




Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|47231818
VIETNAM NATIONAL UNIVERSITY – HO CHI MINH CITY INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF BIOTECHNOLOGY BIOLOGY (BT155IU) Laboratory report
Practical 1: MICROSCOPY, CELL
OBSERVATION & OSMOSIS
Instructor: TRAN THI NGOC DIEP Academic year: 2023-2024 Group: 4 Group members: No. Full name Student ID 1. Phạm Vũ Khánh Linh BTBTIU21219 2. Trương Ngọc Hương Giang BTBTIU21195 3. Nguyễn Lê Anh Kiệt BTBTIU20180 4. Nguyễn Duy Đức BTCEIU21086
(Follow instruction at page 26 - 27 of Biology Lab Manual)
I/ PLANT CELLS AND ANIMAL CELLS OBSERVATION 1. Intro duction : lOMoARcPSD|47231818
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large
and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells.
They can maintain different environments in a single cell that allows them to carry out
various metabolic reactions. This helps them grow many times larger than the prokaryotic cells.
->Plant cells are eukaryotic, which means that they contain a distinct nucleus. Plant
cells have three unique structures which set them apart from other eukaryotes, such
as animal cells: the cell wall, plastids, and vacuoles. Plant cells are microscopic in size
(on the order of 0.01 to 1.0 mm).
->Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and
containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Unlike the eukaryotic cells of
plants and fungi, animal cells do not have a cell wall.
2. Materials and methods: Materials and Equipments: • Onion • animal cells • Distilled water • Glass slides + Coverslips • Blades + Forceps • Microscopes • Tissues
To distinguish between the two types of plant and animal cells, we prepare a solution
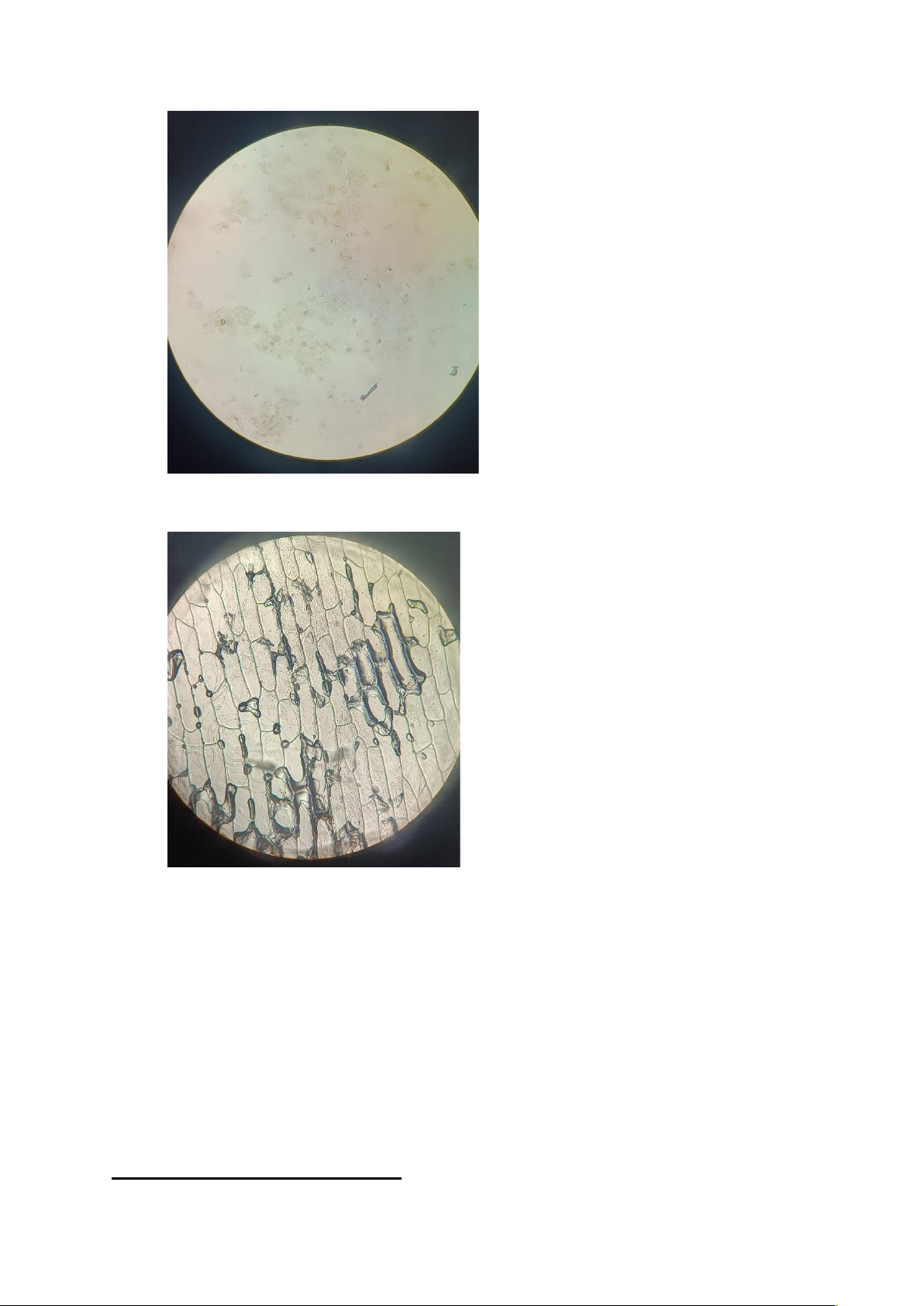
of distilled water then take 2 samples of cells with 1 cuticle removed and put distilled water on top and observe. 3. Results : Picture 1: Animal cells lOMoARcPSD|47231818 Picture 2: Plant cells
a) What is the function of the Lugol solution in these experiments?
The lugol solution in the experiment has the effect of creating a color layer covering the cells to help see the cells more clearly
b) What is the difference between plant cells and animal cells?
The plant cells have chloroplasts, cellulose walls, and vacuoles, but animal cells do not
have. Animal cells have centrosome. The nucleus of an animal cells is located in the middle.
In a plant cells, nucleus is located on one side because the vacuole occupies the area.
II/ OSMOSIS IN PLANT CELLS lOMoARcPSD|47231818 1. Introduction :
Diffusion is specified as the net movement of molecules from the regions of higher solute
concentration to the regions of lower solute concentration. Osmosis is a special form of
diffusion in which water molecules flow across a differentially permeable membrane from a
solution with a lower solute concentration to a solution with a higher solute concentration.
This membrane allows only certain types of molecules to pass through it or permeate it
freely. Cellular membrane is a type of differentially permeable membrane. Osmosis does not
require expenditure of energy but an energetically "downhill" process. Since the water must
lose energy as it moves by osmosis, water must move from an area of greater water
potential to an area of lower water potential:
• Hypertonic solution has water potential outside the cell lower than inside the cell, then
there will be a net movement of water out of the cell.
• Hypotonic solution has water potential outside the cell greater than inside the cell, then
osmosis will be a spontaneous net movement of water into the cell.
• In isotonic solution, the water potential on each side of a cell membrane is the same, there
will be no net movement of water across the membrane.
Osmotic pressure of a solution is proportional to the effective concentration of dissolved
particles, regardless of the size or chemical nature of the particle.
2. Materials and methods : Materials and Equipments: • A leaf of Zebrina pendula • Distilled water
• 5% Sodium chloride solutions
• 0.85% Sodium chloride solutions • Glass slides + Coverslips • Blades + Forceps • Microscopes • Paper towel
To distinguish the effects of 3 types of solvents, which are hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic,
prepare 3 types of solutions: distilled water, 0.85% nacl and 5% nacl, respectively. then take
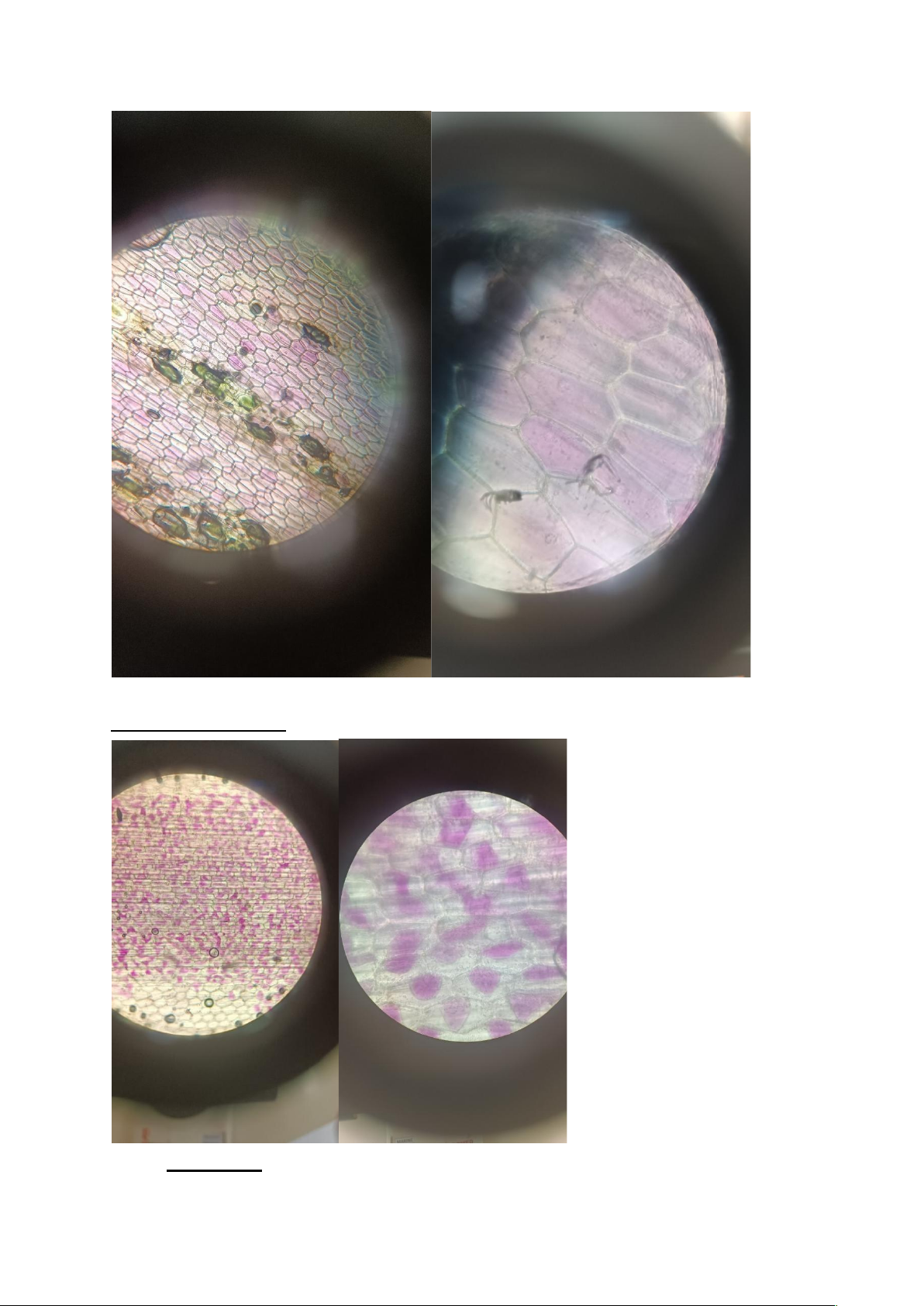
3 samples of Zebrina pendula leaves with one cuticle removed and drop each solution on and observe. 3. Results : Picture 1: 0.85% NaCl () lOMoARcPSD|47231818 Picture 2: Water () lOMoARcPSD|47231818 Picture 3: 5% NaCl () 4. Discussion : lOMoARcPSD|47231818 a) Explain the phenomenon.
In the experiment 1 NaCl 0.85% is an isotonic solution, so no phenomenon occurs
In the experiment 2 distilled water is a hypotonic solution, so there is a larger water
potential outside the cell than inside the cell, then osmosis will be the spontaneous net
movement of water into the plant cell, so the plant cell will stretch to balance the water
potential, but the plant cell wall is so strong that the cell will swell and will become "turgid"
In the experiment3 NaCl 5% is a hypertonic solution so there is a lower water potential
outside the cell than inside the plant cell, then there will be a net movement of water
out of the plant cell so that the purple pigment and cells lose water and shrink and become "flaccid"
b) When putting plant cells in concentrated NaCl, plasmolysis happened.
Whenputting animal cells in water, hemolysis occurred. What makes the
phenomenon in plant cells different from in animal cells?
Plasmolysis is the process by which cells shrink away from the cell wall in a hypertonic
solution as they lose water (through the process of osmosis) (leaving a gap between them).
Because animal cells lack cell walls, plasmolysis only happens in plant cells and not in animal cells.
Moreover, only plant cells possess a cell membrane that is encased in a semi-rigid (or,
in some circumstances, stiff) cell wall.




