Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 49153326 REVISION CONTENT
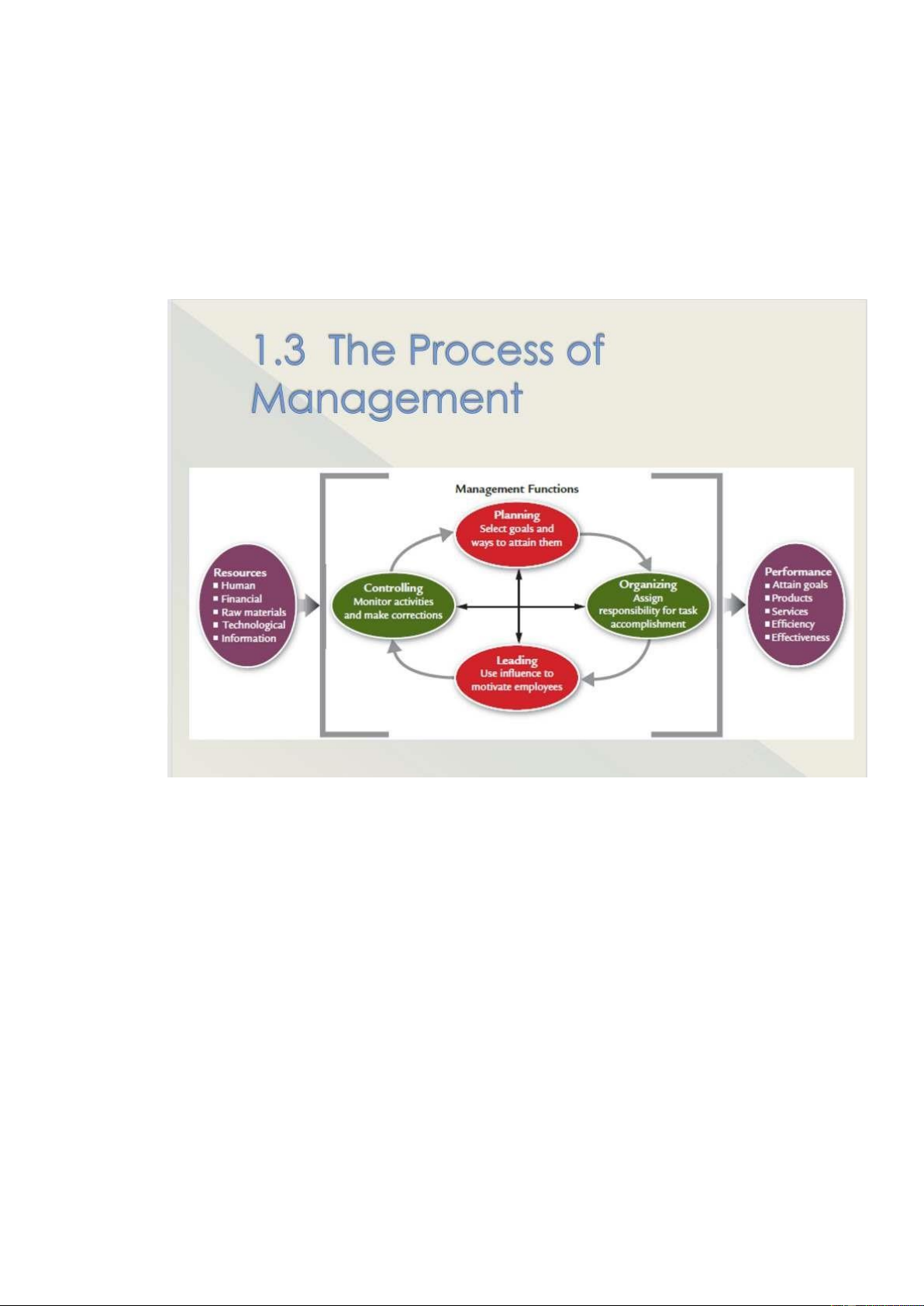
Chapter 1: Innovative Management for a Changing World 1. Definiton of management: -
Management is the attainment of organizational goals in an effective and efÏcient manner
through planning, organizing, leading and controlling organizational resources. -
Managers get things done by coordinating and motivating other people. 2. The Process of management: 3. Management Skills: -
There are three categories of skills:
+ Conceptual skills: Manager’s ability to see the organization as a whole system and the
relationships among its parts (think strategically to identify, evaluate, and solve complex problems)
+ Human skills: Manager’s ability to work with and through other people and to work
effectively as a group member (motivate, facilitate, coordinate, lead, communicate and resolve conflicts)
+ Technical skills: Manager’s ability to demonstrate understanding and proficiency in the
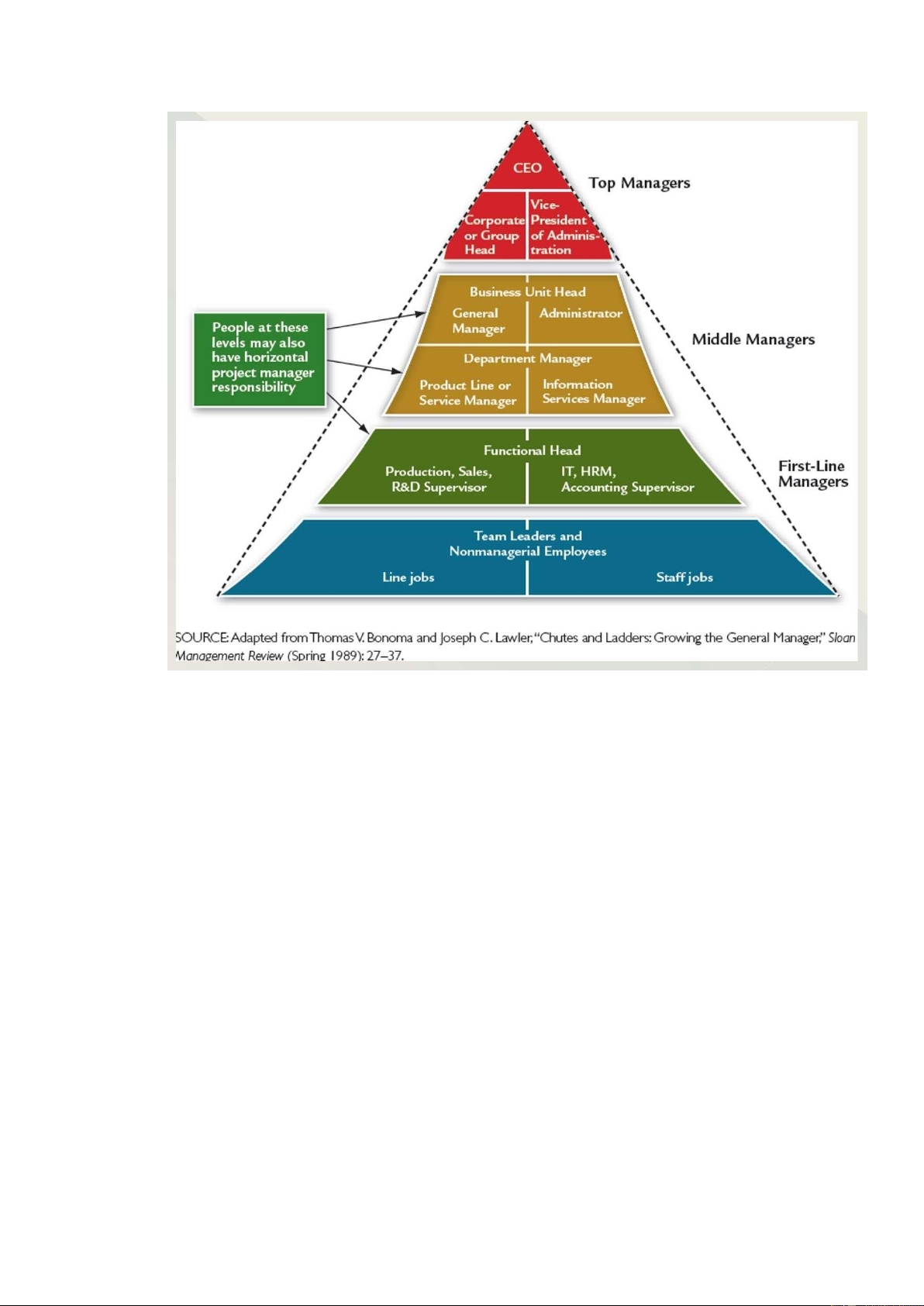
performance of specific tasks (mastery of the methods, techniques, and equipment involved in specific functions). 4. Management Levels: lOMoARcPSD| 49153326 - Chiều dọc: -
Top managers are at the top of the hierarchy and are responsible for the entire organization -
Middle managers work at middle levels of the organization and are responsible for business units and major departments -
First-line managers are directly responsible for the production of goods and services - Chiều ngang: -
Functional managers are responsible for departments that perform a single functional task
and have employees with similar training and skills -
General managers are responsible for several departments that perform different functions 5. Manager Roles: -
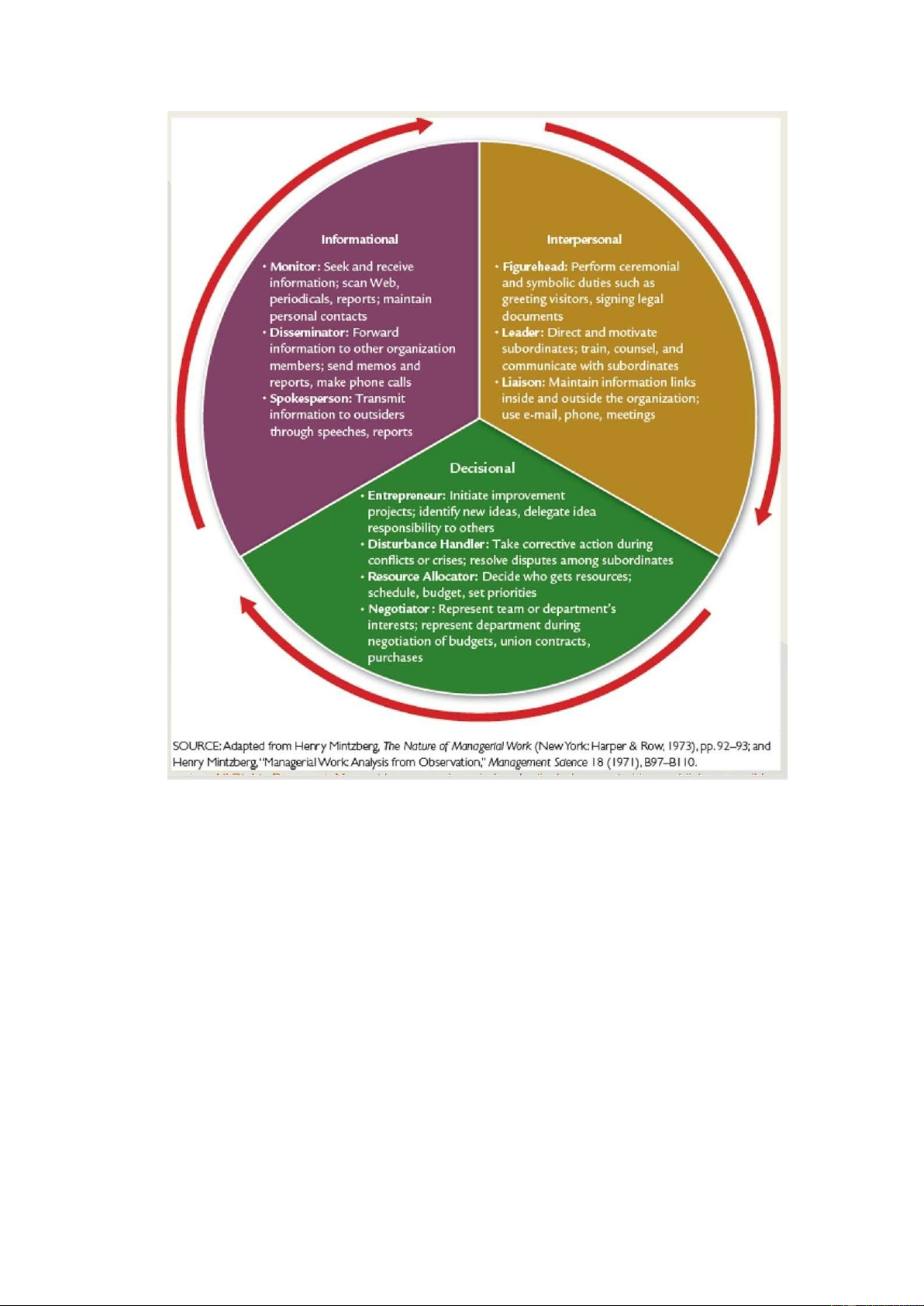
Information roles describe the activities used to maintain and develop an information network. -
Interpersonal roles pertain to relationships with others and are related to the human skills. -
Decisional roles pertain to those events about which the manager must take a choice and take action. - Ten manager roles: lOMoARcPSD| 49153326
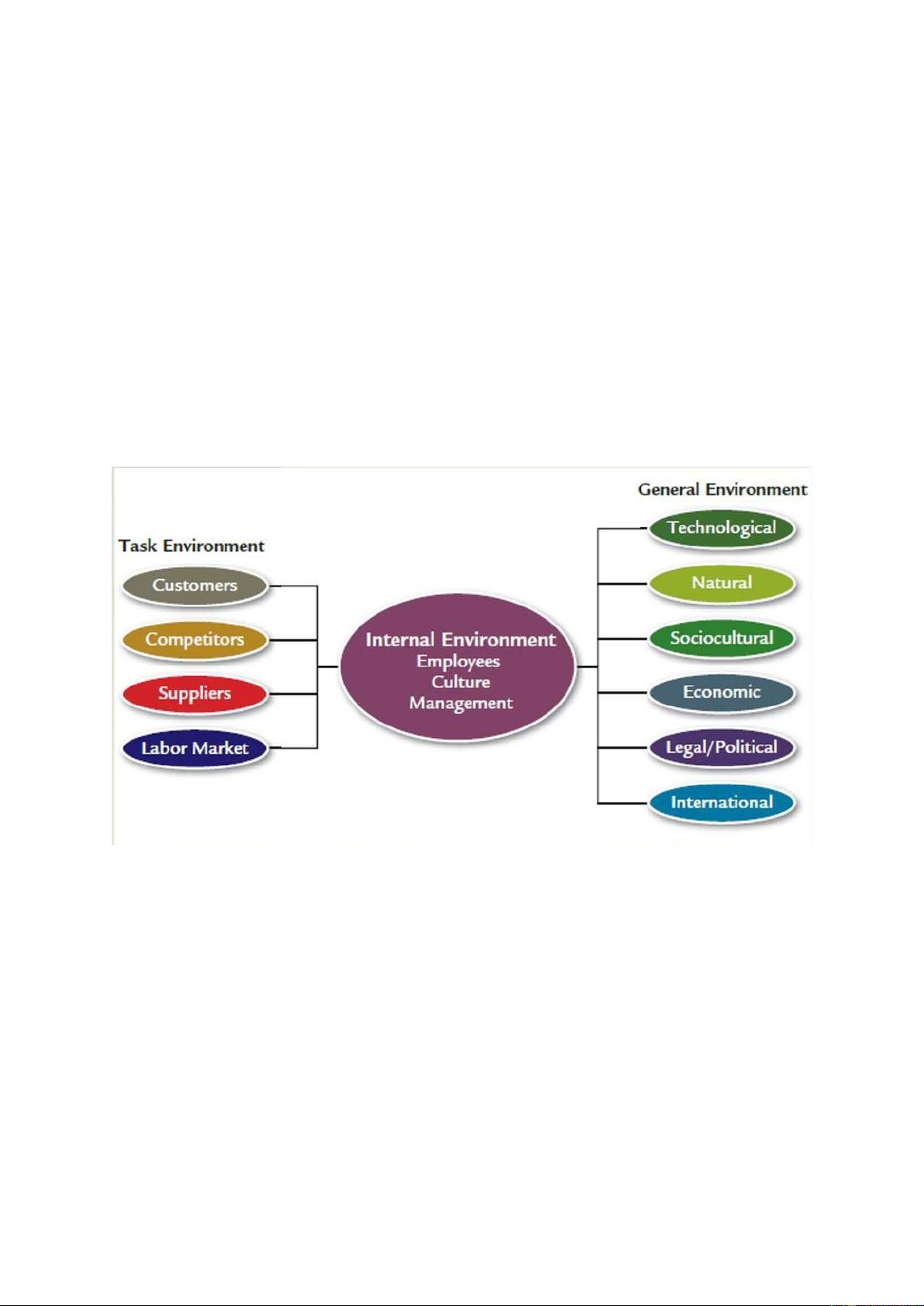
Chapter 3: The environment and corporate culture 1. General Environment: -
General environment affects organizations indirectly:
+ International dimension: Includes events originating in foreign countries
+ Technological dimension: Includes scientific and technological advancements in a specific
industry, as well as in society at large
+ Sociocultural dimension of the general environment represents the demographic
characteristics, norms, customs, and values of the general population.
+ Economic dimension represents the general economic health of the country or region in
which the organization operates – GDP, inflation rate, unemployment rates, exchange
rate,… + Legal-political dimension includes government regulations at the local, state and
federal levels, as well as political activities designed to influence company behavior
+ Natural dimension includes all elements that occur naturally on Earth, including plants,
animals, rocks and resources (air, water and climate,…)
+ Natural dimension: Does not have our voice, growing importance and pressure,… lOMoARcPSD| 49153326 2. Task Environments: -
Task environment is closer to the organization and includes the sectors that conduct day-
today transactions with the organization and directly influence its basic operations and performance.
+ Customers: People and organizations in the environment that acquire goods or services from the organization
+ Competitors: Organizations in the same industry or type of business that provide goods or
services to the same set of customers
+ Suppliers provide the raw materials that the organization uses to produce its output
+ Labor market represents people in the environment who can be hired to work for the organization 3. Internal Environment: - Employees - Culture - Management
4. Strategies to adapt to the environment -
Boundary – spanning roles – link and coordinate the organization with
external environment, seek: + Business intelligence + Big Data analytics -
Interorganizational partnerships – reduce boundaries and begin collaborating with other organizations -
Mergers – occurs when two or more organizations combine to become one -
Joint ventures – strategic alliance or program by two or more organizations 5. Corporate culture: -
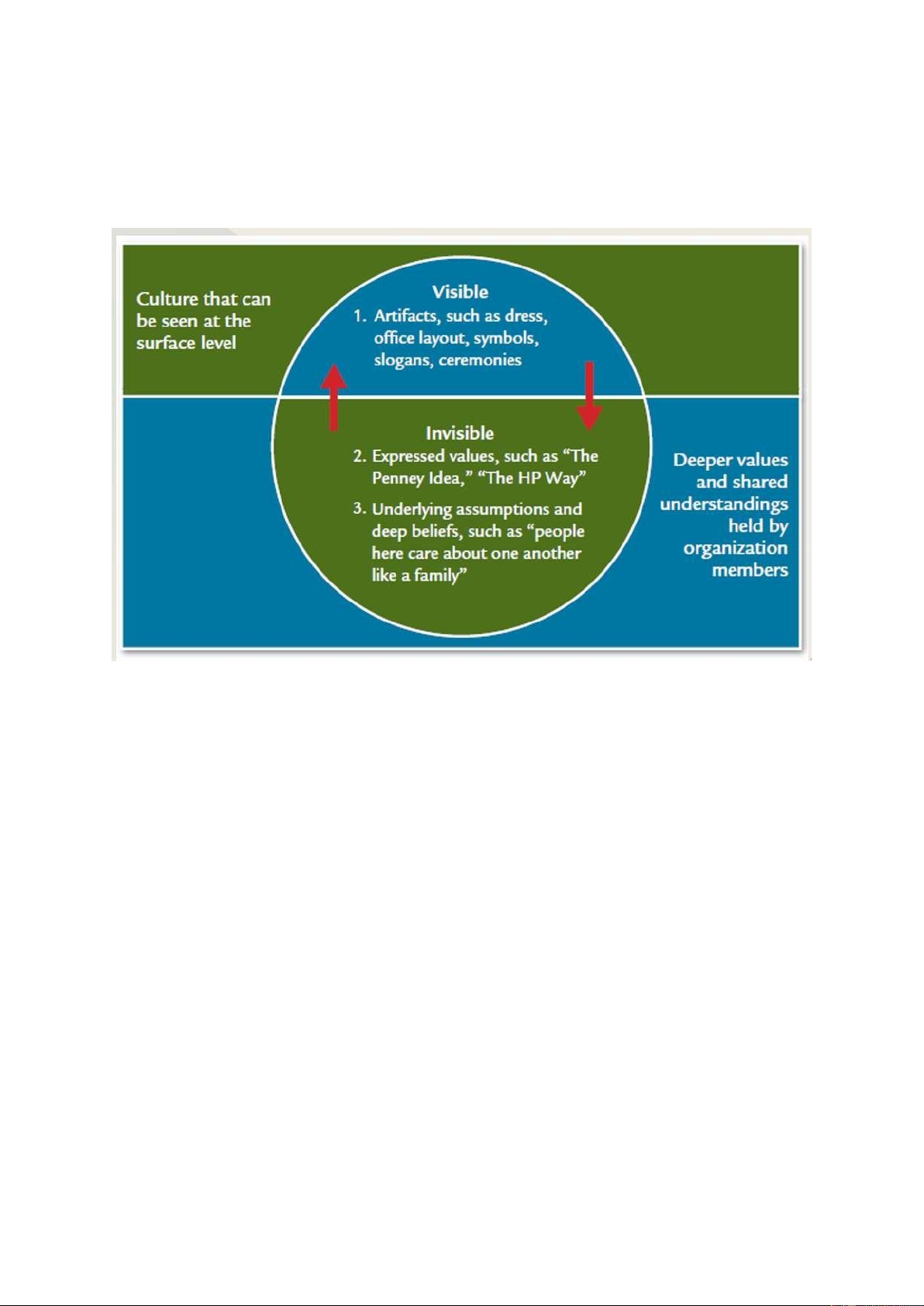
Corporate culture is the set of key values, beliefs, understandings, and norms that members of an organization share + Symbols + Stories lOMoARcPSD| 49153326 + Heroes + Slogans + Ceremonies - Levels of Corporate Culture:
Chapter 4: Managerial Planning and Goal SetÝng
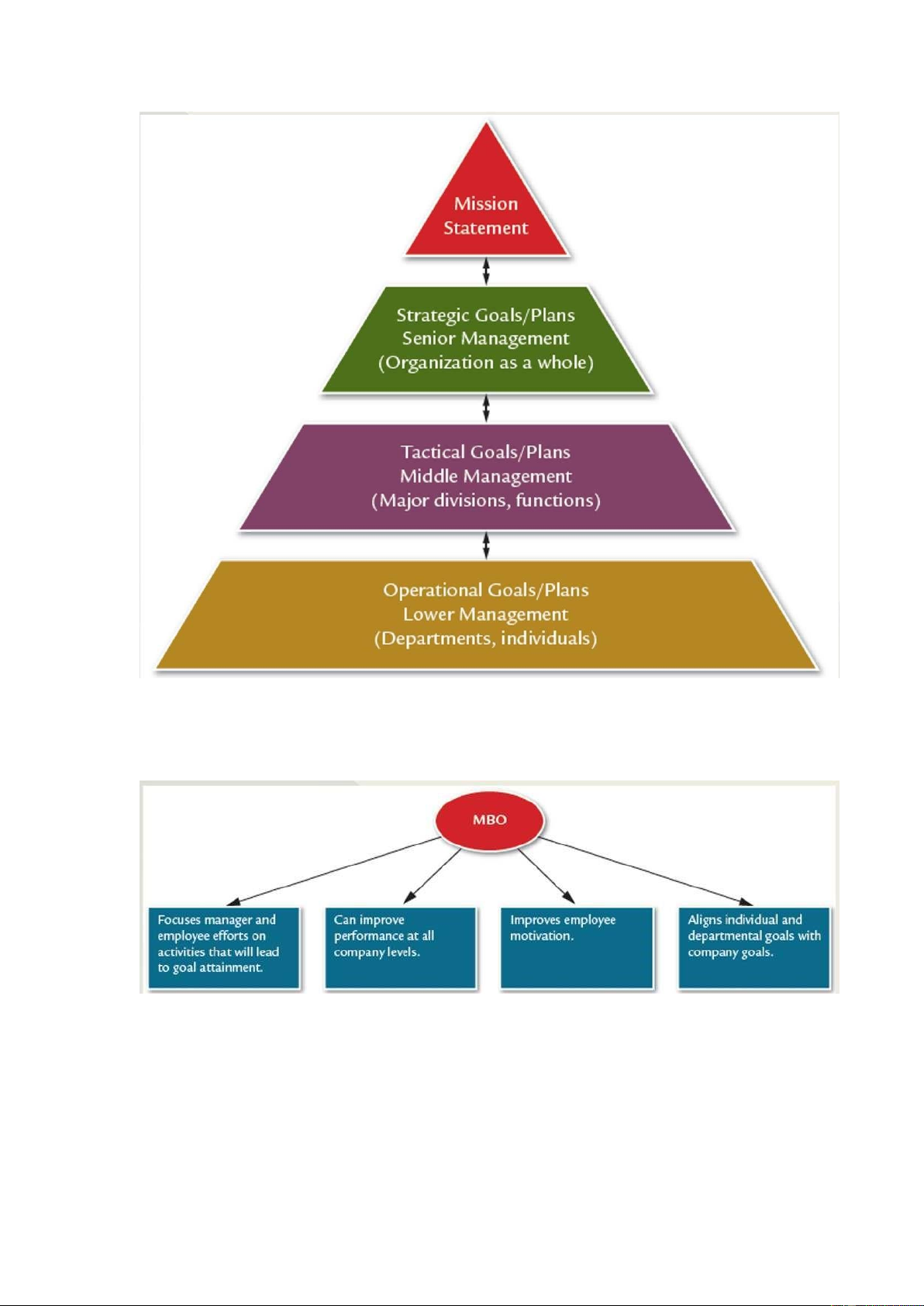
1. Definition of goal and plan -
A goal is a desire future state that the organization attempts to realize -
A plan is a blueprint for goal achievement and specifies the necessary resource, allocations,
schedules, tasks and other actions. =)) PLANNING 2. Levels of goals and plans lOMoARcPSD| 49153326 lOMoARcPSD| 49153326
3. MBO, Singles and Standing Plans - MBO Benefits - Single – Use Plans + Achieve one-time goals + Program and project - Standing Plans + Ongoing plans + Policies, rules, procedures




