



Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938 Intra household relations Extra Resources household relations Behavior Farm household lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938 Peasant economics
Lesson 3. Contents of peasant household economic analysis Luu Van Duy 2022
Department: Agricultural economics and Policies 1 2 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
Contents of household economic analysis
Farmers (HH head) and their family Households resources
Intra- and extra household relations
Farm households socio-economic behaviors
Household economics calculation 3 3.1
Farmers (HH head) and their family
What are Large-scale farming household’s production objectives? TPr.max = TR-TC
Peasant household’s function of production objectiv es: U = U (Xa, Xm, Xi)
Xa: Output for consumption (Social objectives)
Xm: Output for sale (economic objectives)
Xi: Leisure crop time and time for housework (Soci al objectives) Economic objectives Social objectives Enough to eat and wear Health Stable income Entertainment Saving for the future
Less strenuous work and leisur e time Family obligations Social obligations 4 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
How do household's objectives link together? Supplement Or conflict
( Basic needs of households or labour’s strenuousness ?
Subsistence or commercial production ?)
Who decide the household’s objective? 5
Contents of analysis of HH head and their family
Household head’s information (age, gender, educational
and professional degree, production experiences,…)
Household size: 1,2,3,4 generations Family rules/norm/habit
Household members: age, gender, educational and
professional degree, production experiences
Family and, relationship,
Household’s customs and habits
->Why do we should concern the above household’s information? 6 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938 Groups work
Identify household's information needed to collect in order to examine
these following topics:
(1) General information of HH, (2) HH head (3) HH members
Situation assessment of business of rooms for students in
the Trau Quy ward, Gia Lam district, Hanoi ( G 1)
Situation assessment of production and consumption of
safe vegetables by farmers in Van Duc commune, Gia Lam district, Hanoi ( G 2)
Assessment of the role of women in household
economic development in Trau Quy ward, Gia Lam district, Hanoi ( G 3)
Assessment of economic efficiency of aquaculture by
farmers in Thai Binh province (G4). 3.2
Household’s resources Household’s property Public property: - Land - Infrastructure - Labour - Service - Capital - Policy - Technology - Environment - ... - ... 8 7 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938 3.2.1 Household’s land Land area Land source: Be allocated; Be hired Be purchased Land quality Soil fertility; Type of land Related land policies 9 10 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
3.2.2 Household’s labour
Number of people and labour
Proportion of depended person/number of labour Labour source: Family labour Hired labour Exchange labour Labour’s health
Labour’s knowledge and skills Experiences 11 3.2.3
. Household’s capital Capital size
Source of capital: Household own capital, lending c apital Length of capital uses Purpose of capital uses Interest rate 12 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938 3.2.4 . Public property - Infrastructure - Service - Policy - Environment
- What do public properties impact on household
economics? Give examples? 13
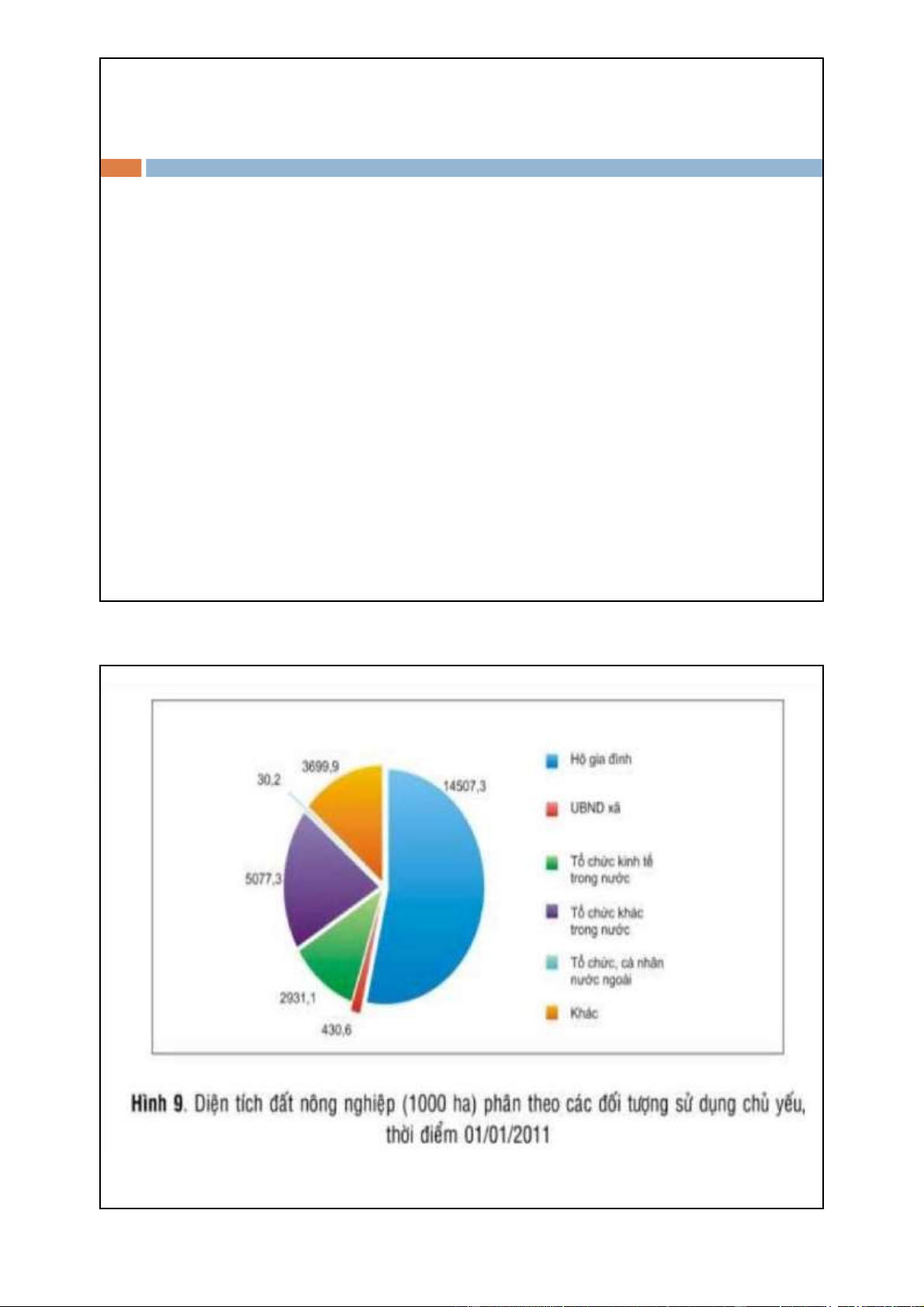
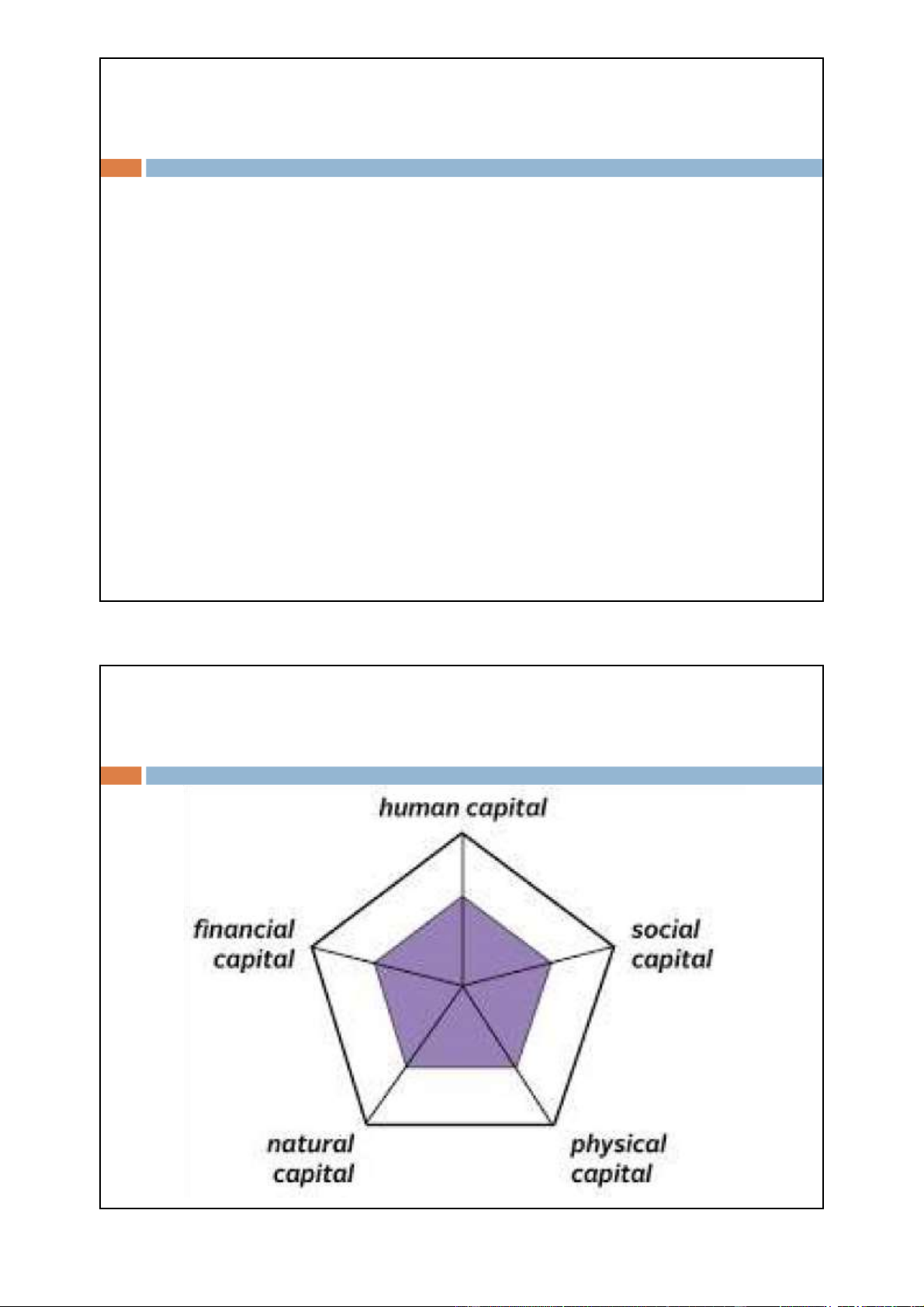
Household’s livelihood capital 14 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
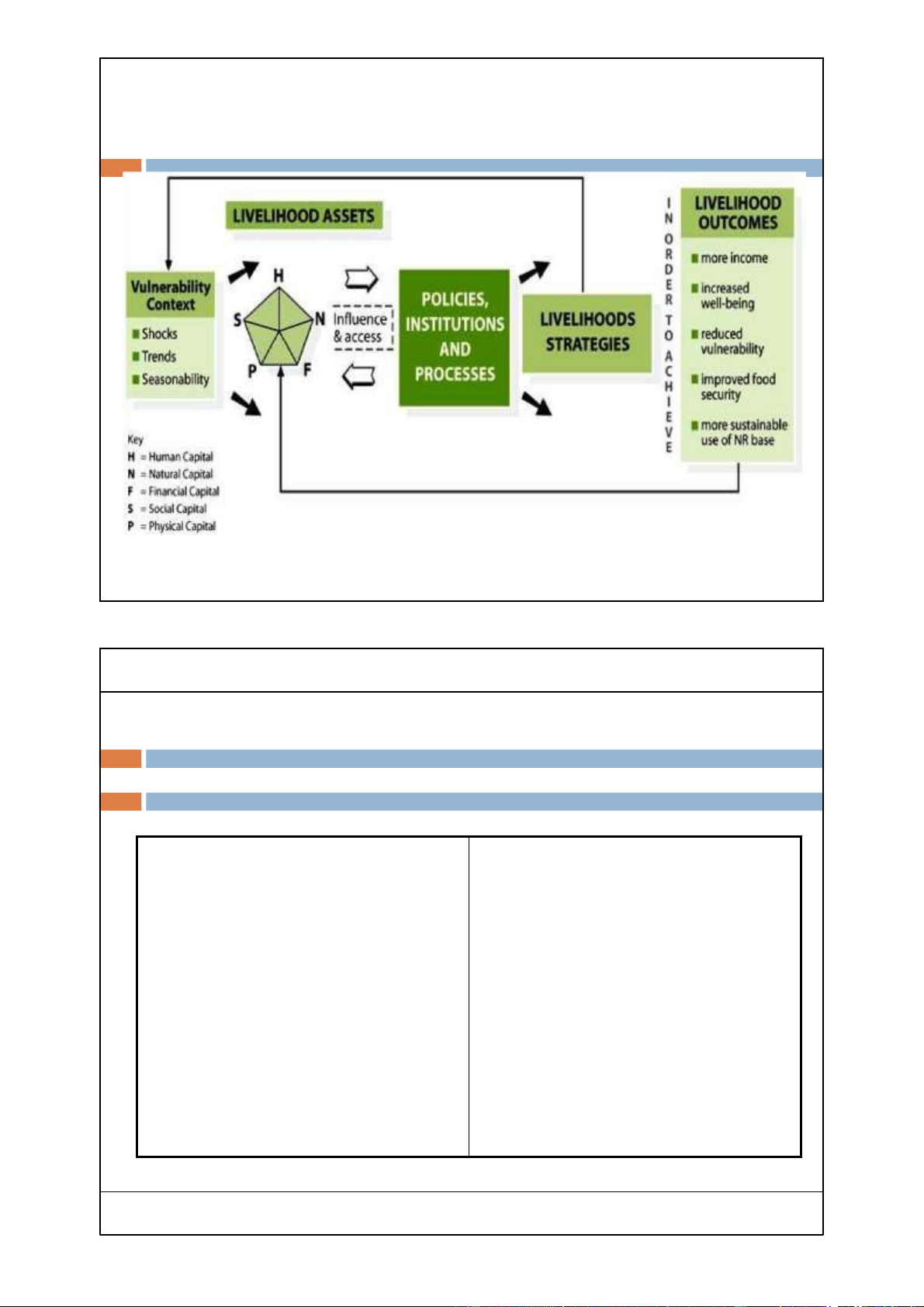
Sustainable livelihood framework 15 Groups work
3.3 Intra household relations and between households and outsiders
Intra household relations: Households and outsiders: - Household head’s role - Kinship - Relations of household - Community members - Society - Gender and decision - Government making, consumption, income and distribution... ... 16 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
Point out household's information needed to collect in order to examine
these following topics: (1) Household’s resources, (2) Public property 1.
Situation assessment of production and sale of safe
vegetables by farmers in Van Duc commune, Gia Lam district, Hanoi 2.
Assessment of economic efficiency of pig raising by
households in Hong Thai, Phu Xuyen, Ha Noi 3.
Assessment of production and consumption by
households in Trau Quy ward, Gia Lam district, Hanoi. 4.
Assessment of the role of women in household economic
development in Trau Quy ward, Gia Lam district, Hanoi 5.
Assessment of economic efficiency of rice cultivation by
smallhoders in Van Duc commune, Gia Lam district
3.3.1 Intra household relations
Household head’s roles :
Decision making of production and consumption; Social behaviors
Wife and husband’s roles :
Division of decision making; Labour division; Spending and saving;
Training and taking care the children;
Leisure and entertainment;
Social activity participation 18 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
3.3.1 Intra household relations ( Cont. )
Parents with their children:
Nurture and training of the children; Vocational guidance;
Inheritance (land, houses, assets) Children with parents : Serve parents; Obey parents; 19 17
Gender issues intra household What is gender?
Refers to a set of different roles and characteristics are
considered suitable for men or women, and vary by
culture and national identity, social class and ages.
Why are gender issues considered in household economics?
Household is a social unit Gender is a social issue
Women’s role has been appropriately considered
Inequality exist between men and women: work time,
income and assets; education and health; position in the family and society ... lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938 20 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
Gender issues intra household (Cont.)
Gender in labour division?
What do women do in households?
What do men do in households?
What factors do impact on division of labour by gen der?
Gender in decision making: consumption, income, and distribution. 21
What do women and men do in households? 22 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
Women’s roles in household economics ( Frank Ellis, 1993)
Number of hours worked by women larger than men
Women mainly engaged in household chores such as
caring for children, daily reproduction, preparatio n of food for domestic uses
Women participate in unpaid works 23
What do women do in households? 24 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
-> What should we do to strength women’s role in household economics? 25
3.3.2 Social and economic relations between
h ouseholds and outsiders Kinship Community
With society through the market
With the state (local government) ? 26 lOMoAR cPSD| 48302938
Related activities in relations Commercial trading Information exchange Engagement in a tontine, Help and assist together Get loan Pay tax Purchase insurance
-> What should we do to strength the above relations? 27
Downloaded by Tran Anh (anhtran1406@gmail.com)




