



Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Steel Structures
Chapter 2 Steel connections Steel connections 1 .Introduction
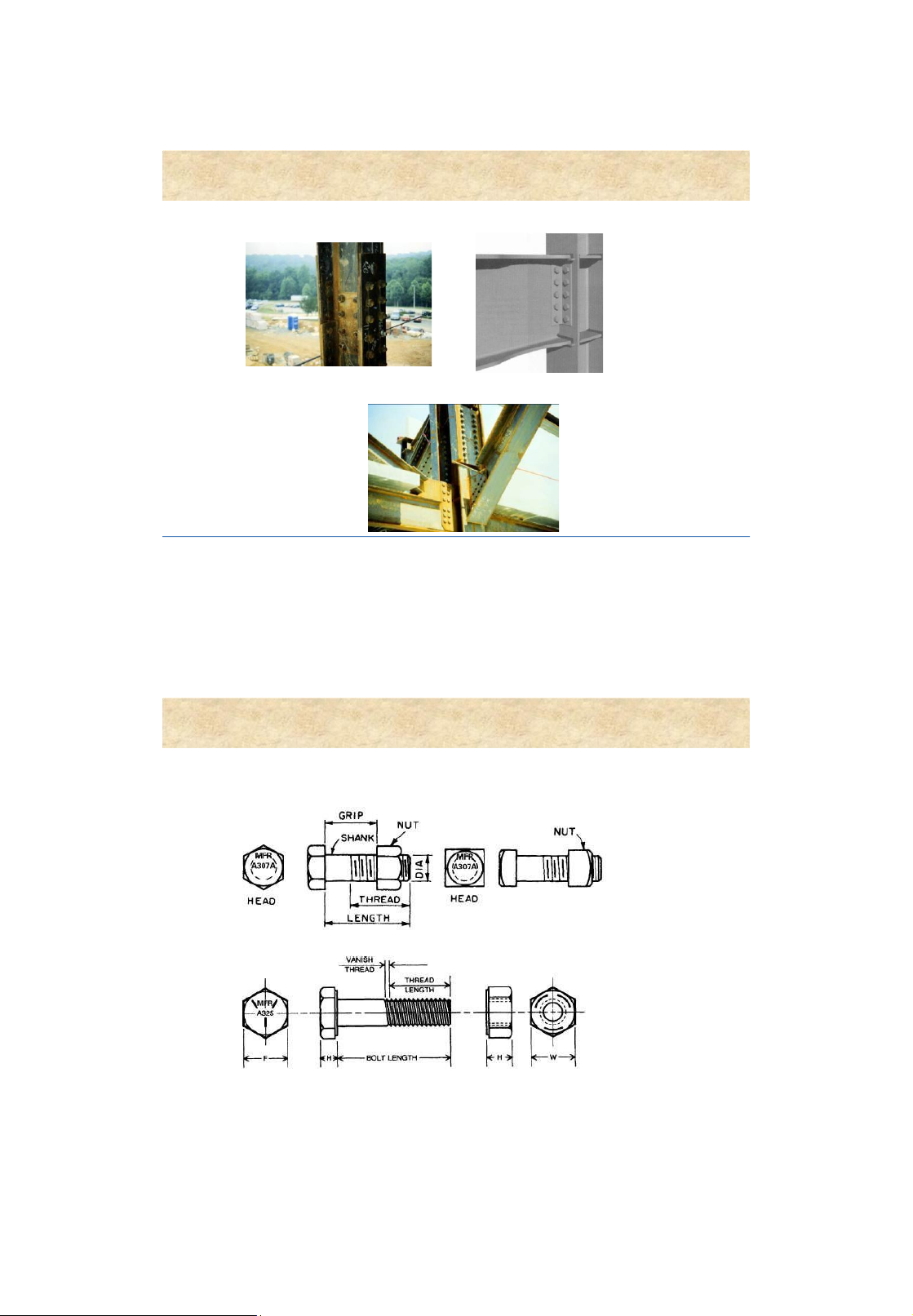
2 .Welded connections 3. Bolted connections 4. Riveted connections 2 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections 1. Introduction Framed connection Bolt column splice Gussetplate connections 3 Bolted connections 2. Bolt types Common, rough bolts High-strength bolts 4 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections 2. Bolt types Black bolts Turned bolts High-strength bolts • Ordinary, rough bolts • Close tolerance bolts • High shear • Least expensive • Expensive resistance • Primarily – light •
Primarily – light structures structures 5 Bolted connections 3. Strength of bolt material Bolt 4.6 4.8 5.6 5.8 6.6 8.8 10.9 class fvb (N/mm2) 150 16 19 20 230 32 400 0 0 0 0 ftb (N/mm2) 170 16 21 20 250 40 500 0 0 0 0 d 16 18 20 22 24 27 30 36 42 48 Bolt thread 2 2,5 2,5 2,5 3 3 3,5 4 4,5 5 step A
2,01 2,54 3,14 3,80 4,52 5,72 7,06 10,1 13,8 18,0 7 5 9 Abn
1,57 1,92 2,45 3,03 3,52 4,59 5,60 8,16 11,2 14,7 0 2 6 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections
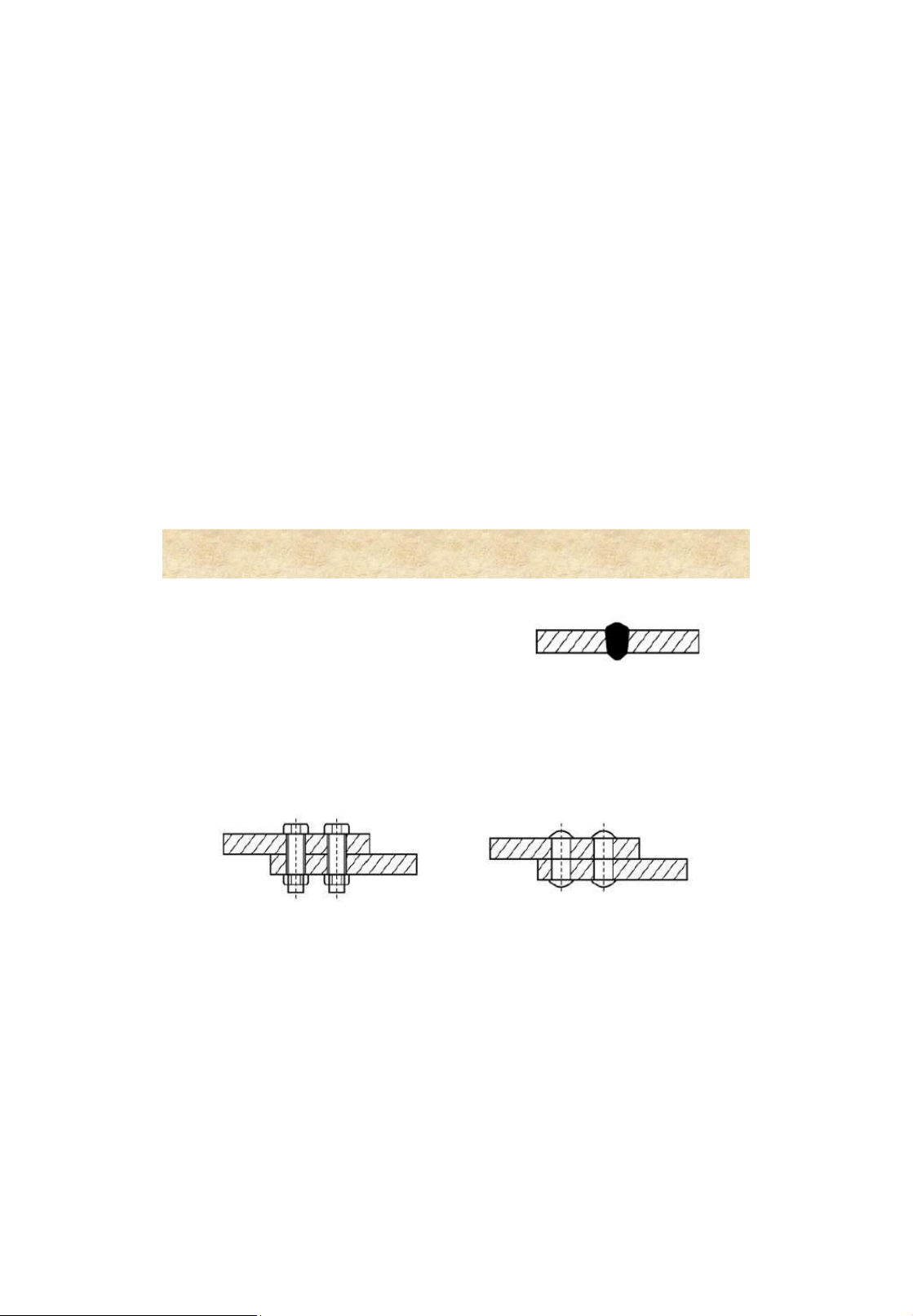
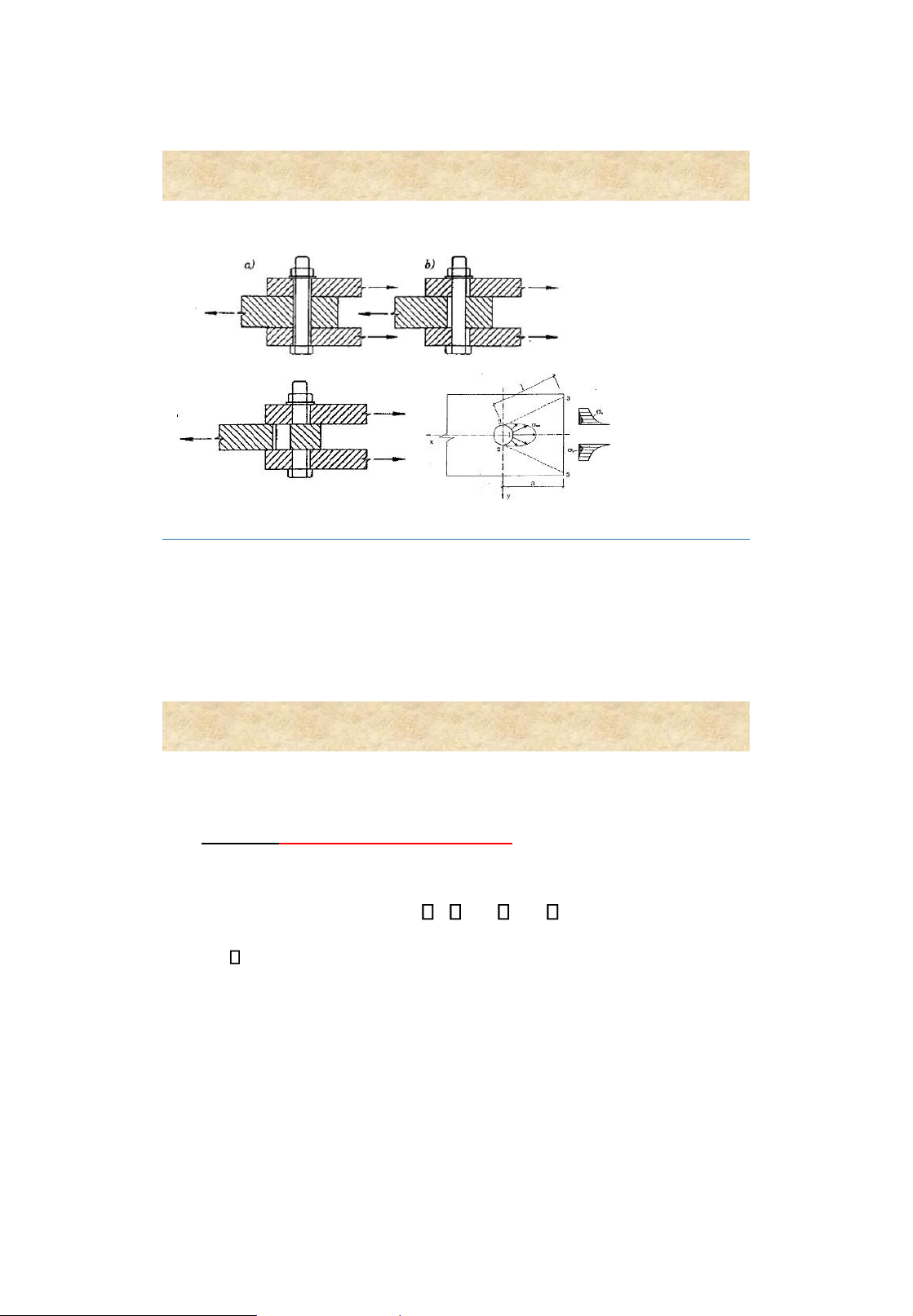
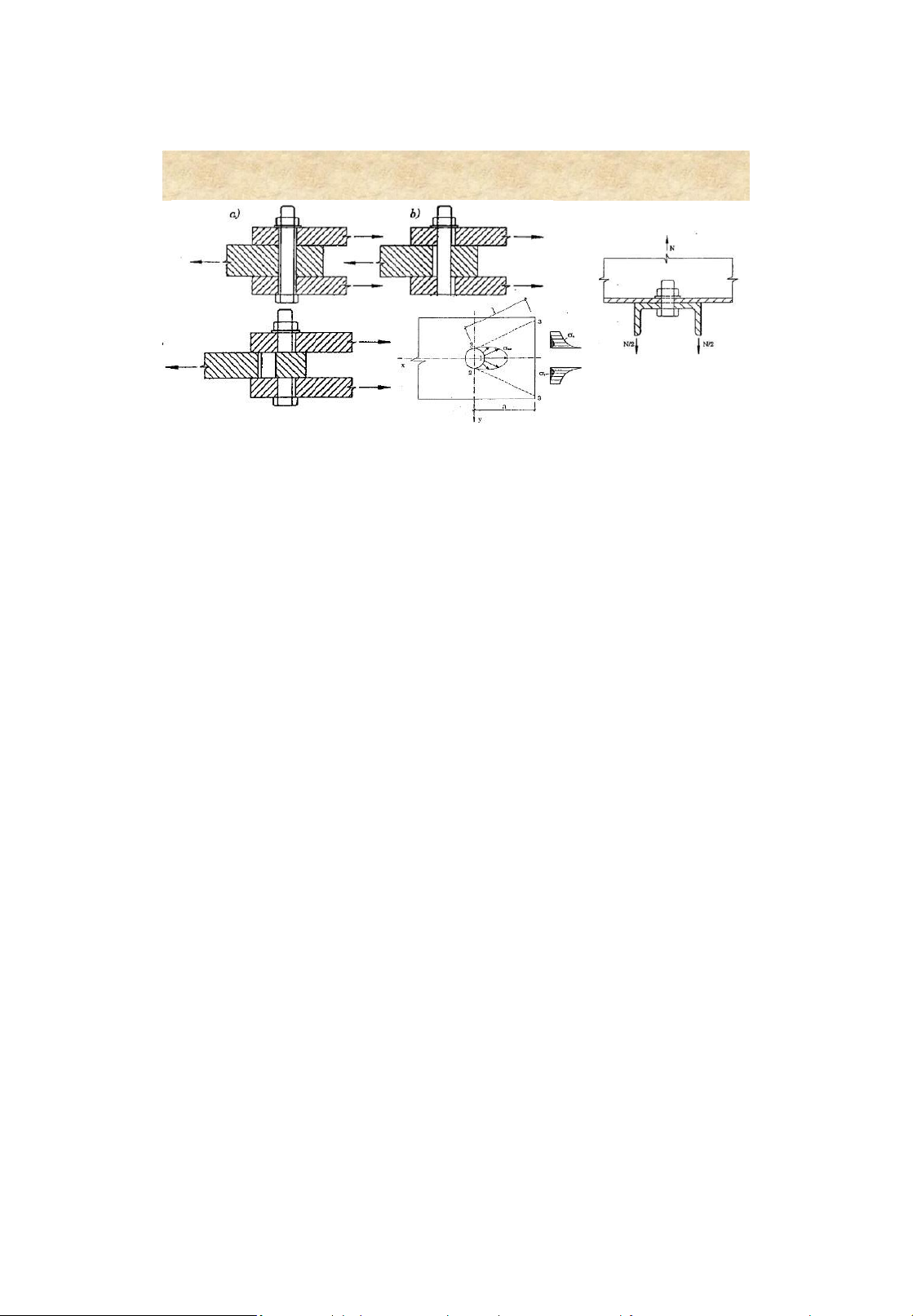
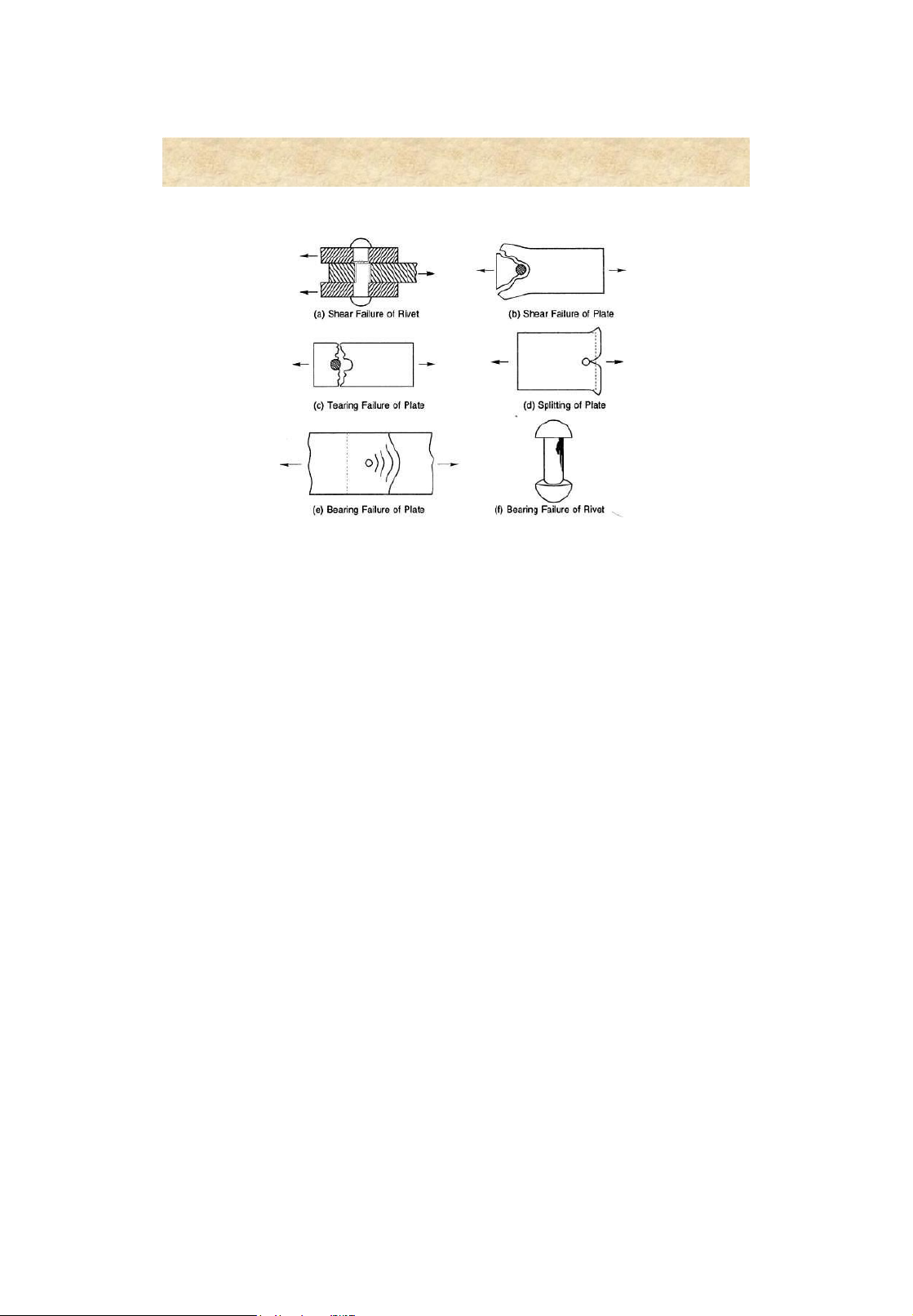
4. Failure of bolted connections Punchhole: D hole =d+(2 – 3 mm ) Dril hole: D hole = d+0.3mm Shear failureof bolt Shear failureof plate 7 Bolted connections 4. Design strength of a bolt
Design shear strength of a bolt [N]vb= b fvb Ab nv
▪ b : working condition factor of the bolted connection (Table 2.8 p.82)
▪ fvb : shear strength of the bolt material (Table I.10, p. 300)
▪ Ab : gross section area of the bolt (Table 2.9, p.82)
▪ nv : number of shear planes in one bolt 8 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections 4. Design strength of a bolt
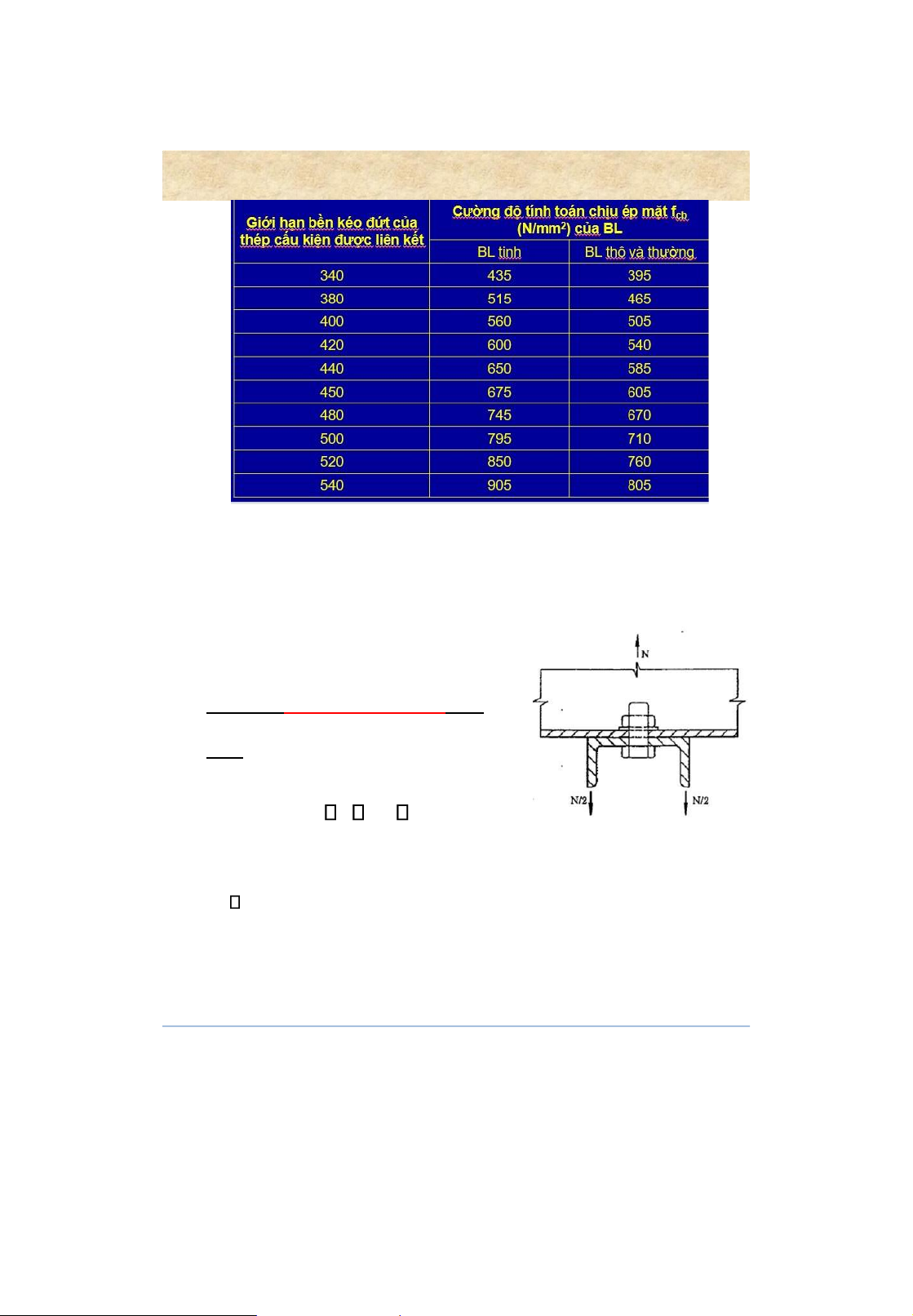
Design crushing strength of a bolt [N]cb= b fcb d ( t)min ▪ b : working condition factor of the bolt connection (Table 2.8 p.82)
▪ fcb : crushing strength of the bolt (Table I.11, p.300) ▪ d : diameter of the bolt
▪ ( t)min : total thickness of the plates being crushed at one side of the bolt shank 9 Bolted connections 4. Design strength of a bolt
Design crushing strength of a bolt lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections Ch.3 Steel Connections 10 4. Design strength of a bolt Design tensile strength of a bolt [N]tb= b ftb Abn
▪ b : working condition co-efficient of the bolted connection (Table 2.8 p.82)
▪ ftb : tensile strength of the bolt material (Table I.10, p. 300)
▪ Abn : net section area of the bolt (Table 2.9, p.82) 11 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections Bolted connections
4. Failure of bolted connections Design
shear strength of a high-strength bolt [N]hb=fhb Abn b1 ( b2) nf
• fhb : tensile strength of the bolt material, fhb=0,7fub (Table I.12)
• Abn : net area of the bolt section (threaded part) • b1 : working
condition factor of the bolted connection. •
: coefficient of friction (Table 2.10) •
b2 : reliability factor (Table 2.10)
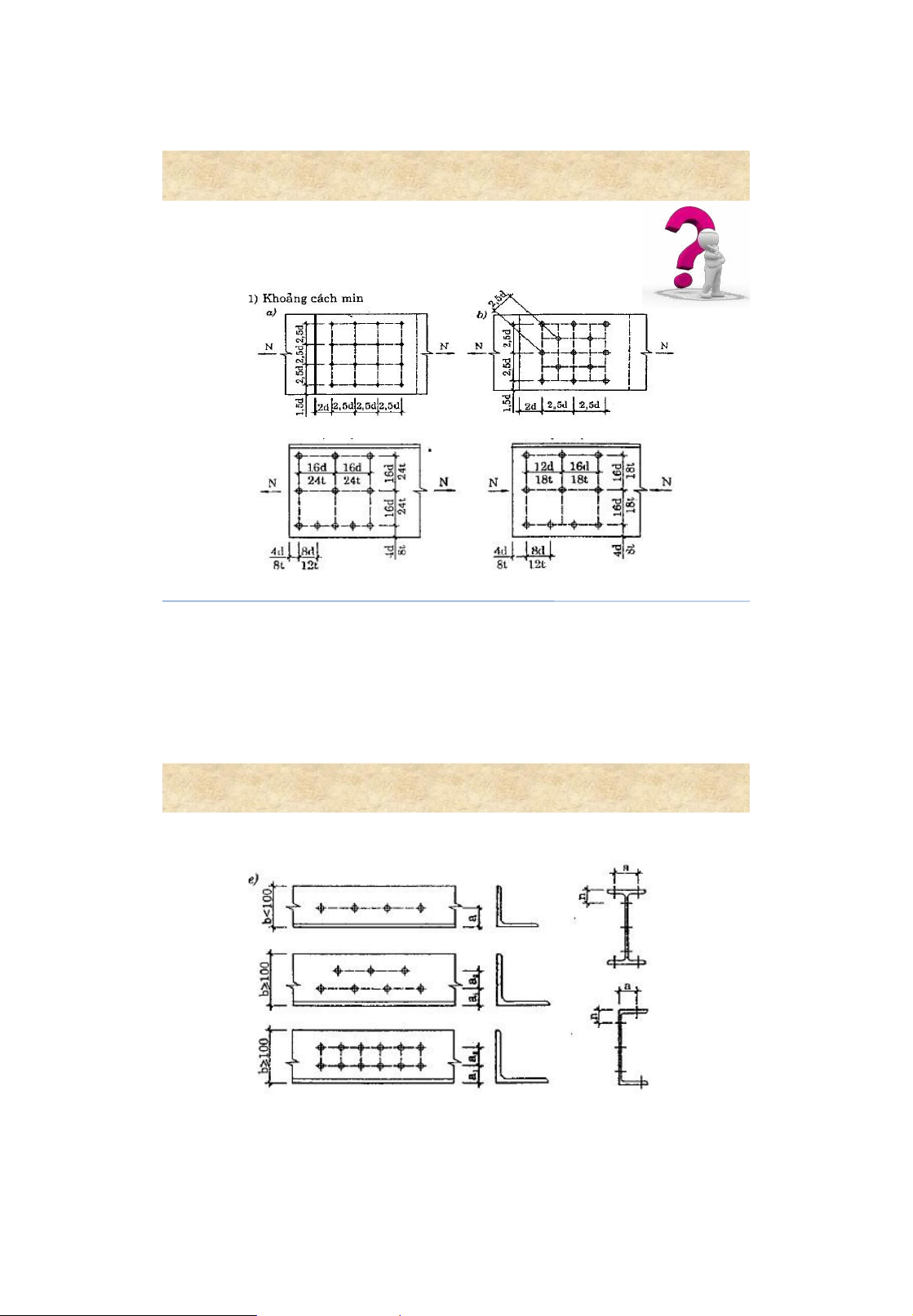
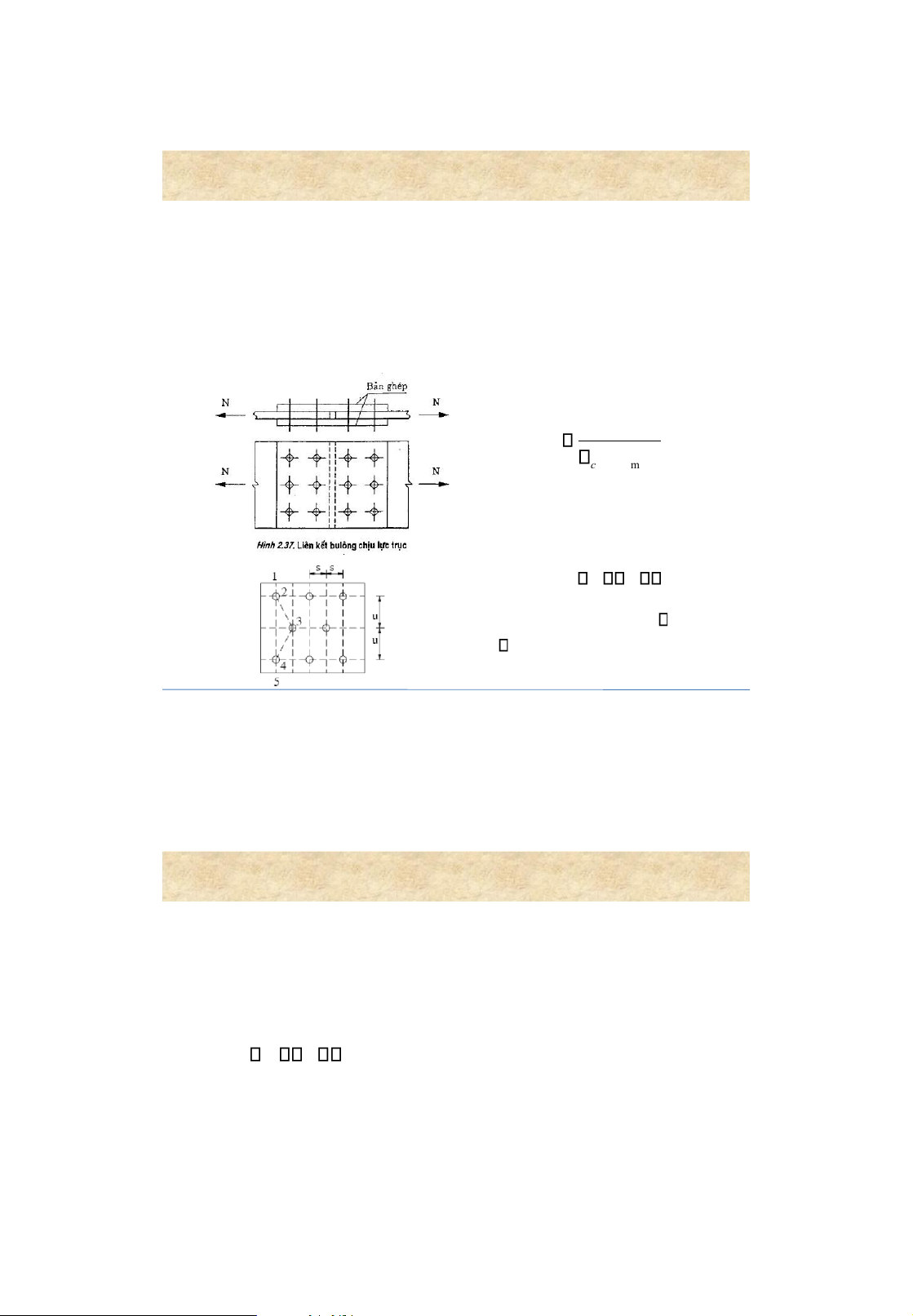
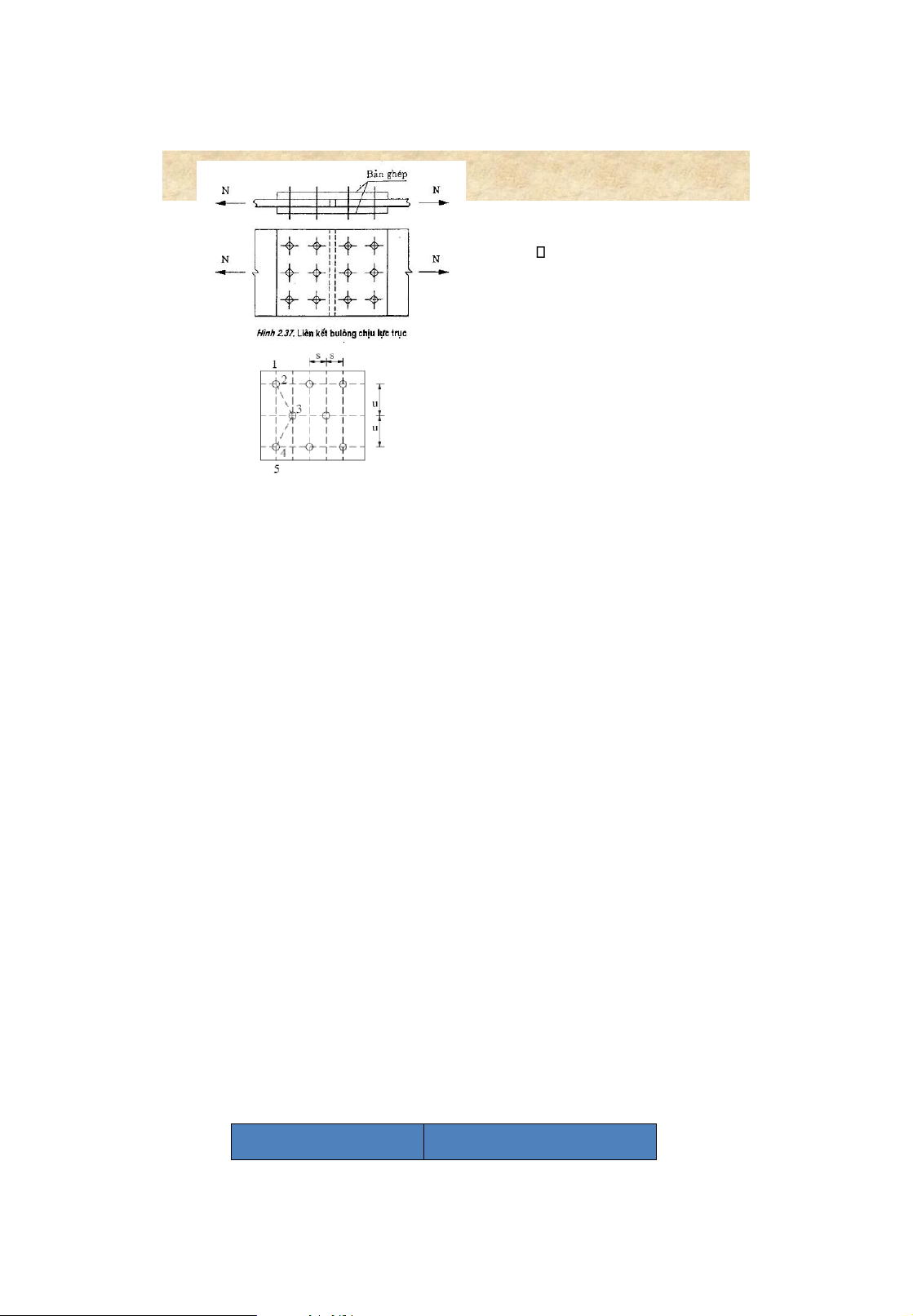
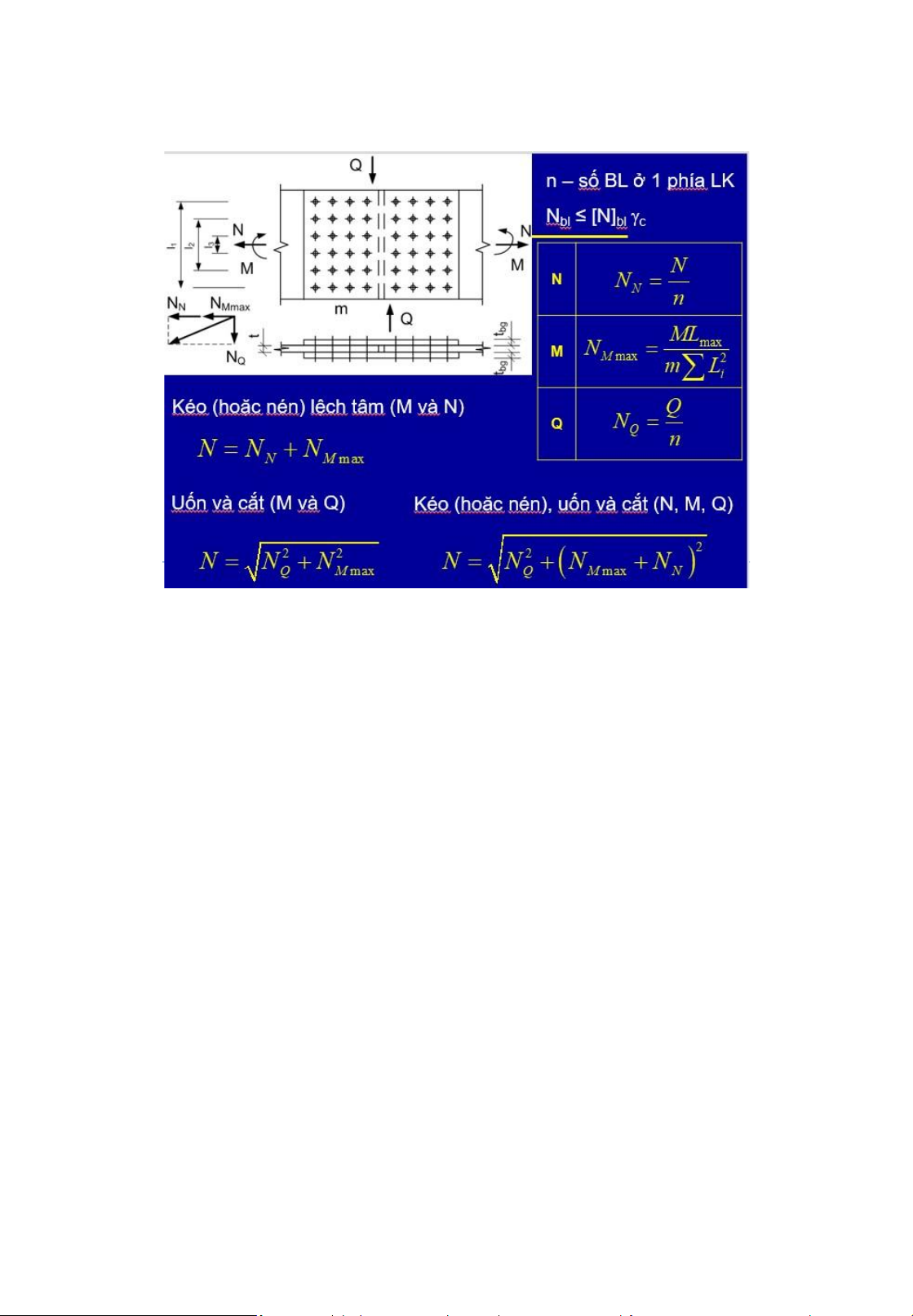
• nf : number of shear planes in one bolt 12 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections 5 . Arrangement of bolts Minimum distance Maximum distance Tension member compression member 13 Bolted connections 5. Arrangement of bolts rolled steel member lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections 14
6. Design of bolted connections straps • Requirednumber of bolts: N n c [] N min b [N
] minb = min([N ] vb ,[N] cb ) • Check the strengthof the
Connection subjected to axial load weakened/critical section: N/A n f bl c • Forbeams,columns,straps: bl =1 , 1 • Forbars: bl =1 , 05 • A n = A – A hole 15 Bolted connections
6. Design of bolted connections • Check the strength of the weakened/critical section N/Ac f bl c lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted straps connections For high-strength bolts •
bl = 1,0 • For static loads: Ac = A (if An ≥ 0,85A)
Ac = 1,18An (if An < 0,85A)
Connection subjected to axial load • For dynamic loads: Ac = An 16
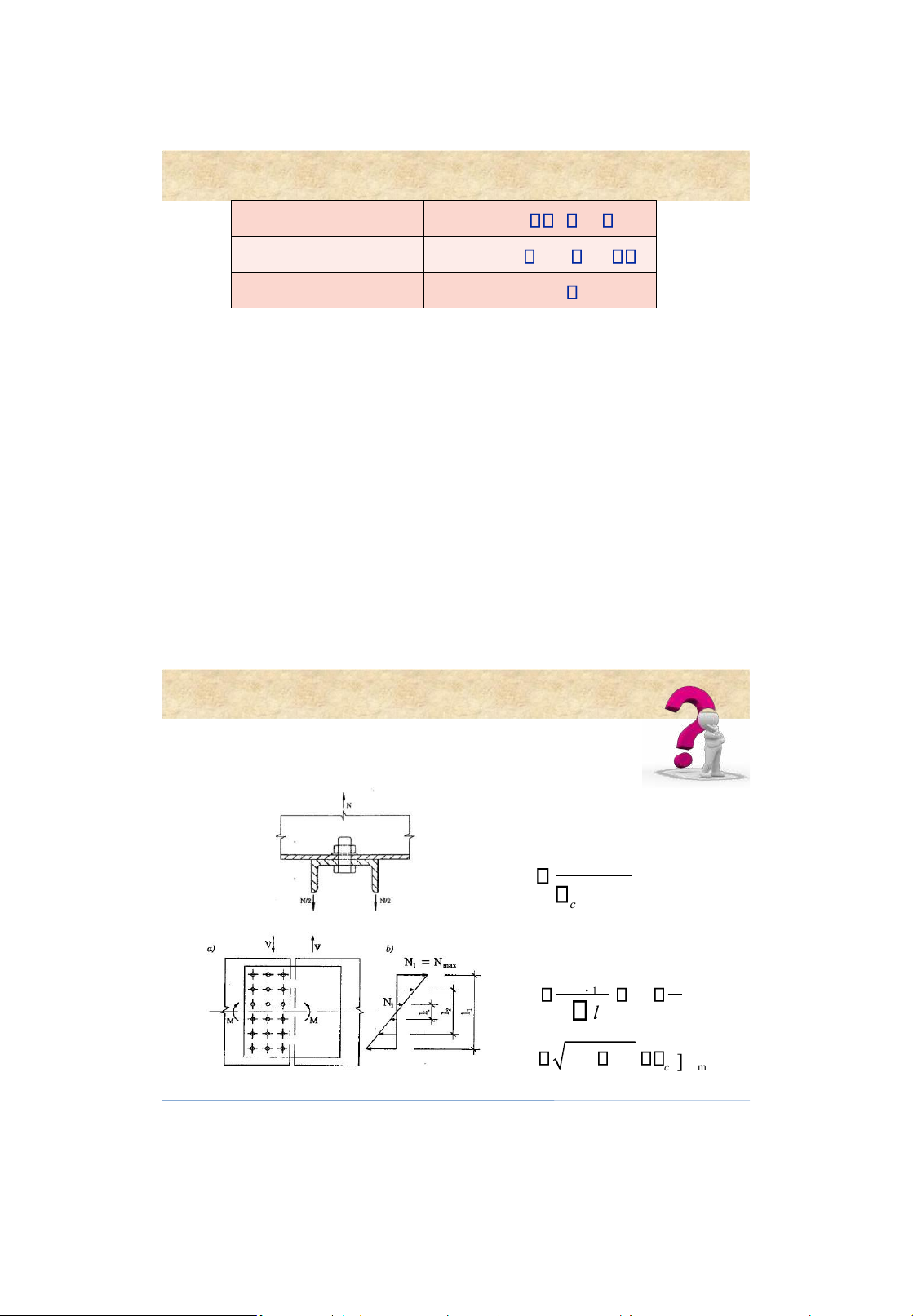
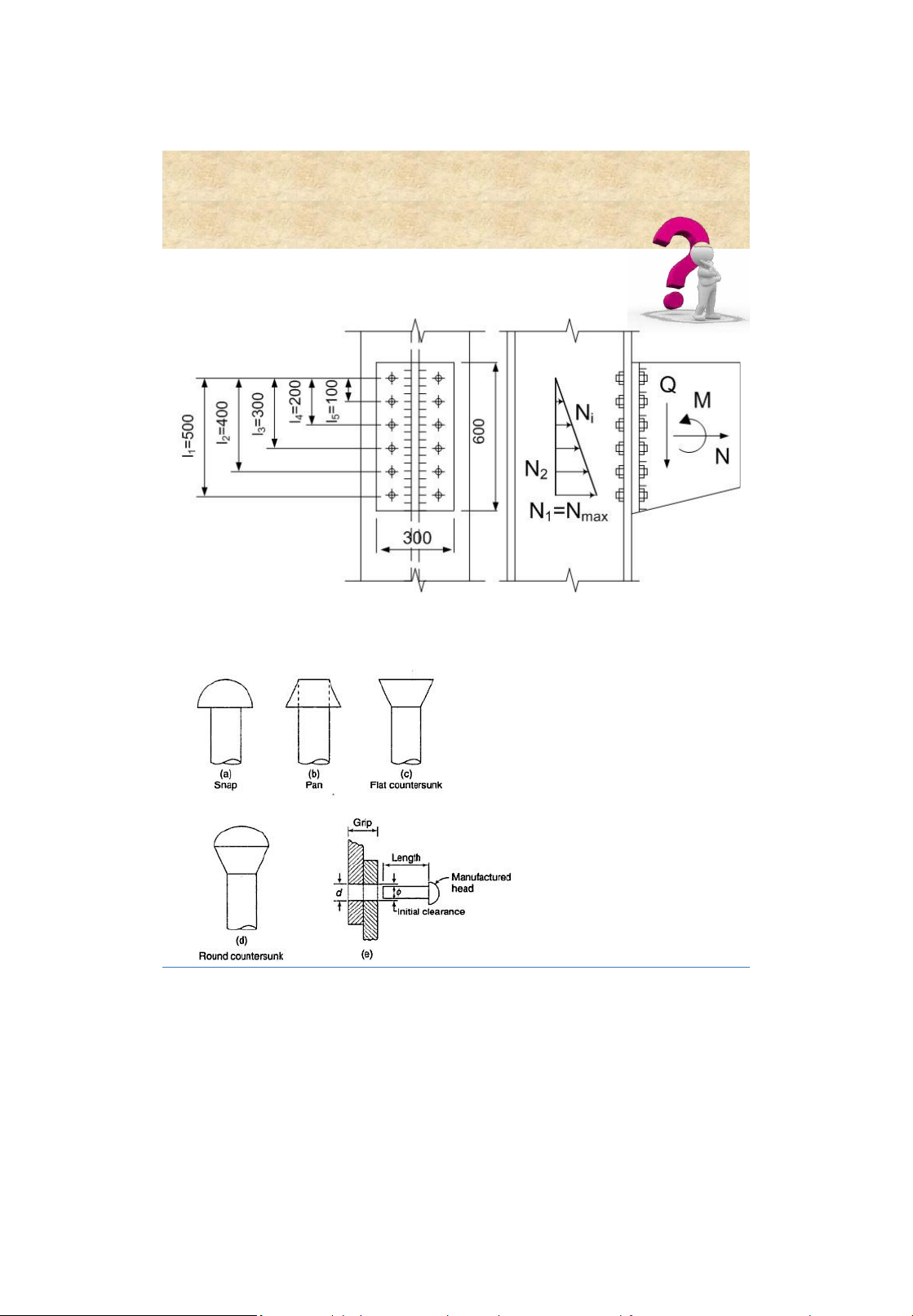
Trạng thái chịu lực Bulông lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections 6. Cắt [N]vb = fvb b A nv Ép mặt [N]cb = d ( t)min fcb b Kéo [N]tb = Abn ftb Design of bolted connections Bolted connections 7 . Worked examples • Requirednumber of bolts N n c [] N tb Bolts under tension • Strength requirement . Ml 1 V N M ; N 2 V m il n 2 2 N bl M NN V c [] N min b
Connection under shear and moment 17 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Bolted connections Bolts under tension 18 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 LTK Ch.3 Steel Connections 19 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 LTK Ch.3 Steel Connections 20 LTK Ch.3 Steel Connections 21 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Riveted connections Bolted connections 7 . Worked examples 22 1. Introduction Advantages • Structure erection can be speed up • Less skilled persons are required 23 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Riveted connections
2. Failure of riveted connections 24 lOMoAR cPSD| 58759230 Riveted connections 3. Design strength of a rivet
• Design shear strength of a rivet [N] v =fv A nv
• Design tensile strength of a rivet [N]t =ft An
• Design crushing strength of a rivet [N] c =fc d ( t)min
Design of riveted conn. ~ that of bolted conn. 25