




Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 49964158
KẾ HOẠCH ÔN TẬP CUỐI KỲ KTVM
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1151U0Zqc5caih4lNLjN5Q2bWx1
ZPBtazL0E7zCcOWjo/edit?usp=sharing Buổi 1: 19/11/2022 Chapter 1
1. Ten Principle of Economics (10 Nguyên lý cơ bản Kinh tế ) Principle 1:
Due to the limited resources →
People face trade-offs people face trade-offs (make decision) Ex: have an amount of money,
choose to put money in the bank or buy new house
Principle 2: Opportunity Cost Whatever must be given up to obtain some item Ex: time for studying vs money for hanging out
Give up is the opportunity cost of decision Make decisions by comparing
Principle 3: People are rational, and marginal benefits and
make decisions at the margin marginal costs Principle 4:
People Respond to Incentives Principle 5:
Trade Can Make People Better Off
Principle 6: Markets are usually a
good way to organize economic lOMoARcPSD| 49964158 activity Principle 7:
Governments can sometimes
improve market outcomes
Principle 8: A country’s standard of
living depends on its ability to
produce goods and services Principle 9:
growth in the quantity of money
Prices rise when the government
-> lost its value-> value of the prints too much money money falls-> inflation
Principle 10: Society faces a short-
run trade-off between inflation and unemployment
1. Scarcity unlimited wants exceed the limited resources available to fulfill those wants
Chapter 2: Measuring a Nation’s Income
1. Microeconomics & Macroeconomics Microeconomics Macroeconomics
firm , company, households,... The whole economy, inflation lOMoARcPSD| 49964158
2. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
• Measure the total income of everyone
• Measure the expenditure on the output of goods and services
3. The measurement of GDP Market value Within a country In a given of time 1. Final Goods and services produced 2. Good and domestically services 3. Produced – Doesn’t include •Leisure
•Value of almost all activity that takes place outside markets •Quality of the environment .
3 The component of GDP Consumption Investment Government Net purchases/ spending Exports ( Export - Import) Spending on DOES NOT NX = 0 goods & services INCLUDE: → by households transfer balance Exception: payments NX > 0 purchases of new → surplus housing NX < 0 → deficit Chapter 2:
1. The Consumer Price Index Fix the Basket Find the prices Compute the Basket ‘s cost lOMoARcPSD| 49964158 -
Cố định giỏ hàng: Thông qua việc khảo sát và nghiên cứu thị trường sẽ xác định
được giá trị của hàng hóa và dịch vụ tiêu biểu, thiết yếu người dùng thường xuyên chi trả. -
Xác định giá cả: Sau khi xác định được những sản phẩm, giá trị của mỗi hàng
hóa sẽ được thống kê trong một thời gian cố định. - Tính chi phí mua giỏ hàng hóa/ dịch vụ
2. GDP Deflator Versus CPI GDP Deflator CPI
1. Reflecting ??? 1. Reflecting ??? 2. Compare: 2. Compare
the price of the same price of a fixed goods and services in the basket of goods and base year services
3. Nominal interest rate & Real interest rate
Nominal interest rate ( Lãi suất danh
Real interest rate (Lãi suất thực nghĩa) tế)
WITHOUT a correction for the
Corrected for the effects effects of inflation of inflation =>
1. REAL .. = Nominal interest rate – Inflation rate 2. xxx 3. QUIZ lOMoARcPSD| 49964158 1. Gross Domestic Product
a. The market value of all final goods and services which are
produced by the people of that country in a given period of time
b. An index is always higher than GNP
c. does not include the value of almost all activity that takes place outside markets.
d. include both the value of intermediate goods and final goods.
2. Which of the following items does not change GDP?
a. Enterprises invest in purchasing new equipment to serve theproduction of goods b. You buy an imported shirt
c. Hanoi invests in repairing roads on the occasion of 1000 years of Thang Long Hanoi
d. Enterprises exporting pangasius and basa to foreign countries3. Which of the following is true:
a. Nominal GDP can be equal to real GDP in some cases.
b. Nominal GDP is always higher than real GDP
c. Nominal GDP is always lower than real GDP
d. No sentence correctly
4. Which of the following is true:
a. The GDP deflator measures the prices of imported goods
b. Transfer payments are Government purchases and are included inthe G expenditure
c. CPI is always greater than 1
d. The GDP deflator measures how a basket of goods changes overthe years.
4. Consumer Price Index (CPI):
a. Reflects the rate of inflation in the economy, while the GDP deflator(D) does not.
b. reflect the price of the basket of goods and services that change
over time that consumers represent.
c. Use a fixed basket of goods and services. d. All of the above is true.
5. Which of the following would cause the CPI to rise more than the GDPdeflator?
a. The price of motorbikes made in Vietnam increased. lOMoARcPSD| 49964158
b. The price of wine bottles made in France and sold in Vietnamincreases
c. The price of the shirt made in Vietnam and exported to Europeincreases d. All of the above are true. • GDP (C,I,G,NX)
• GDP deflator: = GDPn /GDPr (current price/base price)
• Inflation : - GDP deflator / CPI • CPI :
• GDP: the goods and services from one country (hàng hoá sản xuất trong 1 quốc gia)
• CPI : the basket of goods (rổ hàng có thể bao gồm sản phẩm nước ngoài )
=> cun2g đo lường mức giá như nhau Link Các dạng BT Tiếng Việt (nếu cần):
https://www.studocu.com/vn/document/hoc-vien-ngoai-
giaoviet-nam/phuong-phap-nghien-cuu-khoa-hoc-kinh-
te/chuong-2bai-tap-vi-mo/20664150 Chapter 3:
• Growth rate = GDP t - GDP (t-1)/ GDP t-1 x 100
• Production function (hàng sản xuất ) output )Y = Af (K,L,N) - đầu vào K : capital L: labor N : natural resources Af: technology lOMoARcPSD| 49964158
Productivity = measure one labor in the country - how much they produce Y/L
If you compare country A - country B > productivity
> one person in a country - what they produce
How productivity changes - depends on .. Chapter 4:
Y = C+ I + G + NX (zero): closed economy - nền kinh tế đóng • Y - C - G = I
• S(supply of fund : lender ) = I (Demand of fund ) —--->(National savings) Sp = Y- I-G • Sg = T-G Lender - household Firm > want to money • shift and move • r equilibrium INTEREST rate
Phân tích sự kiện đó ??? •
Chính phủ tác động vào investment - shifting •
(government spending/ consumption / tax ) • MOVE > price • SHIFT lOMoARcPSD| 49964158 lOMoARcPSD| 49964158 •
Chapter 10 : The Influence of Monetary and
Fiscal Policy on Aggregate Demand •
The theory of liquidity preference (Keynes’s Theory) •
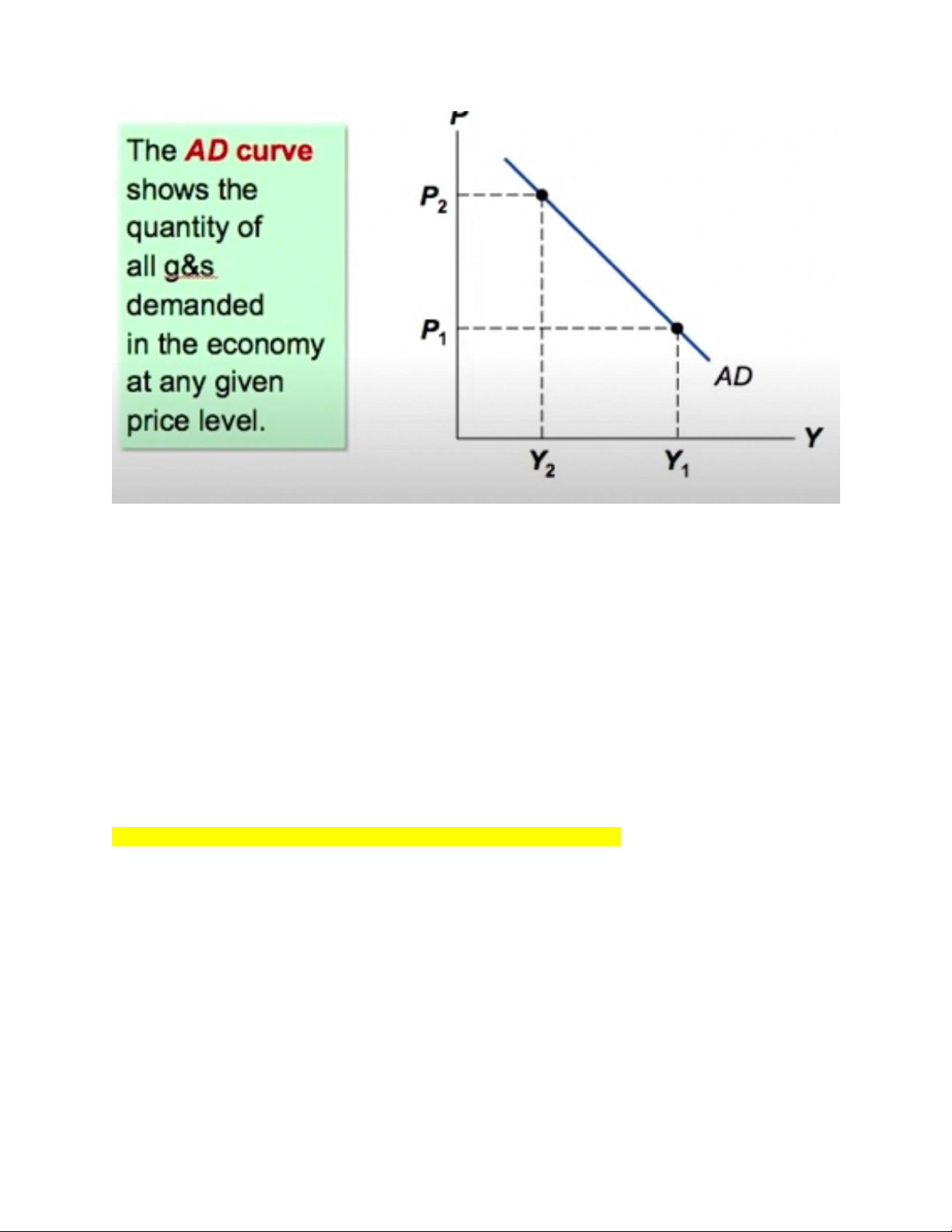
Chapter 9: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
1. 3 key facts of Economic Fluctuations Irregular and
Most macroeconomics fluctuate Output falls, unemployment Unpredictable together rises Business cycle Recessions
2. Most economists use the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply to study fluctuations
2. This model differs from the classical economics theories to explain the long run
>>The previous chapters are based on the ideas of classical economics
1. The Classical Dichotomy - the separation of variables into 2 groups •
Real - quantities, relative prices •
Nominal - measured in terms of money 2. The Neutrality of Money
Change in Money Supply affect Nominal but not Real Variables
>>However, in the short run, change in nominal variables (like the money supply or P) can affect
real variables (like Y or u-rate)
=> USE model: The model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply lOMoARcPSD| 49964158
1. Why do AD curves slope downward? (3 effects ) Wealth effect (C )
Interest-rate effect (I)
Exchange-rate effect (NX)
>> tụi em để ý 3 yếu tố này để áp dụng vào tình huống bài tập nhé.
Có thể họ sẽ hỏi: How change in P affects C, I and NX?
1. The Wealth Effect( P and C)
Suppose P rises : The money people hold buy fewer goods and services> real wealth is lower> People feel poorer > C falls
2. The Interest-rate effects(P and I )
Suppose P rises: Buying g&s require more dollars> To get these dollars, people
sell bonds or other assets> drives up Interest rate > I falls( I depends on negatively on interest rate)
3. The Exchange-rate effects (P and NX) Suppose P rises: US Interest rate rise lOMoARcPSD| 49964158
Higher demand for dollar in foreign exchange market
US exports are more expensive to people abroad, imports cheaper to US residents. > NX falls
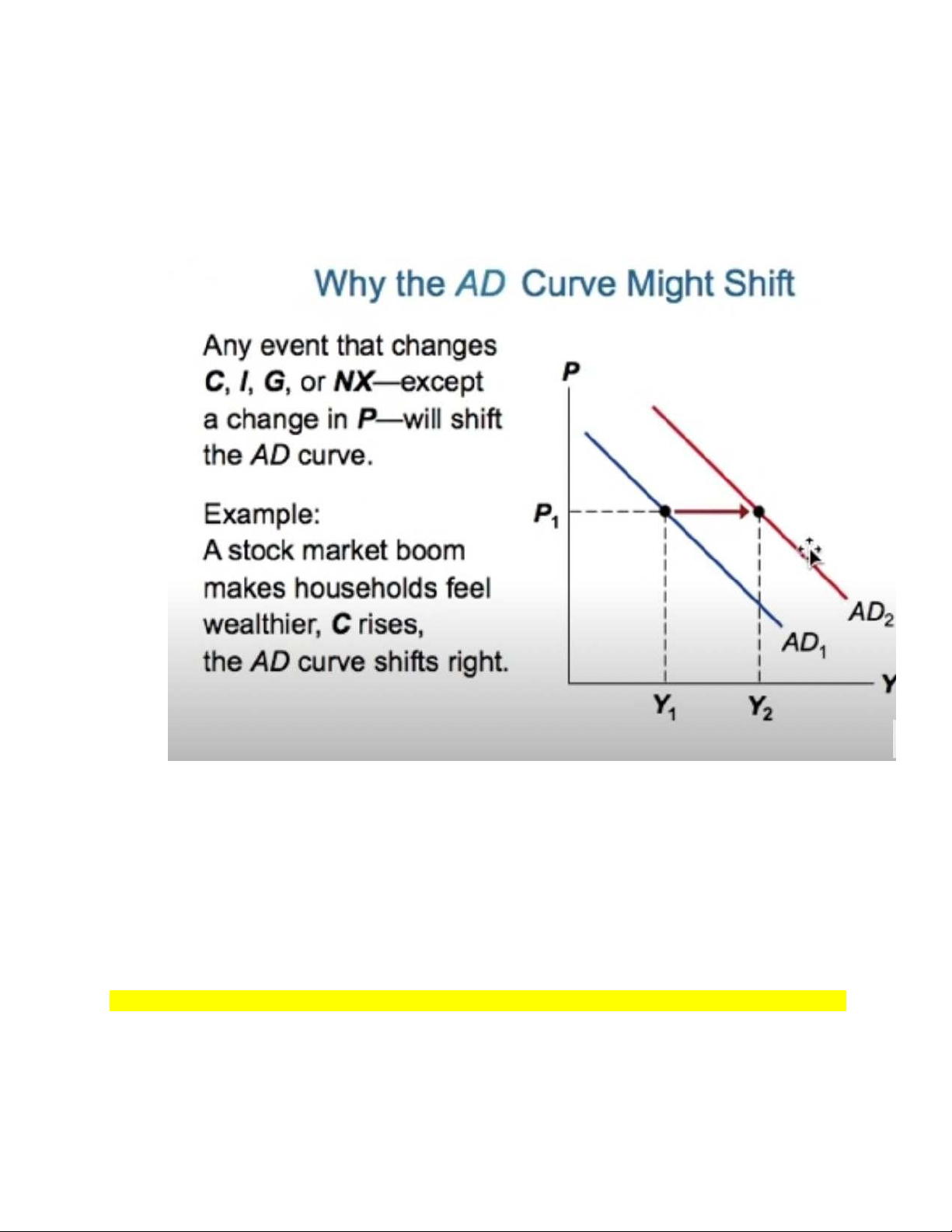
Why might the AD curve shift?
Any events that change C, I, G, NX except a change in P will shift the AD curve
>> For ex: A stock market booms makes households feels wealthier, C rises, AD curves shift right
Why does the AD curve shift?
1. Changes in C (stock market boom/crash, tax hikes/cut)
2. Changes in I (firms buy new computer, equipment, factories; expectation
optimism/pessimism; interest rate/monetary policy; investments tax credit)
3. Changes in G ( state and local spending: roads, school; federal spending: defense)
4. Changes in NX (Boom/recession in country that buy our exports,
appreciation/depreciation resulting from international speculation in foreign exchange market)
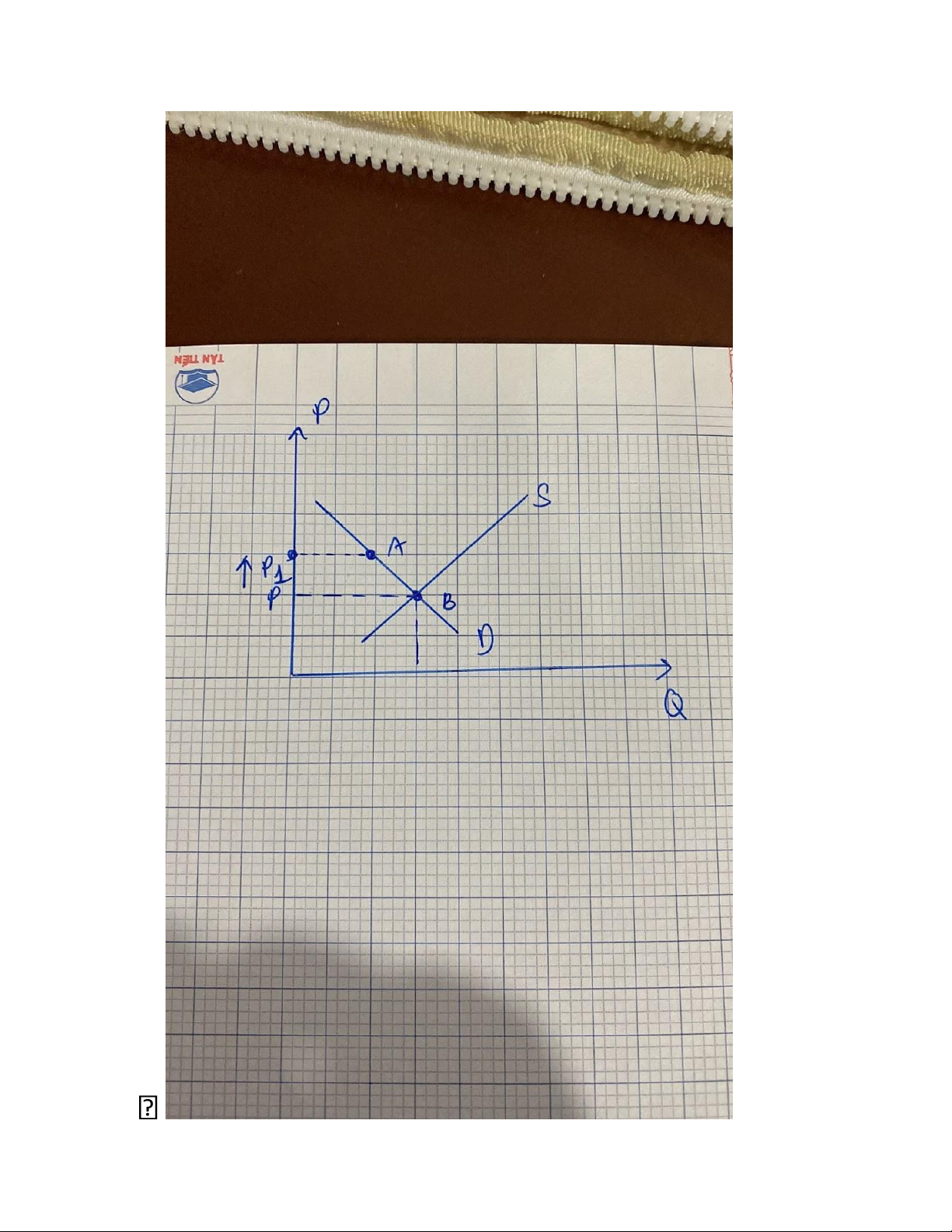
EX1: What happens to the AD curve in each of the following scenarios?
a. A ten year-old tax credit expires b. The US exchange rate falls
c. A fall in prices increases the real value of consumer's wealth
d. State government replace their sales tax with new taxes on interest, dividends and capital gains. lOMoARcPSD| 49964158 Answers: A B C D I falls, AD curve NX rises, AD curve Move down along AD C rises, AD shift shift left shift right curve(wealth effect) right
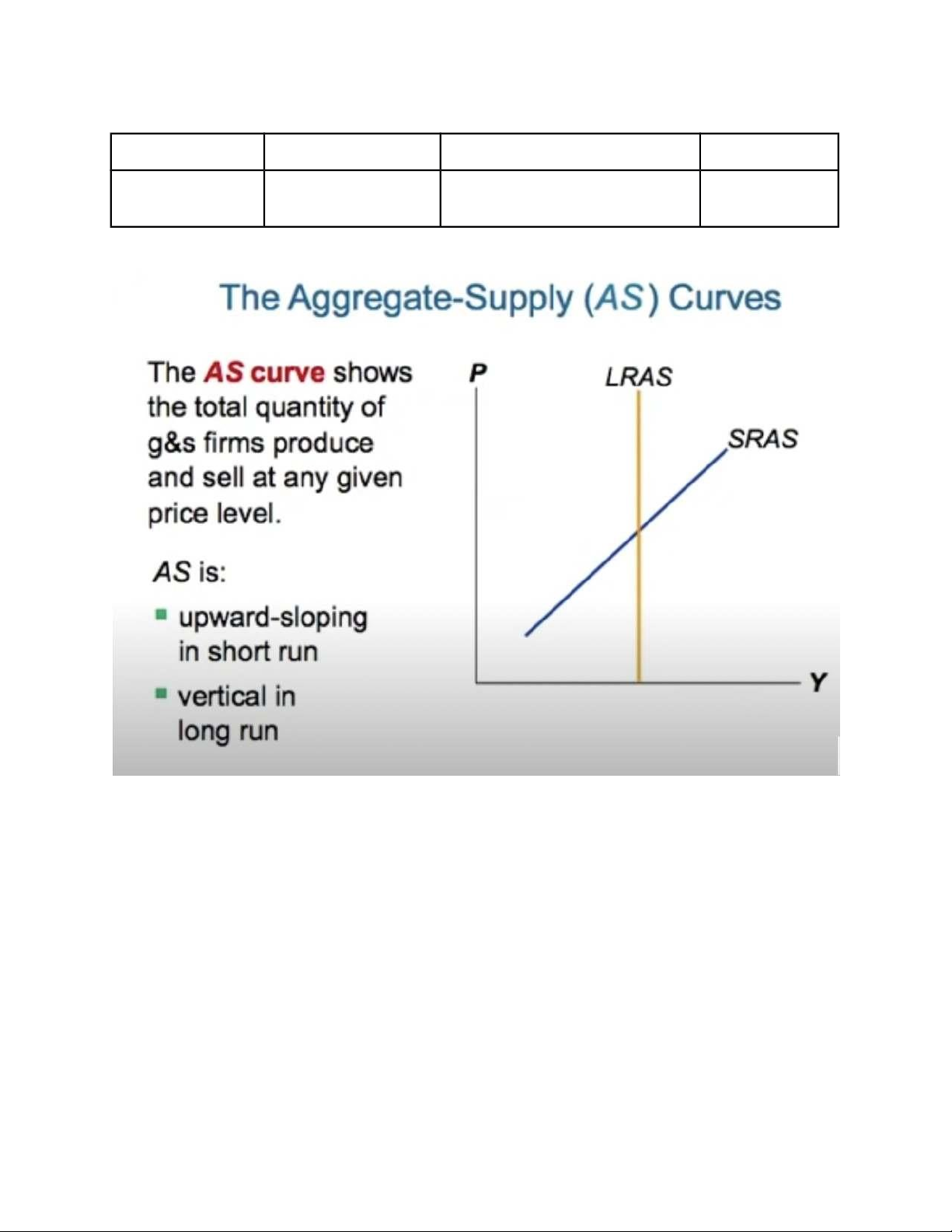
The Aggregate Supply curve (AS)
The Long Run Aggregate Supply curve •
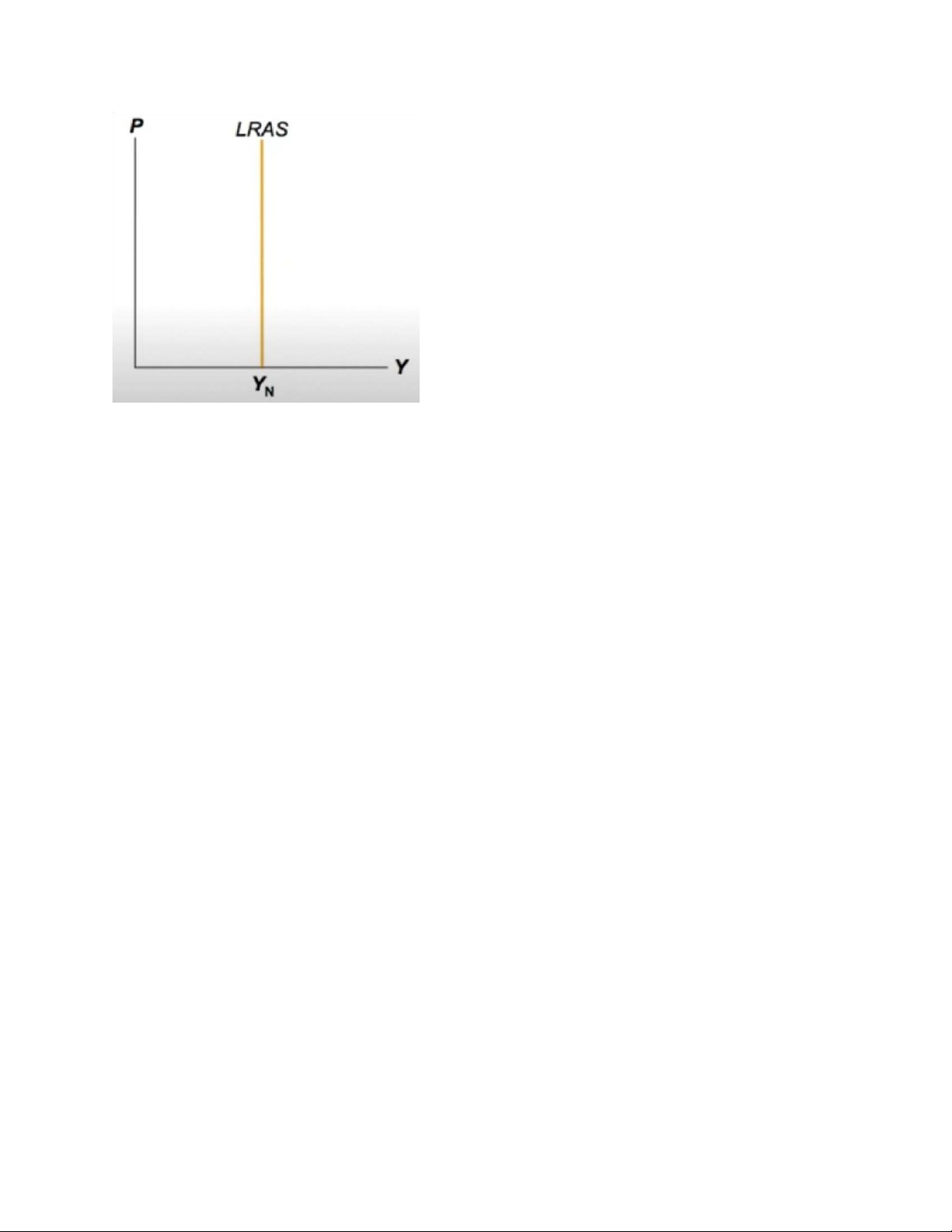
The Natural Rate of Output (Yn ) is the amount of output the economy produces when
unemployment is at its natural rate. •
Yn - also called potential output or full-employment output. lOMoARcPSD| 49964158
Why might the LRAS curve shift?
Any event that changes any of the determinants of Yn will shift LRAS
Ex: Immigration increases L, causing Yn to rise.
1. Changes in L or natural rate of unemployment (Immigration, baby-boomers retire,
government policies reduce u-rate)
2. Changes in K or H (investment in factories, equipment, more people get college
degrees, factories destroyed by hurricane)
3. Changes in Natural resources(discovery of new mineral deposits, reduction in supply of
imported oil, changing weather patterns that affect agricultural production )
4. Changes in Technology (Productivity improvements from technological progress)
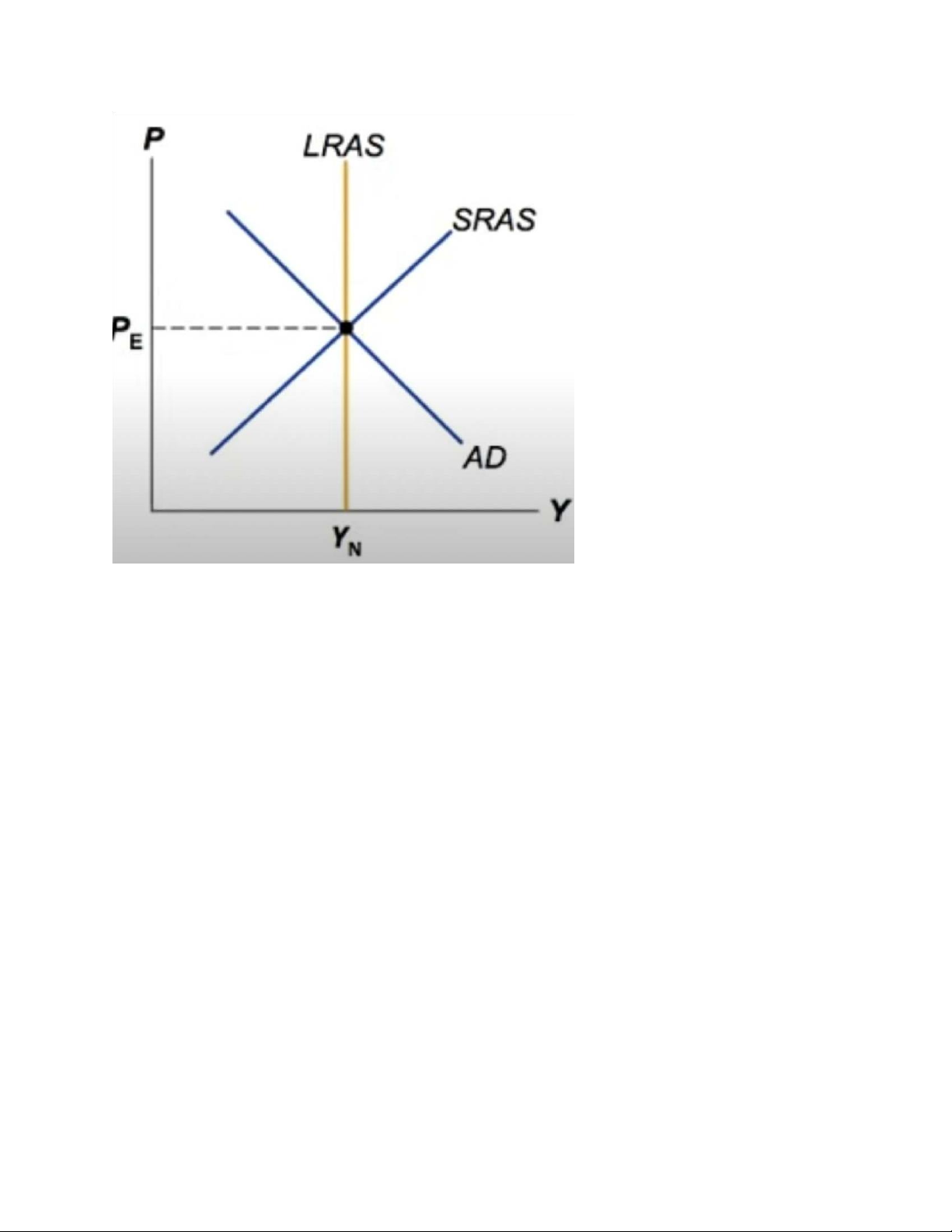
The Long Run Equilibrium
In the Long run Equilibrium, Pe = P, Y= Yn and unemployment is at its natural rate lOMoARcPSD| 49964158 KEY ĐỀ 2 lOMoARcPSD| 49964158 Đề 1 lOMoARcPSD| 49964158 .




