


















































Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|36490632 Lecture 02 Computer Hardware
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Downloaded by Hoa Minh (minhhoaanthea@gmail.com)
w-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved Learning Objectives
1. Outline the major technologies and uses of computer
peripherals for input, output, and storage.
2. Identify and give example of the components and
functions of a computer system.
3. Identify the computer systems and peripherals you
would acquire or recommend for a business of your
choice, and explain the reasons for your selections 3- 2 |36490632 HARDWARE BASICS
• Computer - an electronic device operating under the
control of instructions stored in its own memory that
can accept, manipulate, and store data
• Hardware components include:
1. Central processing unit (CPU) 2. Primary storage 3. Secondary storage 4. Input device 3- 3 5. Output device 6. Communication device 3- 4 |36490632 HARDWARE BASICS 3- 5 3- 6 |36490632
Computer hardware functions • Input
– Keyboards, mouse, optical scanners
– Convert data into electronic form • Processing
– Central Processing Unit (CPU)
• Arithmetic-logic unit performs the arithmetic functions • Control unit • Output 3- 7
– Video display units, printers, etc.
– Convert electronic information into human-intelligible form
Computer hardware functions • Storage
– Primary Storage Unit or memory – Secondary Storage
• Magnetic disks and Optical disks • Control – Control unit of the CPU
– Controls the other components of the computer 3- 8 |36490632
Computer System Components 3- 9 System unit 3- 10 |36490632 Central Processing Unit
• Central processing unit (CPU) (or microprocessor) - the
actual hardware that interprets and executes the program
(software) instructions and coordinates how all the other hardware devices work together
–Control unit - interprets software instructions and literally
tells the other hardware devices what to do, based on the software instructions 3- 11
–Arithmetic-logic unit (ALU) - performs all arithmetic
operations (for example, addition and subtraction) and all
logic operations (such as sorting and comparing numbers)
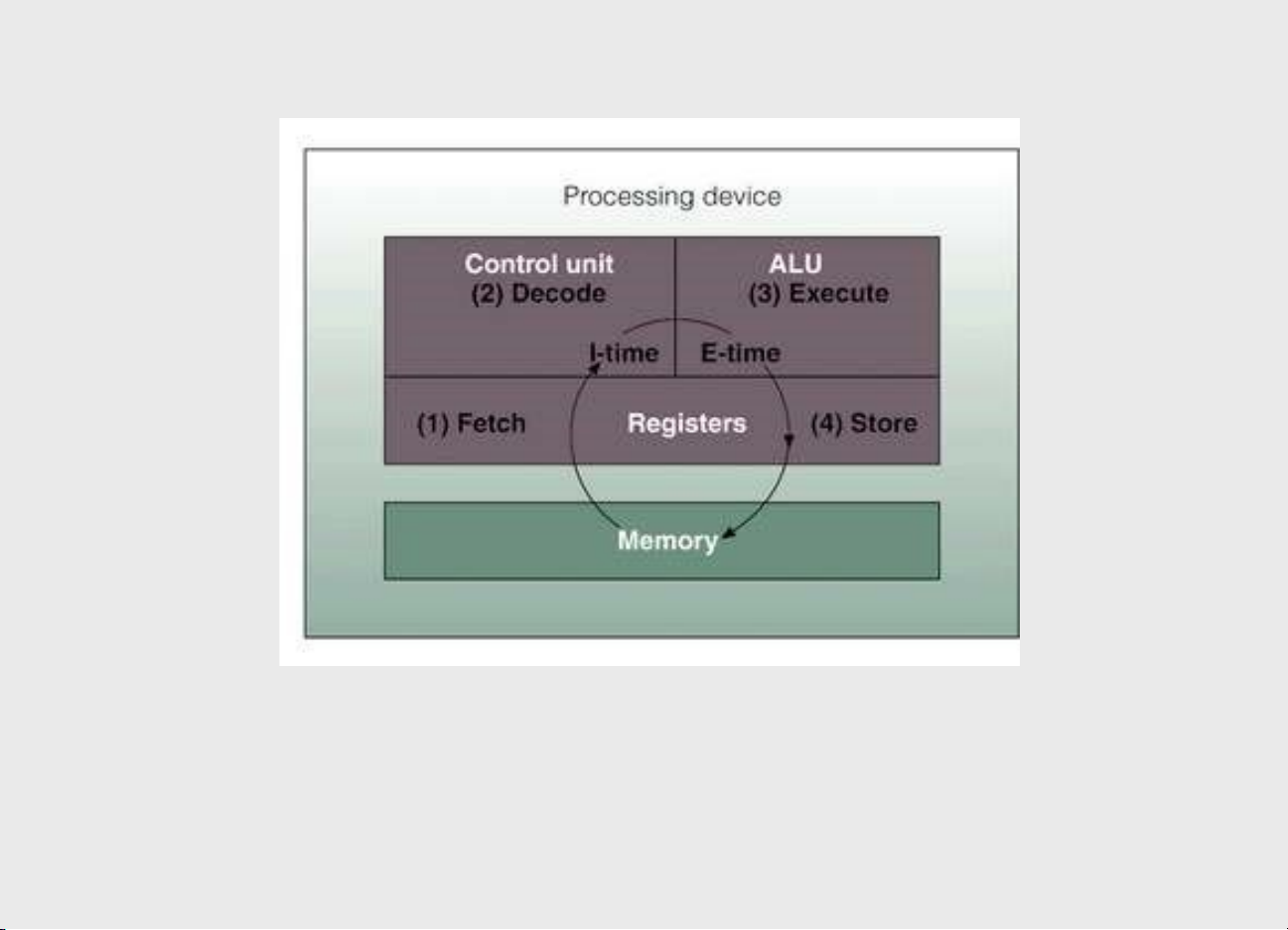
Hardware Components in Action • Instruction phase – Step 1: Fetch instruction
• Access the primary memory by the control unit, computer
program is a sequence of instructions. – Step 2: Decode instruction
• The instruction is decoded the central processor can understand what is to be done. 3- 12 |36490632 • Execution phase
– Step 3: Execute the instruction
• The ALU does what is instructed to do
– Step 4: Store the results in memory 3- 13
Execution of an Instruction 3- 14 |36490632
Computer Processing Speeds
• MIPS – million instructions per second 3- 15
• Teraflops – trillions of floating point operations per second (Supercomputer)
• Clock speed of the computer:
– Megahertz (MHz) – millions of cycles per second
– Gigahertz (GHz) – billions of cycles per second 3- 16 |36490632 Moore’s law suggests that computer power will double every 18 to 24 months 3- 17 Moore’s Law 3- 18 |36490632 Primary Storage
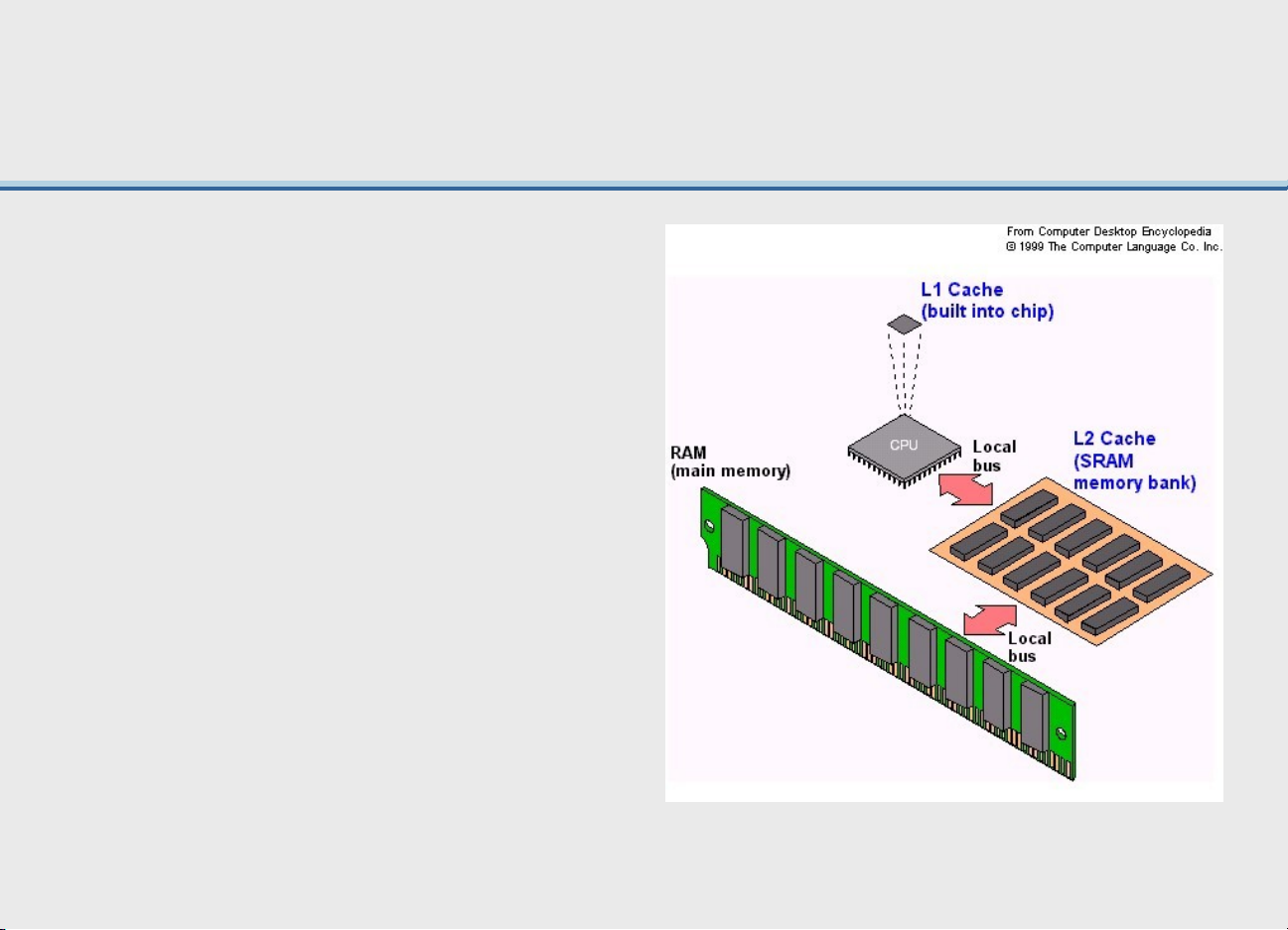
• Primary storage - the computer’s main memory, which
consists of the random access memory (RAM), cache
memory, and the read-only memory (ROM) that is directly accessible to the CPU Semiconductor memory
• Microelectronic semiconductor memory chips • Used for primary storage 3- 19 • Advantage: – Small size – Fast
– Shock and temperature resistance • Disadvantage:
– Volatility: must have uninterrupted electric power or lose memory 3- 20 |36490632
Random Access Memory (RAM) • Random access memory
(RAM) - the computer’s primary working memory, in which program instructions and data are stored so that they can be accessed directly by the CPU via the
processor’s highspeed external data bus 3- 21
– Volatility : do not retain its contents when the power is switched off
– Save work frequently 3- 22 |36490632 • Cache memory – small unit of ultra-fast memory – Used to store recently accessed or frequently accessed data → CPU does
not have to retrieve this data from slower memory such as RAM. 3- 23
Random Access Memory (RAM) 3- 24 |36490632 Read Only Memory (ROM) • ROM: read only memory
– The portion of a computer’s primary storage that does not lose its contents when one switches off the power → Permanent storage – Can be read but cannot be overwritten – Store start-up program : frequently used programs burnt
into chips during manufacturing (Called firmware) 3- 25
• New type of permanent storage
• A special type of rewritable ROM that is compact and portable • Uses semiconductor memory
– Also called jump drives, USB flash drives, thumb drives, USB disk etc. – Memory card, memory stick Flash drive 3- 26 |36490632
Source: Courtesy of Lexar Media. Peripherals
• Peripheral is generic name for all input, output, and
secondary storage devices that are part of the
computer system but are not part of the system unit
(i.e. CPU & primary storage) 3- 27
• Input device - equipment used to capture information and commands – Manual input devices • Joystick • Keyboard • Microphone – Automated input devices • Bar code scanner • Digital camera
• Magnetic ink character reader 3- 28 |36490632 Input Devices 3- 29 Popular input devices • Keyboard: – most widely-used
– provides a set of alphabetic, numeric, punctuation, symbol and control keys. • Mouse
– One or more control buttons housed in a palmsize case and
designed so that one can move it on the table. – Point & click 3- 30 |36490632
• Touchpad – Small rectangular touch-sensitive surface
– Moves the cursor in the direction of finger moves on the pad
• Touch Screen – use computer by touching screen
– Video display screen that emits a grid of infrared beams, sound
waves, or a slight electric current
– Grid is broken when the screen is touched. 3- 31 Pointing Devices 3- 32 |36490632 Pen-based Computing • Used in Tablet PCs and PDAs
• Sensitive layer like touch screen under liquid crystal display screen
• Have software that digitizes
handwriting, hand printing, and hand drawing 3- 33 Automated Input Devices
• Optical data readers : read text or graphic and store as an digital image.
• Optical character recognition : read and convert to text
• Point-of-sale (POS) devices: terminal used in retail
operations to enter sales information into computer system.
• Bar code scanner : point of sales, inventory
• Magnetic strip : Can hold about kilobytes of information. 3- 34 |36490632
• Smartcard : that embed a microprocessor chip and several
kilobytes of memory (like credit card, debit card) Automated Input Devices
• Digital cameras: captures still images or video as a series of 0s and 1s
• Automatic teller machine (ATM) devices: special I/O devices, a
terminal of most bank customers
• Radio-frequency identification (RFID): library, uses active or
passive tags in the form of chips or smart label that can store 3- 35
unique identifier and relay this information to electronic readers. Output Technologies • Video displays
– Cathode ray tube (CRT) like a television • Most desktop PC screens
– Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) 3- 36 |36490632 • Laptop and PDAs, some PCs • Printed Output – Inkjet printer • Spray ink on page – Laser printer
• Electrostatic process like photocopying machine • Voice response systems
Secondary Storage Devices
• Main memory provides only small amount of storage
area for data, instruction, information. 3- 37
• Computer needs store larger amount of data,
instruction and information, more permanently than
primary memory Secondary storage devices
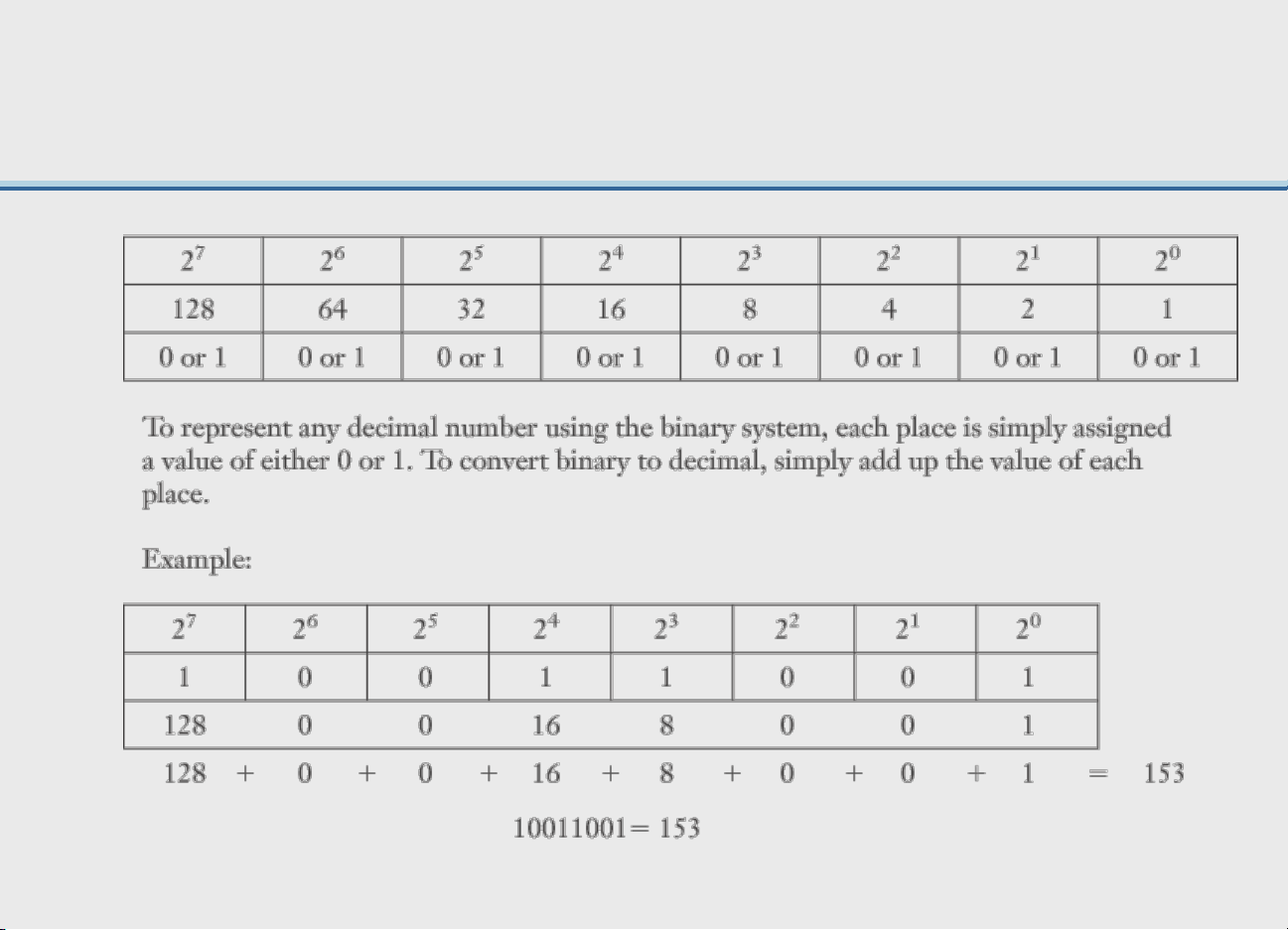
Computer Storage Fundamentals • Binary representation
– Data are processed and stored in computer system through the presence or absence of signals – Either ON or OFF • ON = number 1 • OFF = number 0 3- 38 |36490632 Bit and Byte
• Bit (short for binary digit) – Smallest element of data – Either zero or one • Byte
– Group of eight bits which operate as a single unit
– Represents one character or number 3- 39 (using coding scheme) 3- 40 |36490632
Representing characters in bytes 3- 41
Computers use binary system to calculate 3- 42 |36490632
• Direct Access or Random Access
– Directly store and retrieve data
– Each storage position has unique address
and can be accessed in same length of time
– Semiconductor memory chips, magnetic disks • Sequential Access
Direct and Sequential Access 3- 43
– Data is stored and retrieved in a sequential process
– Must be accessed in sequence by searching through prior data – Magnetic tape 3- 44 |36490632
Direct and sequential access 3- 45 Magnetic Disks • Used for secondary storage
• Fast access and high storage capacity 3- 46 |36490632 Source: Quantum. Source: Corbis. Types of magnetic disks • Floppy disks
– Magnetic disk inside a plastic jacket • Hard disk drives
– Magnetic disk, access arms, and
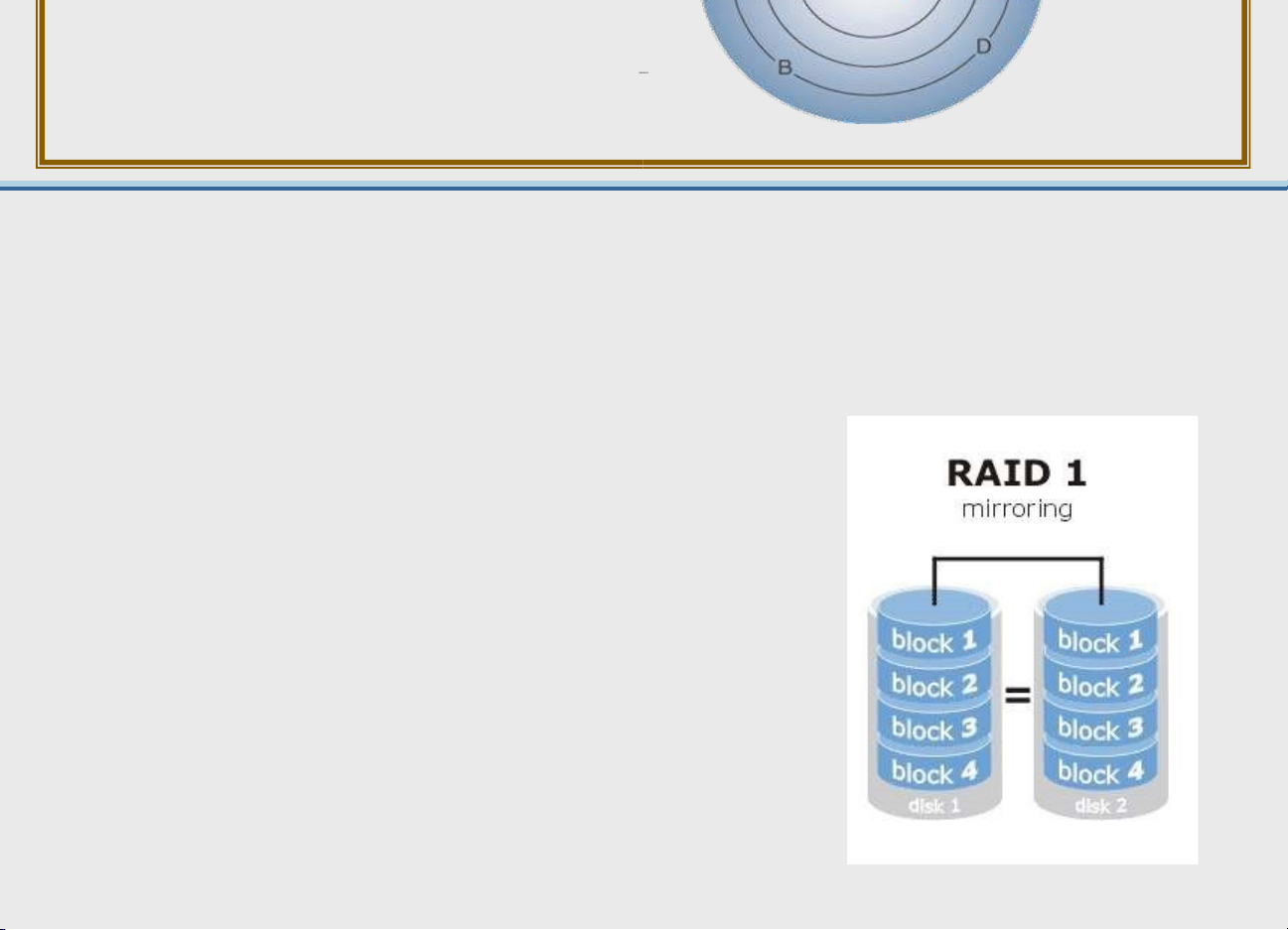
read/write heads in sealed module – RAID (Redundant arrays of independent disks)
• Disk arrays of interconnected hard disk drives
• Fault tolerant with multiple copies on several disks 3- 47 Magnetic Tape • Secondary storage • Tape reels and cartridges
• Used in robotic automated drive assemblies
• Archival storage and backup storage 3- 48 |36490632 Optical Disks 3- 49 3- 50 |36490632 Optical Disks
• Blue-ray Disc: enable recording, rewriting and playback of high-definition 3- 51
video (HD), as well as storing large amounts of data. The format offers more
than five times the storage capacity of traditional DVDs and can hold up to
25GB on a single-layer disc and 50GB on a dual-layer disc. This extra capacity
combined with the use of advanced video and audio codecs will offer consumers
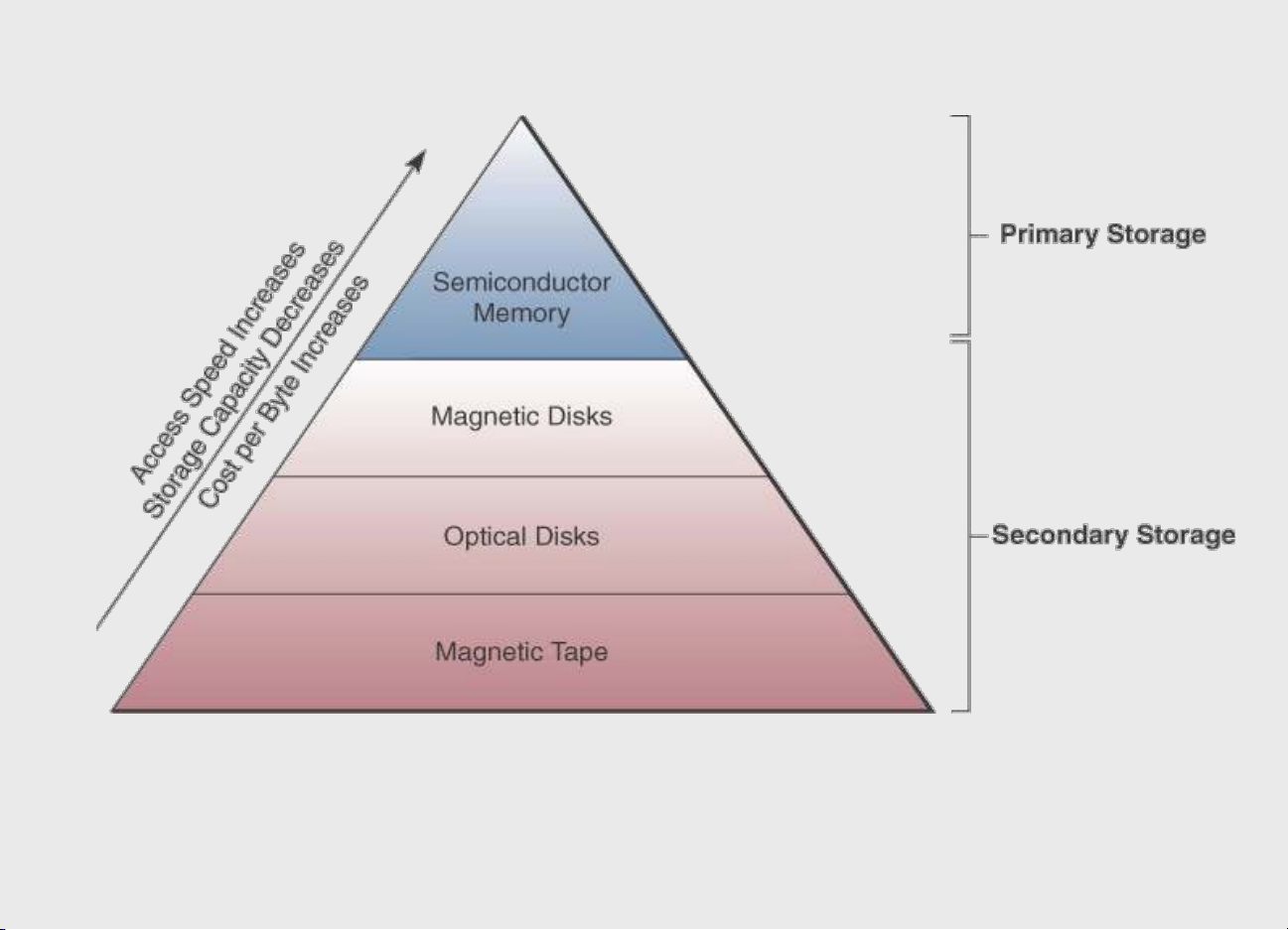
an unprecedented HD experience. 3- 52 |36490632 Storage tradeoffs 3- 53 3- 54 |36490632 Communication Devices
• Communication device - equipment used to send
information and receive it from one location to another – Dial-up access – Cable – Digital subscriber line – Wireless – Satellite 3- 55 3- 56 |36490632 Communication 3- 57
Document Outline
- Learning Objectives
- HARDWARE BASICS
- HARDWARE BASICS
- Computer hardware functions
- Computer hardware functions
- Computer System Components
- Central Processing Unit
- Hardware Components in Action
- Execution of an Instruction
- Computer Processing Speeds
- Primary Storage
- Semiconductor memory
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Peripherals
- Popular input devices
- Pen-based Computing
- Automated Input Devices
- Automated Input Devices
- Output Technologies
- Secondary Storage Devices
- Computer Storage Fundamentals
- Bit and Byte
- Representing characters in bytes
- Direct and Sequential Access
- Direct and sequential access
- Magnetic Disks
- Types of magnetic disks
- Magnetic Tape
- Optical Disks
- Optical Disks
- Storage tradeoffs
- Communication Devices
- Communication




