

Preview text:
Seminar 7: Question
Type I: True/False question (give a brief explanation)
1. Even with market power, monopolists cannot achieve any level of profit they desire
because they will sell lower quantities at higher prices.
Thậm chí với sức mạnh thị trường, nhà độc quyền cũng không có khả năng tăng lợi ích bao
nhiêu xũng được vì họ sẽ bán được số sản lượng thấp hơn ở mức giá cao hơn.
2. Copyrights and patents are examples of barriers to entry that afford firms monopoly pricing powers.
Bản quyền phát minh và sáng chế là ví dụ về các rào cản gia nhập thị trường của các hãng mới.
3. Like competitive firms, monopolies choose to produce a quantity in which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
Giống như hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo, hãng độc quyền chọn sản xuất ở mức sản lượng tại
đó doanh thu cận biên bằng chi phí cân biên.
4. A monopolist does not have a supply curve because the firm’s decision about how
much to supply is impossible to separate from the demand curve it faces.
Hãng độc quyền không có đường cung vì…
5. A monopoly creates a deadweight loss to society because it earns both short-run and
long-run positive economic profits.
Độc quyền tạo ra phần mất không của xã hội vì nó tạo ra cả lợi nhuận trong ngắn hạn và dài hạn.
6. A monopoly creates a deadweight loss to society because it produces less output
than the socially efficient level.
Độc quyền gây ra phần mất không của xã hội vị nó sản xuất ở mức thấp hơn mức hiệu quả.
7. The government may choose to do nothing to reduce monopoly inefficiency
because the “fix” may be worse than the problem.
Chính phủ có thể lựa chọn không làm gì cả vì bất kỳ chính sách nào của chính phủ đều có
thể làm vấn đề tồi tệ hơn.
8. The amount of power that a monopoly has depends on whether there are close substitutes for its product.
Sức mạnh thị trường mà nhà độc quyền có được là phụ thuộc vào số lượng hàng hóa thay thế trên thị trường.
9. Government intervention always reduces monopoly deadweight loss.
Sự can thiệp của chính phủ luôn làm giảm phần mất không.
Type II: Discussion questions S
1. In the market for "home heating" consumers typically have several options (e.g.,
electricity, heating fuel, natural gas, propane, etc.), yet we often think of firms in
this industry as behaving like monopolists. Discuss the context in which your
electricity provider is a monopolist. Is this characterization universally applicable? Explain your answer.
2. Explain how a profit-maximizing monopolist chooses its level of output and the price of its goods.
3. Graphically depict the deadweight loss caused by a monopoly. How is this similar
to the deadweight loss from taxation?
Vẽ đồ thị mô tả phần mất không gây ra bởi nhà độc quyền. Phần mất không này có giống
như phần được tạo ra bởi thuế hay không?
4. What is the deadweight loss due to profit-maximizing monopoly pricing under the
following conditions: The price charged for goods produced is $10. The intersection
of the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves occurs where output is 100 units
and marginal revenue is $5. The socially efficient level of production is 110 units.
The demand curve is linear and downward sloping, and the marginal cost curve is constant.
5. What are the four ways that government policymakers can respond to the problem of monopoly?.
Ans: First, the government can try to make monopolized industries more competitive by
using the power of antitrust laws. Second, the government can regulating the behavior of
monopolies, which usually occurs with natural monopolies. Third, the government can own and run
a monopoly. Four, the government can do nothing.
6. In many countries, the government chooses to "internalize" the monopoly by
owning monopoly providers of goods and services. (In some cases these firms are
"nationalized," and the government actually buys or confiscates firms that operate in
monopoly markets). What would be the advantages and disadvantages of such an
approach to ensure that the "best interest of society" is promoted in these markets? Explain your answer.
Ans: As long as the government "owner" pursues a production and pricing policy that
approaches a competitive outcome, social well-being can be enhanced. In this case the government
ownership would benefit society. However, in most cases, government owners operate much like
private sector monopolists. The political economy of government institutions does not ensure that
government owners will pursue socially optimal policy. Also, governments have no incentive to reduce costs or innovate.
7. Trong các loại hình sản xuất dưới đâ, loại hình nào có khả năng độc quyền nhất? Cung
cấp các lý do để giải thích.
a. Nhà cung cấp dịch vụ điện thoại đường dài
b. Dịch vụ truyền hình cáp địa phương
c. Cửa hàng tiện ích lớn d. Các cây xăng
7. A monopolist has a total cost function 2
TC =0.5Q +10Q+100 , MC = Q+10 and the
demand curve P=70-Q, thus MR = 70-2Q. a. What is the fixed cost?
b. What is the marginal revenue function?
c. What are the quantity and price that the monopolist maximize its profit? Compute this profit.
d. Compute CS, PS, NSB, and the deadweight loss in this case. Draw the figure to represent it.
e. What are the quantity and price that the monopolist maximize its revenue?
Type III: Multiple Choice
1. Vì hãng độc quyền không phải cạnh tranh với các hãng khác, thị trường với độc quyền thường:
a. Không phải lựa chọn tốt nhất cho xã hội.
b. Phúc lợi xã hội thường không được tối ưu. c. Không hiệu quả.
d. Toàn bộ các kết luận trên đều không đúng.
2. Trong các loại hình sản xuất dưới đâ, loại hình nào có khả năng độc quyền nhất?
a. a long-distance telephone service provider b. a local cable TV provider c. a large department store d. a gas station
3. Which of the following statements is true of a monopoly firm?
a. A monopoly firm is a price taker and has no supply curve.
b. A monopoly firm is a price maker and has no supply curve
c. A monopoly firm is a price maker and has a downward-sloping supply curve.
d. A monopoly firm is a price maker and has an upward-sloping supply curve.
4. Which of the following statements is correct for a monopolist?
i) The firm maximizes profits by equating marginal revenue with marginal cost.
ii) The firm maximizes profits by equating price with marginal cost.
iii) Demand equals marginal revenue.
iv) Average revenue equals price. a. i), iii), and iv) only b. i) and iv) only c. i), ii), and iv) only d. i), ii), iii), and iv)
5. Which of the following statements is correct for both a monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm?
i) The firm maximizes profits by equating marginal revenue with marginal cost.
ii) The firm maximizes profits by equating price with marginal cost.
iii) Demand equals marginal revenue.
iv) Average revenue equals price. a. i), iii), and iv) only b. i) and iv) only c. i), ii), and iv) only d. i), ii), iii), and iv)
6. For a monopoly, the level of output at which marginal revenue equals zero is also the level of output at which a. average revenue is zero. b. profit is maximized. c. total revenue is maximized. d. marginal cost is zero.
7. A reduction in a monopolist's fixed costs would
a. decrease the profit-maximizing price and increase the profit-maximizing quantity produced.
b. increase the profit-maximizing price and decrease the profit-maximizing quantity produced.
c. not effect the profit-maximizing price or quantity.
d. possibly increase, decrease or not effect profit-maximizing price and quantity,
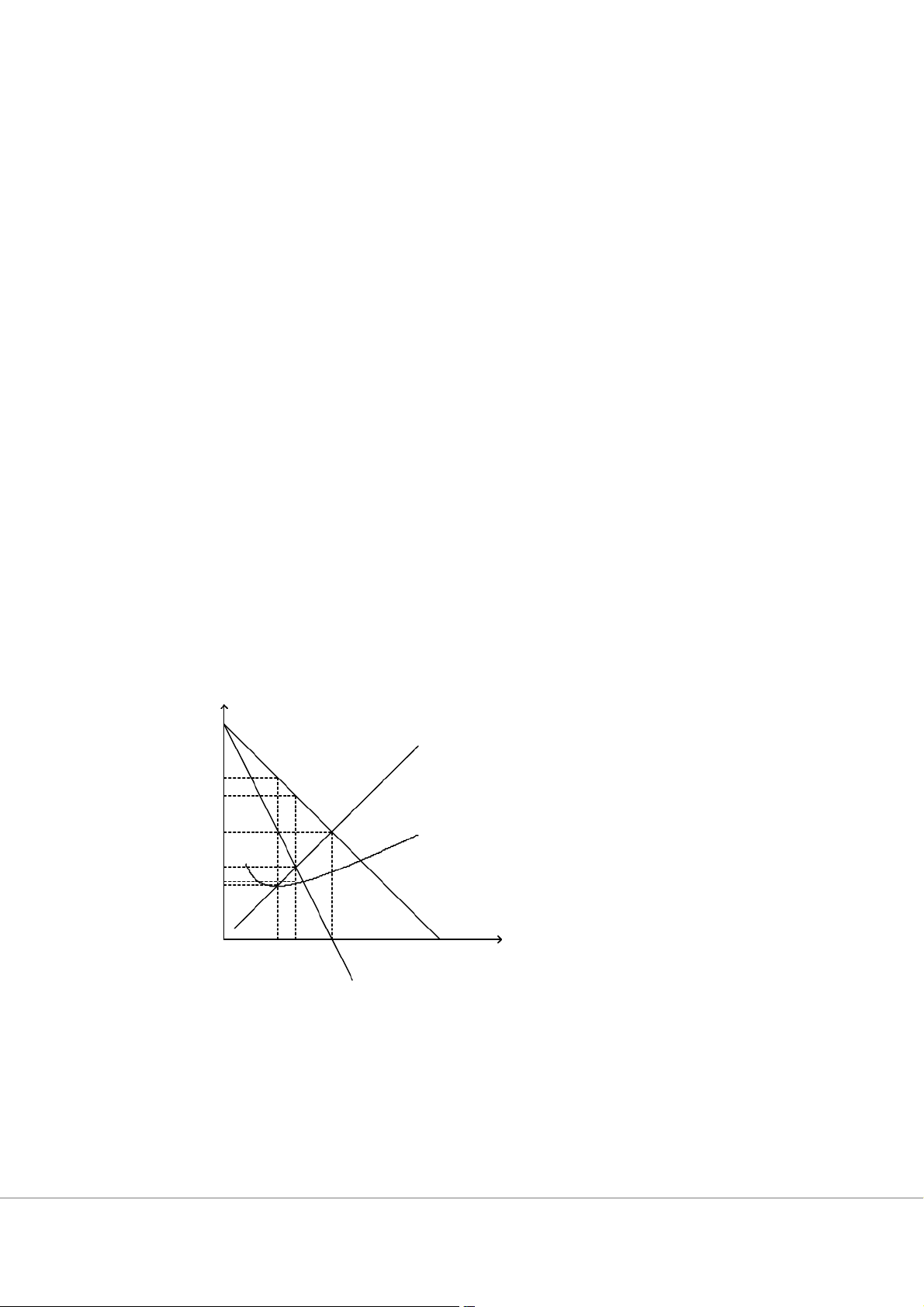
depending on the elasticity of demand. Price P M C A B C ATC F G H D O J K L Quanti ty M R Figure 7-1
8. Refer to Figure 7-1, Đâu là mức giá mà nhà độc quyền sẽ đặt? a. A b. B c. C d. F
9. Refer to Figure 7-1. Đâu là vùng không gian mô tả lợi ích của nhà độc quyền? a. (B-F)*K b. (A-H)*J c. (B-G)*K d. 0.5[(B-F)*(L-K)]
10. The deadweight loss associated with a monopoly occurs because the monopolist a. maximizes profits.
b. produces an output level less than the socially optimal level.
c. produces an output level greater than the socially optimal level.
d. equates marginal revenue with marginal cost.