














Preview text:
Final Exam Review Chapter 13
1. The importance of effective salesforce selection
2. Stages in the recruitment and selection process
3. JD and Personnel specification phải biết phân biệt The title of the job Duties and responsibilities
To whom they will report: you will be managed by what dept
Technical requirements: the skills required to do that job
Location and geographical area to be covered
Degree of autonomy: how you can have the authority to do the task by yourself
(chủ quyền công việc: sự tự chủ trong công việc là gì?)
—> The difference bwn Job Description (the position) and specification (characteristics, knowledge, skills, …)
** Personnel specification 1. Physical requirements 2. Attainments 3. Aptitudes and qualities 4. Disposition 5. Interests 6. Personal circumstances
4. 6 main sources of recruitment
The company’s own staff: staff changes to another dept (nó sẽ có 1 số risk khi luân
chuyển staff nếu staff đó ko biết 1 cái gì về dept đó)
Recruitment agencies (headhunters): navigos, nic, adecco, glints Educational establishments Competitors
Other industries & Unemployed
Tasks: liệt kê ra số đầu công việc (mặc dù bạn không làm hết tất cả các task nhưng
hiển nhiên bạn vẫn có thể apply vì cty sẽ train cho mình)
5. 4 categories of information are usual on application forms
6. Ways in which interviews are used (two stages: setup and conducting) The interview setting Conducting the interview
oStarting with few easy-to-answer questions (introduce about yourself) oOpen-ended rather than closed
oEncouraging candidates to talk about themselves, their experiences,
attitudes, behaviors and expectations oTechniques: Other considerations oTime spent interviewing oControl the interview oClose the interview
7. Criticisms associated with psychological tests: could not measure someone
performance of working experience or personality
8. Role playing (check trong textbook) Chapter 14
1. Why creating and maintaining a well-motivated salesforce is a challenging task:
- Individuals have different life objectives very difficult to set the motivation for the whole team
- Heavily influenced by emotions
- Daily routine tasks (repeated tasks)
2. Result of high levels of motivation
- Higher expectancy higher perfor mance higher rewards 3. Motivation theories
+ The classic motivational model, Maslow 's hierarchy of needs, proposes that there are five fundamental needs
+ Herzberg's dual factor theory distinguished factors which can cause dissatisfaction
but cannot motivate (hygiene factors), and factors which can cause positive motivation
+ Vroom's expectancy theory assumes that people's motivation to exert effort is
dependent upon their expectations for success. (if there are 2 sellers perfoming the
same tasks but the expectancy is different, the result will be different)
+ Adam’s inequity theory: one employee has the feeling of inequity —> gives the
motivation to solve that problem Chapter 15
1. Organizational structures: geographical, product-base (product line, existing/new
product), customer-base (industry-based, account-size structure)
2. Determining number of salespeople (VERY IMPORTANT)
⇒ THE NUMBER OF SALESPEOPLE = TOTAL WORKLOAD / TOAL AVAILABLE SELLING TIME 3. Sales territories 4. Compensation plan design
- Fixed salary: constant salary to the salesperson (dont care about the salesnumber):
20mil/month —> no motivation to sell product, stable income
- Salary+commission: 10mil/month + 1% commission product/product —> most prefered
- Only commission: 5% commission bonus/product —> more motivation, less
income, time comsuming, very competitive
- Bonus=incentive reward: delivered to salespeople according to the customer’s
quality: ex: selling 1 TV existing custom
er: 2% on each transaction, new
customer: 5% on each transaction
- Commission: sell 1 TV 3% on 1 sales transaction (f ixed)
- Commission basis = only commission
- Commission bonus = commission + incentive rewards
5. Darmon’s five types of individual salesperson: i.e. Creatures of habit; Satisfiers; Trad-
off-ers; Goal orientated and Money orientated Chapter 16 1. Planning for forecasting
- Demand/Sales/Market Forecasting: prediction of the product/the trend of demand or product in a particular time
- Market forcasting: market trend —> the accountants
- Sales forecasting: sales number —> revenue —> sales manager
- Short-term forecasts: 3-month forecasting —> trending product/manufacturing
- Medium-term forecasts: 1 year —> build budget for the company
- Long-term forecasts: 3-10 years —> develop company strategies
=> Planning considerations depend on other functions
2. Level of forecasting (small scale to the largest scale) - Product-by-product
- Seasonal: based on time in 1 year (thường là sẽ làm theo quarter) - Geographical:
- International level and ranging down to national levels: international to different
national levels to local levels —> setup level thì forecast từ nhỏ nhất (từ sản phẩm)
lên scale lớn hơn. Đi từ trên xuống là product sẽ ko đc cung cấp đều cho các vùng 3. Qualitative techniques (6)
- Consumer/user survey method: prepare questionaire to perform survey
- Advantage: reliable information
- Disadvantage: time consuming and bias
Questionaire —> Customer 1,2,3 —> Facebook —> Forecasting
- Panels of executive opinion (Jory method): collect opinion from the higher
management level inside the company (meeting with the senior manager to ask for the
opinion —> select the best)
- Disadvantages: domination of opinion
- Salesforce composite: setting salespeople to make their own sales forecast on their
sales territory —> collect and combine all forecasting
- Advantages: accurate, reliable, customer insight
- Disadvantages: time consuming, unbalance salesforce
Questionaire —> salesperson 1 (TV Sales forecast), salesperson 2 (Mobile phone),
salesperson 3 (printers) —> feedback —> combine
- Delphi method: send questionaire to different experts. Then we will send the opinion
of other experts to each other but we will remove the name of the expert —> you will
ask for the feedback of each other about the others’ answers
- Advantages: wide range answwer, high qualified answer, answwer are not influenced
- Disadvantages: very time consuming,
- **Bayesian decision theory:** plan out different scenario with different action and anayse the solution
- Product testing and test marketing: based on the customer’s experience 4. Quantitative techniques (2) a) Time series analysis
- Moving average: calculate the period in 1 certain amount of time (thường là gộp 3
năm, 5 năm, 7 năm average) —> cannot find the trend (Set longer time thì con này mới xài đc)
- Exponential smoothing: —> can find the trend
- Time series analysis —> product boosting sales
- Z charts —> control the total annual self-development for every year (no longer use
this kind of method do sales forecasting đã do accountant forecast) b) Casual techniques
- Leading indicators: estimate the relationship between 2 factors
Vd: sales number of children bicycle: children population (sẽ có 3 loại xe cho 3 loại
độ tuổi: 3 years, 5 years, 7 years) —> classify the population into 3 different types
and then stick them with the suitable types of bicycles (forecast sales numbers của
loại xe đạp cho 3 tuổi phải ứng với 3yo population)
- Simulation: → Cái này giả định trên nhiều techniques phía trên (Bayesian bla bla)
→ Thầy không nói nhiều =))
- Diffusion models (for new product only): measure the adoption rate. (cái này sẽ
không xài toán nhiều do ko có dữ liệu nhiều để forecasting). The criteria:
- Innovation (xét theo quan điểm riêng của customer): continuous (bản nâng cấp
tốt)/dynamically continuous (nâng cấp cực tốt)/discontinuous
- Communication (biết được thông tin qua nguồn thông tin nào): forrmal
(controlled by the company itself: ads and PR, product info, sales support) or informal
(the relationship of customer with the resources)
- Social system (xã hội có chấp nhận sản phẩm đó không)
- Time: quarter or year scales
Vd: có 1 cái band copy từ blackpink mới ra mắt —> analyse tính khả thi
(discontinuous innovation, negative communication, society will not accept this band) —> very low adoption 5. Budget allocation
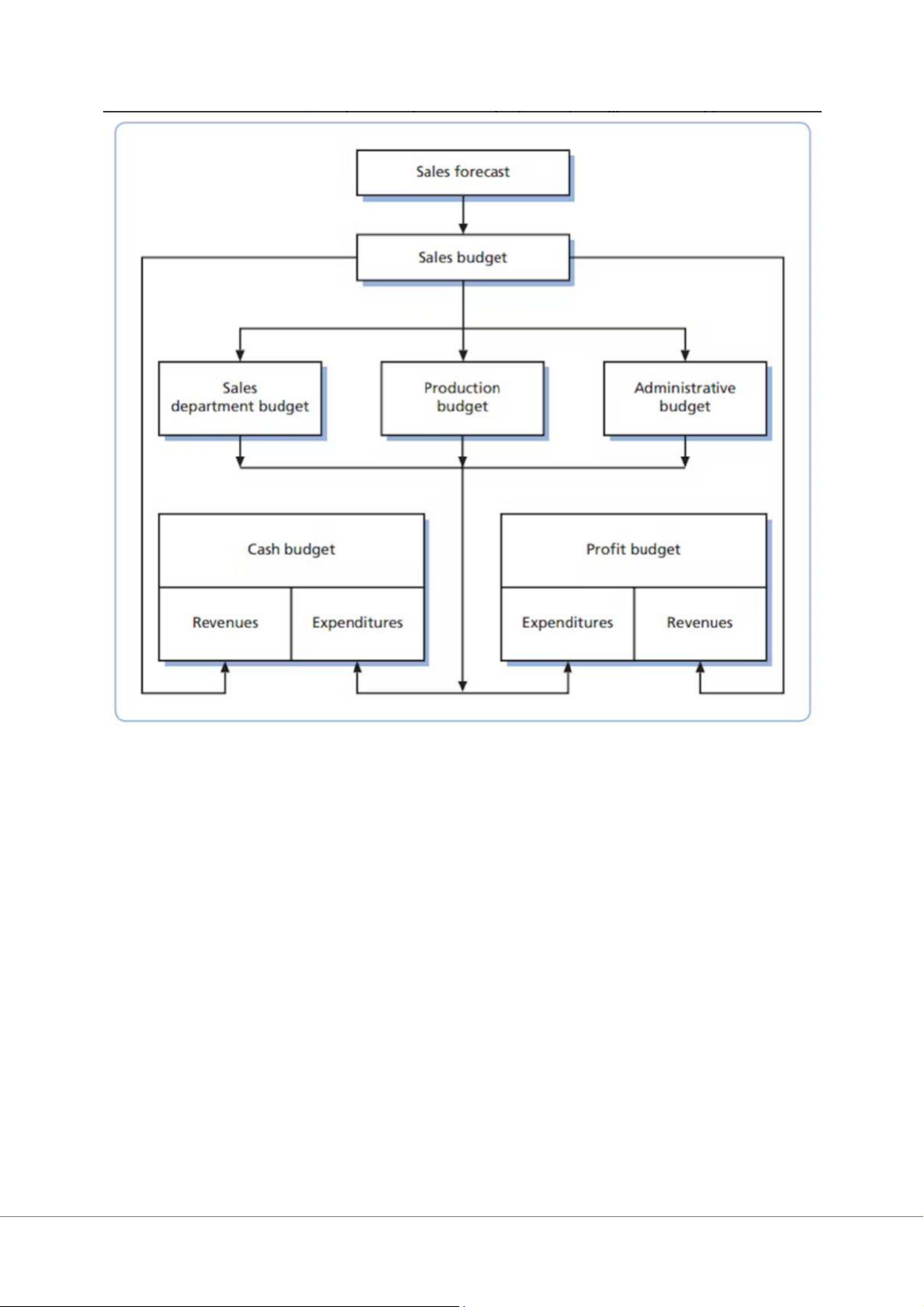
Organization needs to budget to ensure that expenditure does not exceed planned income.
Sales forecast is the starting point for business planning activities A means of control
Budget determination for sales department budget
The selling expense budget: sales personnel salaries and commission, sales expenses and training
The advertising budget: above-the-line promotion (e.g. television advertising), and
below-the-line promotion (e.g. a coupon redemption scheme)
Administrative budget: costs of marketing research, sales administration and support staff Budget allocation
6. Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative forecasting techniques. What are
the advantages and disadvantages associated with each approach?
7. Define the differences between a sales forecast, a demand forecast and a market forecast.
8. Poor forecasting can lead to lost sales, stock markdowns and large inventories.
Through the use of examples to illustrate your answer, justify this statement.
9. What is the tactical or strategic purpose of: (a) short-term forecasts; (b) medium-term forecasts; (c) long-term forecasts?
Quy tắc làm bài này liệt kê ra yêu cầu và bắt đầu xét các dạng commission từ từ. Chỉ
cần 1 cái ko đáp ứng yêu cầu là auto loại
Frequent product intro: new and old product
Boom market market opportunity
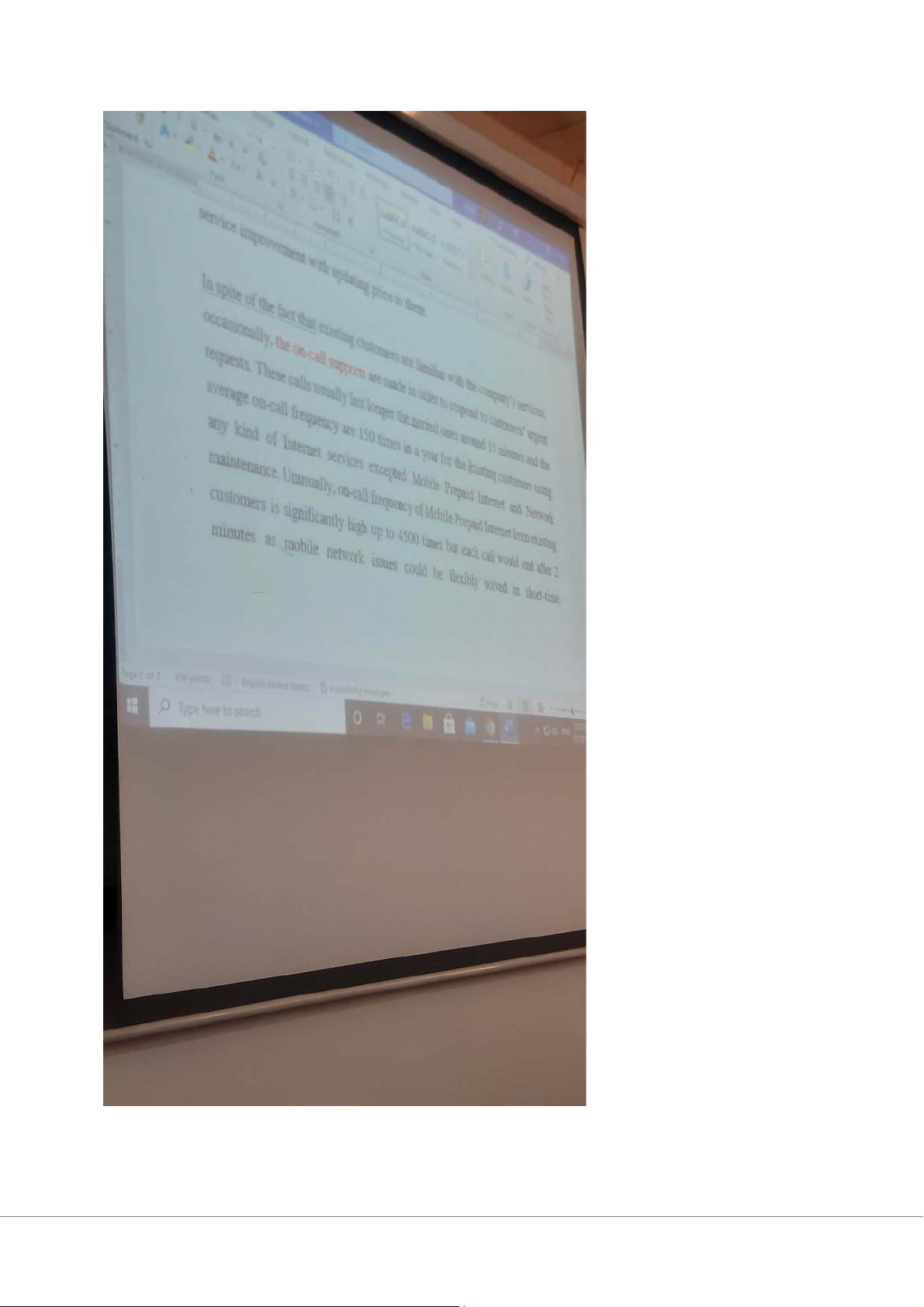
Loose competitive salesforce: controlled sales target + highest sales number of 0.5% of total revenue
On-call support: urgent call for help from the customer
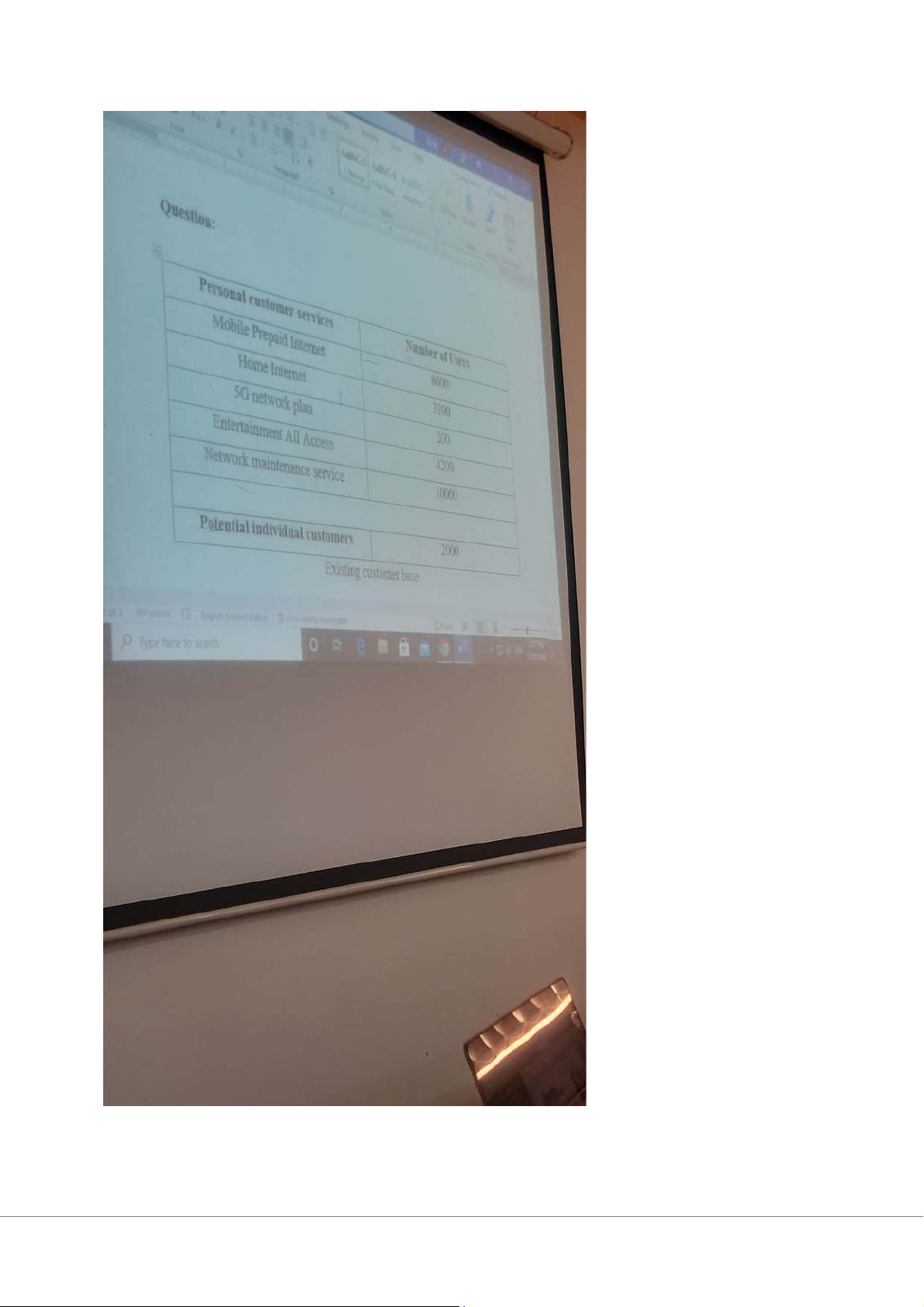
Tính toán các số làm tròn lên theo số thập phân Questions:
1. When OfficeSolutions, a software producer, went into business, it needed to
establish market share quickly. To accomplish this, it decided to pay the sales
force on a commission basis. After two years, however, the company had a
large base business and customers began to complain that salespeople were not
spending enough time with them on post-sale service and problem solving,
important relationship selling activities. The salespeople said they did not make
any money on problem solving and they would rather spend their time finding
new customers. What’s more, salespeople spent little or no time selling the
new products on which OfficeSolutions was staking its future. The salespeople
said they could sell the old products more easily and earn more money for both
themselves and the company. How might the company rework its
compensation plan to begin to resolve this issue? Answer: - Ineffective salesforces
+ Not spending time on post-sales, problem solving + Only focus on new customer + New product This is commission only
Change to salary+ commission plan (giải quyết được 2 vấn đề trên nhưng
nó sẽ ko ảnh hưởng nhiều đến new product) increase the incentives
(commission) for selling new products
2. Apply the expectancy model to respond to a salesperson who says the
following? “Putting all this data in the CRM system keeps me from making
more calls. More calls mean more sales. Thus, data input disrupts my performance”
Effort Expectancy Performance
Instrumentality R
eward Valence Value of reward Answer: Input data x conflict Less calls x conflict Lower sales Low Low performance
3. A university expects to enroll new students for the upcoming year. From the
report, the university finally accepted 500 students from engineering major,
500 students from Management major and another 1000 students attending the
ex-change programs. The consulting team performs calls via phone with the
length for each call approximately 60 minutes for the engineering students and
they are repeatedly called 36 times a year. On the other hand, it only took 30
minutes per call for the exchange program students; so, the consulting team
only 12 times calling a year. In addition, consulting team deliver 15 calls to
management students per year and each call lasts for 15 minutes. Based on
working term of policy, individual salesperson must work for 40 hours per
week and 45 weeks in one year. However, the actual time for selling activities
is up to 50% of the total work time, the remained accounts for non-selling
activities, meeting and travelling. Determine the total number of salespeople required in consulting team. Answer:
Engineering: 500 students - 60 minutes /call = 1 hour/call (length) - repeat 36 times a year (frequency)
Management: 500 students – repeat 15 calls – 0.25 hour/call
Exchange: 1000 students - 30 minutes/call (length)=0.5 hour/call - repeat 12 times a year (frequency)
Working duration: 40 hours/week ; 45 weeks/year
The actual time: 40% total working time The total workload = 500*
36+ 500 * 0.25 * 15 + 1000 * 0.5 * 12 = 25875 hours 1*
Average working time: 40 hours/week ; 45 weeks/year —> Average working time/year: 1800 hours/year
Selling activities: 40% working time —> 1800 * 50% = 900 hours/year
Total salespeople: 25875/900=29 salespeople




