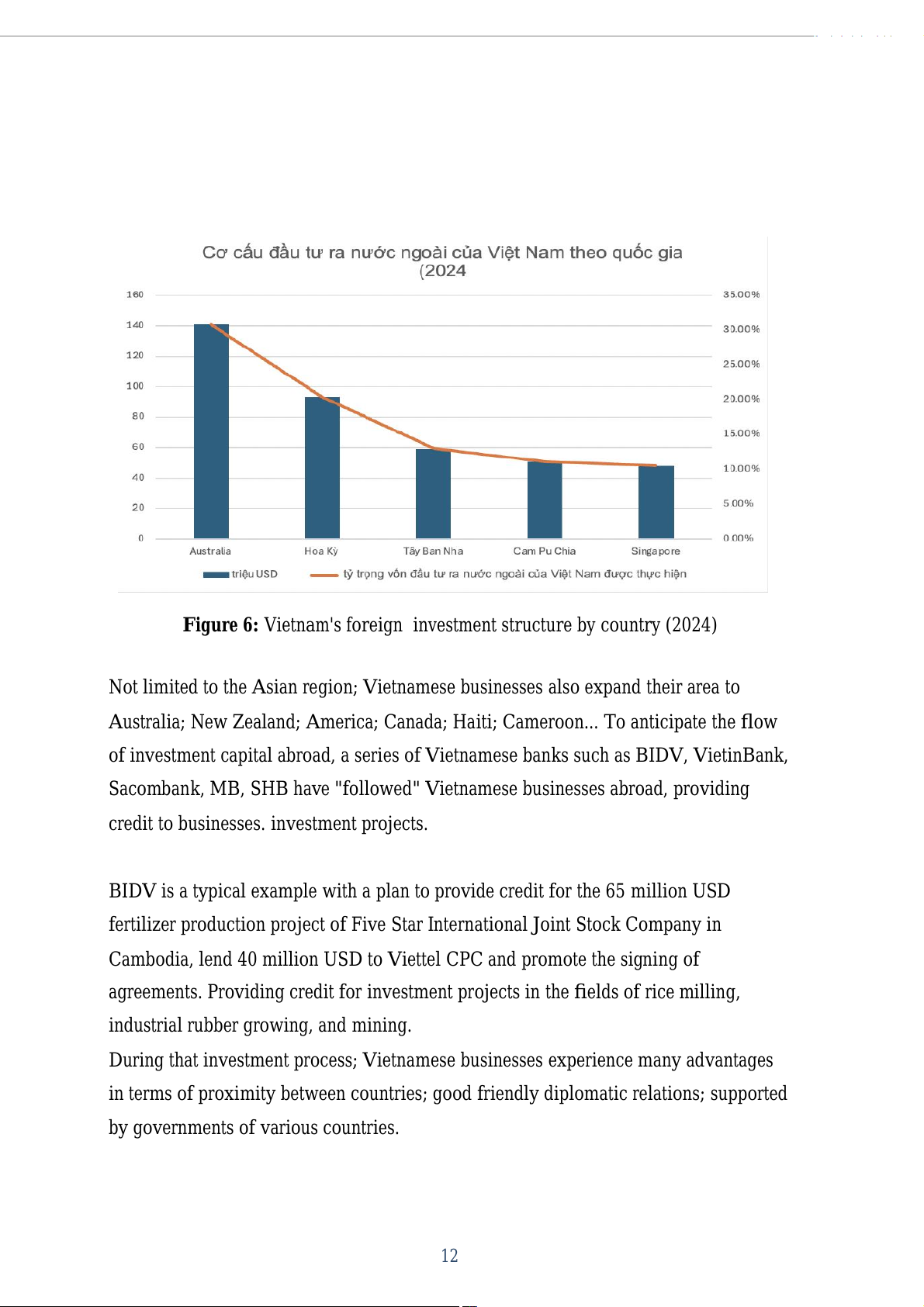
Vietnam has formed a trend of Vietnamese businesses investing in familiar markets
such as Laos and Cambodia, which are countries with the largest number of projects
and total commit ed investment capital. there were 31 countries; Territories receiving
Vietnamese investment; in which Australia is the leading country with 141.3 mil ion
USD; accounting for 30.8%; United States 93;4 mil ion USD; accounting for 20.4%;
Spain 59;8 mil ion USD; accounts for 13%; Cambodia 50;7 mil ion USD; accounting
for 11.1%; Singapore 48 mil ion USD; accounting for 10.5%. 11
Figure 6: Vietnam's foreign investment structure by country (2024)
Not limited to the Asian region; Vietnamese businesses also expand their area to
Australia; New Zealand; America; Canada; Haiti; Cameroon. . To anticipate the flow
of investment capital abroad, a series of Vietnamese banks such as BIDV, VietinBank,
Sacombank, MB, SHB have "fol owed" Vietnamese businesses abroad, providing
credit to businesses. investment projects.
BIDV is a typical example with a plan to provide credit for the 65 mil ion USD
fertilizer production project of Five Star International Joint Stock Company in
Cambodia, lend 40 mil ion USD to Viet el CPC and promote the signing of
agreements. Providing credit for investment projects in the fields of rice mil ing,
industrial rubber growing, and mining.
During that investment process; Vietnamese businesses experience many advantages
in terms of proximity between countries; good friendly diplomatic relations; supported
by governments of various countries. 12
Decree No. 83/2015/ND-CP on investment abroad was issued, the Government of
Vietnam created more favorable conditions for businesses to expand the scope of
investment and business abroad.
The Ministry of Planning and Investment also issued Circular No. 03/2018/TT-
BKHDT guiding and promulgating sample documents for implementing overseas
investment procedures, contributing to standardizing legal procedures and creating an
investment environment. clear privacy.
Thanks to practical support policies and an increasingly perfect investment
environment, Vietnam's FDI activities abroad have made certain impressions.
Many Vietnamese corporations, corporations and businesses have had investment
capital abroad exceeding the threshold of 1 bil ion USD, typical y Vietnam Oil and
Gas Group, Military Telecommunications Group (Viet el), Hoang Gia Joint Stock Company. Anh - Gia Lai.
The success of Vietnamese businesses affirms the competitiveness and great potential of FDI activities abroad.
2.5.2. Some lessons learned from the situation of vietnam's direct investment activities abroad
Vietnamese enterprises' overseas investment activities are growing, but there are stil
many limitations that need to be overcome to improve efficiency. Some key limitations include:
Limited financial capacity and investment experience: Vietnamese businesses are
often smal in scale, have limited capital, and lack experience operating in the
international environment, leading to low competitiveness.
Industry structure is not reasonable: Some industries and fields have potential but
have not at racted many foreign investment projects
Ineffective management: The implementation of the reporting regime is incomplete,
coordination between authorities is limited, and there is a lack of survey teams to
evaluate the effectiveness of overseas investment activities.
Loose relationship with diplomatic representative agencies: When a dispute
occurs, businesses investing abroad have difficulty accessing support from the state. 13
Cumbersome administrative procedures: The legal framework is unclear, the
licensing verification process is lengthy, hindering investment activities.
Inadequate business support: Lack of practical support solutions for finance, market
information, partner connections, etc.
CHAPTER 3: MEASURES TO IMPROVE THE S TO IMPROV EFFECTIVENESS OF EFFECTIV VIETNAM'S FOREIGN DIRECT 'S FOREIG INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES INVESTMENT ACTIVITI
Through analysis and research of Vietnam's foreign direct investment activities, to
at ract FDI more effectively, Vietnam needs to synchronously implement many
solutions, of which the top priorities are:
Perfecting institutions, laws and effective enforcement:
Improve the legal system on investment, ensuring transparency, consistency and
compliance with international practices. Promulgate and amend the Investment Law
and other investment-related laws to ensure transparency and consistency. consistent
and consistent with international practices. Complete the system of legal regulations
on fields and industries at racting FDI and provide complete, easily accessible legal
information for foreign investors.
Strengthen law enforcement, associate with decentralization, decentralization,
individualization of responsibilities and promotion of the responsibilities of leaders.
Improve the law enforcement capacity of state agencies, especial y state management
agencies on investment. Apply strict handling measures for violations of investment laws.
Improve the operational efficiency of state agencies in at racting FDI, creating an
open, safe and stable investment environment for investors.
Enhance endogenous potential:
Develop high-quality human resources with professional qualifications and skil s to
meet the requirements of foreign investors. Improve the management and operating 14




