


Preview text:
Chap 1: •
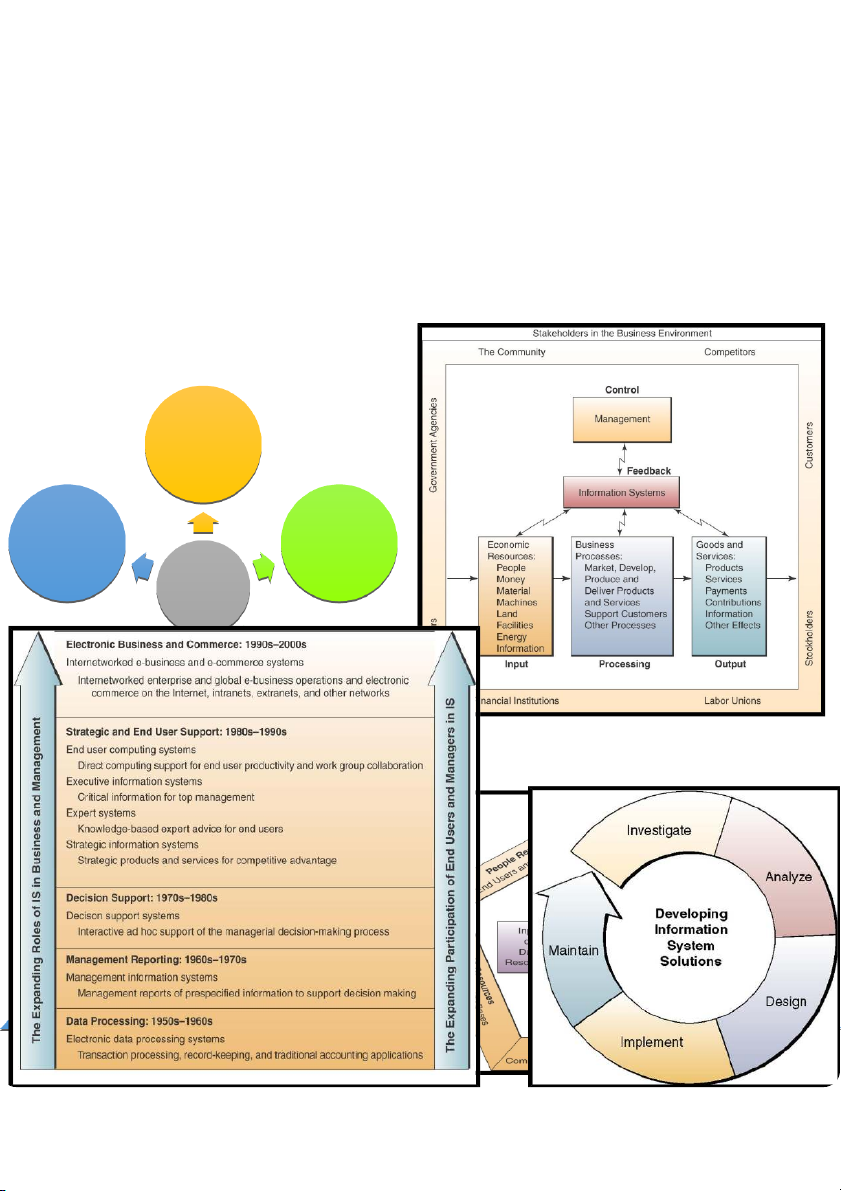
Information system: A group of interrelated or interacting elements forming a unified whole, or a
group of interrelated components working together toward a common goal by accepting
inputs and producing outputs in an organized transformation process (dynamic system). • Activities related to IS -
Input: e.g. optical scanning of bar-code tags on goods -
Processing: e.g. calculating employees’ pay, taxes and payroll deductions -
Output: e.g. producing reports and displays about sales performance -
Storage: e.g. maintaining records on customers, employees and products -
Control: e.g. generating warning signals to indicate mistaken entries of data Components of an IS People Software Hardware IS resources Trends in Information Systems ❖ How likely are Customer customers, relationship Can the risk business management and cost be partners or How likely are mitigated by: ❖ Human competitors to legal actions, resources be affected by: consumer ⬧ Self – management boycotts, work regulation ⬧ stoppages, ❖ Business Infringements ⬧ Advocacy government Intelligence on privacy intervention ⬧ Education Systems ⬧ Inaccurate and other ⬧ Codes of ❖ Electronic information threats to ethics Commerce ⬧ Collusion occur? ⬧ Incentives Systems ⬧ Exclusion ⬧ Certification from business resources Information Systems Management Operations Support Others Support System Systems Transaction Management Processing Information Expert Systems Systems Systems Decision Knowledge Process Control Support Management Systems Systems Systems Enterprise Executive Strategic Collaboration Information Information Systems Systems Systems Information system resources •
People resources, e.g. specialists, users,... •
Hardware resources, e.g. machines, media,... •
Software resources, e.g. programs, procedures,... •
Data resources, e.g. product descriptions, customer records, employee files, inventory,... •
Network resources, e.g. communication media and processors, network access,...
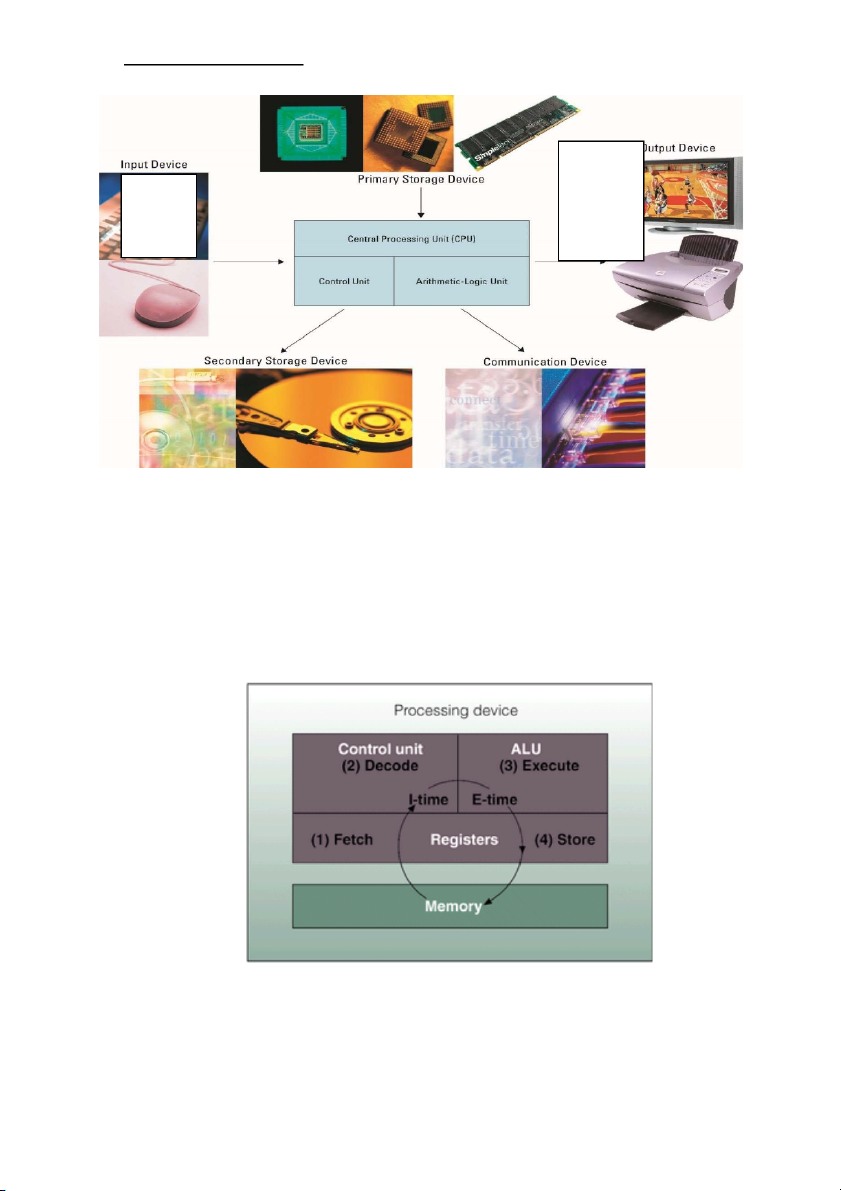
Chap 2: Computer hardware Convert electronic Convert information data into into human- electronic intelligible form form
● Central processing unit (CPU) (or microprocessor) - the actual hardware that interprets and
executes the program (software) instructions and coordinates how all the other hardware devices work together Control unit: in
terprets software instructions and literally tells the other hardware
devices what to do, based on the software instructions
Arithmetic-logic unit (ALU) - performs all arithmetic operations (for example,
addition and subtraction) and all logic operations (such as sorting and comparing numbers) •
Primary storage - the computer’s main memory, which consists of the random access memory
(RAM), cache memory, and the read-only memory (ROM) that is directly accessible to the CPU •
Random access memory (RAM) - the computer’s primary working memory, in which program
instructions and data are stored so that they can be accessed directly by the CPU via the
processor’s high-speed external data bus
• Volatility : do not retain its contents when the power is switched off
• Save work frequently Semiconductor memory •
Microelectronic semiconductor memory chips • Used for primary storage • Advantage: • Small size • Fast
• Shock and temperature resistance • Disadvantage:
• Volatility: must have uninterrupted electric power or lose memory • Cache memory
• small unit of ultra-fast memory
• Used to store recently accessed or frequently accessed data � CPU does not have to
retrieve this data from slower memory such as RAM. • ROM: read only memory
• The portion of a computer’s primary storage that does not lose its contents when one
switches off the power � Permanent storage
• Can be read but cannot be overwritten
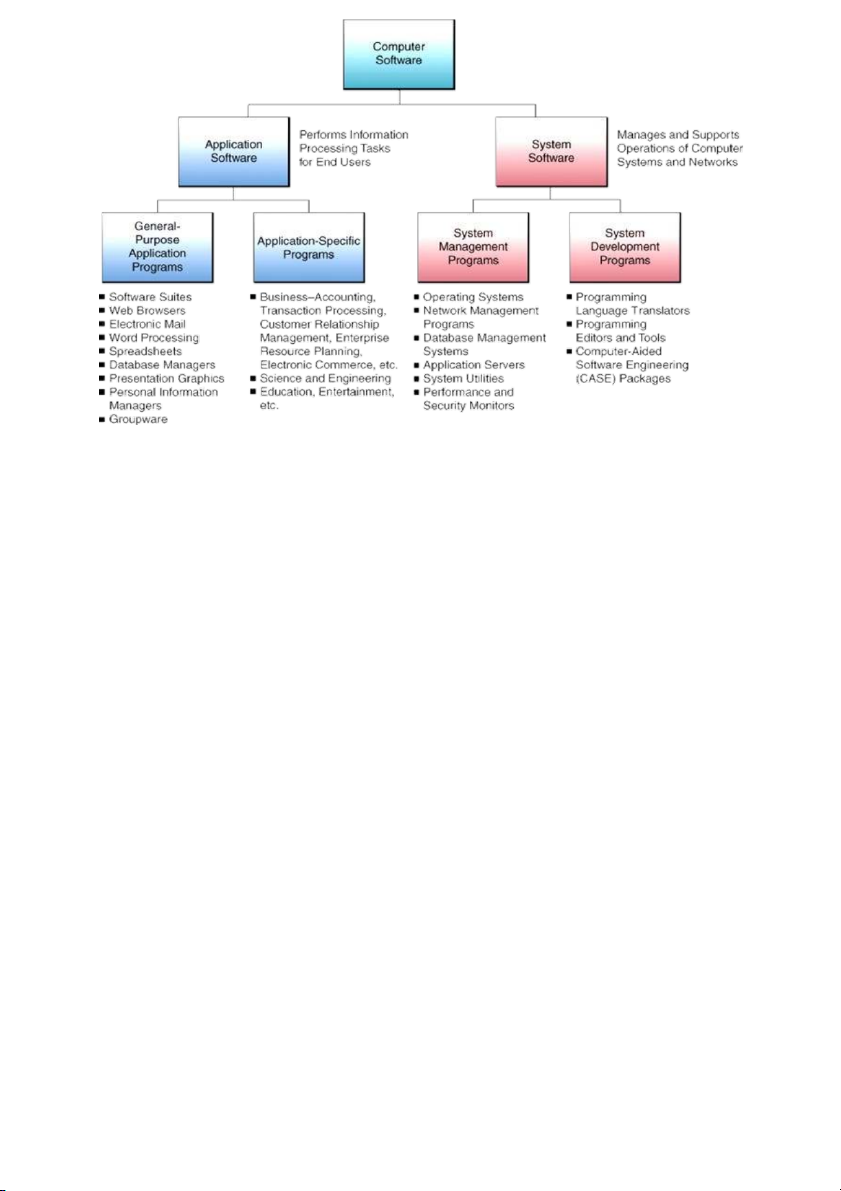
• Store start-up program : frequently used programs burnt into chips during manufacturing (Called firmware) Chap 3: Software •
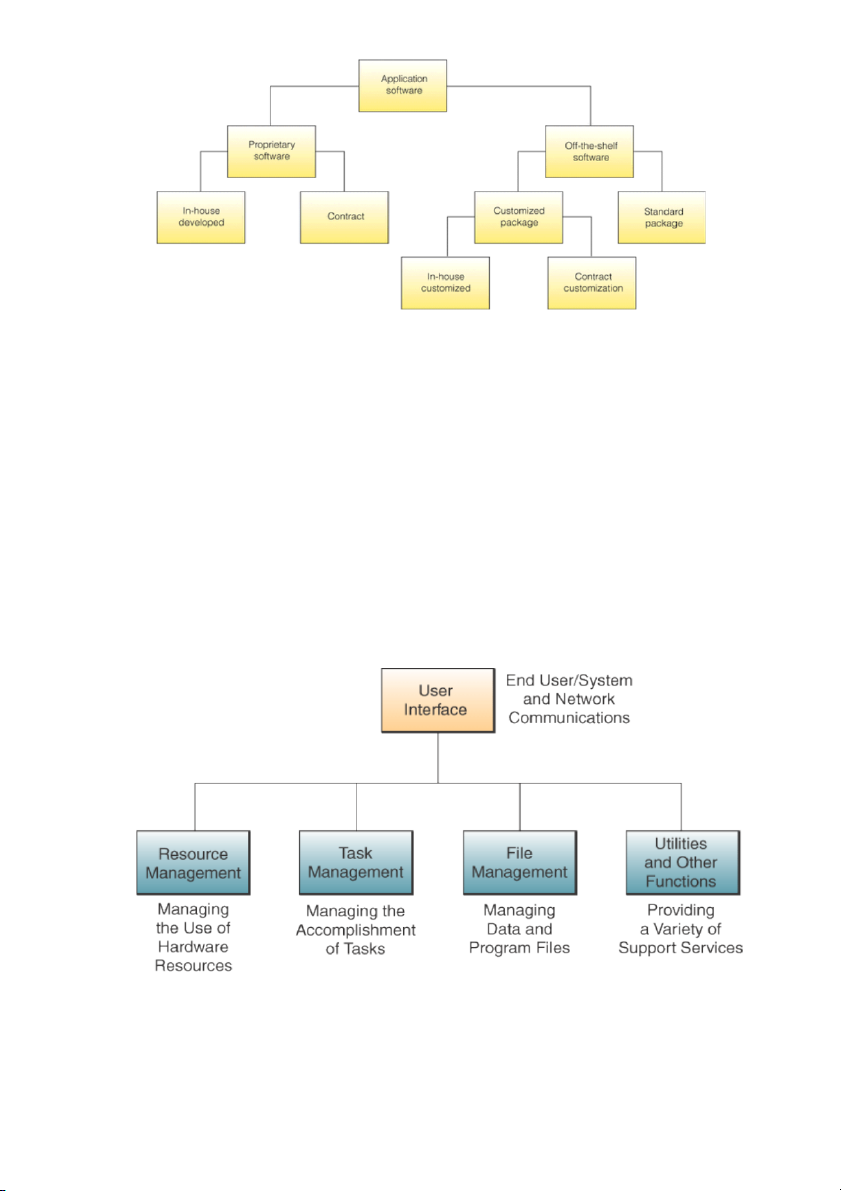
Classify based on how it was developed -
Custom software: Software applications that are developed within an organization for use by that organization -
COTS software (Commercial Off-the-shelf (COTS)): Software developed with the intention
of selling the software in multiple copies •
Software suites integrate software packages Advantages:
Cost less than buying individual packages All have a similar GUI Work together well Disadvantages Features not used by all users Take a lot of disk space • Integrated packages
Combine the functions of several programs into one package
E.g., Microsoft Works, AppleWorks Advantages:
Many functions for lower price and smaller disk space Disadvantage Limited functionality ● System softwares -
Software that manages and supports a computer system - System management programs
+ Programs that manage hardware, software, network, and data resources
+ E.g., operating systems, network management programs, database management systems, systems utilities - Systems development programs
+ Programs that help users develop information system programs ● Operating system -
Integrated system of programs that
+ Manages the operations of the CPU
+ Controls the input/output and storage resources and activities of the computer system
+ Provides support services as computer executes applications programs Resource management •
Part of operating system that manages the hardware and networking resources of a computer system
Includes CPU, memory, secondary storage device, telecommunications, and input/output peripherals • Virtual memory
Swapping parts of programs and data between memory and magnetic disks
File management: Part of the operating system that controls the creation, deletion, and access of files of data and programs
Task Management: Part of the operating system that manages the accomplishment of computing tasks of the end users
Machine Languages: First-generation languages. All program instructions had to be written using binary
codes unique to each computer. Programmers had to know the internal operations of the specific type of CPU
Assembler Languages: Second-generation languages. Symbols are used to represent operation codes and
storage locations. Need language translator programs to convert the instructions into machine
instructions. Used by systems programmers (who program system software)
High-Level Languages: Third-generation languages. Instructions that use brief statements or arithmetic
expressions. Macroinstructions: each statement generates several machine instructions when translated by
compilers or interpreters; easier to learn than assembler; machine independent, less efficient than assembler
Fourth-Generation Languages: Variety of programming languages that are nonprocedural and conversational -
Nonprocedural – users specify results they want while computer determines the sequence of
instructions that will accomplish those results -
Natural Language – very close to English or other human language
Object-Oriented Languages: Most widely used software development languages today (Visual Basic, C++, Java…) -
Easier to use and more efficient for graphics-oriented user interfaces -
Reusable: can use an object from one application in another application
Chap 4: E-commerce: � Business-to-consumer
Example: Bookstore selling books to customers (amazon.com)
Annual online spending in 2002 was $85 billion � Business-to-business
Example: A data processing company handling data services for a company (adp.com) $5.3 trillion impact by 2005 � Consumer-to-consumer
Example: A customer selling goods to another customer (ebay.com) Advantages: - Cut transaction costs -
Speed flow of goods and information - Improve customer service -
Coordinate manufacturers, suppliers, and customers
Conversion to e-commerce supply chain management provides businesses with an opportunity to: -
Increase revenues or decrease costs by eliminating time-consuming and labor-intensive steps
throughout the order and delivery process -
Improve customer satisfaction by enabling customers to view detailed information about
delivery dates and order status -
Reduce inventory including raw materials, safety stocks, and finished goods -
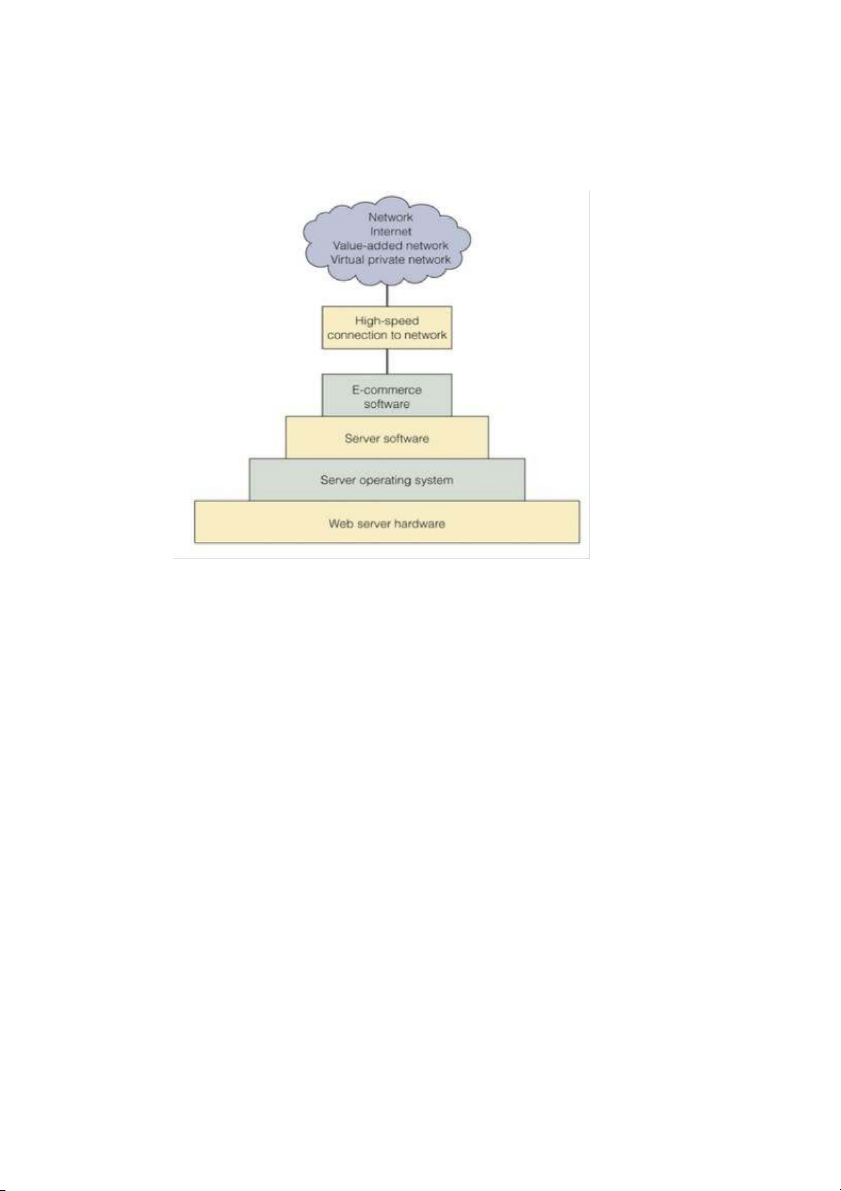
Hardware: The amount of storage capacity and computing power required of the Web server depends primarily on two things:
the software that must run on the server
the volume of e-commerce transactions that must be processed Software � Web server software Apache Server
Microsoft Internet Information Server � Web site development tools FrontPage, NetStudio
� Web page construction software
Static Web page: Always the same information (ISE 100 Web page)
Dynamic Web page: Content created based on demand (Google search results) � Database management system SQL Server Oracle � E-commerce software Catalog software Product configuration software Electronic shopping cart
Catalog Management Software: Combines product data formats into a standard format creates a central
repository of product data; catalog resides on a database
Product Configuration Software: Allow buyers to build the products they want to buy
Electronic Shopping Cart: Track items selected for purchase, let buyers modify their choices (add or
delete items); let buyers “checkout” (begins a purchase transaction) => Wish list
Electronic Payment Systems: Electronic cash, Electronic wallets; Credit, charge, debit, and smart cards
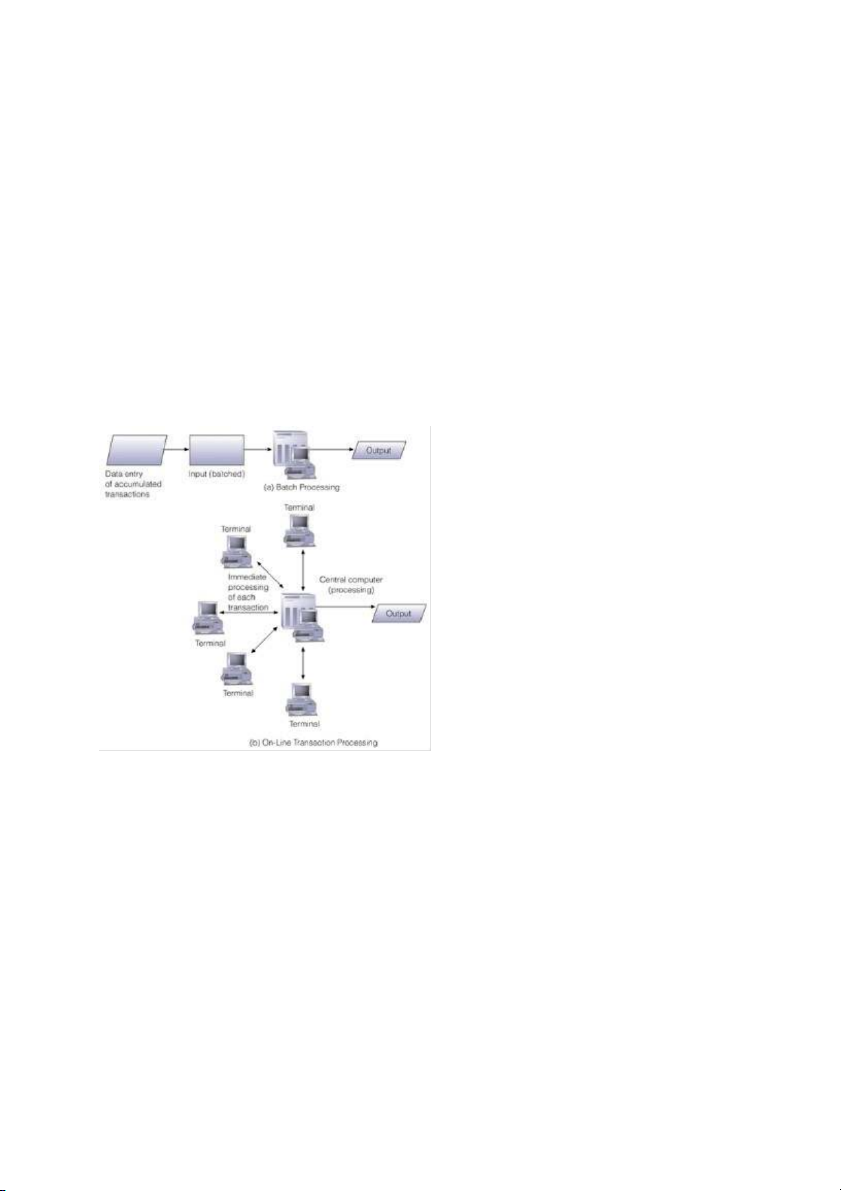
Traditional Transaction Processing Methods
� Batch processing – method of computerized processing in which business transactions are
accumulated over a period of time and prepared for processing as a single unit
� On-line transaction processing (OLTP) - method of computerized processing in which each
transaction is processed immediately and the affected records are updated
Transactions activities: consist of all the components of a CBIS, including databases,
telecommunications, people, procedures, software, and hardware devices to process transactions. -
Data collection: Capturing data necessary for the transaction -
Data editing: Check validity and completeness
Ex: 400 hours/week instead of 40 hours/week -
Data correction: Correct the wrong data -
Data manipulation: Calculate, summarize -
Data storage: Update transactions -
Document production and reports: Create end results (paychecks)




