























Preview text:
5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch THE UNIVERSITY OF DANANG
UNIVERSITY OF FOREIGN LANGUAGE STUDIES FACULTY OF ENGLISH -----🙞🙞🙞🙞🙞----- TRANSLATION THEORY Students : Class : Translation theory Teacher : Nguyễễn Th Th ị u Hướ ng Danang, July 2022 CONTENT:
COURSE 1 (03/06)........................................................................................................................................2
# ENTRY 1: WHAT IS TRANSLATION?..................................................................................2 1 about:blank 1/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch
# ENTRY 2: THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERPRETATION & TRANSLATION........5
COURSE 2 : (08/06)......................................................................................................................................6
#ENTRY 1: THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERPRETATION & TRANSLATION.........6
COURSE 3 : (10/06)......................................................................................................................................8
#ENTRY 1: THE ANALYSIS OF TEXT....................................................................................8
COURSE 4 : (17/06)....................................................................................................................................13
# ENTRY 1: LANGUAGE AND CULTURE:..........................................................................13
# ENTRY 2: PROBLEMS OF EQUIVALENCE......................................................................15
COURSE 5 : (22/06)....................................................................................................................................18
# ENTRY 1: TRANSLATION EQUIVALENCE......................................................................18
COURSE 6 : (24/06)....................................................................................................................................19
# ENTRY 1: UNTRANSLATABLILITY?................................................................................19
# ENTRY 2: LOSS AND GAIN?..............................................................................................20
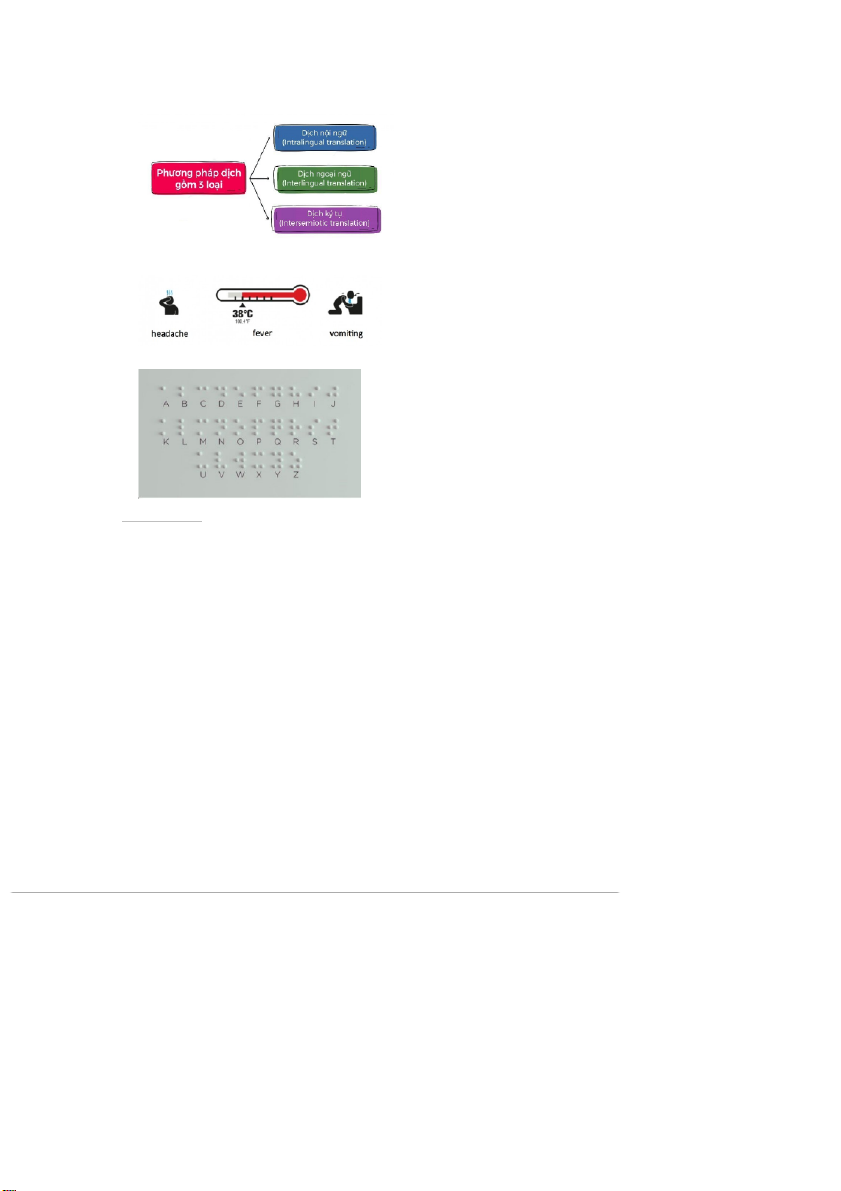
# ENTRY 3: TRANSLATION METHODS..............................................................................21
COURSE 7 : (29/06)....................................................................................................................................24
# ENTRY 1: SEMANTIC AND COMMUNICATIVE TRANSLATION.................................24
# ENTRY 2: THE TRANSLATION OF METAPHORS AND SIMILES.................................25
# ENTRY 3: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSLATION.....................................................................26
# ENTRY 4: THE TRANSLATION OF PROPER NAMES AND INSTITUTIONAL NAMES.
...................................................................................................................................................26 COURSE 1 (03/06)
# ENTRY 1: WHAT IS TRANSLATION?
1. What is translation? / Definition: -
Translation is the replacement of textual material in one language ( source language) by
equivalent material in another language (target language). Textual material: ng ữ liệ u
If we translate an English song to a Vietnamese version.
English - source language, Vietnamese – target language. -
Translation is the process of conveying messages across linguistic and cultural barriers. Convey: chuyển đổ i
Message is an underlying meaning. Ex: What time is it? -> for
m(gram&vocab): Mấấy gi r ờ ồồi con?
(But When you play video games at 10p.m)
-> message (underlying meaning): Có biễất gi là ờ mấấy gi ờ rồồi khồng hả ? Explicit: It’s 10p.m
Implicit: It’s too late. Unless you go to bed now, you will regret.
Linguistic: grammar & lexis
Cultural barrier: Khỏ e như trấu 2 about:blank 2/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 3/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch ✿ LOOKING B ACK: 1. Exercise 1:
1) In translation, the form oft he source language (the language of the text that is to be translated)
is replaced by the form of the target language (the language of the translated text).
2) The purpose of translation is to transfer the meaning of the source language (SL) into the target language (TL).
3) This is done by going from the form of the first language to the form of a second language by
way of semantic structure . It is meaning which is being transferred and must remain unchanged. Only the form changes.
4) Translation not only involves understanding the general meaning of the communication but calls
upon the ability to understand the culture of the communication. 2. Exercise 2: -
The translator must have a perfect understanding of his author’s message and meaning . 4 about:blank 4/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch -
The translator should have complete mastery of both source and target language. -
The translator should not translate word for word . -
The translator should beware of Latinisms and use idiomatic language. -
The translator should strive after a smooth, and elegant, unpretentious and even style.
3. Exercise 3: Laws of translation: -
The translation should give a complete transcript of the ideas if the original work.
(B n dả ch ịnễn ph i trảuyễồn t i đ ả ấồy đ ủý nghĩa c a ủ văn b n ả gồấc đó.) -
The style and manner of writing should be of the same character as that of the original.
(Phong cách và đ c điặ m vểiễất c a v ủ ăn b n d ả ch ịcấồn ph i t ả ư n
ơ g ứng vớ i bả n gồấc.) -
The translation should have all the ease of the original composition. (B n d ả chị ph i đ ả c ư d ợ ễễ đ c ọ nh b ư ản gồấc.) 4. Exercise 4: -
L1: the first (and normally native) language of the writer, reader, speaker, etc. -
L2: the second language of the writer, reader, speaker, etc. (often their strongest foreign language) -
SL: source language (the language the text was originally written in) -
ST: source text (the original text) -
TL: target language (the language of the translation) -
TT: target text (the translated text).
# ENTRY 2: THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERPRETATION & TRANSLATION INTERPRETATION TRANSLATION Oral/ Speak Written/ Write
Little time, immediately, simultaneous. A lot of time On-the-spot Dictionary No need a complete accuracy Need a complete accuracy
Convey the essence of the message
Convey all ideas including details of the source immediately text.
Performance is more like that of an actor
Performance is more like that of a writer. -
Complex tasks in the field of translation and interpretation: General knowledge Cultural knowledge
Specific translative/ interpretive skills. ✿ LOOKING BACK: 1. Exercise 1:
Translation implies carefully analyzing the message given within the context of a particular
linguistic code and transferring this message into another written linguistic code and
transferring this message into another written linguistic code. Interpretation, on the other hand,
means doing the same but orally and simultaneously. 5 about:blank 5/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 6/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch Type
Speed (no time-> have time)
Accuracy (exact->summarized) Prepared translation 4 (plenty of time) 1 (the most accurate) Sight translation 3 2 Consecutive interpretation 2 3 Simultaneous interpretation 1 (simultaneously, fastest) 4 ✿LOOKING BACK:
1. Exercise 2: Match of definition. -
Prepared translation: involves the preparation of a translation outside class and it is then
constructively criticized by both students and teachers. -
Sight translation: includes an immediate , oral rendition based on a written text. -
Consecutive interpretation: is the process of listening to a speech or lecture in one language and
at a certain moment, transcribing and summarizing it orally, in another language. The time lapse
between the speech and your interpretation varies. -
Simultaneous interpretation: involves the immediate ,s imultaneous interpretation of whati s
being said into another language.
2. Extra exercise: the different translation version in different content.
a. The extract is taken from the subtitles from the episode “Hannah Montana” retrieved from YouTube.
“Look at the size of this bad boy
He put up quite a battle, too. It was him, then it was me,
then it was him, then it was me
Dad, you got it from the fish mart
Yeah, but you should’ve seen the size of the lady that tried to take him from me
It was her, then it was me, then it was
Alright. Alright, Dad, I get it.”
So, what’s it gonna be, Bucky, pan-fried or barbecued ? -
Barbecued -> đồồ nướ ng
b. The text is taken from the website of Brisbane city council (Australia). The website is
available in many languages including Chinese, Korean, Japanese and Vietnamese. - “ Swimming pools in Brisbane
There are 20 Council swimming pools across Brisbane offering opportunities for fun, fitness and
recreation. Come to one of Council’s pools to cool off, relax, learn to swim, do stroke
development, attend swimming club or swim laps.
There are indoor and outdoor pools, with a number of pools being heated. Water polo is played
at a number of locations. Many pools have these disabled access/ facilities. Other facilities may
include slides and play equipment, barbecued, and kiosks. All pools have change rooms with hot and cold showers. 7 about:blank 7/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch -
Barbeques -> barbeques (remain unchanged in translation version).
The reason why there is a difference between the two translation versions from English into Vietnamese is the cite. -
In the first one, it’s cited from Youtube, and the most general audience of the video can be
Vietnamese, living in Vietnam. They might have no idea about English. Therefore, translators
translated the word “barbeques” into the Vietnamese word “đồồ nướng”. -
In the second one, it’s cited from the website of Brisbane city council and posted on the
Australian website. Most readers can be Australian- Vietnamese and they know English.
Therefore, translator remained unchanged when translating into Vietnamese in order to keep
cultural meaning of “barbeques” perfectly.
Draw a lesson: In order to have a good translation, we need to identify the type of readers and
whether they can understand the target languages through the platform of poses, on top of
approaching the situation, and context of a source language. COURSE 3 : (10/06) #ENTRY 1: THE ANALYSIS OF TEXT 1. 4 types of text style: -
Narrative: a dynamic sequence of events with emphasis on verbs, verb- nouns, phrase verbs. -
Description: static with emphasis on linking verbs (am/is/are, feel, look, become, sound, taste), adjectives, -
Discussion: a treatment of ideas with emphasis on abstract noun (concepts), verbs of thought
(believe, suppose, think), mental activity (consider, argue), logical argument and connectives. -
Dialogue: with emphasis on colloquialisms and phaticisms. 1.1.Looking back -
Narrative: A few years ago, I spent a week in the Dominican Republic. The week was over, and I
was at the airport ready to leave when I discovered, to my dismay, that I had forgotten one of my suitcases at my hotel… - Description: The fil
m is set in America and tells the story of a young boy who runs a lonely,
isolated motel with his elderly mother. They live in a large, old house next to the motel, but
although we often hear their conversation, we never see the mother in person… -
Discussion: It is my opinion that too many people are controlled by television. The reason for
this is that they become addicted and only sit at home and watch it. -
Dialogue: Oh, we got married last year. We live in Birmingham now. Look, why don’t you come
up and visit us sometimes? Pat would love to see you again. 2. Stylistic scales: Formal Officialese
The consumption of any nutriments whatoever is categorically
prohibited in this establishment. Official
The consumption of nutriments is prohibited. Formal
You are requested not to consume food in this establishment. Neutral Neutral Eating is not allowed here. Informal Informal Please don’t eat here. Colloquial
Please can’t feed your face here. Slang Lay off the nosh. 8 about:blank 8/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 9/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch -
Non- verbal elements: images… 4. Exercise:
Source text: The text is taken from the website of Brisbane city council (Australia). The website is
available in many languages including Chinese, Korean, Japanese and Vietnamese. Swimming pools in Brisbane
There are 20 Council swimming pools across Brisbane offering opportunities for fun,
fitness and recreation. Come to one of Council’s pools to cool off, relax, learn to swim, do stroke
development, attend swimming club or swim laps.
There are indoor and outdoor pools, with a number of pools being heated. Water polo is
played at a number of locations. Many pools have these disabled access/ facilities. Other
facilities may include slides and play equipment, barbecued and kiosks. All pools have change
rooms with hot and cold showers. Target source: Các bể b i ơ t i ạ Brisbane Có 20 b b i ể cơ a H
ủ i độồồng trễn khăấp n ư c
ớ đi khăấp Brisbane tạ o cơ h ộ i vui ch ơ i, rèn lu ệ y n ơ c t ể h và ngh nỉg i.
ơ Hãy t iớ m tộ trong nh n ữ g b b ể i ơ c a ủ h i ộ đồồng để t ậ n h ưở ng, th ư giãn, h ọ c b ơ i, phát tri nể các ki u ể b i ơ, tham d ựm t ộ l p ớ h c
ọ , gia nhập cấu lạc bộ bơ i ộ l i hặo c các vòng ơ b i.
H i đồộồng cung cấấp hàng lo t ạcác b b ể i ơ trong nhà ho c ặ ngoài tr i
ờ, trong đó có m tộ sồấ mộ t sồấ để n c ấấ ư m ớ . Rấất nhiễồu b b ể i
ơ có các tiện nghi/ lồấi đi dành cho ngườ i tàn tậ t các tiệ n nghi. Các ti ệ n nghi khác gồồm các đ ng ưtr ờ t ư th ợ iễ ở ất b vuịi ch i, d ơ ng ụ c bụóng n c ư ,
ớ barbecued và các quấồy kiồất. Tấất c ả các b bể i
ơ đễồu có phòng thay đồồ và vòi hoa sen nóng lạ nh. TEXT ANALYSIS
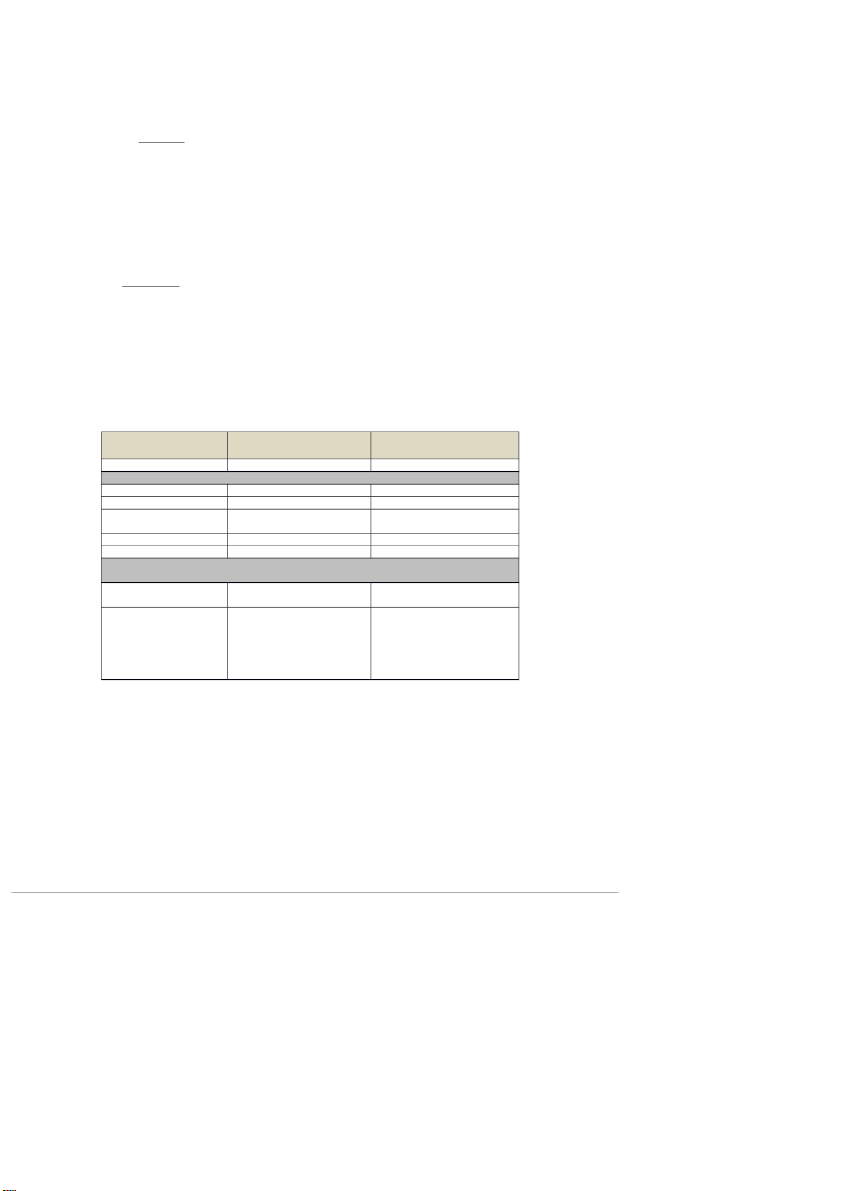
Text: Swimming pools in Brisbane Source text
Target text (situation you think the translation can be used) Text type Article Article Extratextual features Author Brisbane city council The translator Text function informative informative Audience/ Reader Brisbane citizens, visitors Vietnamese Australians, and general readers, Vietnamese readers in Vietnam Medium (Phương tiệ n) website Leaflet… Place/time Australia, 2015 Vietnam, 2022
Intratextual features (Note down features of the ST and changes to be made in the TT or your solutions/ strategies) Subject matter Swimming pool, Swimming pool, Brisbane city facilities Brisbane city facilities Vocabulary: Neutral, simple Cultural words: barbecue.
Barbecue: kept--------changed to Proper name: Brisbane council neutral words H i ộđồồng 10 about:blank 10/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 11/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 12/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 13/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 14/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 15/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 16/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 17/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 18/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 19/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 20/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 21/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 22/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 23/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 24/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 25/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 26/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 27/28 5/10/24, 4:47 PM Portfolio lý thuyết dịch about:blank 28/28




