
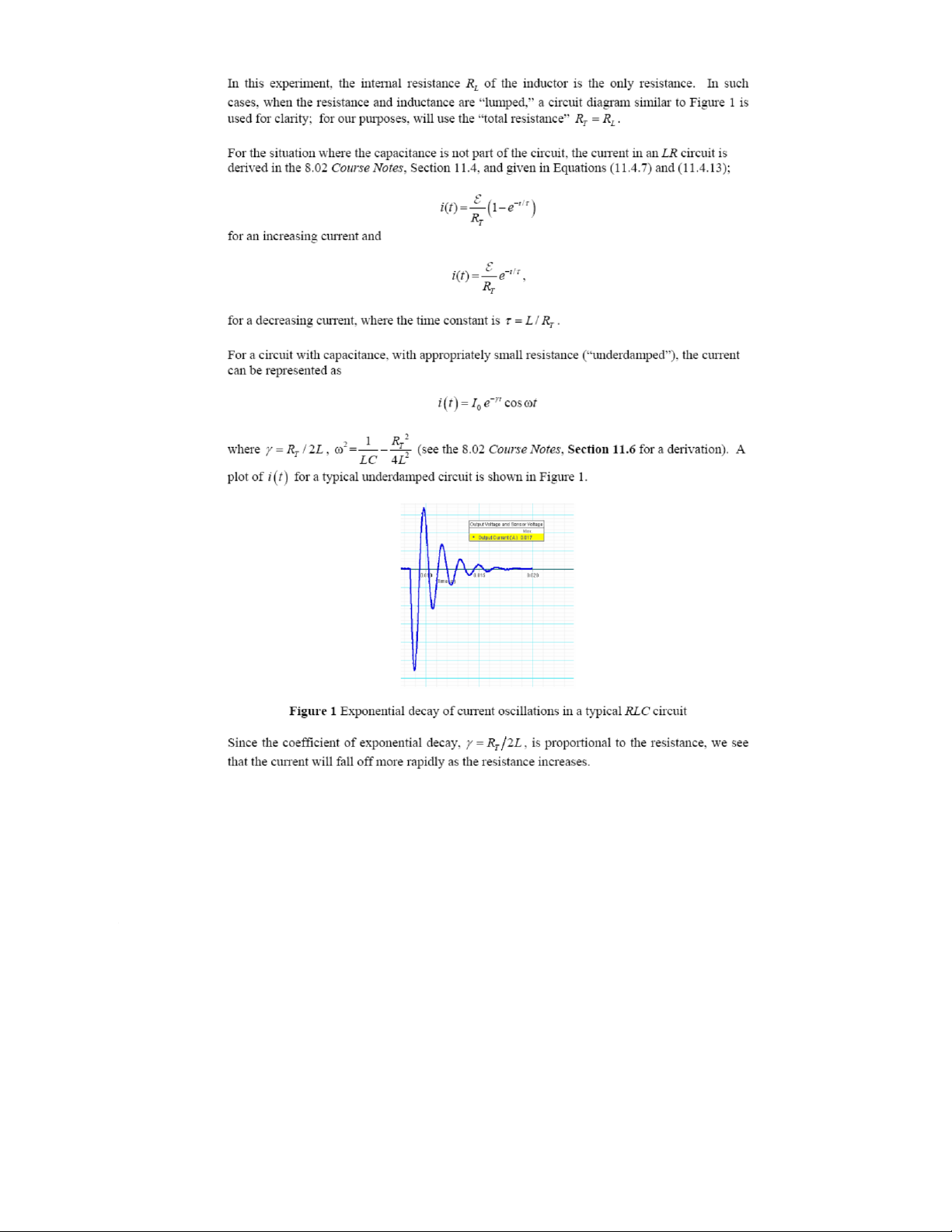







Preview text:
EXPERIMENT 3
Investigation of Electric Oscillation of RL and RLC Circuits Equipment and Materials
Science Workshop 750 Interface Power Amplifier
Lab circuit board with available inductor coil Iron rod for coil core Capacitor of 10 μF Objectives
Understanding the current across an inductor-resistor and the RLC circuits, then calculate the
energy of the oscillation RLC circuit.
How to process the experimental results
Part 1. Resistance and Inductance of the Coil
Question 1: Measure and calculate the resistance RL of your coil L.
Question 2: Calculate the inductance of your coil with and without the iron core based on the value
of slope obtained by Datastudio software.
Coil inductance without core: Lw/o = mH
Coil inductance with core: Lw = mH
Part 2: Free Oscillations of the RLC circuit
Question 3: Calculate the frequency, fmeasured = 1/T (Hz) based on the period of oscillation
determined by tools of Datastudio software. 1
Question 4: For your circuit parameters, compute the expected value of fprediction =( L H C z) π 2
and compare it to your measured value. Do you expect your result to be greater, equal, or less than
the measured value (Δf = prediction − fmeasured )?
Part 3: Observe the Energy in the RLC Circuit
Question 5: The circuit is losing energy most rapidly at times when the graph of total energy is
steepest; these times occur at about the same times that the magnetic energy reaches a local maximum. Briefly explain why.




