

Preview text:
VIETNAM NATIONAL UNIVERSITY - HO CHI MINH CITY
INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF BIOTECHNOLOGY REPORT Submitted to
Practice in Biology course Due date: 15/11/2022
Instructor: Le Minh Thong
Tuesday Afternoon class Group 3’s members: Huỳnh Lê Tuyết My - BTFTIU18165 Nguyễn Thanh Hằng - BTBTWE21109 Nguyễn Lê Trúc My - BTBTWE21093 Đào Uyên Nhi - BTCEIU21034 TABLE OF CONTENT
LAB 1: MICROSCOPY, CELL OBSERVATION & OSMOSIS REPORT 1 I.
PLANT CELLS AND ANIMAL CELLS OBSERVATION 1. Introduction:
Animal cells are the smallest unit and are capable of independent function. Basically,
millions of cells make up an animal or plant. Cells divide in a self-duplicate way and
produce a wide variety of new cell types. Upon receiving nutrients from food, cells
convert them into energy. Obviously, animal and plant cells differ from one another in
structure and other aspects. Knowledge of the differences between plant and animal
cells is provided by this experiment. 2. Procedure:
- Take pieces of cells from onion and human cheeks and place it on clean slides - Add a few drops of water
- Place coverslips on top of them
- Place the sample under the microscope
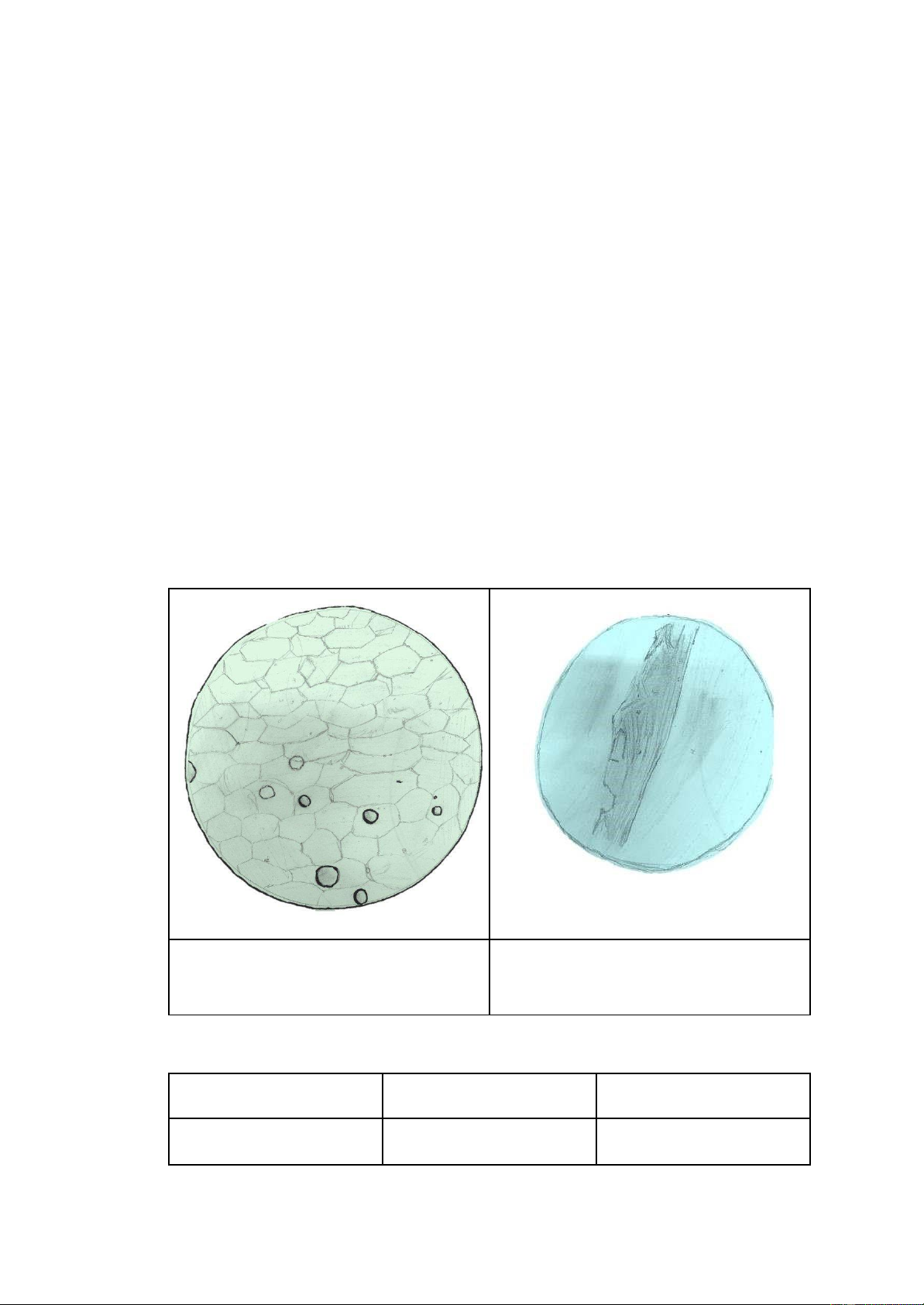
- Examine it using various objective lenses (4x, 10x, and 40x) to see the cell's structure 3. Results: Onion cell Observe at Cheek cell Observe at 40x objective 40x objective 4. Discussion:
What is the difference between plant cells and animal cells? Plant cells Animal cells Size Langer Smaller 1 Cell wall Yes No Nucleus Near the cell wall At the center Shape Regular shape Irregular shape Vacuole Many small vacuoles Only one large vacuole
II. OSMOSIS IN PLANTS CELLS 1. Introduction:
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a
region of lower concentration. Osmosis is a type of diffusion in which water molecules
move through a permeable membrane into a high concentration region. Osmosis does
not require any energy, however, the energy in water molecules is lost when water
moves from a higher potential area to a lower potential area. 2. Procedure:
- Peel a thin epidermis layer (purple side) of the Zebrina pendula leaf.
- Place the peeled layer on the slide.
- Add a drop of 0.85% NaCl. Add a coverslip.
- Examine the plant cells with the high power lens (40x). Locate the region where the cells are not too dense.
- Make another sample by repeating from step 1 to step 4. This time add a drop of
5% NaCl to the slide, instead of 0,85% NaCl.
- Make another sample by repeating from step 1 to step 4. This time add a drop of
distilled water, instead of 0,85% NaCl.
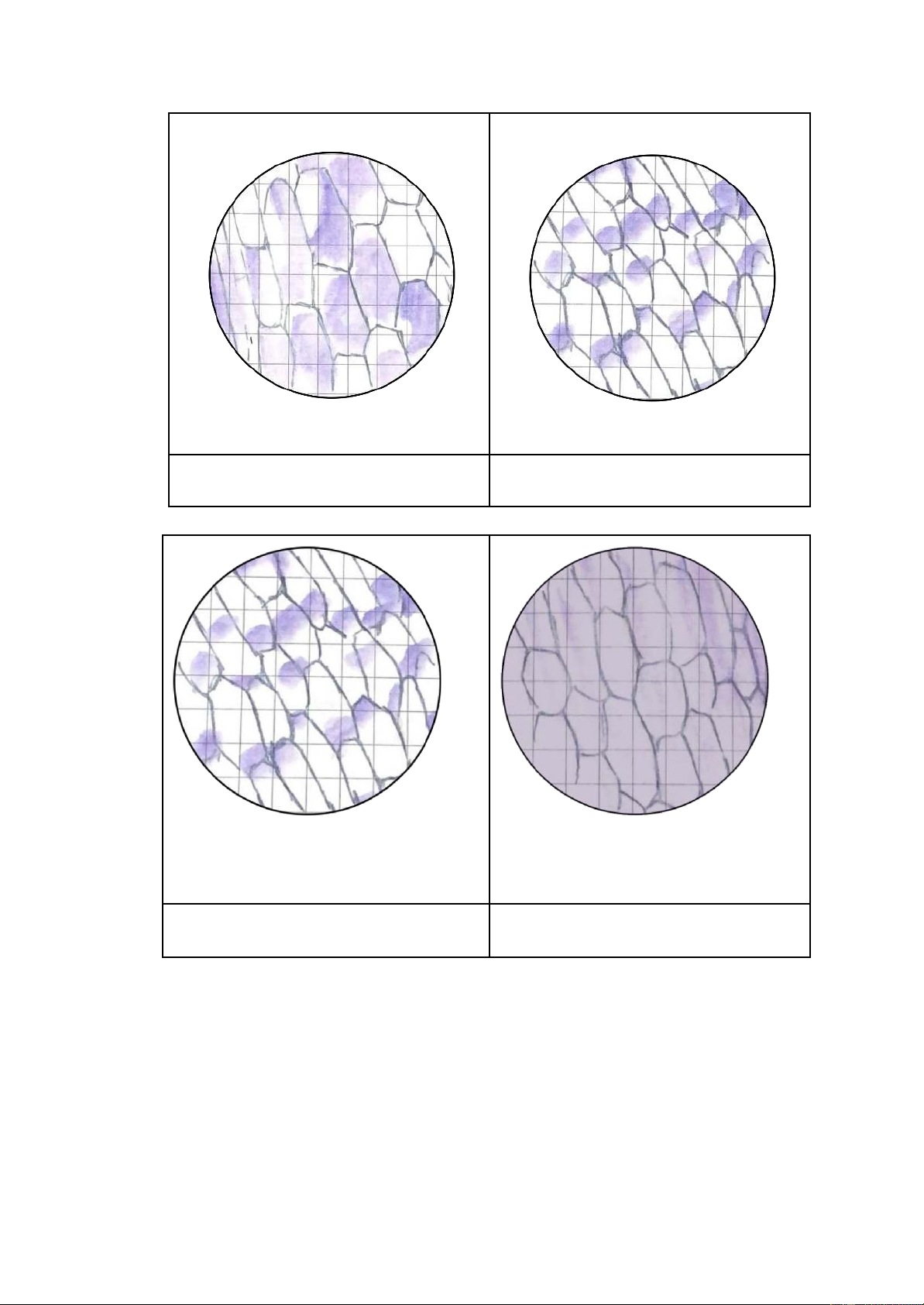
3. Results: Observed at 40x objective 2 Isotonic (0,85% NaCl) Hypertonic (5% NaCl)
→ The cells shrink in size and the purple areas are distributed distinctly. Hypertonic (5% NaCl) Hypotonic (Distilled water)
→ The cells become larger and the purple areas get closer to each other. 4. Discussion:
a. Explain the phenomenon.
Isotonic is an environment in which the concentration of solute is equal to that of the
intracellular environment. Physiological saline is a 0.85% sodium chloride solution, 3
called "physiological" because it is an isotonic solution, with an osmotic pressure
equivalent to body fluids (blood, tears,...) under normal conditions. When adding
0.85% Nacl to the sample, the cells will not shrink or enlarge.
Hypertonic is an environment in which the concentration of solute is greater than that
of the intracellular environment. When 5% NaCl is added to the sample, the water
potential outside the plant cell is lower than the water potential inside the cell, it leads
to water from inside the cell will move out causing the cell to shrink.
Hypotonic is an environment in which the concentration of solutes is lower than that of
the intracellular environment. When distilled water is dropped into the sample, the water
potential outside the plant cell is higher than inside the cell, resulting in osmotic
pressure that will cause water molecules outside to move into the cell, which can cause the cell to enlarge.
b. When putting plant cells in concentrated NaCl, plasmolysis happened.
When putting animal cells in water, hemolysis occurred. What makes the
phenomenon in plant cells different from in animal cells?
The primary distinction between plant and animal cells is that plant cells have a thick
cell wall surrounding them. When plant cells are immersed in concentrated NaCl, water
moves from inside to outside of the cells, and the contents of the cells shrink, pulling
away from the cell wall. However, when animal cells are immersed in water, water
enters the cell faster than it exits, and animal cells lack a cell wall. As a result of this,
the cell swells and ruptures, releasing hemoglobin. 4




