

















Preview text:
NATIONAL ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY NEU BUSINESS SCHOOL ✵✵✵ ------ ------
MICROECONOMICS - FINAL GROUP PROJECT TOPIC THE BEER INDUSTRY
Lecturer: Dr. Tran Thi Hong Viet Group 3 – EBDB 5
Lương Thị Bạch Dương – 11230676
Phạm Thị Nguyệt Thảo – 11230724
Nguyễn Trung Kiên – 11230702
Hoàng Trọng Hiếu – 11230689
Trương Thu Thủy – 11230726 Cao Văn Tài – 11230720 Hanoi - December 2023 TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. INTRODUCTION..................................................................................................... 3
B. BODY......................................................................................................................... 3 I.
THE BEER INDUSTRY IS MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION (Is the
industry the commodity is in, closer to pure competition or monopoly? Explain your
reasoning)....................................................................................................................... 3
1. Definition................................................................................................................ 3
2. Characteristics....................................................................................................... 4
2.1. Number of firms.............................................................................................. 4
2.2. Nature of products........................................................................................... 5
2.4. Barriers to entry.............................................................................................. 7
2.5. Non-price competition..................................................................................... 7
II. EFFECTS OF NON-PRICE FACTORS ON SUPPLY AND DEMAND (Explain
the main factors that have affected the supply and the demand of the commodity chosen
over the last years).......................................................................................................... 8 1.
Overall................................................................................................................. 8 2.
Demand................................................................................................................ 9
2.1. Income of consumers....................................................................................9
2.2. Individual Preferences and the number of consumers...............................10
2.3. Expectations................................................................................................11
2.4. International market...................................................................................11 3.
Supply................................................................................................................ 12
3.1. Prices of input.............................................................................................12
3.2. Technology...................................................................................................13
3.3. The number of producers............................................................................13
3.4. International market...................................................................................14 4.
Government interventions................................................................................15 5.
Potential and Challenge....................................................................................16
C. ENDING................................................................................................................... 18
REFERENCES...............................................................................................................19 2 A. INTRODUCTION
The beer industry in Vietnam is among the most important businesses contributing to the
national economy. This industry has undergone significant development over recent years as it
is becoming one of the most popular beverages and being favored by a wide range of
consumers. According to the General Statistics Office of Vietnam, in 2022, the amount of beer
was 3,8 million liters, which made up 2,2% of the global market. Moreover, Vietnam is the
leading country in beer consumption in Southeast Asia, the third in Asia, just following China
and Japan, and ranks 9th in the world.
Above all, the beer market is an active and typical one in Vietnam's economy, which
attracts us to choose it to be our topic. In this final group project, we are going to undertake in-
depth research and provide a detailed insight into this field. Our project will include thorough
analysis, different charts, reliable statistics, and data with the aim of explaining two important
questions given. In addition to defining its market structures, we will also point out numerous
factors affecting the supply and demand of the beer industry in Vietnam over the years. B. BODY
I. THE BEER INDUSTRY IS MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION (Is the industry the
commodity is in, closer to pure competition or monopoly? Explain your reasoning) 1. Definition
What is pure competition?
Pure competition is a marketing situation where many sellers offer similar products for
similar prices. In purely competitive markets, corporations have little control of a product's
price. Pure competition is the opposite of a monopoly, where one company has complete price
control because of little competition. Monopoly and pure competition represent each end of the
commerce spectrum that marketers can use to evaluate existing industries. (According to Indeed - Career Guide) What is monopoly?
A monopoly is a market structure where a single seller or producer assumes a dominant
position in an industry or a sector. Monopolies are discouraged in free-market economies as
they stifle competition and limit substitutes for consumers. (According to ) Investopedia What is oligopoly?
An oligopoly is a type of market structure that exists within an economy. In an oligopoly,
there is a small number of firms that control the market. A key characteristic of an oligopoly is
that none of these firms can keep the other(s) from having significant influence over the
market. The concentration ratio measures the market share of the largest firms. There is no 3
precise upper limit to the number of firms in an oligopoly, but the number must be low enough
that the actions of one firm significantly influence the others. An oligopoly is different from a
monopoly, which is a market with only one producer. (According to Investopedia)
The difference between pure, oligopoly and monopoly Market Pure Oligopoly Monopoly structures competition Number of Many small A small number of large Single firm dominates firms firms. firms dominate the market. the entire market. Product Products are Products may be Unique product with no Differentiation
identical or very standardized or close substitutes. similar. differentiated. Entry and Exit Easy entry and Barriers to entry are Significant barriers to exit for firms. relatively high, making it entry, making it difficult difficult for new firms to for new firms to enter enter the market. the market. Control over No individual
Firms have some degree of The monopolist has Price firm has control control over the market significant control over over the market price; they may engage in the market price. It is a price; they are
price competition or collude price maker. price takers. to set prices Examples Agricultural Automobile industry, Public utilities (natural markets where telecommunications, soft monopolies), such as many farmers drinks. water and electricity sell identical providers, or a company products like with exclusive patent wheat or corn. rights for a product. 2. Characteristics 2.1. Number of firms
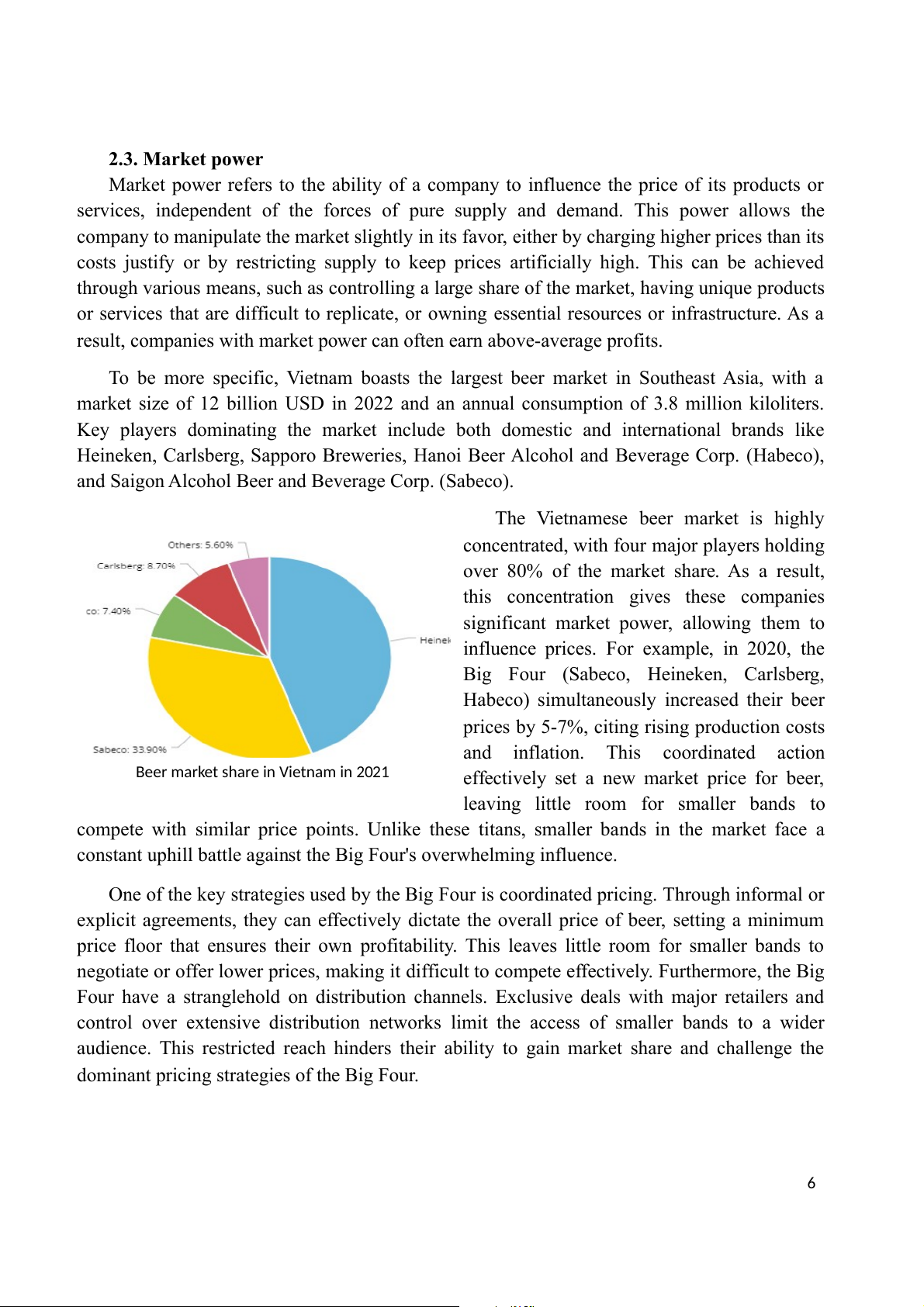
In 2021, 90% of Vietnam's beer market belongs to 4 big players: Sabeco, Heineken,
Habeco and Carlsberg based on total sales volume. In which, Sabeco accounted for 33.9%, 4
Heineken Vietnam accounted for 44.4%, Habeco accounted for 7.4%, Carlsberg Vietnam
accounted for 8.7%, the rest belonged to other beer companies. 2.2. Nature of products
Either homogeneous or differentiated products may be made by firms in an oligopoly.
Homogeneous products, for example gasoline and steel, are the same or very much alike.
Differentiated products, such as cars or soft drinks, are slightly different or have different
brand names. The nature of the product affects the degree of competition and the pricing strategy of the firms.
In Vietnam's beers industry, we can see that all the beers have alcohol and gas. The
difference that makes one spot out is the choice of ingredients, tastes, and packaging.
Some famous brands of beer in Viet Nam
Case analysis: Sabeco and Heineken are two beer brands with strong positions in the
competitive market in Vietnam and what sets
them apart is the ingredients and flavors.
Sabeco’s beer, compared to other brands, had a
slightly higher alcohol content (5.3%) and a
bitter and more flavorful taste, combined with
a cheap price, suitable for the majority of
consumers in Vietnam. However, beer
Heineken has a alcohol content lower than that
of Sabeco about 2%, so it has a higher
production cost, targeting high-income
consumers who love the unique and luxurious. 5 2.3. Market power
Market power refers to the ability of a company to influence the price of its products or
services, independent of the forces of pure supply and demand. This power allows the
company to manipulate the market slightly in its favor, either by charging higher prices than its
costs justify or by restricting supply to keep prices artificially high. This can be achieved
through various means, such as controlling a large share of the market, having unique products
or services that are difficult to replicate, or owning essential resources or infrastructure. As a
result, companies with market power can often earn above-average profits.
To be more specific, Vietnam boasts the largest beer market in Southeast Asia, with a
market size of 12 billion USD in 2022 and an annual consumption of 3.8 million kiloliters.
Key players dominating the market include both domestic and international brands like
Heineken, Carlsberg, Sapporo Breweries, Hanoi Beer Alcohol and Beverage Corp. (Habeco),
and Saigon Alcohol Beer and Beverage Corp. (Sabeco).
The Vietnamese beer market is highly
concentrated, with four major players holding
over 80% of the market share. As a result,
this concentration gives these companies
significant market power, allowing them to
influence prices. For example, in 2020, the
Big Four (Sabeco, Heineken, Carlsberg,
Habeco) simultaneously increased their beer
prices by 5-7%, citing rising production costs
and inflation. This coordinated action
Beer market share in Vietnam in 2021
effectively set a new market price for beer,
leaving little room for smaller bands to
compete with similar price points. Unlike these titans, smaller bands in the market face a
constant uphill battle against the Big Four's overwhelming influence.
One of the key strategies used by the Big Four is coordinated pricing. Through informal or
explicit agreements, they can effectively dictate the overall price of beer, setting a minimum
price floor that ensures their own profitability. This leaves little room for smaller bands to
negotiate or offer lower prices, making it difficult to compete effectively. Furthermore, the Big
Four have a stranglehold on distribution channels. Exclusive deals with major retailers and
control over extensive distribution networks limit the access of smaller bands to a wider
audience. This restricted reach hinders their ability to gain market share and challenge the
dominant pricing strategies of the Big Four. 6 2.4. Barriers to entry
There are high barriers to entry in an oligopoly market, such as economies of scale, brand
loyalty, government regulations, and distribution networks. These barriers prevent new entrants
from entering the market and competing with the existing firms.
- Regulations and policies: The development of beer markets may be hindered by
regulatory and policy issues relating to the production, marketing, or advertising of
beer. For beer producers and traders, regulation on taxes, licenses, approval procedures
for quality checks can create substantial problems and costs.
- Law restriction: Vietnamese’s government has implied the law that the person who
drive a vehicle with alcohol in the blood or breath will be fined a penalty and revoked the driver license.
- Health awareness: With increased health awareness, some consumers may reduce beer
consumption. The growth in the beer market may be affected by increased trends such
as less alcohol consumption, or healthy eating.
The table below illustrates the start-up cost to launch a brewery.
Starting a beer production business can be a lucrative venture if executed correctly and it
requires several critical considerations to get off the ground.
2.5. Non-price competition
Companies focus on things like style, quality, location, or service. And the goal is to
distinguish their product from their competitors. The most recognizable form of non-price competition is advertising.
In 2022, Vietnam ranked 2nd in Southeast Asia and 3rd in Asia in terms of average alcohol
consumption per person. The average alcohol consumption per person in liters of pure alcohol
per year is 8.3 liters, equivalent to one person drinking about 170 liters of beer per year. 7
Obviously, Vietnam is a "profitable" market for beer companies, but the level of competition is brutal.
From 2015 until now, there has been no year that Sabeco spent less than a trillion billion
on advertising and promotions. This cost has continuously increased since 2018, especially in
the last 2 years when the number significantly jumped to nearly 2,200 billion in 2021 and
exceeded 3,000 billion in 2022.
Habeco also spends hundreds of billions of VND each year on advertising and promotions.
However, there has never been a year when Habeco really spent heavily on this activity, and
even reduced it sharply during the COVID-19 period. In 2022, Habeco's campaigns to increase
brand recognition, the costs also jumped to nearly 650 billion but still not equal to pre- pandemic levels (2019).
Costs of advertising and promotions (billion VND)
Non-price competition can help firms differentiate their products and gain market share.
II. EFFECTS OF NON-PRICE FACTORS ON SUPPLY AND DEMAND (Explain the
main factors that have affected the supply and the demand of the commodity chosen over the last years) 1. Overall
Vietnam’s beer market has fluctuated between 2018 and 2023. In 2018, the total beer
production in Vietnam reached 4.6 billion liters, the consumption reached 4.2 billion liters. In
2019, the beer market increased. The total beer production in Vietnam reached over 5 billion
liters, an increase of 22.9% compared to the same period in 2018. Consumption also reached
4.6 billion liters, showing a growth of 29.1%compared to the previous year. However, due to 8
the prolonged impact of social distancing measures from the Covid-19 pandemic and
additional management policies imposed by the government, specifically the Decree
100/2019/ND-CP regulations on penalties for administrative violations in the field of road and
railway traffic, the business operations of beer companies suffered significant losses. From
2020 to 2021, the beer market experienced a decline of 20%-30% in consumption.
After successfully controlling the Covid-19 outbreak, various service and entertainment
industries, such as karaoke and bars, resumed their operations. As a result, the beer
consumption market gradually recovered and showed promising signs. In 2022, the total beer
production in Vietnam reached over 6 billion liters, an increase of 52.5% compared to the same
period in 2021, surpassing the total output of 2019. The consumption reached 3.8 billion liters.
According to VIRAC's forecast, Vietnam's beer industry will have a CAGR growth rate of
11%/year in the period 2023-2026. This growth forecast is concluded based on the recovery of
tourism and the economy after Covid. 2. Demand 2.1. Income of consumers
The average income of consumers in Vietnam witnessed a significant variation over the
period of 5 years. Before the outbreak of Covid-19, the average income per capita experienced
a gradual growth within several years. The year 2019 marked an important change in the data
recorded with the arrival of the Covid-19 epidemic, which was followed by a dramatic decline
from 4.295 thousand VND to 4.205 thousand VND (2021). From 2021 on, the economy had a
remarkable recovery after the epidemic; therefore, the average salary increased to 4.673 thousand VND in 2022. 9
The Vietnamese’s average monthly income
The beer consumption in Vietnam per capita (2018-2022) (2018 - 2022) 5,000 4,673 4,295 4,250 4,205 5 4,500 3,874 4.5 4,000 4 D 3,500 3.5 3,000 3 2,500 liters 2.5 n 2,000 2 usand VN 1,500 llio 1.5 Bi Tho 1,000 1 500 0.5 0 0 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
The change in buyers’ income will consequently result in the change in their behaviors
toward the goods, particularly beer. Their expenditure on normal goods, namely beer, will vary
positively depending on consumers’ income. Owing to the income being lowered, consumers
had to tighten their budget, control their expenditure, and turn their attention to necessities.
And as a matter of fact, the demand for beer during this recorded period also decreased when
the salary of buyers dropped due to the pandemic from 2019 to 2021:
“Before 2019, the beer industry grew 5-6% annually. With that speed, the beer
market in 2022 had to reach 20% higher compared to the year 2019 but in fact,
this figure declined 5-7% in 2022. In 2023, the beer market has not seen any
revival.” (Mr. Nguyen Van Viet - the President of Vietnam Beer Alcohol Beverage
Association - brandsvietnam.com)
Despite a rise in the income per capita in 2022, the demand for this commodity kept
decreasing because of the residual effects of Covid-19.
2.2. Individual Preferences and the number of consumers
These days, with the residents’ awareness of health, especially after the epidemic,
consumers tend to search for healthier goods such as dietary supplements and functional foods
to improve the immune system and protect their health. A report of the General Statistics
Office in September 2020 said that among 50% purchasers who spent more on nutritions, there
were about 63,7% buyers who chose to lower the expenditure on beers. Noticeably, the number
of beer consumers reduced subsequently because their tastes and preferences had altered,
which led to a reduction in demand for beers. 10 2.3. Expectations
Customers’ expectations vary greatly, which
depends on different individuals. Their expectations can
include affordable prices, high reputation and
credibility, quality…If the producers can meet their
consumers’ expectation, the demand as well as supply
will consequently grow and vice versa.
A striking instance for this factor is the practical
application in 2020 of Heineken Vietnam brewery with
the innovation in the manufacture of non-alcoholic beer
with totally natural ingredients. And its project was
successful when the demand for these products rose
dramatically at that time. It was the criteria about
quality that came up to buyers’ expectation regarding
health issues when this non-alcoholic beer was said to be safe for consumption, especially for
driving. Moreover, this product also aims at a balanced lifestyle that many people nowadays are enjoying.
2.4. International market
International trade is also one of the primary factors which directly influenced the
demand of the beer industry in Vietnam, especially in the era of international economic
integration. With a large number of consumers every year, Vietnam is demonstrated to
be one of the most auspicious beer consumption markets and that is the reason why
many foreign brands have chosen this country to be their market partner and imported
their products into Vietnam.
Imported beer brands in Vietnam
According to a report of the newspaper, Vietnam Investment Review (VIR), the
internal beer market is facing intense competition from imported brewing businesses 11
after taking part in the Trans-Pacific Partnership and under the agreement, Viet Nam's
tax on imported beer will be decreased to 0% compared to 35% at first (2014). With the
appearance of new products and unique marketing campaigns of foreign beer producers,
domestic consumers will tend to seek something new to experience. As a result, the
indigenous market will meet more difficulties in approaching its customers as the higher
demand for external goods will cause a decline in the demand for domestic beers. 3. Supply 3.1. Prices of input
Beer is made from four main ingredients: barley, hops, yeast, and water. Therefore,
these ingredients are also the input of beer.
The price of input for beer has risen in Viet Nam because of the following main
reasons: transport fee is high due to the consequences of the covid 19 pandemic and
Russia-Ukraine tensions. Leaders of Hanoi Beer - Alcohol - Beverage Corporation
(Habeco) assessed that 2022 is a difficult year for the beer industry due to a sharp
increase in production costs. Accordingly, the price of raw materials for production has
increased by 50%. In addition, the Russia-Ukraine conflict caused the supply chain to
break, leading to the transportation costs to increase by 20%. Moreover, climate change
causes a decrease in barley production. A report by the US National Academy of
Sciences (NAS) also shows that with each degree Celsius increase in the earth, the
average grain production will decrease by 6%. In the barley segment, major suppliers in
Europe are suffering from heat waves and unusual weather changes. A 2021 report 12
found that Europe accounts for 60% of global barley production, but droughts and
heatwaves caused the region to lose 12.1% of production between 1964 and 2015.
Therefore, it can be concluded that input prices will greatly affect the supply of beer in Vietnam. 3.2. Technology
Some advanced technological equipment used in beer production include brewing
equipment, fermentation equipment, filtration equipment, packaging equipment, quality
control equipment...These advanced technological equipments in beer production will
help increase productivity which means producers can produce more beer in a short
time. In addition, this will also help businesses to reduce the costs of hiring workers.
Furthermore, technology applied in beer production also saves energy in beer
production, contributing to minimizing the impact on the environment.
3.3. The number of producers
According to statistics from the Vietnam Beer - Alcohol - Beverage Association
(VBA), by 2023, Vietnam will have about 200 beer manufacturers, including 100 large
beer manufacturers, accounting for about 90% of the beer market share. Large beer
producers in Vietnam include: Sabeco, Heineken, Habeco, Carlsberg. In addition, there
are many small, medium, and small - scale beer producers, concentrated in provinces
and cities. These brewers mainly produce craft beer, serving the needs of local
consumers. The large number of beer producers in Vietnam brings an increase in the supply of beer. 13
3.4. International market
The beer production in Vietnam The beer market is one of the (2018 - 2022)
largest beverage markets in the 7 world. According to Mordor 6 Intelligence, the global beer 5
market size is estimated to reach rs e 4 691.63 million USD in 2023 and 3 lion lit is expected to reach 872.67 Bil 2 million USD in 2028. 1 0 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
The beer market is divided into some main regions, including:
- Asia is the world's largest beer-consuming region, accounting for about 37% of the global market share.
- Europe is the world's second-largest beer-consuming region, accounting for
about 32% of the global market share.
- North America: North America is the third largest beer-consuming region in
the world, accounting for about 25% of the global market share.
This data shows that the supply of beer in the world is also increasing. The amount
of quality beer produced in Vietnam is so large that it can be exported to the international beer market: 14
4. Government interventions
Despite bringing abundant tax revenue to the state budget, the beer industry as well
as the entire alcoholic beverage industry is considered to have a negative impact on
consumer health and Social Security. Therefore, the government as well as many
societies have had many activities to limit the growth of organizations of the beer
industry, such as organizing propaganda and education about the harmful effects of beer
and alcohol, or most aggressively, increasing special consumption taxes. Joining the
WTO, Vietnam will apply a special consumption tax on all beer products, regardless of packaging.
The measures that the government has put in place have the potential to have a
direct and significant impact on the production of beer. To counteract the negative
impacts of alcohol misuse, the government has released national policies. As a result,
there exist laws governing the making, selling, and consumption of alcoholic drinks,
including beer. Alcohol trading is restricted as a regulated product by Commercial
Law. The Investment Law considers alcohol business as a conditional sector, and the
conditions are specified in Government Decree 105/2017/ND-CP regarding alcohol
business. These rules forbid selling alcohol to people younger than eighteen (18), set
licensing requirements for those under the age of eighteen who want to produce or
distribute alcohol, and establish guidelines for issuing licenses for the production,
distribution, wholesale, retail, and on-site consumption of alcohol. Decree 17/2020/ND-
CP dated February 5, 2020 of the Government amending and supplementing a number
of articles of Decrees related to business investment conditions in the field of state
management of the Ministry of Industry and Trade. Decree 24/2020/ND-CP of the 15
Government dated February 24, 2020 detailing a number of articles of the Law on
Prevention and Control of Harmful Effects of Alcohol and Beer. Decree 100/2019/ND-
CP regulations on penalties for administrative violations in the field of road and railway
traffic specifies alcohol concentration limits for drivers of motor vehicles, including cars
and trucks. According to statistics at the beginning of 2020, the number of customers at
restaurants decreased by 30-50% compared to the annual average. After the penalty
regulations were considered strong enough to deter drink-driving, many bars fell into a
deserted state, and people also tended to reduce drinking outside, causing businesses in
the industry to Beer and alcohol from here are also significantly affected. Policy on the
beer market has staggered before the government's prohibition law. These government
regulations have a significant impact on the beer market and its production processes.
The beer business has seen a fall in production as a
result of government policies that have had a substantial
impact on revenue. The implementation of these policies has also affected demand.
For example: Hanoi Beer-Alcohol-Beverage
Corporation (Habeco) experienced a nearly 50% drop in
revenue in the first quarter of 2020 compared to the same
period in 2019, resulting in a 55% decrease in profit
equivalent to 148 billion VND.
Specifically, beer is liable to a specific consumption tax, the current rate of which is
65%. Drinking too much beer can have detrimental effects on one's health as well as
other grave repercussions for society. Consequently, to cover the tax and maintain their
revenue, beer vendors must raise their prices. Thus, the amount of beer consumed is
reduced. Furthermore, these policies have an impact on the manufacturing of beer.
5. Potential and Challenge
With current research results and statistics, the beer industry in Vietnam can be
considered a promising market. Vietnam has a golden population structure, rapidly
increasing income. Especially, Vietnam ranks the third in Asia and 9th in the world. At
the same time, the growth rate of Vietnam's middle class is also among the fastest in
Asia. According to Nielsen and VBA, in 2020 there will be about 33 million middle-
class consumers under 30 years old and will spend approximately 173 billion USD. A
market that is both large, has growth momentum, and has strong purchasing power like
Vietnam has been a lucrative land for beer companies to exploit. 16
Potential for the export market: Vietnam's strong
export markets (ASEAN countries, China...) are all
markets with high growth rates in food and beverage
consumption. Along with a series of signed Free
Trade Agreements, Vietnamese food and beverages
have largely been able to access key export markets freely (without tariffs).
In addition, many new types of beer with diverse
designs are produced to meet the diverse needs of
consumers, such as non-alcoholic beer suitable for women and people who need to stay
alert, such as when driving a car. Advances in technology also contribute to the
development of the beer industry, increasing the output.
However, besides the opportunities, the beer market also faces many challenges.
Raw material prices also impact on supply. The specific nature of the beer industry
requires certain ingredients, some of which may need to be imported. The increase in
raw material costs can cause beer prices to increase. This leads to increased supply and decreased demand.
For example, under the influence of the Covid-19 pandemic and the energy crisis in
Europe, as well as the Russia-Ukraine conflict, supply chains have been
disrupted. International supply chains can increase production and transportation
costs. Because of increasing ingredient prices, some beer manufacturing companies
have had to raise their prices. Because prices increased dramatically, consumers tended
to consume substitute products or limit beer consumption. It led to the consumption of
beer falling causing a reduction in supply of goods to avoid surplus. However, some
companies may choose to maintain their original prices in order to meet the
demands of their customers. This approach has limitations as it may result in lower
revenue for the company. In the long term, this can also impact the production process.
Beer or alcoholic beverages in general affect human health, so the government and
social organizations are increasingly tightening regulations on production, business, and
consumption of this product. These regulations affect both brands and consumers. At
the same time, the government also imposes high taxes on these items.
People's awareness is increasingly raised. Since covid 19, they tend to spend more
on healthy products. At the same time, Vietnamese people's preference for foreign 17
products will also be a big challenge for domestic beer companies along with threats
from competitors such as imported beer and foreign beer.
So, we can evaluate that the beer market in Vietnam is full of opportunities for
development but at the same time, it also brings many difficulties and challenges.
Brands need to come up with a reasonable business strategy suitable to the social
situation as well as invest in improving technology and diversifying products to meet
consumer needs. More importantly, they need to aim for long-term development goals. C. ENDING
By analyzing the beer market in Vietnam, we can have a better grasp of information
about how the market works and the factors that affect the supply and demand of a
market... The characteristic of this market is that it is large, and long-standing and beer
is a popular product in Viet Nam's market, which sticks to the development of this country.
Our analysis of key characteristics reveals that the beer industry in Vietnam operates
within an oligopolistic market structure. We further identify several key factors
influencing the demand and supply of this product. To gain a clear understanding of this
market structure, we analyzed data from relevant firms, with a focus on major Vietnamese brands.
Through this project, we have acquired valuable knowledge about the Vietnamese
beer industry, aiming to apply these insights in practical settings. The findings provide 18
an updated perspective on this market type, benefiting both ourselves and other economic learners. 19 REFERENCES 1.
Beer industry overview at the beginning of 2023 – Challenges and
opportunities for recovery in the second half of the year. Viracresearch.com
(https://viracresearch.com/overview-challenges-of-vietnams-beer-industry/) 2.
Tác động kép của dịch covid 19 và nghị định số 100/2019/NĐ-CP tới ngành
công nghiệp sản xuất đồ uống. Gso.gov.vn
(https://www.gso.gov.vn/du-lieu-va-so-lieu-thong-ke/2021/06/tac-dong-kep-cua-dich-
covid-19-va-nghi-dinh-so-100-2019-nd-cp-toi-nganh-cong-nghiep-san-xuat-do-uong/) 3.
Henry Sheykin. 2023. How Much Does It Cost To Start Beer Production:
Unveiling The Capital Expenditures. Finmodelslab.com
(https://finmodelslab.com/blogs/startup-costs/beer-production-startup-costs) 4.
Hạ Linh. 2023. Hai “ông lớn” ngành bia Sabeco và Habeco đang “đốt”
bao nhiêu tiền cho quảng cáo, khuyến mại? Brandsvietnam.com
(https://www.brandsvietnam.com/23521-Hai-ong-lon-nganh-bia-Sabeco-va-Habeco-
dang-dot-bao-nhieu-tien-cho-quang-cao-khuyen-mai) 5.
Celina Pham. 2022. Why SEA Craft Beer Brewers are Choosing Vietnam. Vietnam-briefing.
(https://www.vietnam-briefing.com/news/vietnams-craft-beer-industry-2022.html/) 6.
Sản phẩm của chúng tôi. Heineken.com
(https://www.heineken.com/vn/vi/san-pham-cua-chung-toi) 7.
Phân tích quy mô thị phần bia - Xu hướng & dự báo tăng trưởng (2023 -
2028). Mordorintelligence.com
(https://www.mordorintelligence.com/vi/industry-reports/beer-market#:~:text=Quy
%20m%C3%B4%20th%E1%BB%8B%20tr%C6%B0%E1%BB%9Dng%20bia
%20%C6%B0%E1%BB%9Bc%20t%C3%ADnh%20%C4%91%E1%BA%A1t
%20691%2C63,%C4%91%E1%BB%99%20CAGR%20l %C3%A0%204.76%25%20trong)
8. Nghiên cứu thị trường bia Việt Nam. Ocd.vn
(https://ocd.vn/nghien-cuu-thi-truong-bia-viet-nam/) 20



