

Preview text:
Student Name:… Student ID: …
MULTI-CRITERIA DECISION MAKING
Exercises – SAW, TOPSIS & AHP
SAW (Simple Additive Weighting) & TOPSIS (Technique for Order Preference by
Similarity to the Ideal Solution)
Question 1: Bank Evaluation Problem
Consider a bank evaluation problem where the performance of banks is assessed based on four key criteria:
• Investment income (x1): Represented in millions.
• Number of customers (x2): Measured in total customer count.
• Brand image (x3): Rated on a scale (1 to 10), where higher values indicate a better image.
Number of branches (x4): Total number of bank branches.
Suppose we have five banks (A, B, C, D, and E), and their performance is summarized in the table below: Bank
Investment Income (x1) Number of Brand Number of (in millions)
Customers (x2)
Image (x3)
Branches (x4) A 2,500 160,000 6 12 B 2,300 120,000 8 17 C 1,900 150,000 5 18 D 3,100 100,000 7 14 E 2,800 130,000 7 10
Each criterion is assigned a weight representing its importance in the evaluation:
• Investment income: 0.30
• Number of customers: 0.20 • Brand image: 0.25
• Number of branches: 0.25 Task:
Using the above information, evaluate the banks based on their performance across all criteria,
using Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) technique. 1 Student Name:… Student ID: …
Question 2: Problem of Choosing a Warehouse Location for a Retailer
A large retailer is looking to establish a new regional warehouse to improve its distribution network.
To make an informed decision, the retailer evaluates four different locations (L1, L2, L3, and L4)
based on several key criteria:
• Proximity to Major Markets (P1): Distance to key markets in kilometers.
• Construction Cost (P2): The estimated cost of building the warehouse, measured in millions of dollars.
• Labor Availability (P3): A score from 1 to 10 representing the availability of skilled labor.
• Infrastructure Quality (P4): A rating of local infrastructure, scored from 1 to 10.
The retailer has gathered data for each location as shown below: Location Proximity to Construction Cost Labor Infrastructure Markets (km) (P1) (P2) (million $) Availability (P3) Quality (P4) L1 50 12 8 7 L2 75 10 7 9 L3 60 11 9 6 L4 55 13 7 8
The company assigns the following importance weights to each criterion:
• Proximity to Major Markets (P1): 0.38
• Construction Cost (P2): 0.28
• Labor Availability (P3): 0.20
• Infrastructure Quality (P4): 0.14 Task:
Use the Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) method to determine the most suitable warehouse location.
Question 3: Problem of Selecting the Best 3PL (Third-Party Logistics) Provider
A company in the electronics manufacturing industry is looking to partner with a 3PL (ThirdParty
Logistics) provider to manage its warehousing, transportation, and distribution. The company has
identified five potential 3PL providers (P1, P2, P3, P4, and P5) and must evaluate them based on the following criteria:
• Cost (C1): The total cost of logistics services, measured in millions of dollars.
• Delivery Speed (C2): The average time it takes to deliver products to customers, measured in hours.
• Service Reliability (C3): The percentage of on-time deliveries, measured as a percentage. 2 Student Name:… Student ID: …
• Technology Integration (C4): The 3PL’s ability to integrate with the company’s existing
systems, rated on a scale from 1 to 10.
The data collected for each 3PL provider is presented in the following table: 3PL Cost (C1) Delivery Speed Service Reliability Technology Provider (million $) (C2) (hours) (C3) (%) Integration (C4) P1 3.2 48 92 8 P2 3.0 36 85 7 P3 3.5 40 95 7 P4 2.8 50 90 8 P5 3.1 42 88 9
The company assigns the following importance weights to the criteria:
• Cost (C1): 0.33
• Delivery Speed (C2): 0.22
• Service Reliability (C3): 0.27
• Technology Integration (C4): 0.18 Task:
Using the TOPSIS (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to the Ideal Solution) method,
evaluate the five 3PL providers and determine which provider is the best choice for the company.
Question 4: Problem of Choosing a Distribution Center for E-commerce Fulfillment
An e-commerce company is planning to open a new distribution center to improve its order
fulfillment process. The company has shortlisted four locations (L1, L2, L3, and L4) and will
evaluate them based on five important criteria:
• Operational Cost (C1): Total annual operational cost in millions of dollars.
• Proximity to Customer Base (C2): Average distance to major customer regions in kilometers.
• Labor Availability (C3): A score from 1 to 10, with higher values indicating better
availability of skilled labor.
• Warehouse Capacity (C4): Maximum storage capacity in thousands of square meters.
• Environmental Impact (C5): A sustainability score from 1 to 10, with higher values
indicating better environmental practices.
The following table shows the data collected for each location, along with the assigned weights for each criterion: Location C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 Weight 3 Student Name:… Student ID: … L1 12.0 250 8 50 7 0.25 L2 10.5 300 7 55 9 0.20 L3 11.0 200 9 45 6 0.30 L4 12.5 220 8 60 8 0.25 Task:
Use the TOPSIS (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to the Ideal Solution) method to
determine which location is the most suitable for the new distribution center.
AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process)
Question 5: Warehouse Location Selection
A company is considering four potential locations for a new warehouse. They need to evaluate
these locations based on three criteria:
- Cost: The initial setup and ongoing operational cost of the warehouse.
- Proximity to Suppliers: The distance from major suppliers, affecting transportation costs and delivery times.
- Labor Availability: The availability of skilled labor in the area.
Pairwise Comparison Matrix for Criteria Criteria Cost Accessibility Proximity to Suppliers Cost 1 3 Accessibility 0.5 1 2 Proximity to 1 Suppliers Location Scores
It is known that the lower score given in criterion Cost, the better alternative is. Criterion Location X Location Y Location Z Location W Cost 8 6 7 5 Proximity to Suppliers 7 9 6 8 4 Student Name:… Student ID: … Labor Availability 6 7 8 5 Task:
a. Develop the weight of criteria and check consistency of the pairwise comparison in the
table of Pairwise Comparison Matrix for Criteria.
b. Use the AHP method to determine the best warehouse location for this problem.
Question 6: Problem of Supplier Selection for a Manufacturing Firm
A manufacturing firm needs to select the most suitable supplier for a critical component used in
their production process. The decision involves evaluating several potential suppliers based on
multiple criteria. The firm has identified four potential suppliers and the following criteria for selection:
• Cost: The total cost of purchasing the component from the supplier.
• Quality: The quality of the component, as measured by defect rates and adherence to specifications.
• Delivery Time: The average lead time for the supplier to deliver the component.
• Reliability: The supplier’s track record in meeting delivery schedules and handling issues.
• Customer Service: The level of support and communication provided by the supplier. Given Data
1. Potential Suppliers: Supplier A, Supplier B, Supplier C, Supplier D
2. Comparision of Criteria Criteria Cost Quality Delivery Time Reliability Cost 1 2 Quality 3 1 4 Delivery Time 0.5 1/3 Reliability 2 1/2 1
3. Supplier Scores for Each Criterion (on a scale of 1-10, where 10 is the best performance, except Cost criteria) 3.1. Supplier A: - Cost: 8 - Quality: 7 - Delivery Time: 6 - Reliability: 8 3.2. Supplier B: 5 Student Name:… Student ID: … - Cost: 7 - Quality: 9 - Delivery Time: 5 - Reliability: 7 3.3. Supplier C: - Cost: 6 - Quality: 6 - Delivery Time: 8 - Reliability: 6 3.4. Supplier D: - Cost: 9 - Quality: 5 - Delivery Time: 7 - Reliability: 9 Task
a. Formulate the AHP Model: Create the hierarchical structure with the goal at the top
(selecting the best supplier) and the criteria and sub-criteria (if any) below.
b. Pairwise Comparison: Construct pairwise comparison matrices for the based on the given
weights and scores and check its consistency.
c. Compute the Weights: Use the AHP methodology to calculate the weight of each supplier
based on the given scores and the criteria weights.
d. Rank the Suppliers: Determine the overall score for each supplier and rank them to identify the most suitable supplier. Question 7:
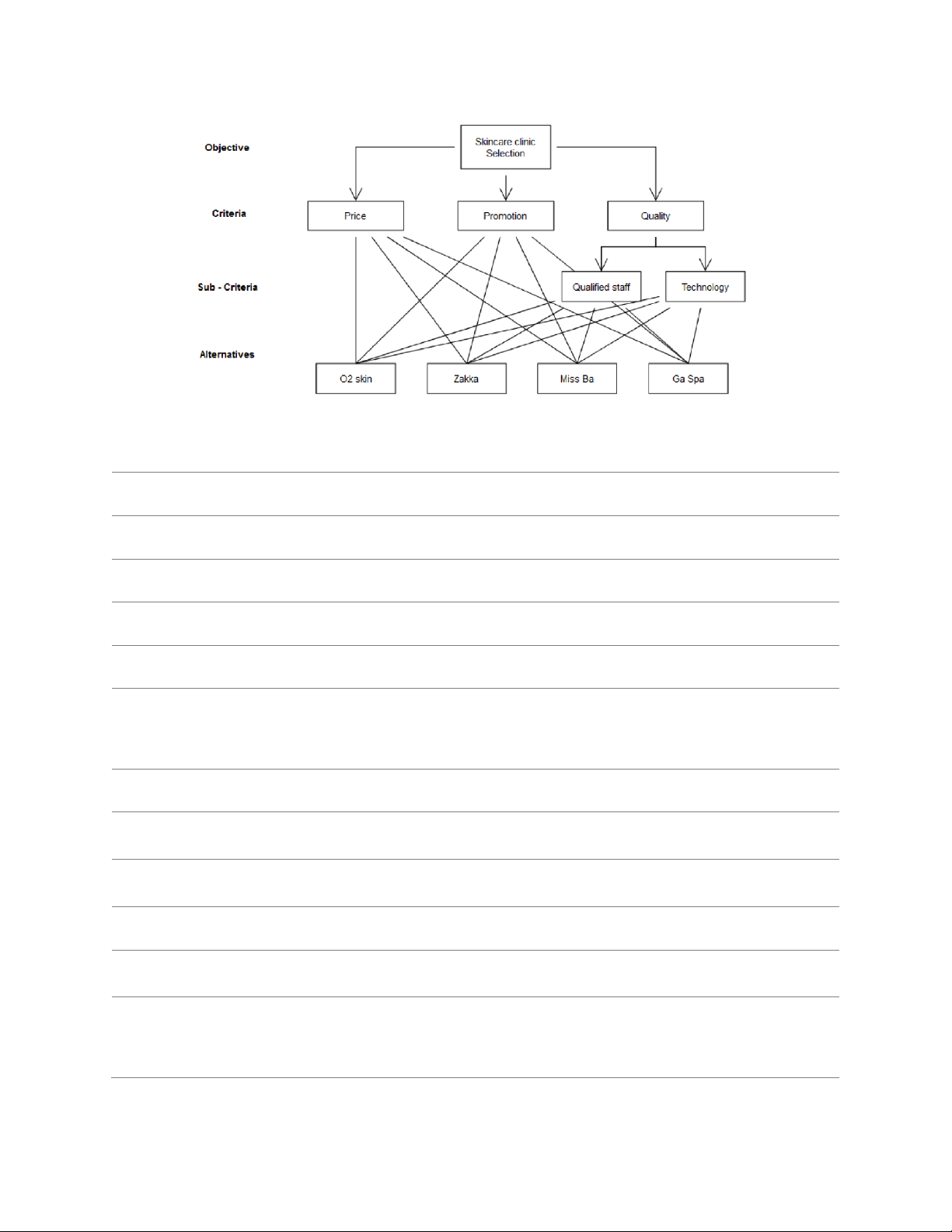
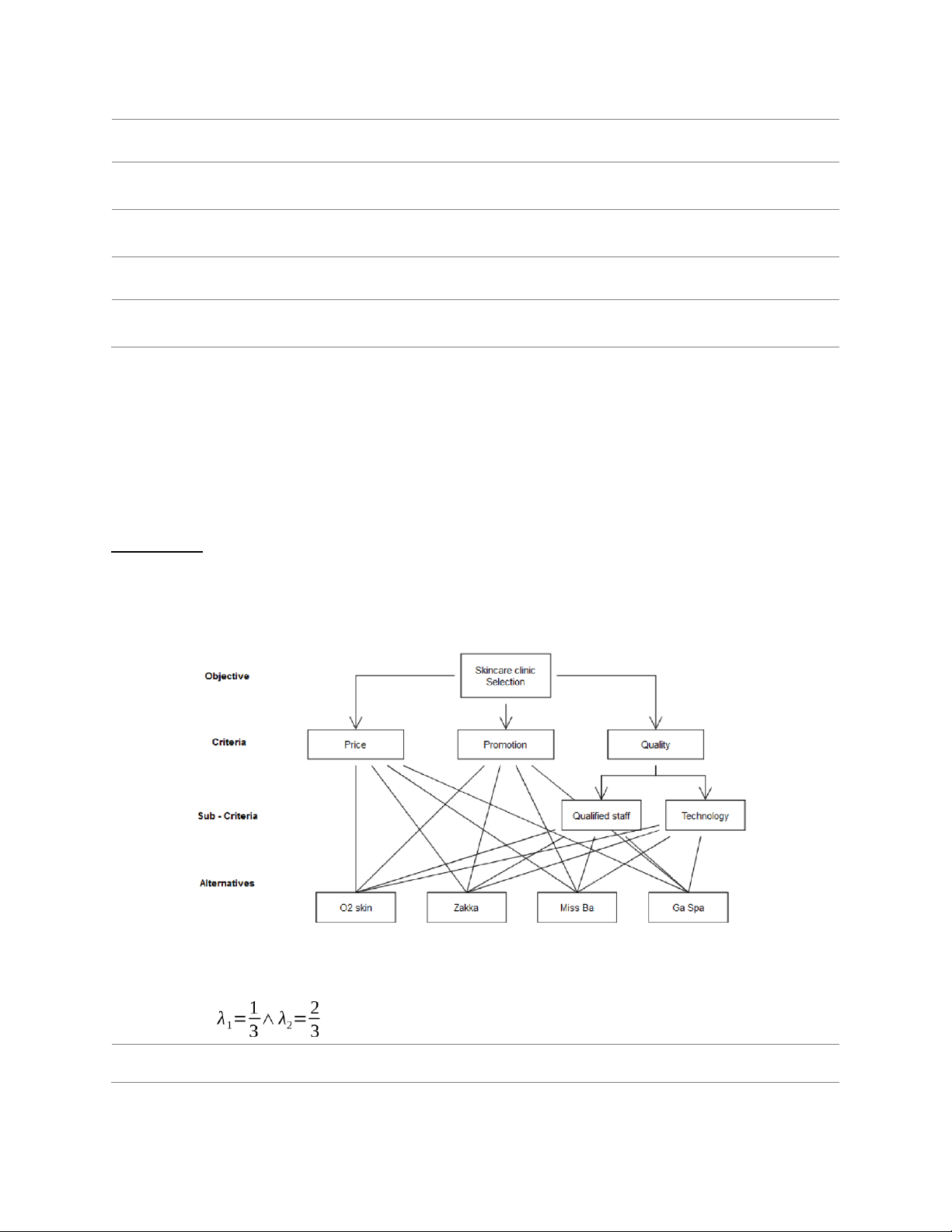
Given an AHP problem with the hierarchy presented in the figure below and the alternatives’
weights are shown in the Table 1. It is known that the lower score given in criterion Price, the better alternative is. 6 Student Name:… Student ID: …
Skincare clinic selection problem hierarchy
Table 1: Alternatives’ weight Price Technology Qualified staffs Promotion O2 0.26 0.26 0.12 Zakka 0.56 0.56 0.06 Miss Ba 0.06 0.12 0.25 Ga Spa 0.12 0.06 0.57
Table 2: Comparison of criteria Price Technology Qualified staffs Promotion Price 1 3 Technology 3 1 3 Qualified staffs 5 3 1 5 Promotion 1
Table 3: Alternatives’ score toward Price criterion 7 Student Name:… Student ID: … Price O2 Skin Zakka Miss Ba Ga Spa O2 Skin 1 3 Zakka 1 Miss Ba 5 7 1 2 Ga Spa 3 5 1 Task:
a. Develop the weight of alternatives for the criteria Price to complete Table 1.
b. Develop the weight of criteria and check consistency of the pair – wise comparison in Table 2.
c. Use AHP method to determine the best alternative for this problem
Question 8: AIJ/AIP method (Group decision)
Given an AHP problem with the hierarchy presented in the figure below and the alternatives’
weights are shown in Table 1. It is known that the lower score given in criterion Price, the better alternative is.
Skincare clinic selection problem hierarchy
Regarding the weight of criteria, the group of decision makers include Male and Female IU students with
respectively. And their assessments of criteria are as follows: Male (A1) Price Technology
Qualified staffs Promotion 8 Student Name:… Student ID: … Price 1 3 Technologies 5 1 3 5 Qualified staffs 3 1 5 Promotion 1 Female (A2) Price Technology
Qualified staffs Promotion Price 1 5 Technologies 3 1 3 Qualified staffs 7 3 1 7 Promotion 1 Task:
Calculate the aggregated weight of criteria using AIJ and AIP method. Check whether male and
female students have reached score consensus or not.
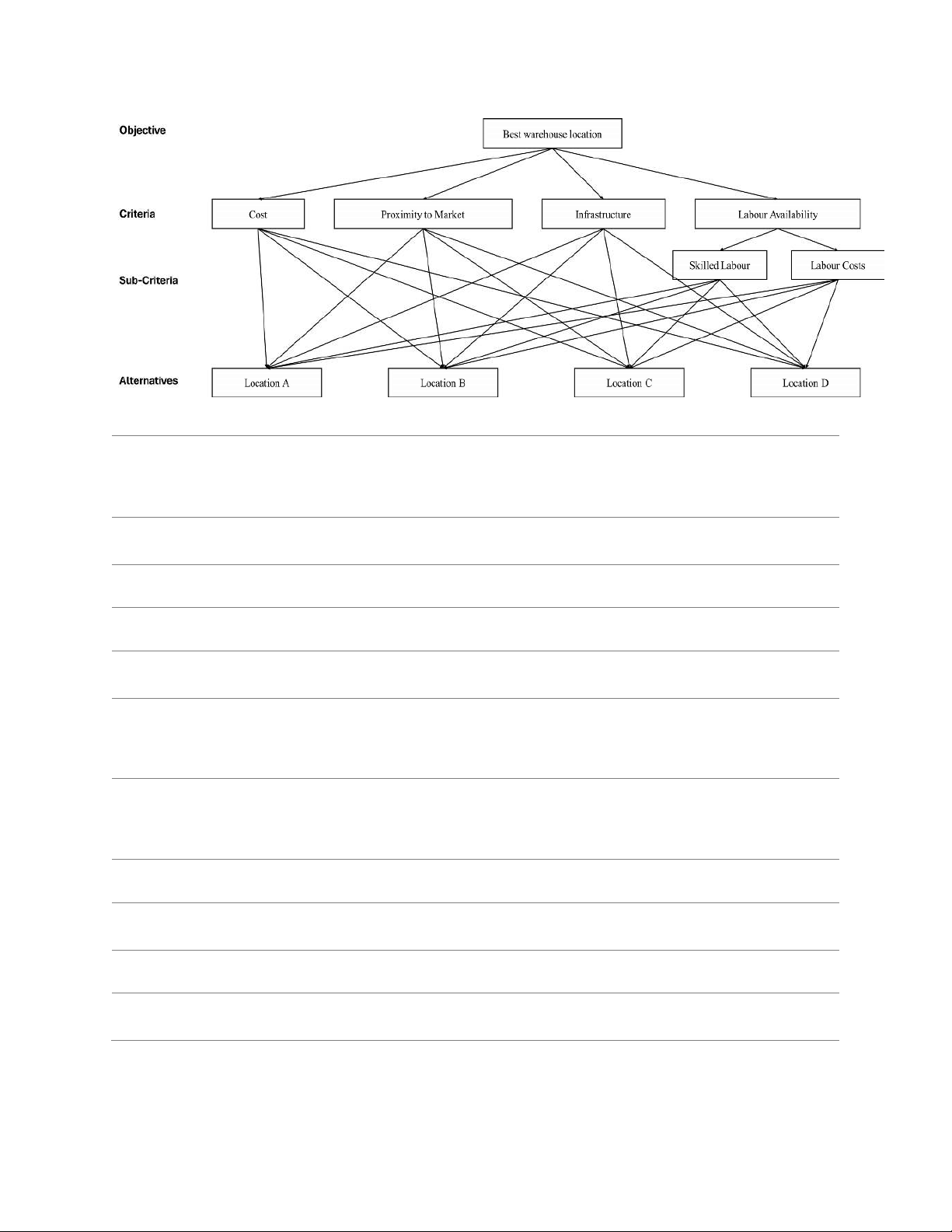
Question 9: AIJ/AIP Method - Group Decision in Warehouse Location Selection
You are tasked with selecting the best location for a new distribution warehouse based on input
from a group of decision-makers. The decision-makers consist of Senior Managers and 2 1
Operations Staff, with weights λ1=3 for Senior Managers and λ2=3 for Operations Staff.
Their assessments focus on four key criteria: Cost, Proximity to Market, Infrastructure, and Labor Availability.
Hierarchy of the Problem 9 Student Name:… Student ID: …
Table 1: Senior Managers’ (A1) Pairwise Comparison Matrix Proximity to Infrastructure Labor Criteria Cost Availability Market Cost 1 3 5 Proximity to Market 1 3 5 Infrastructure 1/5 1 4 Labor Availability 1/7 1
Table 2: Operations Staff’s (A2) Pairwise Comparison Matrix Proximity to Infrastructure Labor Criteria Cost Availability Market Cost 1 7 3 Proximity to Market 1/5 1 Infrastructure 1/4 1 3 Labor Availability 1/3 1/2 1 Task: 10 Student Name:… Student ID: …
a. Calculate the Aggregation of Individual Judgement (AIJ) matrix using the given pairwise
comparison matrices from the two decision-making groups (Senior Managers and
Operations Staff) with equal weights.
b. Calculate the Aggregation of Individual Priorities (AIP) for each criterion.
c. Check whether the two decision-making groups have reached consensus or not based on the aggregated result 11