















Preview text:
1: OVERVIEW OF INTERNAL CONTROL
I. Definition Internal control (định nghĩa Kiểm soát nội bộ): XEM SÁCH/12
v Internal control is a process, effected by an entity's board of directors, management, and other personnel,
designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of objectives relating to operations,
reporting and compliance (KSNB là một quá trình bị chi phối bởi HĐQT, nhà quản lý và các nhân viên của đơn
vị, nó được thiết lập để cung cấp một sự đảm bảo hợp lý nhằm đạt được các mục tiêu về hoạt động, báo cáo và tuân thủ).
v Objectives (các mục tiêu của KSNB):
• Operations objectives (mục tiêu hoạt động) - Related to the effectiveness and efficiency of the entity’s
operations, including operational and financial performance goals, and safeguarding assets against loss (này liên
quan đến hiệu quả và hữu hiệu của các hoạt động của đơn vị, bao gồm các mục tiêu về hiệu quả hoạt động và
tài chính, và bảo vệ tài sản khỏi mất mát).
• Reporting objectives (mục tiêu báo cáo) - Related to internal and external financial and non-financial reporting
to stakeholders, which would encompass reliability, timeliness, transparency, or other terms as established by
regulators, standard setters, or the entity’s policies (liên quan đến báo cáo tài chính và phi tài chính nội bộ và
bên ngoài và có thể bao gồm độ tin cậy, tính kịp thời, tính minh bạch hoặc các điều khoản khác theo quy định,
bộ đặt tiêu chuẩn hoặc chính sách của đơn vị).
• Compliance objectives (mục tiêu tuân thủ) - Related to adhering to laws and regulations that the entity must
follow (liên quan đến việc tuân thủ luật pháp và các quy định mà đơn vị phải tuân theo).
II. History and developmental process: XEM SLIDE TOPIC 1 TRANG 3
III. COSO report development process: XEM SLIDE TOPIC 1 TRANG 6
IV. COSO report (báo cáo theo COSO):
v Structure of COSO report (1992):
• Part 1: Executive summary (Tóm tắt nội dung).
• Part 2: Framework of internal control (Khung kiểm soát nội bộ).
• Part 3: Reporting to an external users (Báo cáo cho người dùng bên ngoài).
• Part 4: Internal control system assessment tool (Công cụ đánh giá hệ thống kiểm soát nội bộ).
v Structure of COSO report (2013):
• IC – Integrated Framework Executive Summary
• IC – Integrated Framework and Appendices
• IC – Integrated Framework Internal Control over External
Financial Reporting: A Compendium of Approaches and Examples
• IC – Integrated Framework Illustrative Tools for Assessing Effectiveness of a System of IC
v Components of the IC (các thành phần của KSNB):
• Control environment (môi trường kiểm soát).
• Risk assessment (đánh giá rủi ro).
• Control activities (hoạt động kiểm soát).
• Information & Communication (thông tin & truyền thông).
• Monitoring activities (giám sát).
v Relationship between objectives and parts of IC system (Mối quan hệ giữa mục tiêu và các bộ phận của hệ thống KSNB):
• Vertical relationship (Mối quan hệ dọc).
• Horizontal relationship (Mối quan hệ ngang).
• IC related to each department, each activity of the organization and the whole organization in general (IC liên
quan đến từng bộ phận, từng hoạt động của tổ chức và toàn bộ tổ chức nói chung).
V. The effectiveness of IC system (Sự hiệu quả của hệ thống KSNB):
v To conclude that your system of IC is effective, the 5 components of IC and all 17 relevant principles must be
(Để kết luận rằng hệ thống IC có hiệu quả, 5 thành phần của IC và tất cả 17 nguyên tắc liên quan phải):
• Present and functioning (Hiện diện và hoạt động).
• Operating together in an integrated manner (Hoạt động cùng nhau theo cách tích hợp).
VI. IC and Management process (KSNB và quá trình quản lý): Manager’s activities Internal control Set goals on a unit-wide level Strategic planning
Building elements of the control environment ü
Set goals at the department level
Risk identification and analysis ü Risk management
Carrying out control activities ü
Information collection & communication ü Monitor ü
Corrective actions (correction of errors)
VII. Responsibilities for IC (trách nhiệm đối với KSNB):
1) Board of Directors (HĐQT): XEM SÁCH/43
v Approve and monitor (Phê duyệt và giám sát):
• Policies regarding the mission, vision and strategy of organization (Các chính sách liên quan đến sứ mệnh,
tầm nhìn và chiến lược của tổ chức).
• Risk management strategy (developed by management) (Chiến lược quản lý rủi ro (do ban lãnh đạo xây dựng)).
• Development and effectively functioning of an IC system (Phát triển và vận hành hiệu quả hệ thống IC).
• Play an important role in defining expectations of honesty and ethical values, transparency and accountability
(Đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc xác định kỳ vọng về các giá trị trung thực và đạo đức, tính minh bạch và
trách nhiệm giải trình).
v Requirements for members of the Board of Directors (Yêu cầu đối với thành viên Hội đồng quản trị):
• Independent, competent and questionable (Độc lập, có năng lực và luôn đề ra các vấn đề).
• Understanding the operations and operating environment of the entity and dedicating enough time to carry out
its administrative responsibilities (Hiểu rõ hoạt động và môi trường hoạt động của đơn vị và dành đủ thời gian
để thực hiện các trách nhiệm hành chính của mình).
• Use resources as necessary to investigate issues that arise and have open, unlimited communication with
employees, internal auditors, independent auditors, legal consultant,… (Sử dụng các nguồn lực cần thiết để điều
tra các vấn đề phát sinh và trao đổi cởi mở, không hạn chế với nhân viên, kiểm toán viên nội bộ, kiểm toán độc
lập, tư vấn pháp luật,…).
2) Board of Supervisors/Audit Committee (Ban Kiểm soát/Ban Kiểm toán):
v Board of Supervisors (ban Kiểm soát):
• Supervise the Board of Directors, and CEO in the management and administration of the company (Giám sát
HĐQT, Tổng GĐ trong việc quản lý, điều hành công ty)
• Review, test and evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the company’s internal control, risk management
and early warning systems (Rà soát, thử nghiệm và đánh giá hiệu lực, hiệu quả của hệ thống kiểm soát nội bộ,
quản trị rủi ro và cảnh báo sớm cho công ty).
v Audit Committee (ban Kiểm toán):
• As a committee under the Board of Directors, with members (at least 2) are selected by the Board of Directors
The Chairman of the Audit Committee must be an independent member of the Board of Directors. Committee
members must be non-executive Board members (Là một ủy ban trực thuộc Hội đồng quản trị với số thành viên
(ít nhất là 2) do Hội đồng quản trị lựa chọn, Trưởng Uỷ ban Kiểm toán phải là thành viên Hội đồng quản trị độc lập).
• Responsibilities of Audit Committee:
Ø Review of IC and risk management systems (đánh giá hệ thống KSNB và hệ thống quản lý rủi ro).
Ø Check annual financial statements (Kiểm tra báo cáo tài chính thường niên).
Ø Select an independent auditing company; work and discuss directly with the independent auditors about
issues arising in the audit including weaknesses of the internal control system (Lựa chọn công ty kiểm toán độc
lập; làm việc và trao đổi trực tiếp với kiểm toán viên độc lập về các vấn đề phát sinh trong cuộc kiểm toán bao
gồm cả những yếu kém của hệ thống kiểm soát nội bộ).
Ø Detect and take appropriate actions in case the Board of Directors goes beyond the internal control system
(Phát hiện và có hành động xử lý phù hợp trong trường hợp HĐQT có hành vi quá trớn, vượt ra ngoài hệ thống kiểm soát nội bộ).
3) Management (Nhà quản lý): XEM SÁCH/43
v Being the decisive factor, building a solid foundation for the control environment and other parts of the
internal control (Là nhân tố quyết định, tạo nền tảng vững chắc cho môi trường kiểm soát và các bộ phận khác
của hệ thống kiểm soát nội bộ).
v Responsibilities of Management:
• Responsible for the development and function of an effective internal control (Chịu trách nhiệm xây dựng và
thực hiện chức năng của hệ thống kiểm soát nội bộ hữu hiệu).
• Participate in setting goals and strategies (Tham gia xây dựng các mục tiêu và chiến lược).
• Define integrity expectations, competence, key policies and information requirements (Xác định các kỳ vọng
về tính chính trực, năng lực, các chính sách chính và yêu cầu thông tin).
• Identify and deal with risks (internal and external) as well as develop mechanisms to identify and select
countermeasures (Xác định và xử lý các rủi ro (nội bộ và bên ngoài) cũng như phát triển các cơ chế để xác định
và lựa chọn các biện pháp đối phó).
4) Internal auditors (KTV nội bộ): XEM SÁCH/44
• Evaluate the effectiveness of the internal control (đánh giá sự hữu hiệu của hệ thống KSNB).
• Suggest measures to increase the effectiveness of the internal control (Đề xuất các biện pháp nâng cao hiệu
quả của kiểm soát nội bộ).
5) Staff/Employee (Nhân viên): XEM SÁCH/44
• Internal control concerns the responsibilities of every member of an entity through its day-to-day operations
(Kiểm soát nội bộ liên quan đến trách nhiệm của mọi thành viên trong đơn vị thông qua hoạt động hàng ngày của đơn vị).
• Employees contribute to the risk assessment or monitoring process (Nhân viên đóng góp vào quá trình đánh
giá hoặc giám sát rủi ro).
• The main employee is the person who operates the internal control system at the unit (Nhân viên chính là
người vận hành hệ thống kiểm soát nội bộ tại đơn vị).
6) Outside parties (Các đối tượng khác bên ngoài): XEM SÁCH/45
• External auditors (such as independent auditors, public auditors) (Kiểm toán viên bên ngoài (chẳng hạn như
kiểm toán viên độc lập, kiểm toán viên nhà nước).
• Legislators or regulators (Nhà lập pháp hoặc cơ quan quản lý).
• Customers and suppliers can also provide useful information through their dealings with the organization
(Khách hàng và nhà cung cấp cũng có thể cung cấp thông tin hữu ích thông qua các giao dịch của họ với tổ chức).
• Others outside the organization such as financial analysts, the media,… (Những người khác bên ngoài tổ chức
như nhà phân tích tài chính, giới truyền thông,…).
2: FRAUDS & RESPONSES
I. Definition of frauds (định nghĩa về Gian lận): XEM SÁCH/51
v Frauds is exploits of position and knowledge in the enterprise to benefit oneself through the misuse of
resources of the enterprise (Là lợi dụng địa vị, tri thức có được trong doanh nghiệp để tư lợi thông qua việc sử
dụng sai các nguồn lực của doanh nghiệp).
v Elements of fraud (các yếu tố trong 1 hành vi gian lận):
While each type of fraud may require different levels of evidence, proving fraud generally requires 3
components under common law (Mặc dù mỗi loại gian lận có thể yêu cầu các mức độ bằng chứng khác nhau,
nhưng việc chứng minh gian lận thường yêu cầu 3 thành phần theo luật thông thường):
The making of a false statements with intent to deceive (cố ý trình bày sai một thông tin với ý định lừa dối).
The reliance of the victim on the false statement (Sự tin cậy của nạn nhân vào thông tin bị sai).
Damages resulting from the reliance on the false statement (nạn nhân chịu thiệt hại do ra quyết định trên).
v Responsibility for frauds (Trách nhiệm đối với hành vi gian lận):
• Management (nhà quản lý): have the highest responsibility for prevention and detection of frauds in an
organization (có trách nhiệm cao nhất trong việc ngăn chặn và phát hiện gian lận trong tổ chức).
" Develop and maintain an effective internal control system (Phát triển và duy trì hệ thống kiểm soát nội bộ hiệu quả).
• Governace board: oversight of that responsibility (giám sát liệu nhà quản trị có làm tròn trách nhiệm đó hay không). v GONE theory: G = Greed O = Opportunity N = Need E = Exposure
II. Typical research works on frauds (các công trình nghiên cứu về gian lận):
1. Edwin H. Sutherland: XEM SÁCH/52
v Focus on frauds of management (white collar) (tập trung vào hành vi gian lận được thực hiện bởi nhà quản
lý, những đối tượng này gọi là những tội phạm cổ cồn). v 2 main conclusions:
• Criminal behavior is often the result of socialized learning (is learned in interaction with other persons) (Hành
vi phạm tội thường là kết quả của quá trình học tập xã hội hóa (được học khi tương tác với người khác)).
• The study of crime as a social phenomenon through various principles (Nghiên cứu tội phạm như một hiện
tượng xã hội thông qua các nguyên tắc khác nhau).
2. Donald R. Cressey: XEM SÁCH/53
v Father of “Fraud Triangle” (cha đẻ của “mô hình Tam giác gian lận”).
v There are 3 factors that must be simultaneously present in order for an ordinary person to commit fraud (Có 3
yếu tố cần phải có đồng thời để một người bình thường thực hiện hành vi gian lận):
• Pressure (a non-shareable problem) (Áp lực (một vấn đề không thể chia sẻ))
• Opportunity (lack of internal control) (Cơ hội (thiếu kiểm soát nội bộ)).
• Rationalization (the ability to justify one’s action) (Hợp lý hóa (khả năng biện minh cho hành động của một người)).
(1) Pressure: XEM SÁCH/54 v 6 main reason:
• Financial debts (khó khăn tài chính).
• Personal failures (hậu quả từ thất bại cá nhân).
• Gambling habits (thói quen cờ bạc)
• Lavish lifestyles (lối sống hoang phí)
• Being isolated (bị cô lập)
• Employer – employee relationship (mối quan hệ chủ - thợ)
(2) Opportunity: XEM SÁCH/55 v 2 related components:
• Information (khả năng nắm bắt thông tin)
• Skill (kỹ năng thực hiện gian lận)
(3) Rationalization: XEM SÁCH/56 v 3 related components:
• Ethical values (giá trị đạo đức)
• Instinct (bản năng)
• Surrounding environment (môi trường xung quanh)
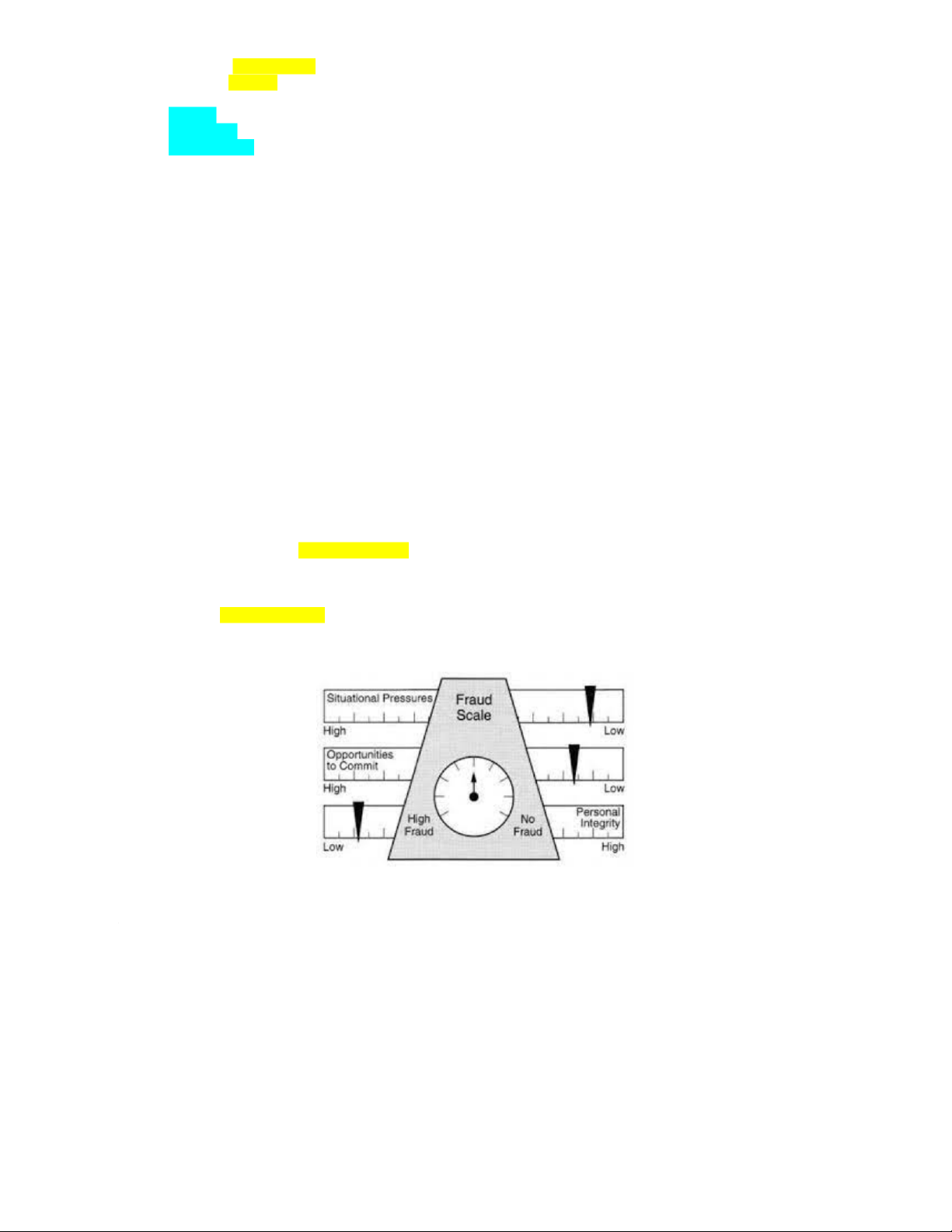
3. D. W. Steve Albrecht: XEM SÁCH/56
v Examine 212 fraud cases (phân tích 212 trường hợp gian lận).
v Focus on identifying “Red Flag Indicators” from employees and organization (tập trung vào xác định “Các
dấu hiệu báo động đỏ” từ dấu hiệu của nhân viên và đặc điểm của tổ chức).
v Author of book names “Deterring fraud: the internal auditor perspective” (tác giả của cuốn sách: Ngăn ngừa
gian lận: góc nhìn của KTV nội bộ).
v Suggest Fraud Scale model (xây dựng mô hình “bàn cân gian lận”). • Pressure • Opportunity
• Integrity (tính trung thực)
(1) Red Flag Indicators from employees (dấu hiệu đỏ liên quan đến nhân viên): XEM SÁCH/57
(2) Red Flag Indicators from organization (dấu hiệu đỏ liên quan đến tổ chức): XEM SÁCH/57
4. Richard C. Hollinger & P.Clark:
v The main cause of fraud is working conditions (nguyên nhân chủ yếu của gian lận là do điều kiện làm việc).
v There is a link between incomes, ages, positions and job satisfaction with frauds (mối liên hệ giữa thu nhập,
tuổi tác, vị trí và mức độ hài lòng trong công việc với tình trạng biển thủ).
v Authors of book named “Theft by employees” (tác giả cuốn sách “Khi nhân viên ăn cắp”).
v Measures to prevent fraudulent acts in the organization (Các biện pháp ngăn chặn các hành vi gian lận trong tổ chức):
• Clearly define unacceptable behavior within the organization (quy định rõ ràng những hành vi không được
chấp nhận trong tổ chức).
• Disseminate the organization’s regulations to all employees (Phổ biến các quy định của tổ chức tới toàn thể nhân viên).
• Execute the approval in practice (thực hiện việc phê chuẩn trong thực tế).
• Make approval public (công khai các phê chuẩn) III. Introduce to ACFE: 1. ACFE:
v The world’s first organization to study frauds (Tổ chức đầu tiên trên thế giới nghiên cứu về gian lận)
v Founded in 1988, 45000 members in 125 countries (Được thành lập vào năm 1988, 45000 thành viên ở 125 quốc gia)
v CFE specializes investigation, fraud liability and criminology (CFE chuyên điều tra, trách nhiệm pháp lý đối
với gian lận và tội phạm học)
v More than 50% of CFEs are internal auditors/fraud specialists (Hơn 50% CFE là kiểm toán viên nội
bộ/chuyên gia về gian lận).
v More than 60% of CFEs have direct or indirect experience with fraud (Hơn 60% CFE có kinh nghiệm trực
tiếp hoặc gián tiếp về gian lận).
v On average, CFE has more than 15 years of experience (trung bình, CFE có hơn 15 năm kinh nghiệm)
2. Founder & Chairman of ACFE: XEM SLIDE 23 TOPIC 1
3. Reports by ACFE on frauds (Báo cáo của ACFE về gian lận):
• Costs of frauds (tổn thất do gian lận)
• Common forms of frauds (các loại gian lận phổ biến)
• Perpetrators (người thực hiện gian lận): XEM SÁCH/65
• Times to detect frauds (thời gian phát hiện ra gian lận)
• Principles of fraud examination (các nguyên tắc điều tra gian lận)
4. Common forms of frauds (những phương pháp gian lận phổ biến):
• Asset misappropriation (biển thủ tài sản): XEM SÁCH/62 Ø Cash (tiền mặt)
Ø Inventories/other assets (HTK/ tài sản khác)
• Corruption (tham ô): XEM SÁCH/63
• Fraudulent FS (gian lận trên BCTC): XEM SÁCH/63 Ø Financial Ø Non-financial
5. Principles of fraud examination (các nguyên tắc điều tra gian lận):
v Start from a forecast or hypothesis (Bắt đầu từ một dự báo hoặc giả thuyết).
v Forecast are situations that could lead a prudent, skilled person to believe that a fraud has occurred, is
occurring, or will occur (Dự báo là những tình huống có thể khiến một người thận trọng, có kỹ năng tin rằng
một hành vi gian lận đã xảy ra, đang xảy ra hoặc sẽ xảy ra).
v Apply Fraud Theory Approach (Áp dụng Phương pháp Tiếp cận Lý thuyết Gian lận). IV. Fraud Theory Approach:
v The fraud theory approach provides that, when conducting investigations into allegations or signs of fraud,
fraud examiners should make a hypothesis (or theory) of what might have occurred based on the known facts
(phương pháp lý thuyết gian lận quy định rằng, khi điều tra các cáo buộc hoặc dấu hiệu gian lận, các nhà kiểm
tra gian lận nên đưa ra các giả thuyết (hoặc lý thuyết) về những gì có thể xảy ra dựa trên các sự kiện đã được biết).
v Once fraud examiners have created a hypothesis, they should test it through the acquisition of new
information (or correcting and integrating known information) to determine whether the hypothesis is provable
(Một khi các nhà kiểm tra gian lận đã tạo ra một giả thuyết, họ nên kiểm tra nó bằng cách lấy thông tin mới
(hoặc sửa đổi và tích hợp thông tin đã biết) để xác định liệu giả thuyết đó có thể được chứng minh hay không)
v If, after testing a hypothesis, fraud examiners determine that it is not provable, they should continually revise
and test their theory based on the known facts until it is provable, they conclude that no fraud is present, or they
find that the fraud cannot be proven (Nếu sau khi kiểm tra một giả thuyết, các nhà kiểm duyệt gian lận xác định
rằng giả thuyết đó không thể chứng minh được, họ nên liên tục sửa đổi và kiểm tra lý thuyết của họ dựa trên
những sự thật đã biết, cho đến khi giả thuyết đó có thể chứng minh được, họ kết luận rằng không có gian lận,
hoặc họ phát hiện rằng gian lận không thể chứng minh được). Step: Ø Analyzing available data Ø Creating hypothesis Ø Testing hypothesis Ø Refining hypothesis
3: COSO’S INTEGRATED FRAMEWORK OF INTERNAL CONTROLS A. CONTROL ENVIRONMENT
v The control environment is the set of standards, processes, and structures that provide the basis for carrying
out internal control across the organization (môi trường kiểm soát là tập hợp các tiêu chuẩn, quy trình và cấu
trúc làm nền tảng cho việc thiết kế và vận hành KSNB trong một đơn vị).
v The Board of directors and senior management establish the tone at the top regarding the importance of
internal control and expected standards of conduct (Hội đồng quản trị và quản lý cấp cao thiết lập quan điểm từ
cấp cao nhất về tầm quan trọng của kiểm soát nội bộ và các chuẩn mực ứng xử được kỳ vọng).
v There are 5 principles relating to control environment:
1) The organization demonstrates a commitment to integrity and ethical values (đơn vị thể hiện sự cam kết về
tính trung thực và các giá trị đạo đức).
2) The Board of directors demonstrates independence from management and exercises oversight of the
development and performance of internal control (HĐQT thể hiện sự độc lập với ban quản lý và đảm nhiệm
chức năng giám sát việc thiết kế và vận hành hệ thống KSNB tại đơn vị).
3) Management establishes, with board oversight, structures, reporting lines, and appropriate authorities and
responsibilities in the pursuit of objectives (dưới sự giám sát của HĐQT, nhà quản lý xây dựng cơ cấu, các cấp
bậc báo cáo, cũng như phân định trách nhiệm và quyền hạn phù hợp cho việc thực hiện các mục tiêu của đơn vị).
4) The organization demonstrates a commitment to attract, develop, and retain competent individuals in
alignment with objectives (đơn vị thể hiện sự cam kết sử dụng nhân lực thông qua thu hút, phát triển và giữ
chân các cá nhân có năng lực phù hợp với mục tiêu của đơn vị).
5) The organization holds individuals accountable for their internal control responsibilities in the pursuit of
objectives (đơn vị chỉ rõ trách nhiệm giải trình của từng cá nhân liên quan đến trách nhiệm kiểm soát của họ
để đạt được mục tiêu được thiết lập).
I. Demonstrates a commitment to integrity and ethical values (đơn vị thể hiện sự cam kết về tính trung
thực và các giá trị đạo đức):
v Integrity is an important ethical and moral principle (trung thực là một nguyên tắc đạo đức và luân lý quan trọng).
v Morality helps people distinguish between right and wrong; it enables them to see the consequences of their
actions, and it motivates and direct them to do what is right (Đạo đức giúp con người phân biệt đúng sai; nó
giúp họ thấy được hậu quả của hành động của mình, nó thúc đẩy và hướng dẫn họ làm điều đúng).
v People that want to be respected should behave ethically (Con người muốn được tôn trọng thì phải cư xử có đạo đức).
v Enterprises that want to create and maintain a good reputation as well as develop sustainably should adhere to
ethical principles, in which integrity is the most important (Doanh nghiệp muốn tạo dựng và duy trì danh tiếng
tốt cũng như phát triển bền vững thì phải tuân thủ nguyên tắc đạo đức, trong đó trung thực là quan trọng nhất). Point of focus:
1) Sets the tone at the top (quan điểm của người lãnh đạo cấp cao nhất trong đơn vị).
2) Establishes Standards of Conduct (các tiêu chuẩn ứng xử)
3) Evaluates adherences of Standards of Conduct (đánh giá sự tuân thủ của các tiêu chuẩn ứng xử).
4) Address deviations in a timely manner (Giải quyết kịp thời những sai lệch).
1. Sets the tone at the top (quan điểm của người lãnh đạo cấp cao nhất trong đơn vị): XEM SÁCH/84
v BODs and management at all levels: demonstate through their directives, actions, behaviors the importance of
integrity and ethical values (HĐQT và ban quản lý các cấp thể hiện thông qua các chỉ thị, hành động, hành vi
của họ về tầm quan trọng của tính trung thực và các giá trị đạo đức).
v Top management (Ban lãnh đạo cấp cao):
• Develops and communicate the expectations of integrity and ethical values through the entity’s mission and
values statements, code of conduct, policies and practices, directives and guidelines, actions and decisions of
management of all levels and of BODs (Phát triển và truyền đạt các kỳ vọng về tính trung thực và các giá trị
đạo đức thông qua các tuyên bố về sứ mệnh và giá trị cốt lõi của đơn vị, quy tắc ứng xử, chính sách ban hành
và thực tiễn áp dụng, chỉ thị và hướng dẫn, hành động và quyết định của quản lý các cấp và của HĐQT).
• Leads by example and applied consistently (đi đầu làm gương mẫu và được áp dụng triệt để).
Æ Tone is impacted by the operating style and personal conduct of management and BODs (quan điểm bị ảnh
hưởng bởi phong cách điều hành & ứng xử của ban lãnh đạo và HĐQT).
2. Establishes Standards of Conduct (các tiêu chuẩn ứng xử): XEM SÁCH/86 v Standards of Conduct:
• Established what is right and wrong (thiết lập điều gì được xem là đúng và điều gì bị cho là sai).
• Provides guidance for navigating what lies in between (đưa ra các hướng dẫn để phân biệt đúng sai, đồng
thời cân nhắc đến các rủi ro có liên quan).
• Reflects legal and regulatory requirements, moral, social, environmental principles of responsible conduct, and
various stakeholders’ expectations (tiêu chuẩn thiết lập phải phản ánh các quy định, luật lệ của nhà nước và
các mong đợi khác của các bên liên quan, ví dụ như trách nhiệm XH của DN).
v Top management establish Standards of Conduct and mechanisms for the entity to understand and adhere it
(nhà quản lý cấp cao cần xây dựng các tiêu chuẩn và cơ chế để mọi người trong đơn vị có thể hiểu và trung
thành với nguyên tắc “làm điều đúng”).
v Integrity and ethical values are core messages in the entity’s communications and training (Các giá trị đạo
đức và trung thực là những thông điệp cốt lõi trong hoạt động truyền thông và đào tạo của đơn vị).
3 & 4. Adherence & Deviations (đánh giá sự tuân thủ và không tuân thủ của các tiêu chuẩn ứng xử): XEM SÁCH/87
v Process are in place to evaluate the performance of individuals and teams against the entity’s expected
standards of conduct (Có sẵn quy trình để đánh giá hiệu suất của các cá nhân và nhóm so với các tiêu chuẩn
ứng xử dự kiến của tổ chức).
• Define set of indicators (Xác định bộ chỉ số).
• Establish continual and periodic compliance procedures (Thiết lập các quy trình tuân thủ liên tục và định kỳ).
• Identify, analyze and report business conduct issues to senior management and BODs (direct reporting lines,
HR functions, and hotlines) (Xác định, phân tích và báo cáo các vấn đề về hành vi kinh doanh cho quản lý cấp
cao và HĐQT (kênh báo cáo trực tiếp, bộ phận nhân sự, và đường dây nóng)).
v Deviations are identified and remedied in a timely and consistent manner (các hành vi vi phạm cần được xác
định và khắc phục một cách kịp thời và nhất quán).
II. Exercises oversight responsibility (HĐQT thể hiện sự độc lập với người quản lý và đảm nhiệm chức
năng giám sát việc thiết kế và vận hành hệ thống KSNB): v Point of focus:
1) Establishes oversight responsibilities 2) Applies relevant expertise 3) Operates independently
4) Provide oversight for IC system
1. Authorities & Responsibility (Quyền hạn & trách nhiệm của HĐQT): XEM SÁCH/88
v BODs often maintains the oversight responsibility (HĐQT thường duy trì trách nhiệm giám sát).
v The board has the authority to hire as well as terminate, and establish succession planning for CEO or
President (HĐQT có quyền tuyển dụng cũng như chấm dứt hợp đồng và lập kế hoạch kế nhiệm cho TGĐ hoặc Chủ tịch).
v The board is responsible for providing oversight and constructive challenge to management (HĐQT chịu
trách nhiệm giám sát và đưa ra những thách thức mang tính xây dựng đối với ban điều hành).
v While BODs retains oversight responsibility, CEO and senior management bear direct responsibility for
developing and implementing the IC system (Trong khi HĐQT vẫn giữ trách nhiệm giám sát, TGĐ và quản lý
cấp cao chịu trách nhiệm trực tiếp chịu trách nhiệm phát triển và triển khai hệ thống KSNB).
2 & 3. Independence & Relevant expertise (độc lập & có chuyên môn phù hợp): XEM SÁCH/89
v BODs is independent from management (board independence and size) (HĐQT độc lập với nhà quản lý).
v The board demonstrates relevant skills and expertise in carrying out its oversight responsibilities (board
composition) (HĐQT thể hiện các kỹ năng và chuyên môn liên quan để thực hiện trách nhiệm giám sát của
mình (thành phần HĐQT)).
Æ The board should be actively engaged at all times and be prepared to question and scrutinize management’s
activities, present alternative views, and have the courage to act in the face of obvious or suspected
wrongdoings (Hội đồng quản trị phải luôn tích cực tham gia và sẵn sàng chất vấn và xem xét các hoạt động
của Ban quản lý, đưa ra các ý kiến thay thế và can đảm hành động khi đối mặt với hành vi sai trái rõ ràng hoặc đáng ngờ).
4. Oversight for IC system (giám sát của HĐQT về hệ thống KSNB): XEM SÁCH/91
BODs retains oversight responsibility for management’s design, implementation, and conduct of IC through
each of the 5 components (HĐQT giữ trách nhiệm giám sát đối với việc thiết kế, triển khai và thực hiện hệ
thống KSNB của ban quản lý thông qua từng thành phần trong số 5 thành phần).
III. Establishes structure, authority & responsibility (dưới sự giám sát của HĐQT, nhà quản lý xây dựng
cơ cấu, các cấp bậc báo cáo, cũng như phân định trách nhiệm và quyền hạn phù hợp cho việc thực hiện
các mục tiêu của đơn vị): XEM SÁCH/92 v Point of focus:
1) Considers all structures of the entity (xác định cơ cấu tổ chức của đơn vị).
2) Establishes reporting lines (thiết lập các cấp bậc báo cáo).
3) Defines, assigns, and limits authorities and responsibilities (phân định trách nhiệm và quyền hạn)
IV. Demonstrates commitment to competence (đơn vị thể hiện sự cam kết sử dụng nhân lực thông qua
thu hút, phát triển và giữ chân các cá nhân có năng lực phù hợp với mục tiêu của đơn vị): XEM SÁCH/95 v Point of focus:
1) Establishes policies and practices (thiết lập chính sách nguồn nhân lực và áp dụng trong thực tế).
2) Evaluates competence and address shortcomings (Đánh giá năng lực và giải quyết các thiếu sót).
3) Attracts, develops, and retains individuals (thu hút, phát triển và giữ chân các cá nhân có năng lực).
4) Plans and prepares for succession (lên kế hoạch và chuẩn bị cho việc kế nhiệm).
V. Enforces accountability (đơn vị chỉ rõ trách nhiệm giải trình của từng cá nhân liên quan đến trách
nhiệm kiểm soát của họ để đạt được mục tiêu được thiết lập): XEM SÁCH/98 v Point of focus:
1) Enforces accountability through structures, authorities and responsibilities (xác lập trách nhiệm giải trình
thông qua cơ cấu, quyền hạn và trách nhiệm).
2) Establishes performance measures, incentives and rewards (xác lập tiêu thức đo lường kết quả hoạt động và
các biện pháp khuyến khích, khen thưởng)
3) Evaluates performance measures, incentives and rewards for ongoing relevance (Đánh giá các thước đo hiệu
suất, khuyến khích và khen thưởng cho sự liên quan đang diễn ra).
4) Considers excessive pressures (xem xét các áp lực quá mức)
5) Evaluates performance and rewards or disciplines individuals (đánh giá hiệu quả làm việc, khen thưởng và kỷ luật) B. RISK ASSESSMENT
v Risk assessment involves a dynamic and iterative process for identifying and analyzing risks to achieving the
entity’s objectives, forming a basis for determining how risks should be managed (Đánh giá rủi ro liên quan
đến một quy trình năng động và lặp đi lặp lại để xác định và phân tích rủi ro nhằm đạt được các mục tiêu của
đơn vị, tạo cơ sở để xác định cách thức quản lý rủi ro).
v Management considers possible changes in the external environment and within its own business model that
may impede its ability to achieve its objectives (Quản lý xem xét những thay đổi có thể xảy ra trong môi trường
bên ngoài và mô hình kinh doanh của họ để xem có thể cản trở khả năng đạt được mục tiêu của họ hay không).
v There are 4 principles relating to risk assessment:
6) The organization specifies objectives with sufficient clarity to enable the identification and assessment of
risks relating to objectives (đơn vị cụ thể hoá mục tiêu tạo điều kiện cho việc nhận dạng và đánh giá rủi ro liên
quan đến đạt được mục tiêu)
7) The organization identifies risks to the achievement of its objectives across the entity and analyzes risks as a
basis for determining how the risks should be managed (đơn vị nhận dạng các rủi ro đe doạ mục tiêu và phân
tích rủi ro để quản lý các rủi ro này)
8) The organization considers the potential for fraud in assessing risks to the achievement of objectives (đơn vị
nhân nhắc khả năng có gian lận khi đánh giá rủi ro đe doạ mục tiêu của đơn vị)
9) The organization identifies and assesses changes that could significantly impact the system of internal control
(đơn vị nhận dạng và đánh giá các thay đổi có thể ảnh hưởng đáng kể đến hệ thống KSNB)
v Entity-wide objectives (mục tiêu toàn đơn vị):
• Top management has established entity-wide objectives (Quản lý cấp cao đặt ra các mục tiêu cho toàn bộ đơn vị).
• Include board statements of what an entity desires to achieve and are supported by related strategic plans (Bao
gồm các tuyên bố của hội đồng quản trị về những gì tổ chức mong muốn đạt được và được hỗ trợ bởi các kế
hoạch chiến lược liên quan).
• Communicated to employees and BODs (Truyền đạt tới nhân viên và HĐQT).
• Related to and consistent with the entity’s strategies (Liên quan đến và nhất quán với chiến lược của tổ chức).
• Entity-wide objectives, strategic plans and current conditions are the basis for developing business plans and
budgets (Các mục tiêu, kế hoạch chiến lược và điều kiện hiện tại của toàn bộ đơn vị là cơ sở để xây dựng kế
hoạch kinh doanh và ngân sách kinh doanh).
v Activity-level objectives (Các mục tiêu ở cấp độ hoạt động):
• Flow from and are linked with entity-wide objectives (liên kết với các mục tiêu của toàn bộ đơn vị).
• Consistent with each other (Nhất trí với nhau).
• Frequently stated as goals with specific targets and deadlines for all significant business processes (Thường
được thể hiện dưới dạng các mục tiêu và thời hạn cụ thể cho tất cả các quy trình kinh doanh quan trọng).
• Management has identified what activity level objectives are important (critical success factors) to achieve
entity-wide level (Ban quản lý xác định mục tiêu cấp độ hoạt động nào là quan trọng (yếu tố thành công quan
trọng) để đạt được cấp độ toàn đơn vị).
VI. Specifies suitable objectives (đơn vị cụ thể hoá mục tiêu): v Operations objectives v Reporting objectives
• External financial reporting
• External non-financial reporting • Internal reporting v Compliance objectives
1. Operations objectives: XEM SÁCH/103
v Reflects management’s choices (ex: providing customers with a broad range of products at prices consistently
lower than its competitors) (Phản ánh các lựa chọn của ban quản lý (ví dụ: cung cấp cho khách hàng nhiều loại
sản phẩm với giá luôn thấp hơn so với đối thủ cạnh tranh)).
v Considers tolerances for risk (cân nhắc ngưỡng chịu đựng rủi ro).
v Includes operations and financial performance goals (ex: increasing net income by 5% the following year)
(Bao gồm các mục tiêu về hoạt động và hiệu quả tài chính (ví dụ: tăng thu nhập ròng thêm 5% vào năm sau)).
v Forms a basis for committing of resources (tạo nên nền tảng cho những cam kết tài nguyên).
Æ Do not based on external requirements (Không dựa trên yêu cầu bên ngoài)
Æ The achievement may change due to changes in the external environment (những thành tựu có thể thay đổi
bởi những thay đổi bên ngoài).
Æ An operations objective can be complementary and reinforcing a compliance or reporting objectives (Mục
tiêu hoạt động có thể bổ sung và củng cố mục tiêu tuân thủ hoặc báo cáo).
2. Reporting objectives: XEM SÁCH/104
v Pertain to the preparation of reports that encompass reliability, timeliness, transparency and other terms as set
forth by regulators, standard-setting bodies, or by the entity’s policies (Liên quan đến việc lập các báo cáo bao
gồm độ tin cậy, kịp thời, minh bạch và các điều khoản khác do cơ quan quản lý, cơ quan thiết lập tiêu chuẩn
hoặc chính sách của đơn vị đưa ra).
• External financial reporting complies with applicable accounting standards, considers materiality, and reflects
the entity’s activities (Báo cáo tài chính bên ngoài phù hợp với các chuẩn mực kế toán hiện hành, xem xét tầm
quan trọng và phản ánh các hoạt động của đơn vị).
• External non-financial reporting complies with laws, rules, regulations, standards and frameworks, considers
precision, and reflects the entity’s activities (Báo cáo phi tài chính tuân thủ pháp luật, quy tắc, quy định, tiêu
chuẩn và khuôn khổ, cân nhắc đến độ chính xác và phản ánh các hoạt động của đơn vị).
• Internal reporting complies with management’s choice, considers precision, and reflects the entity’s activities
(Báo cáo nội bộ phù hợp với sự lựa chọn của ban quản lý, xem xét tính chính xác và phản ánh các hoạt động của đơn vị).
Æ Based on external requirements (dựa trên yêu cầu bên ngoài)
Æ The achievement is largely under the entity’s control (Thành tựu này phần lớn nằm dưới sự kiểm soát của đơn vị).
3. Compliance objectives: XEM SÁCH/104
v Reflects external laws and regulations (Phản ánh các luật và quy định bên ngoài).
v Considers tolerances for risk (Cân nhắc ngưỡng chịu đựng rủi ro).
Æ Based on external requirements (dựa trên yêu cầu bên ngoài)
Æ The achievement is largely under the entity’s control (Thành tựu này phần lớn nằm dưới sự kiểm soát của đơn vị).
Æ A compliance objective sometimes prevents an operations objective (Mục tiêu tuân thủ đôi khi cản trở mục tiêu hoạt động).
VII. Identifies & Analyzes risks (vị nhận dạng các rủi ro đe doạ mục tiêu và phân tích rủi ro để quản lý các rủi ro này):
1. Identifies risks (nhận dạng các rủi ro): XEM SÁCH/105
v Identifies risks at the entity, subsidiary, division, operating unit, functional level relevant to the achievement
of objectives (entity-wide and activity-level) (Xác định rủi ro tại đơn vị, công ty con, bộ phận, đơn vị điều
hành, cấp độ chức năng liên quan đến việc đạt được các mục tiêu (toàn đơn vị và cấp độ hoạt động)).
v Considers both external and internal factors and their impact on the achievement of objectives (Xem xét cả
các yếu tố bên ngoài và bên trong và tác động của chúng đối với việc đạt được các mục tiêu).
v Puts into place effective risk identification mechanisms that involve appropriate level of management (Xây
dựng cơ chế xác định rủi ro hiệu quả liên quan đến mức độ quản lý thích hợp).
2. Analyzes the identified risks (phân tích các rủi ro đã nhận dạng): XEM SÁCH/108
v Estimates the significance of risks indentified (Ước tính tầm quan trọng của các rủi ro đã xác định).
v Assesses the likelihood of their occurring (Đánh giá khả năng xảy ra của chúng).
3. Determines how to respond to risks identified and analyzed (xác định cách ứng phó với các rủi ro đó): XEM SÁCH/109
v Considers how the risks should be managed and whether to accept, avoid, reduce or share the risks (Cân nhắc
cách quản lý rủi ro và liệu có nên chấp nhận, tránh, giảm thiểu hoặc chia sẻ rủi ro). Specify objectives È Identify risks È
Estimate the significance of risks È The entity’s risk tolerance È YES Accept the risks No action NO Sharing Avoidance Reduction
Determine actions to respond to YES the risk, select and develop associated control activities NO NO Residual risk exceeding No action risk tolerance? YES Revisit and revise the response/actions as well as associated control activities Risk identification Risk analysis Risk response (1) Risk identification:
v Entity level risks: XEM SÁCH/105 External PEST analysis: factors + P – political + E – economic + S – Social + T – technological
And natural environment and foreign operations
The 5 forces model – Michael Porter:
- Bargaining power of suppliers (Khả năng thương lượng của nhà cung cấp).
- Bargaining power of buyers (Khả năng thương lượng của người mua).
- Rivalry among existing competitors (cạnh tranh giữa các đối thủ).
- Threat of substitute products or services (mối đe doạ từ các sp&dv thay thế).
- Threat of new entrants (Mối đe dọa từ những người mới tham gia).
- Infrastructure (Cơ sở hạ tầng).
- Management structure: a change in management responsibilities (Cấu trúc quản lý: thay đổi về Internal
trách nhiệm quản lý). factors
- Personnel: the quality of personnel hired (Nhân sự: chất lượng của nhân sự được tuyển dụng).
- Access to assets (Tiếp nhận tài sản).
- Technology: a disruption of IS processing (công nghê … : hê …
thống xử lý thông tin bị gián đoạn)
v Transaction level risks: XEM SÁCH/107
Risks should be identified and analyzed in every business process as follows: • Purchasing/procurement • Sales • Production/manufacturing • Marketing • Finance • R&D
(2) Risk analysis: XEM SÁCH/108
v Assessment of the likelihood of the risk occurring and estimation of its impact (Đánh giá khả năng xảy ra rủi
ro và ước tính tác động của nó).
v Level of management: the entity puts in place effective risk assessment mechanisms that involve appropriate
level of management with expertise (Mức độ quản lý: Đơn vị đã thiết lập một cơ chế đánh giá rủi ro hiệu quả,
bao gồm mức độ quản lý phù hợp với chuyên môn).
v Significant risk: likelihood of risk occurring and impact, velocity or speed of impact, persistence or duration
of time of impact (Rủi ro đáng kể: khả năng rủi ro xảy ra và ảnh hưởng, tốc độ hoặc tốc độ ảnh hưởng, thời
gian hoặc thời gian ảnh hưởng).
v Inherent and residual risk: management should consider both (Rủi ro tiềm tàng và rủi ro còn lại: Ban quản lý nên xem xét cả hai).
(3) Risk response: XEM SÁCH/109
v A risk response is a management’s action to manage the risk identified and assessed in order to ensure residual
risk not exceeding the level of risk acceptance (Ứng phó rủi ro là hành động của ban quản lý để quản lý rủi ro
được xác định và đánh giá nhằm đảm bảo rủi ro còn lại không vượt quá mức chấp nhận rủi ro).
• Acceptance: no action is taken (Chấp nhận : không có hành động nào được thực hiện).
• Avoidance: get rid of the activities giving rise to risk (Tránh: loại bỏ các hoạt động làm phát sinh rủi ro).
• Reduction: action is taken to reduce risk (Giảm thiểu: hành động được thực hiện để giảm rủi ro).
• Sharing: reducing risk by transferring or sharing a portion of the risk (ex: buying insurance, forming joint-
venures) (Chia sẻ: giảm rủi ro bằng cách chuyển giao hoặc chia sẻ một phần rủi ro (ví dụ: mua bảo hiểm,
thành lập liên doanh)). VIII. Assess fraud risk: v Point of focus:
1) Considers various types of fraud (Xem xét các loại gian lận).
2) Assess incentive and pressures (Đánh giá động cơ và áp lực): XEM SÁCH/112
3) Assess opportunities (Đánh giá cơ hội): XEM SÁCH/112
4) Assess attitude & rationalizations (Đánh giá thái độ và sự biện minh cho hành vi gian lận): XEM SÁCH/113
1. Types of fraud: XEM SÁCH/111
• Fraudulent reporting (gian lận trong việc lập và trình bày báo cáo)
• Corruption (tham ô)
• Misappropriation of assets (biển thủ tài sản)
• Management override (nhà quản lý lạm dụng quyền): XEM SÁCH/111
IX. Identifies & Analyzes significant change: v Point of focus:
1) Assess changes in the external environment (Đánh giá thay đổi môi trường bên ngoài)
2) Assess changes in business model (Đánh giá thay đổi mô hình kinh doanh)
3) Assess changes in leadership (changing significant personnel) (Đánh giá thay đổi lãnh đạo (thay đổi nhân sự
quan trọng)): XEM SÁCH/115
1. Changes in the external environment: XEM SÁCH/114
• Changing regulatory and economic environment (Thay đổi môi trường pháp lý và kinh tế).
• Changing physical environment like natural disasters, diseases,… (Thay đổi môi trường vật lý như thiên tai, dịch bệnh,...).
2. Changes in business model: XEM SÁCH/114
• Entering new business lines (Tham gia các lĩnh vực kinh doanh mới).
• Significant acquisition or divestitures (Mua lại hoặc thoái vốn đáng kể).
• Foreign operations (mở rộng hoạt động ra nước ngoài)
• Rapid growth (tăng trưởng nhanh chóng)
• New technology (kỹ thuật mới) C. CONTROL ACTIVITIES
v Control activities are the actions established by policies and procedures to help ensure that management
directives to mitigate risks to the achievement of objectives are carried out (Các hoạt động kiểm soát là các
hành động được thiết lập bởi các chính sách và thủ tục giúp đảm bảo rằng các chỉ thị quản lý được thực hiện
nhằm giảm thiểu rủi ro đối với việc đạt được mục tiêu).
v Control activities are performed at all levels of the entity and at various stages within business processes, and
over the technology environment (Các hoạt động kiểm soát được thực hiện ở tất cả các cấp của đơn vị, ở tất cả
các giai đoạn của quy trình kinh doanh và trong môi trường công nghệ).
v There are 3 principles relating to control activities:
10) The organization selects and develops control activities that contribute to the mitigation of risks to the
achievement of objectives to acceptable levels (đơn vị lựa chọn và xây dựng các hoạt động kiểm soát để giảm
thiểu rủi ro xuống mức thấp nhất có thể chấp nhận được).
11) The organization selects and develops general control activities over technology to support the achievement
of objectives (đơn vị lựa chọn và xây dựng các hoạt động kiểm soát chung đối với công nghệ nhằm hỗ trợ cho
việc đạt được các mục tiêu của đơn vị)
12) The organization deploys control activities through policies that establish what is expected and procedures
that put policies into place (đơn vị triển khai các hoạt động kiểm soát thông qua chính sách và thủ tục kiểm soát).
v Types of control activities:
• Preventive versus detective controls (Kiểm soát phòng ngừa và phát hiện).
• Compensating controls (Kiểm soát bù trừ): controls are designed to detect and compensate for the lack or
deficiency of desired controls (Kiểm soát được thiết kế để phát hiện và bù đắp cho việc thiếu kiểm soát cần thiết).
• Manual versus automated controls (Kiểm soát thủ công so với tự động).
• Controls with audit trails and without audit trails (Kiểm soát có theo dõi kiểm tra và không theo dõi kiểm tra).
• General versus application controls (Kiểm soát chung và kiểm soát ứng dụng).
v Types of transaction control activities:
• Segregation of duties (Phân chia nhiệm vụ).
• Authorizations and Approvals (Ủy quyền và Phê duyệt).
• Verifications (Xác minh).
• Physical controls (Kiểm soát vật lý).
• Controls over standing data (Kiểm soát dữ liệu hiện có)
• Reconciliations (Đối chiếu).
• Supervisory controls (Giám sát và kiểm soát)
(1) Segregation of duties (Phân chia nhiệm vụ):
v Duties should be divided or segregated among different people to reduce the risk of error or inappropriate of
fraudulent actions (Các nhiệm vụ nên được phân chia hoặc tách biệt giữa những người khác nhau để giảm rủi
ro sai sót hoặc hành vi gian lận không phù hợp).
v Entails generally dividing the responsibility of recording, authorizing and approving transactions and
handling the related assets (Nói chung là phân chia trách nhiệm ghi chép, ủy quyền và phê duyệt các giao dịch
và xử lý các tài sản liên quan).
v Separation among the following functions (Tách biệt giữa các chức năng sau):
• Approval and custody of assets (Phê duyệt và bảo quản tài sản).
• Recording/book-keeping and custody of assets (Ghi chép/ kế toán và bảo quản tài sản).
• Approval and recording (Phê duyệt và ghi chép).
(2) Authorizations and Approvals (Ủy quyền và Phê duyệt):
v Authorization is the delegation of authority that may be general or specific (ủy quyền chung hoặc cụ thể).
• General authorization (ủy quyền chung): giving a department permission to expend funds from an approved
budget (cho phép một bộ phận chi tiêu tiền từ ngân sách đã được phê duyệt).
• Specific authorization (Ủy quyền cụ thể): requiring the signature or electronic approval of a transaction by a
person with approval authority (yêu cầu chữ ký hoặc phê duyệt điện tử của một giao dịch bởi người có thẩm quyền).
v Approval is to affirm that a transaction is valid (Phê duyệt là xác nhận rằng giao dịch là hợp lệ).
(3) Physical controls (Kiểm soát vật lý):
v Measures to deter or prevent unauthorized access to equipment, inventories, securities, cash and other
sensitive assets (Các biện pháp phát hiện hoặc ngăn chặn truy cập trái phép vào thiết bị, hàng tồn kho, chứng
khoán, tiền mặt và các tài sản nhạy cảm khác).
(4) Verifications versus Reconciliations (Xác minh & Đối chiếu):
v Verifications compare 2 or more items with each other or compare an item with a policy and perform a
follow-up action when they do not match (Xác minh so sánh hai hoặc nhiều mục với nhau hoặc so sánh một
mục với chính sách và thực hiện theo dõi nếu không phù hợp).
v Reconciliations compare 2 or more data elements and if differences are identified, action is taken to bring the
data into agreement, ex: bank, AR and AP reconciliations with the bank, the clients and the suppliers (So sánh 2
hoặc nhiều yếu tố dữ liệu và nếu phát hiện sự khác biệt, thực hiện các biện pháp để thống nhất dữ liệu, ví dụ:
đối chiếu ngân hàng, các khoản phải thu và các khoản phải trả với ngân hàng, khách hàng và nhà cung cấp).
(5) Controls over standing data (Kiểm soát dữ liệu hiện có):
v Standing data such as the price mater file, is often used to support the processing of transactions within a
business process (Dữ liệu cố định, chẳng hạn như tệp giá, thường được sử dụng để hỗ trợ xử lý các giao dịch
trong quy trình kinh doanh).
v Controls over the processes to populate, update and maintain the accuracy, completeness, and validity of this
data (Kiểm soát quá trình điền, cập nhật và duy trì tính chính xác, đầy đủ và hợp lệ của dữ liệu này). v There are:
• General controls (Kiểm soát chung):
Ø Govern the design, security and use of computer programs and the security of data files in general throughout
the entity’s IT infrastructure (Quản lý việc thiết kế, bảo mật và sử dụng các chương trình máy tính cũng như
bảo mật các tệp dữ liệu nói chung trong toàn bộ cơ sở hạ tầng CNTT của đơn vị)
Ø Apply to all computerized applications and consist of a combination of hardware, software, and manual
procedures that create an overall control environment to IT (Áp dụng cho tất cả các ứng dụng được vi tính hóa
và bao gồm sự kết hợp giữa phần cứng, phần mềm và các quy trình thủ công để tạo ra một môi trường kiểm soát tổng thể cho CNTT).
Ø Include software controls, physical hardware controls, computer operations controls, data security controls,
controls over the systems implementation process, and administrative controls (Bao gồm kiểm soát phần mềm,
kiểm soát phần cứng vật lý, kiểm soát hoạt động máy tính, kiểm soát bảo mật dữ liệu, kiểm soát quá trình triển
khai hệ thống và kiểm soát quản trị).
• Application controls (Kiểm soát ứng dụng):
Ø Are specific controls unique to each computerized application, such as payroll, revenue, expenditure,
inventory cycles (mỗi ứng dụng máy tính có các biện pháp kiểm soát cụ thể như tiền lương, thu nhập, chi phí, chu kỳ hàng tồn kho).
Ø Include both automated and manual procedures that ensure that only authorized data are completely and
accurately processed by that application (Bao gồm cả quy trình tự động và thủ công để đảm bảo rằng chỉ những
dữ liệu được ủy quyền mới được ứng dụng đó xử lý đầy đủ và chính xác).
Ø Can be classified as (có thể được phân loại thành):
¡ Input controls (kiểm soát đầu vào)
¡ Processing controls (kiểm soát quá trình)
¡ Output controls (kiểm soát đầu ra)
(6) Supervisory controls (kiểm soát giám sát):
v Assess whether other transaction control activities are being performed completely, accurately, and according
to the policy and procedures (Đánh giá xem các hoạt động kiểm soát giao dịch khác có được thực hiện đầy đủ,
chính xác và tuân theo chính sách và quy trình).
v Are typically performed by the management of a business process or executive team members (Thường được
thực hiện bởi ban quản lý quy trình kinh doanh hoặc thành viên nhóm điều hành).
v Some types of supervisory controls (Một số loại kiểm soát giám sát):
• Review and double check over high risk transactions (Xem xét và kiểm tra kỹ các giao dịch có rủi ro cao).
• Employee performance reviews (Đánh giá hiệu suất của nhân viên).
• Budget vs actual analysis (Phân tích ngân sách so với thực tế).
D. INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION
v Information is necessary for the entity to carry out IC responsibilities to support the achievement of its
objectives (Thông tin là cần thiết cho một đơn vị để thực hiện nhiệm vụ IC của mình để hỗ trợ đạt được mục tiêu của mình).
v Communication is the continual, iterative process of providing, sharing, and obtaining necessary information
(Truyền thông là một quá trình lặp đi lặp lại liên tục để cung cấp, chia sẻ và thu thập thông tin cần thiết).
• Internal communication: the means by which information is disseminated throughout the entity, flowing up,
down and across the entity (Truyền thông nội bộ: cách thông tin được truyền đi trong toàn bộ đơn vị).
• External communication: includes inbound communication of relevant external information and providing
information for external parties in response to requirements and expectations (Truyền thông bên ngoài: bao gồm
truyền thông bên trong về thông tin bên ngoài có liên quan và cung cấp thông tin cho các bên bên ngoài để đáp
ứng các yêu cầu và mong đợi).
v There are 3 principles relating to control activities:
13) The organization obtains or generates and uses relevant, quality information to support the functioning of
internal control (đơn vị thu thập, tạo lập và sử dụng các thông tin thích hợp và có chất lượng nhằm hỗ trợ cho
sự vận hành của KSNB)
14) The organization internally communicates information, including objectives and responsibilities for internal
control, necessary to support the functioning of internal control (đơn vị truyền thông trong nội bộ các thông tin
cần thiết nhằm hỗ trợ cho sự vận hành của KSNB).
15) The organization communicates with external parties regarding matters affecting the functioning of internal
control (đơn vị truyền thông với bên ngoài các vấn đề có tác động tới việc vận hành của KSNB).
XIII. Generates and uses relevant, quality information (tạo lập và sử dụng các thông tin thích hợp và có chất lượng): v Point of focus:
• Identify information requirements (Xác định nhu cầu thông tin)
• Capture internal and external sources of data (Thu thập các nguồn dữ liệu bên trong và bên ngoài).
• Process relevant data into information (Xử lý dữ liệu liên quan thành thông tin).
• Maintain quality throughout processing (Duy trì chất lượng trong suốt quá trình).
• Consider costs and benefits (Xem xét chi phí và lợi ích).
v Information quality (thông tin chất lượng cần đảm bảo): Accessible (dễ dàng
Easy to obtain by those who need it (thông tin phải thuận tiện cho. người có nhu cần truy cập) sử dụng khi cần) Correct (đúng đắn)
Accurate and complete (thông tin phải chính xác và đầy đủ) Current (cập nhật)
Updated (thông tin phải cập nhật, phản ánh tình hình hiện tại). Protected (bảo mật)
Access to sensitive information is restricted to authorized persons (các thông tin
nhạy cảm thì chỉ người được uỷ quyền mới có thể tiếp cận) Retained (lưu trữ)
Available over an extended period of time (thông tin phải được lưu trữ đủ lâu để
phục vụ yêu cầu của đối tượng bên trong và bên ngoài)
Sufficient (đủ chi tiết) Enough information at the right level of detail relevant to information requirement
(thông tin phải đủ chi tiết theo yêu cầu của người sử dụng) Timely (kịp thời)
Available when needed (thông tin lưu trữ trên hệ thống phải đảm bảo đáp ứng kịp thời khi có yêu cầu) Valid (có thật)
Obtained from authorized sources (thông tin phải xuất phát từ nguồn đáng tin cậy,
được xử lý theo đúng quy trình và phản ánh những sự kiện diễn ra trên thực tế). Verifiable (có thể xác
Supported by evidence (phải có bằng chứng để kiểm tra lại khi cần thiết và có minh được)
người chịu trách nhiệm về chất lượng thông tin)
XIV. Communicates internally (truyền thông trong nội bộ): v Point of focus:
• Communicate IC information (Trao đổi thông tin về IC).
• Communicate with BODs (Trao đổi với HĐQT).
• Provide separate communication lines: whistle-blower hotlines (Cung cấp các đường dây liên lạc riêng:
đường dây nóng của người tố cáo).
• Select relevant methods of communication (Lựa chọn các phương thức liên lạc phù hợp).
XV. Communicates externally (truyền thông trong bên ngoài): v Point of focus:
• Communicate to external parties (Giao tiếp với bên ngoài).
• Enable inbound communications (Cho phép truyền thông trong nước)
• Communicate with BODs (Trao đổi với HĐQT).
• Provide separate communication lines: whistle-blower hotlines (Cung cấp các đường dây liên lạc riêng:
đường dây nóng của người tố cáo).
• Select relevant methods of communication (Lựa chọn các phương thức liên lạc phù hợp).
E. MONITORING ACTIVITIES
v Evaluate the quality of IC over time (Đánh giá chất lượng của IC theo thời gian).
v Assess whether each of the 5 components and relevant principles is present and functioning (Đánh giá xem
từng thành phần trong số 5 thành phần và các nguyên tắc có liên quan có hiện diện và hoạt động hay không). v There are:
• Ongoing (đánh giá thường xuyên)
• Separate evaluations (giám sát định kỳ).
v There are 2 principles relating to monitoring activities:
16) The organization selects, develops and performs ongoing and/or separate evaluations to ascertain whether
the components of internal control are present and functioning (đơn vị lựa chọn, xây dựng và thực hiện giám sát
thường xuyên hoặc định kỳ để đảm bảo rằng các bộ phận của KSNB hiện hữu và hoạt động hữu hiệu).
17) The organization evaluates and communicates internal control deficiencies in a timely manner to those
parities responsible for taking corrective action, including senior management and the BODs, as appropriate
(đơn vị đánh giá và truyền đạt kịp thời các khiếm khuyết về KSNB cho các cá nhân có trách nhiệm để họ thực
hiện các hành động sửa chữa, bao gồm các nhà quản lý cấp cao và HĐQT, khi cần thiết)
(1) Ongoing evaluations (đánh giá thường xuyên):
v Monitoring activities are built into business processes and performed on a real-time basis, react to changing
conditions (Các hoạt động giám sát được xây dựng trong các quy trình kinh doanh và được thực hiện trên cơ sở
thời gian thực, phản ứng với các điều kiện thay đổi).
v Are performed by line operating and functional managers (được thực hiện bởi các nhà quản lý chức năng và điều hành).
v Ex: monthly or periodical meetings with line operating and functional managers; review of performance
reports (tổ chức các cuộc họp hàng tháng hoặc thường xuyên với các nhà quản lý hoạt động tuyến đầu và các
nhà quản lý chức năng; Đánh giá báo cáo hiệu suất).
(2) Separate evaluations (giám sát định kỳ):
v Monitoring activities are NOT built into business processes and performed periodically (Hoạt động giám sát
KHÔNG được xây dựng trong quy trình nghiệp vụ và thực hiện định kỳ).
v Are usually performed by internal auditors, external auditors to take a fresh look (Thường được thực hiện bởi
kiểm toán viên nội bộ, kiểm toán viên bên ngoài xem xét lại).
v How to evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls
• Achievement of objectives (Hoàn thành mục tiêu).
• Relevant principles (Nguyên tắc liên quan).
• Component operating together (Các thành phần làm việc cùng nhau)
v Evaluating tools and methods
• Tools: checklist, questionnaire and flowcharts • Methods:
Ø Benchmark with other companies (known for effectiveness of internal control) (So sánh với các công ty khác
(được biết đến với hiệu quả của kiểm soát nội bộ)).
Ø Service from consulting agencies (Dịch vụ tư vấn). v Documented evaluations:
• Depends on the size and complexity of each business (Tùy thuộc vào quy mô và độ phức tạp của từng DN).
• Large enterprises always have policy manuals (Các doanh nghiệp lớn luôn có sổ tay chính sách).
• Small business often pay little attention to documentation (Các doanh nghiệp nhỏ thường ít chú ý đến tài liệu).




