
Preview text:
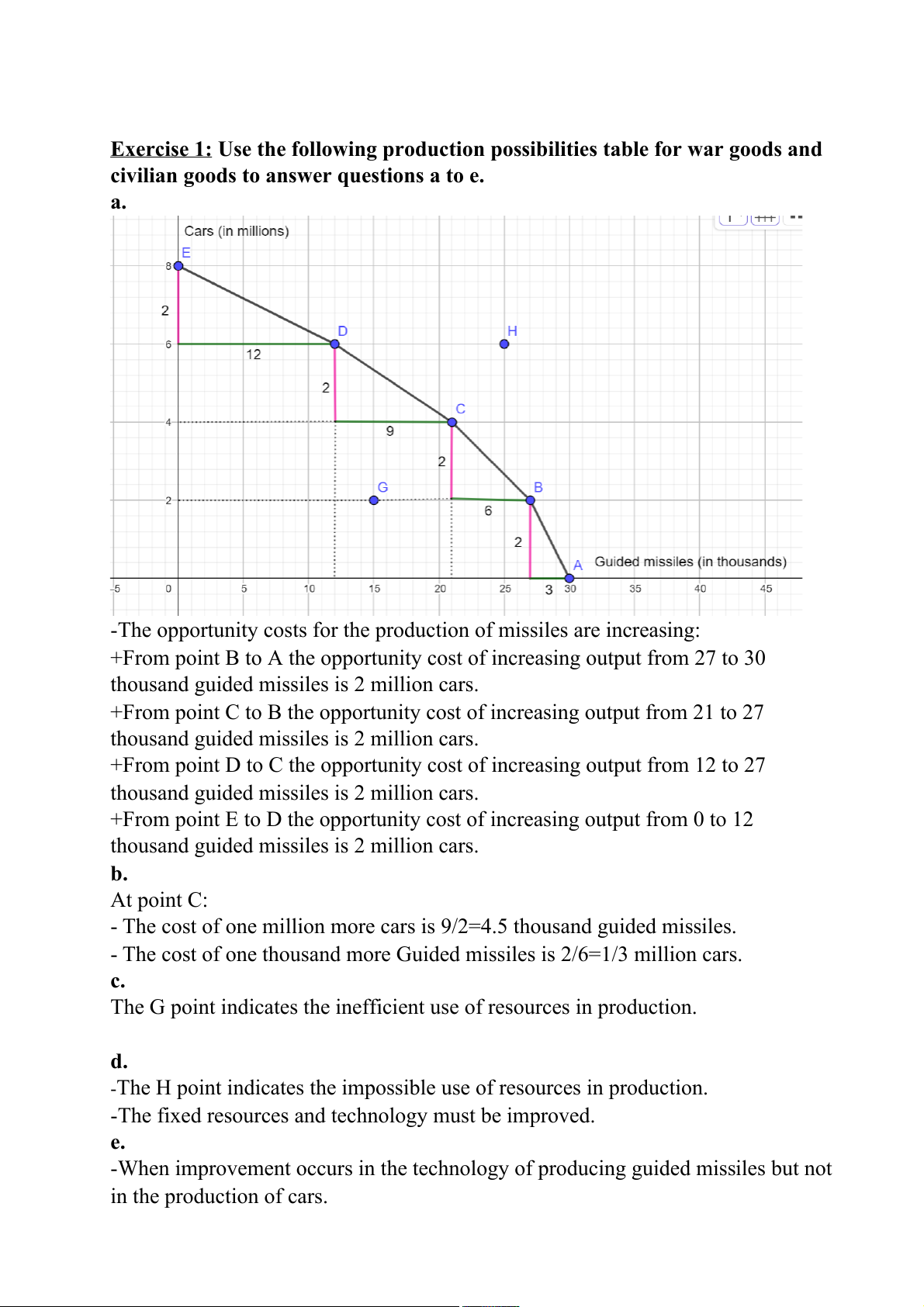
Exercise 1: Use the following production possibilities table for war goods and
civilian goods to answer questions a to e. a.
-The opportunity costs for the production of missiles are increasing:
+From point B to A the opportunity cost of increasing output from 27 to 30
thousand guided missiles is 2 million cars.
+From point C to B the opportunity cost of increasing output from 21 to 27
thousand guided missiles is 2 million cars.
+From point D to C the opportunity cost of increasing output from 12 to 27
thousand guided missiles is 2 million cars.
+From point E to D the opportunity cost of increasing output from 0 to 12
thousand guided missiles is 2 million cars. b. At point C:
- The cost of one million more cars is 9/2=4.5 thousand guided missiles.
- The cost of one thousand more Guided missiles is 2/6=1/3 million cars. c.
The G point indicates the inefficient use of resources in production. d.
-The H point indicates the impossible use of resources in production.
-The fixed resources and technology must be improved. e.
-When improvement occurs in the technology of producing guided missiles but not in the production of cars.
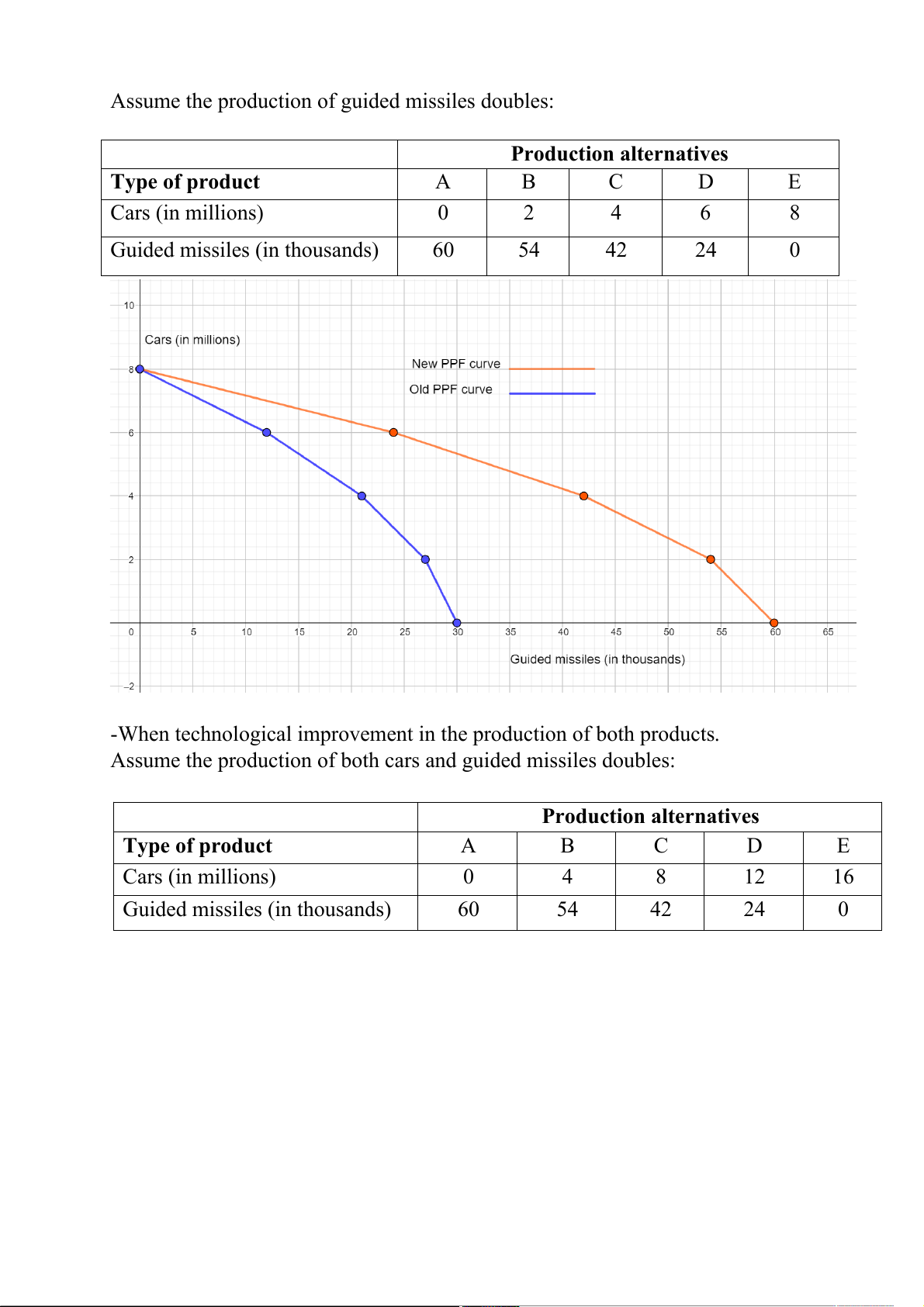
Assume the production of guided missiles doubles: Production alternatives Type of product A B C D E Cars (in millions) 0 2 4 6 8 Guided missiles (in thousands) 60 54 42 24 0
-When technological improvement in the production of both products.
Assume the production of both cars and guided missiles doubles: Production alternatives Type of product A B C D E Cars (in millions) 0 4 8 12 16 Guided missiles (in thousands) 60 54 42 24 0
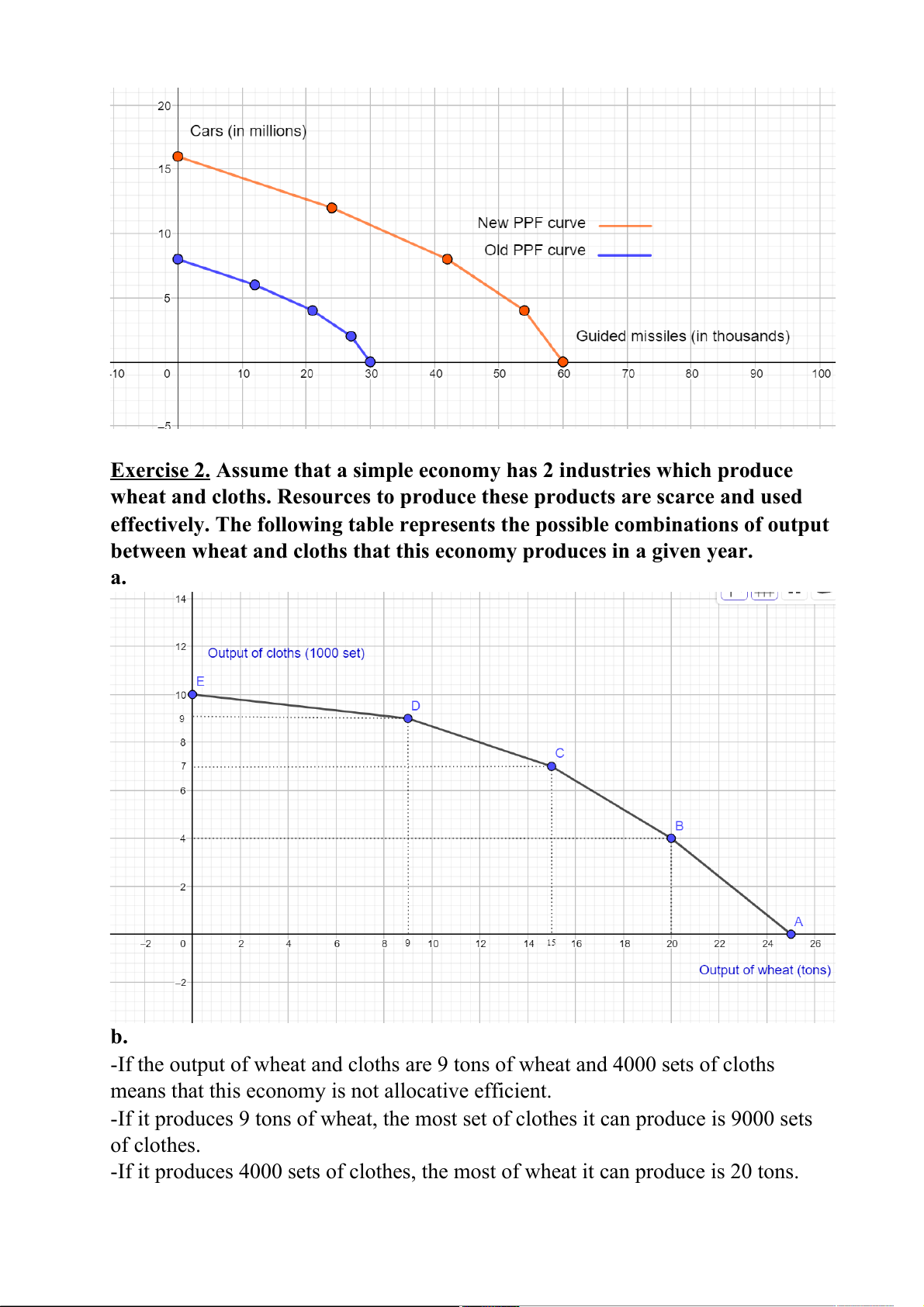
Exercise 2. Assume that a simple economy has 2 industries which produce
wheat and cloths. Resources to produce these products are scarce and used
effectively. The following table represents the possible combinations of output
between wheat and cloths that this economy produces in a given year. a. b.
-If the output of wheat and cloths are 9 tons of wheat and 4000 sets of cloths
means that this economy is not allocative efficient.
-If it produces 9 tons of wheat, the most set of clothes it can produce is 9000 sets of clothes.
-If it produces 4000 sets of clothes, the most of wheat it can produce is 20 tons.
So when there are 9 tons of wheat and 4000 sets of cloths, the company is wasting resources. c.
-This economy can not produce 20 tons of wheat and 10000 sets of cloths.
-If it produces 20 tons of wheat, it can only produce 4000 sets of cloths.
-If it produces 10000 sets of cloths, it can not produce any ton of wheat. d.
-Opportunity costs of producing cloths:
+ AB: The opportunity cost of producing 4 thousand set of cloths is 5 tons of wheat.
+ BC: The opportunity cost of producing 3 thousand sets of cloths is 5 tons of wheat.
+ CD: The opportunity cost of producing 2 thousand sets of cloths is 6 tons of wheat.
+ DE: The opportunity cost of producing 1 thousand sets of cloths is 9 tons of wheat.
- Opportunity costs of producing wheat:
+ ED: The opportunity cost of producing 9 tons of wheat is 1 thousand sets of cloths.
+ DC: The opportunity cost of producing 6 tons of wheat is 2 thousand sets of cloths.
+ CB: The opportunity cost of producing 5 tons of wheat is 3 thousand sets of cloths.
+ BA: The opportunity cost of producing 5 tons of wheat is 4 thousand sets of cloths.




