



Preview text:
Đề cương tự luận vimo Answer T or F
1. If demand increase and supply simultaneously decreases, equilibrium price will rise.=> T
2.In attempting to maximise profits,a firms will always produce at the ouput
where total revenues are at a maximum.->F
3.In perfect competition,like the market demand curve,the firm’s demand
curve is a negative slope. Answer: False
In perfect competition, the market demand curve is negative slope means,which
means that as the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded by consumers
increase However, because each firm in perfectly competitive market is a small
player,it has no influence over the marker price. Therefore, the firm faces a
perfectly elastic demand curve , meaning it can sell as much as it wants at the
market price but cannot increase the price without losing all of its costumers.As a
result, the firm’s demand curve is a horizontal line at the market price. 4 If demand decrease and supply simultaneously increases,equilibrium quantity will fall. Answer: False
If demand decreases and supply simultaneously increases, there will be surplus as
supply exceeds demand so the price will fall to eliminate that surplus. However,
the equilibrium quantity can be either more or less than before, depending on
whether the supply shifted by a greater margin than demand or not.
-> the equilibrium quantity is ambiguous
5. A decrease in income will shift the demand curve to the left. Answer: False
Normal goods :Incom giảm -> Demand giảm
Inferior goods: Income giảm -> Demand tăng.
6. Economics is the study of how to use unlimited resources to satisfy wants. Answer: False
The resources is limited and our wants is unlimited so the economics is the study
of how to use the limited resources to satisfy our unlimited wants
7.The supply curve of a monopoly firm is its marginal cost curve.F Answer False
A monopoly firm doesn’t have supply curve because at any given demand and cost
conditions, there is 1 profit maximising price output combination SessionC Caau 1:
1. Identify on Figure 1 the profit maximising output Qm and price Pm and
show clearly the total maximum profit (Пmax) and total revenue (TR) for the firm (1.0 mark) Answer
The profit maximizing output is 60 at the price $5,5 The total maximum profit
Пmax= Q* (P* -ATC*)= 60 (5,5-4,5) =60$
Total revenue :TR =PQ=5,5*60=330$
2. Demand curve in the Figure 1 shows a perfectly competitive firm or
imperfectly competitive firm? Why? (1.0 mark) Answer
Under perfect competition,the demand curve is perfectly elastic .It is due to the
existence of a large number of firms. Price of the product is determined by the
industry number and each firms has to accept that price.
On the other hand, under imperfectly competitive, average revenue curve slopes
downward .Average revenue and marginal revenue are separate from each other.
Price is determined by the monopolist.
3.Explain why the demand schedule in Figure 1 differs from that of a perfectly competive firm?
+)Firms are “price taker” -> at every level of output thay have to sell with the
same price -> Price remains unchanged.
There is a substantial number of firms in the market-> Consumer also have a
numerous number of choices-> quantity demanded is prone to change.
->Perfectly competitive D curve is perfectly elastic. +) Imperfect competitive
Firms have more market power-> they can now determine the price.
The number of firms is less than that of perfect competition market -> Consumers
also have less choices-> quantity demanded is less prone to change.
Imperfect competive D curve is more inelastic than the perfect competitive one. 3Caau 2:
A monopoly faces a demand function as follow: D: P ($) =50-Q
The firm's total cost function is given by: TC ($) =Q^2+6Q+40
1. Assuming that the firm wants to maximize its profit, determine the
quantity and price? Find the profit of the firm. Answer: Πmax MR=MC 2 +6Q+40)’ ((50-Q).Q)’=(Q 50-2Q=2Q+6 => Q* =11 (units) => P*=50-11=39 ($)
Πmax=TR-TC=39.11-(112+6.11+40) =202($)
2. Assuming that the government imposes a specific tax as $5 per unit on this
firm, how do price, quantity and profit change? What are tax burdens by consumers and producers? Answer: TC 2 2=TC1+5Q=Q +11Q+40 MC2=2Q+11
The new optinal profit: MR=MC 50-2Q=2Q+11 Q2*=9,75(units) P2*=50-9,75=40,25(units) Π 2
max= 40,25.9,75-(9,75 +11.9,75+40) =150,125($)
Tax incident: Consumer share tax burdent= P2*-P1*=40,25-39=1,25($/unit)
Producer’s share tax burdent=5-1,25=3,75($/units) Caau 3:
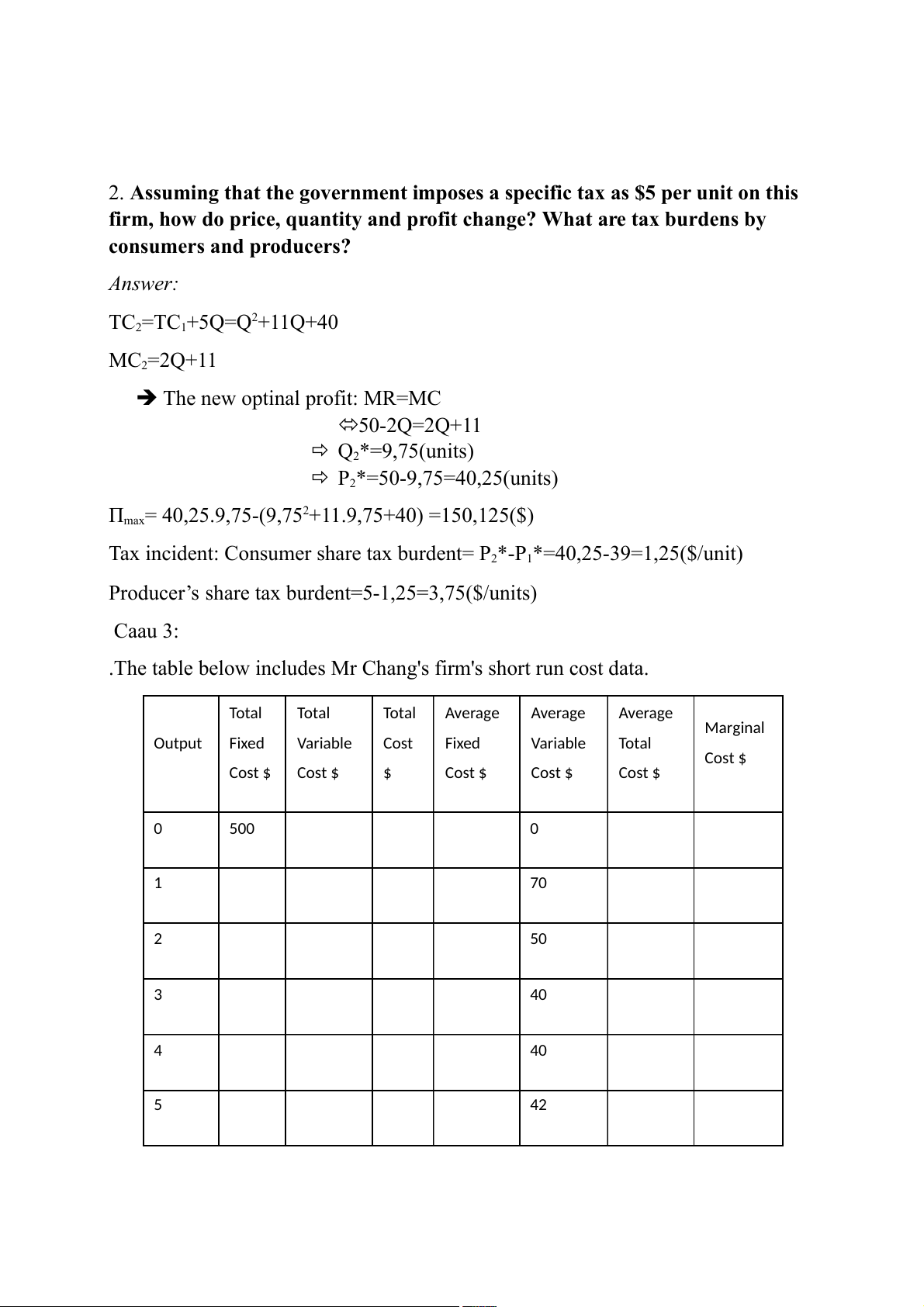
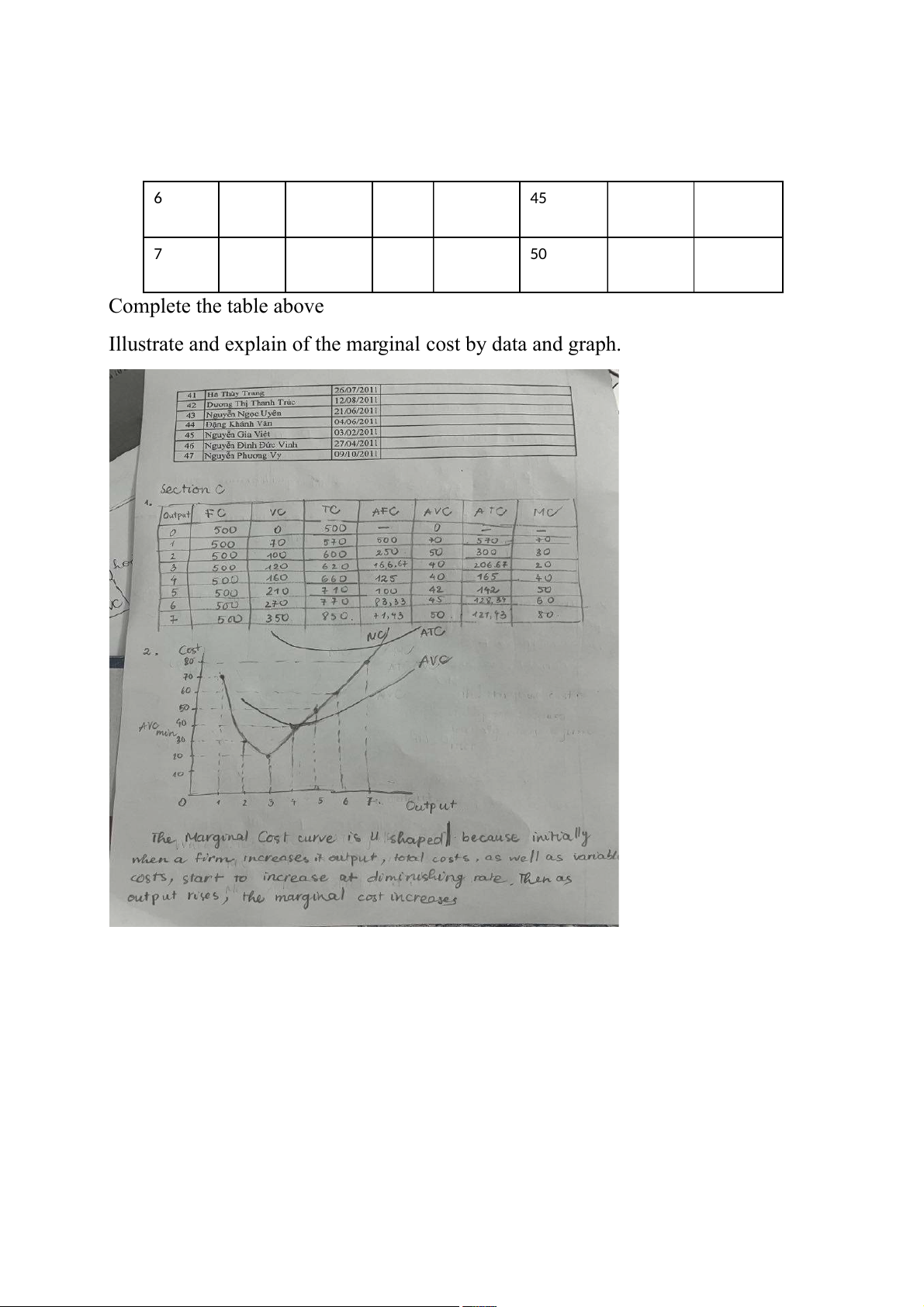
.The table below includes Mr Chang's firm's short run cost data. Total Total Total Average Average Average Marginal Output Fixed Variable Cost Fixed Variable Total Cost $ Cost $ Cost $ $ Cost $ Cost $ Cost $ 0 500 0 1 70 2 50 3 40 4 40 5 42 6 45 7 50 Complete the table above
Illustrate and explain of the marginal cost by data and graph.



