









Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 Đề 1: (40 câu)
1. The production possibilities frontier illustrates
a. the combinations of output that an economy should produce.
b. the combinations of output that an economy should consume.
c. the combinations of output that an economy can produce.
d. All of the above are correct.
2. Jean-Paul says that he will spend exactly 75 cents a day on M&Ms, regardless of the
price of M&Ms. Jean-Paul’s demand for M&Ms is a perfectly elastic. b unit elastic. c perfectly inelastic.
d None of the above answers is correct.
3. Demand for a good is said to be inelastic if the quantity demanded increases
substantially when the price falls by a small amount
4. The deadweight loss from a $1 tax will be smallest in a market with
a. inelastic supply and elastic demand.
b. inelastic supply and inelastic demand.
c. elastic supply and elastic demand.
d. elastic supply and inelastic demand.
5. It does not matter whether a tax is levied on the buyers or the sellers of a good because
a. sellers always bear the full burden of the tax.
b. buyers always bear the full burden of the tax.
c. buyers and sellers will share the burden of the tax.
d. None of the above is correct; the incidence of the tax does depend on whether
the buyers or the sellers are required to pay the tax.
6. Total surplus with a tax is equal to .
consumer surplus plus producer surplus. b.
consumer surplus minus producer surplus. c.
consumer surplus plus producer surplus minus tax revenue. d.
consumer surplus plus producer surplus plus tax revenue. lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 7.
When the government imposes taxes on buyers and sellers of a good, society
loses some of the benefits of market efficiency. 8.
When a tax is imposed on buyers, consumer surplus decreases but producer surplus increases. 9.
The slope of the budget constraint reveals the relative price of good X compared to good Y. 10.
If consumers purchase more of a good when their income rises, the good is a normal good. 11.
If the price elasticity of supply is 2 and the quantity supplied decreases by 6%,
then the price must have decreased by 3%.
12) Which of the following would be true as the price elasticity of supply approaches infinity?
a) Very small changes in price lead to very large changes in quantity supplied.
b) Very large changes in price lead to very small changes in quantity supplied.
c) Very small changes in price lead to no change in quantity supplied.
d) Very large changes in price lead to no change in quantity supplied
13. The principle of comparative advantage asserts that: a.
not all countries can benefit from trade with other countries b.
the world price of a good will prevail in all countries, regardless of whether those
countries allow international trade in that good c.
countries can become better off by exporting goods, but they cannot become better off by importing goods d.
countries can become better off by specializing in what they do best
14) When quantity moves proportionately the same amount as price, demand is
a) elastic, and the price elasticity of demand is 1.
b) perfectly elastic, and the price elasticity of demand is infinitely large.
c) perfectly inelastic, and the price elasticity of demand is 0. lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
d) unit elastic, and the price elasticity of demand is 1.
15)To determine whether a good is considered normal or inferior, one could examine the value of the…
b) price elasticity of demand for that good.
c) price elasticity of supply for that good.
d) demand responds to a change in supply.
16. Accountants often ignore implicit costs.
17. In the long run, a factory is usually considered a fixed plant.
18. Diminishing marginal productivity implies decreasing total product.
19) The slope of the budget constraint is determined by the
a. relative price of the goods measured on the axes
b. relative price of the goods measured on the axes and the consumer’s income
c. endowment of productive resources
d. preferences of the consumer
20) When a firm is making a profit-maximizing production decision, which of the
following principles of economics is likely to be most important to the firm's decision? a.
The cost of something is what you give up to get it. b.
A country's standard of living depends on its ability to produce goods and services. c.
Prices rise when the government prints too much money. d.
Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes.
21) The amount of money that a firm pays to buy inputs is called a. total cost. b. variable cost. c. marginal cost. d. fixed cost.
22. The perfectly competitive firm’s supply curve is the same as its average total cost curve.
23. In a perfectly competitive industry, all firms are price takers. lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
24. Suppose that competitive pressures drive the price of motorcycles downward.
Which of the following statements is an accurate description of the situation that results? a.
Revenues and profits are reduced. b.
Revenues fall, while profits remain constant. c.
The supply curve shifts to the left. d. Marginal cost rises. e.
The demand curve shifts to the right. 25. Table 4-1 lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 Price Aaron’s Angela’s Austin’s Alyssa’s Quantity Quantity Quantity Quantity Demanded Demanded Demanded Demanded $0.00 20 16 4 8 $0.50 18 12 6 6 $1.00 14 10 2 5 $1.50 12 8 0 4 $2.00 6 6 0 2 $2.50 0 4 0 0
Refer to Table 4-1. Whose demand does not obey the law of demand? a.
Aaron’s b Angela’s c Austin’s d Alyssa’s
26. Suppose Spencer and Kate are the only two demanders of lemonade. Each month,
Spencer buys six glasses of lemonade when the price is $1.00 per glass, and he
buys four glasses when the price is $1.50 per glass. Each month, Kate buys four
glasses of lemonade when the price is $1.00 per glass, and she buys two glasses lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
when the price is $1.50 per glass. Which of the following points is on the market demand curve?
(quantity demanded = 2, price = $1.50)
(quantity demanded = 4, price = $2.50)
(quantity demanded = 10, price = $1.00)
(quantity demanded = 16, price = $2.50)
27) In the market for widgets, the supply curve is the typical upwardsloping straight
line, and the demand curve is the typical downwardsloping straight line. The
equilibrium quantity in the market for widgets is 200 per month when there is no tax.
Then a tax of $5 per widget is imposed. As a result, the government is able to raise
$750 per month in tax revenue. We can conclude that the equilibrium quantity of widgets has fallen by a) 25 per month. b) 50 per month. c) 75 per month. d) 100 per month.
28.The following table contains a supply schedule for a good. Price Quantity Supplied $10 100 $20 ?
If the law of supply applies to this good, then “?” could be lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 a 0. b 50. c 100. d 150.
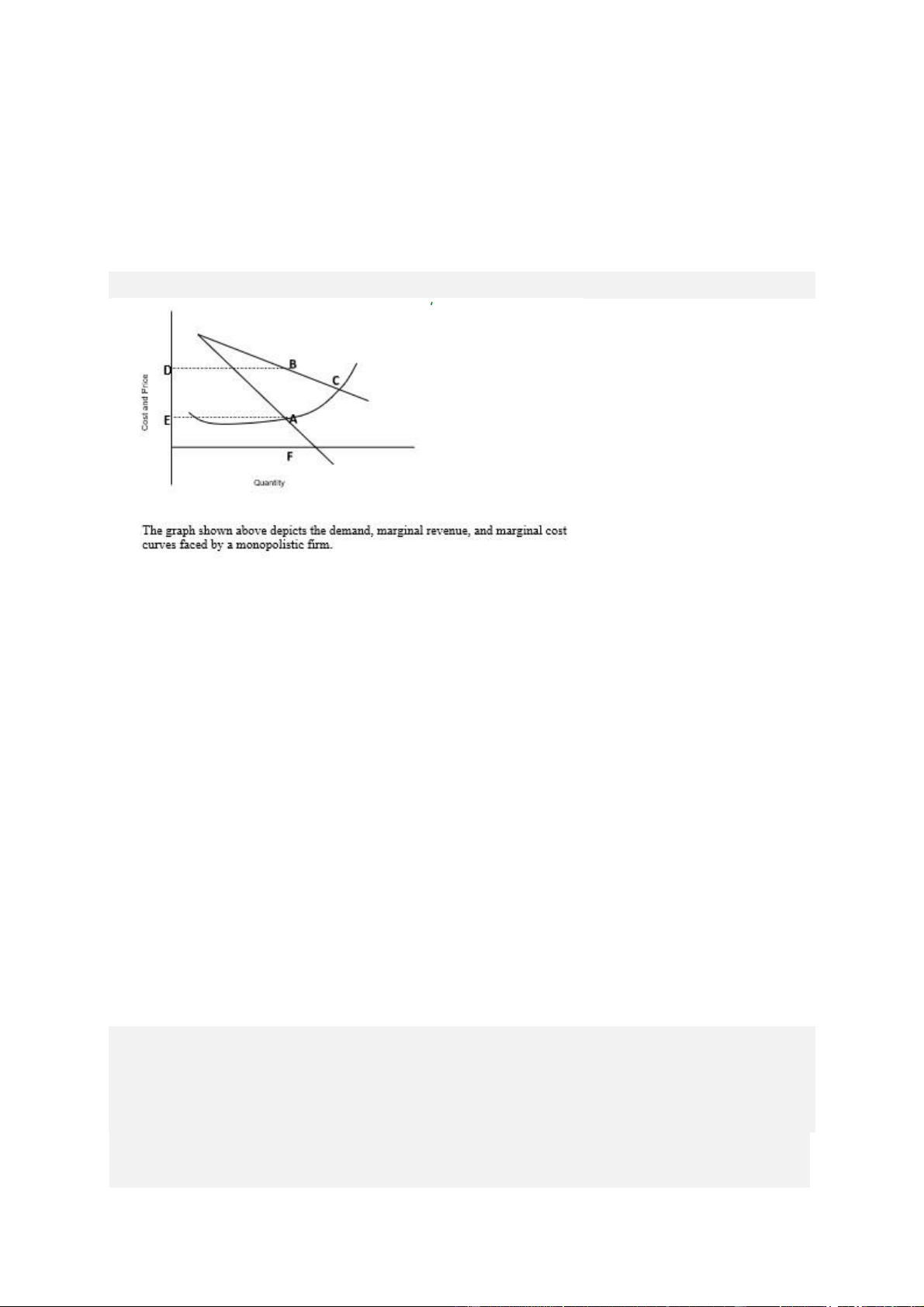
29) Which of the following statements is false? a.
When the firm chooses a level of production F, buyers will pay a price E. b.
Point A is on the marginal cost curve. c.
Point B shows the level of demand that corresponds to the profit maximizing level of production. d.
Point C indicates the price and quantity of production that would exist in a competitive equilibrium. e.
Because the firm described by this graph is a monopoly, production is lower and
price is higher than they would be at competitive equilibrium.
30. Causes of market failure include:
a. Externalities and a perfectly competitive market
b. Externalities and public goods
c. Imperfect information and perfect competition
d. Externalities and imperfect information 31)
For good X, the supply curve is the typical upward-sloping straight line, and
the demand curve is the typical downward-sloping straight line. A tax of $10 per unit
is imposed on good X. The tax reduces the equilibrium quantity in the market by 100
units. The deadweight loss from the tax is . $2,000 a. $1,000 lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 b. $500 c. $250 32)
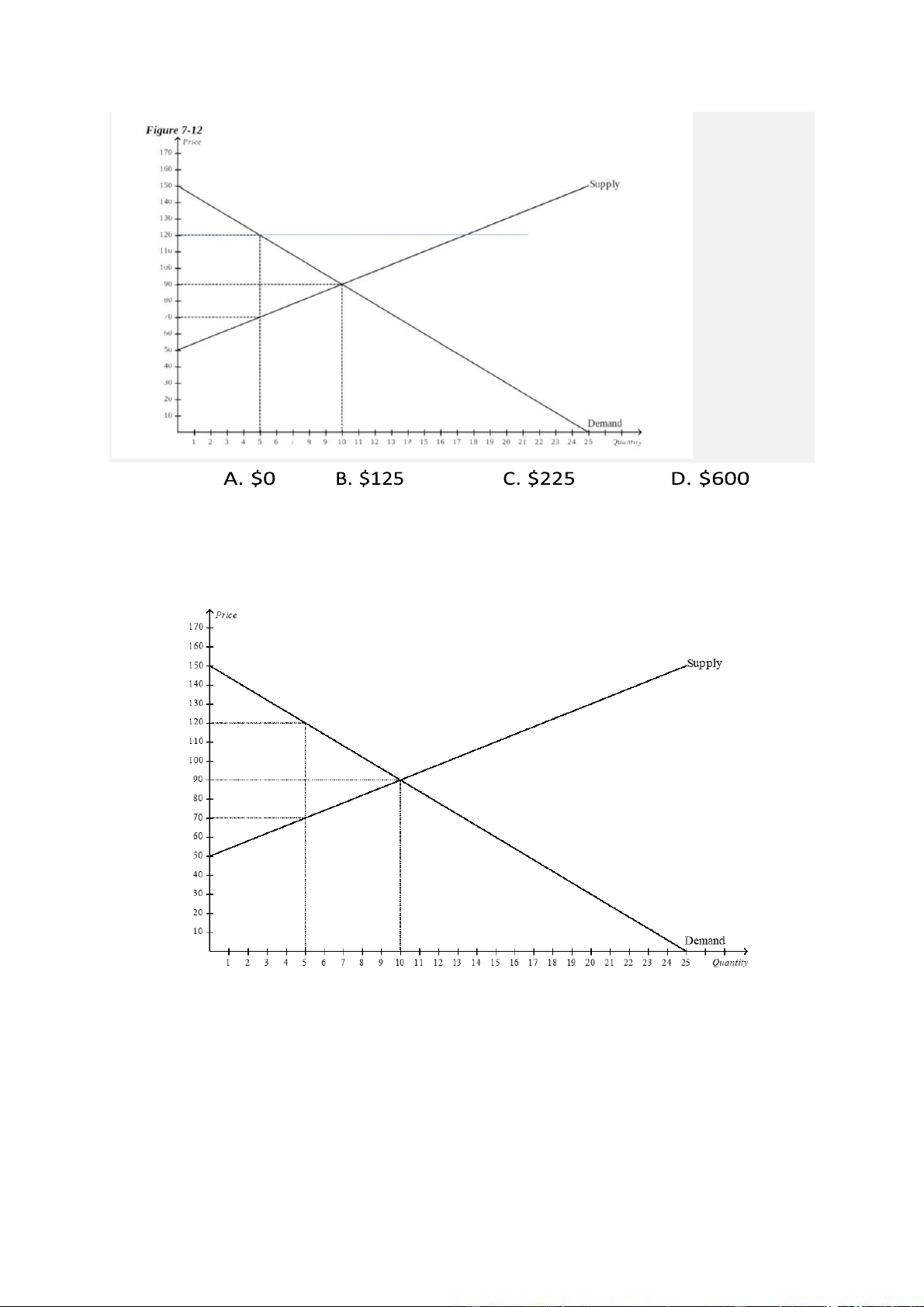
If the government imposes a price ceiling of $120 in this market, then total surplus will dercrease by: . $0 b. $125 c. $225 d. $600
33. We can conclude that the post tax quantity of widgets is ( 59 và 60 cho cùng thành
1 câu hỏi) a. 50 per month. b. 75 per month. c. 100 per month. d. 150 per month. 34.
In the market for widgets, the supply curve is the typical upwardsloping
straight line, and the demand curve is the typical downwardsloping straight line. The
equilibrium quantity in the market for widgets is 200 per month when there is no tax.
The price paid by buyers increases by $11 and the after-tax price received by sellers
falls by $19. The government is able to raise $750 per month in revenue from the tax.
The deadweight loss from the tax is a. $2625 b. $2600 c. $2650 d. $2675 35.
Suppose a firm can sell one unit of product for $50, two units for $45 each,
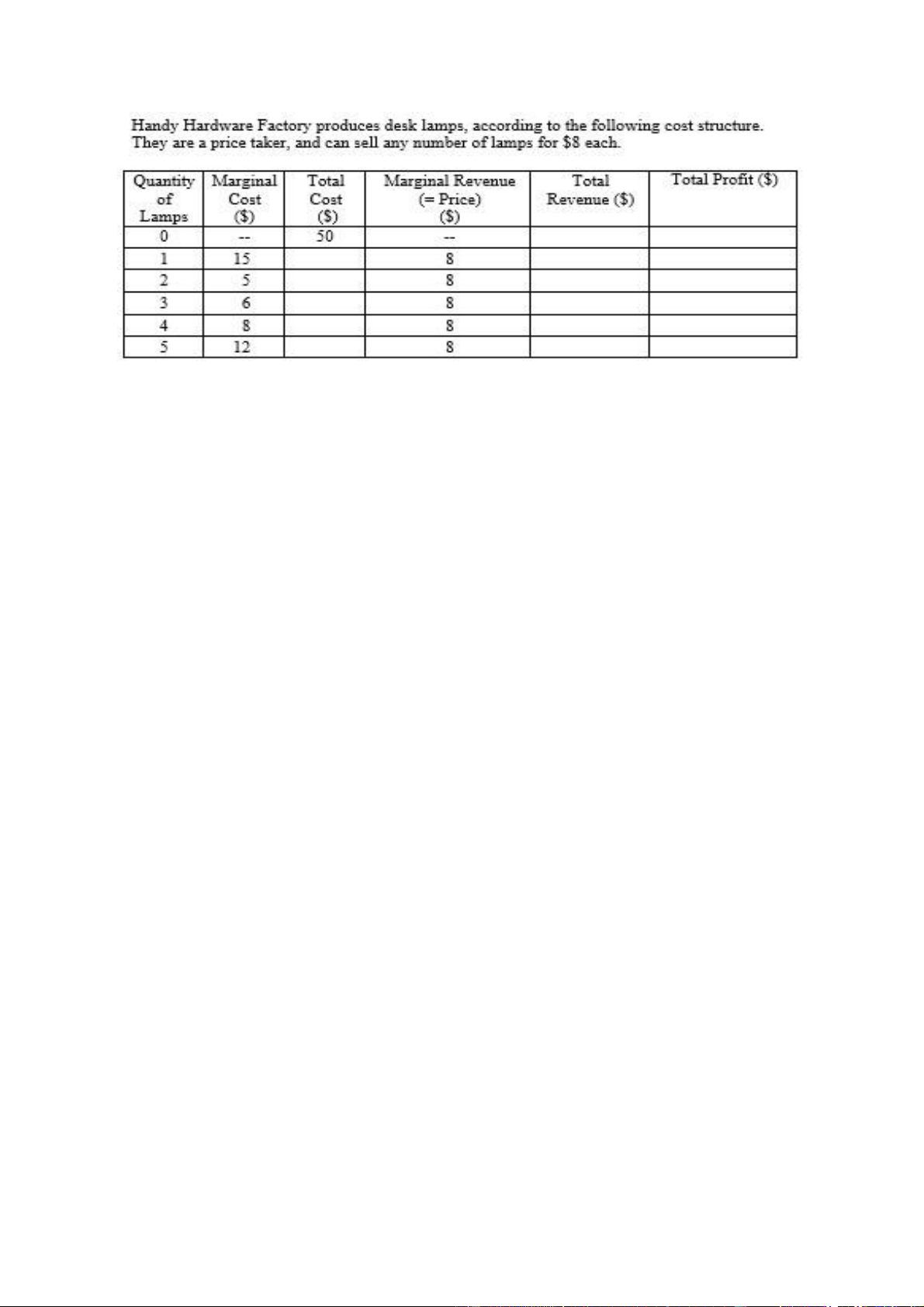
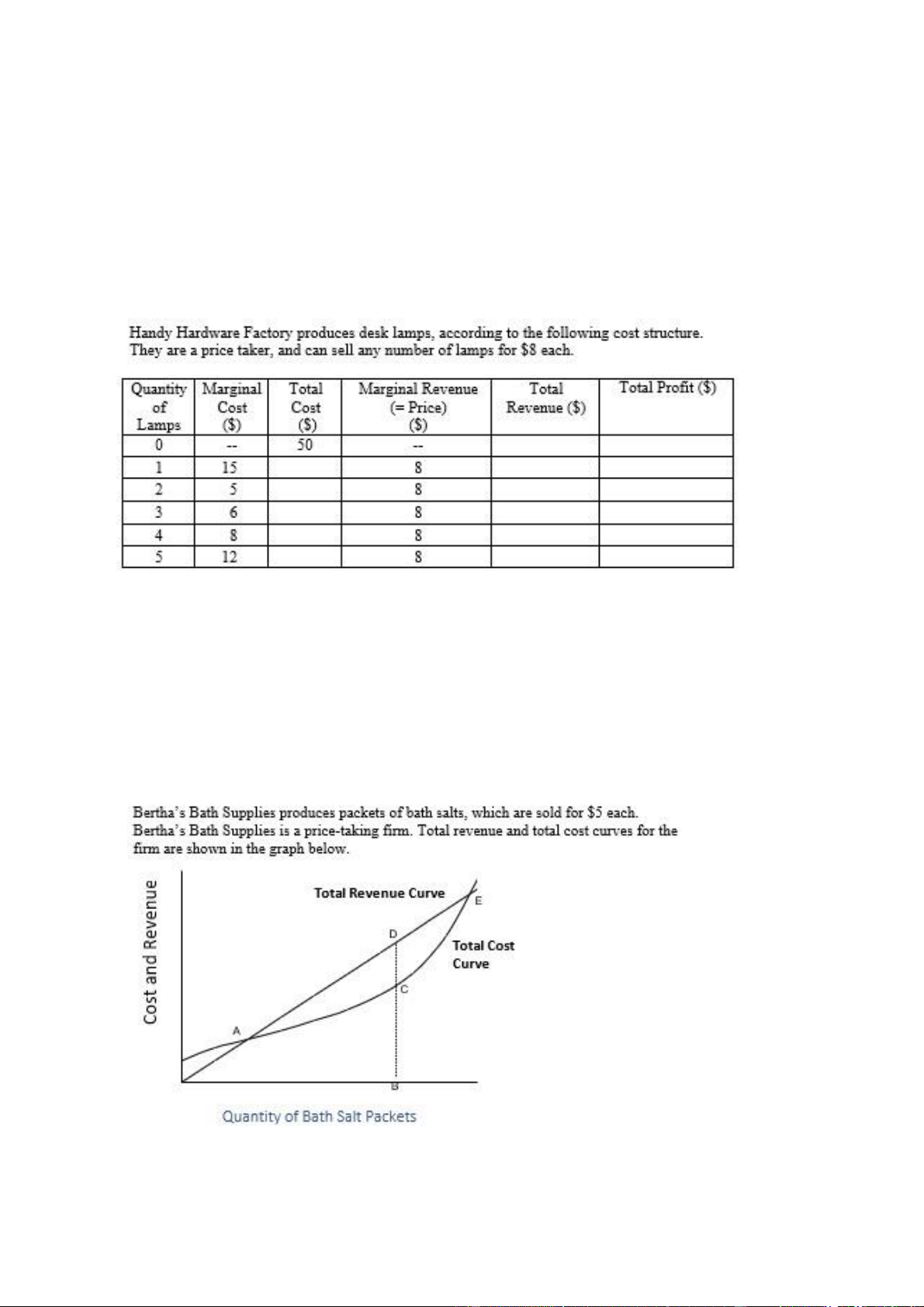
three units for $40 each, or four units for $35 each. When the firm sells four units, marginal revenues is equal to a. $5. b. $20 c. $25. d. $30. e. $35. 36) Figure below lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
What is the total cost of producing 3 lamps? a. $ 6 b. $ 8 c. $ 50 d. $ 76
37. Which of the following could be the cross-price elasticity of demand for two goods that
are complements? a -1.3 b 0 c 0.2 d 1.4
38. Suppose that when the price of good X falls from $10 to $8, the quantity demanded of
good Y rises from 20 units to 25 units. Using the midpoint method, a the cross-price
elasticity of demand is -1.0, and X and Y are complements. b.
the cross-price elasticity of demand is -1.0, and X and Y are substitutes. c.
the cross-price elasticity of demand is 1.0, and X and Y are complements. d.
the cross-price elasticity of demand is 1.0, and X and Y are substitutes.
39. Suppose the cross-price elasticity of demand between hot dogs and mustard is -2.00.
This implies that a 20 percent increase in the price of hot dogs will cause the quantity of mustard purchased to a. fall by 200 percent. b. fall by 40 percent. c. rise by 200percent. d. rise by 40 percent. lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
40) For good X, the supply curve is the typical upward-sloping straight line, and the
demand curve is the typical downward-sloping straight line. A tax of $10 per unit is
imposed on good X. The tax reduces the equilibrium quantity in the market by 100
units. The deadweight loss from the tax is . $2,000. a. $1,000. b. $500. c. $250 . Đề 2: (40 câu) Theory (24 câu)
1. An increase in the price of a product will reduce the amount of it purchased because:
A. supply curves are upsloping.
B.the higher price means that real incomes have risen.
C.consumers will substitute other products for the one whose price has risen.
D.consumers substitute relatively high-priced for relatively lowpriced products.
2. Cocoa and marshmallows are complements, so an increase in the price of cocoa
will cause a decrease in the demand for marshmallows. A. True B. False
3. An increase in income will increase the demand for all goods. A. True B. False
4. Today’s supply curve for iPhones could shift in response to a change in A. Today’s price of Iphones
B. The number of buyers of Iphones
C. The expected future price of Iphones D. All of the above 5. Fill in the blank: lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
_______is the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase at a specific price
6. If automobile manufacturers are producing cars faster than people want to buy them,
A.There is an excess supply and price can be expected to decrease
B. There is an excess supply and price can be expected to increase.
C. There is an excess demand and price can be expected to decrease.
D. There is an excess demand and price can be expected to increase
7. When studying how some event or policy affects a market, elasticity provides information on the
A equity effects on the market by identifying the winners and losers. B. magnitude of the effect on the market.
C. speed of adjustment of the market in response to the event or policy.
D. number of market participants who are directly affected by the event or policy.
8. Which of the following is not a determinant of the price elasticity of demand for a good? A. the time horizon B.
the steepness or flatness of the supply curve for the good C.
the definition of the market for the good D.
the availability of substitutes for the good
9. The principle of comparative advantage asserts that:
a.not all countries can benefit from trade with other countries
b.the world price of a good will prevail in all countries, regardless of whether those
countries allow international trade in that good
c.countries can become better off by exporting goods, but they cannot become better off by importing goods
D. countries can become better off by specializing in what they do best
10. Total surplus is always equal to the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 A. True B. False
11. When the government imposes taxes on buyers and sellers of a good, society
loses some of the benefits of market efficiency. A. True B. False
12. Suppose a tax is imposed on the buyers of fast - food French fries. The burden of the tax will A.
fall entirely on the buyers of fast - food French fries B.
fall entirely on the sellers of fast - food French fries C.
be shared equally by the buyers and sellers of fast - food French fries D.
be shared by the buyers and sellers of fast - food French fries but not necessarily equally
13. Specialization and trade are closely linked to A. absolute advantage B. comparative advantage C.
gains to some traders that exactly offset losses to other traders D. shrinkage of the economic pie
14. Which of the following statements is NOT correct? A.
Trade allows for specialization B.
Trade has the potential to benefit all nations C.
Trade allows nations to consume outside of their production possibilities curves D.
Absolute advantage is the driving force of specialization
15. A tax on an imported good is called a A. Quota B. Tariff C. Supply tax D. Trade tax
16. A budget constraint illustrates bundles that a consumer prefers equally, while
an indifference curve illustrates bundles that are equally affordable to a consumer. A. True B. False
17. The theory of consumer choice provides the foundation for understanding the A. Structure of a firm B. Profitability of a firm
C. Demand for a firm’s product D. Supply of a firm’s product lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
18. When a consumer’s budget _____, consumption possibilities expand
19. Implicit costs are costs that do not require an outlay of money by the firm A. True B. False
20. Which of the following would be an example of an implicit cost? (i)
forgone investment opportunities (ii) wages of workers (iii) raw materials costs A. (i) only B. (ii) only C. (ii) and (iii) only D. (i) and (iii) only
21. A difference between explicit and implicit costs is that A. explicit costs are greater than implicit costs.
B. explicit costs do not require a direct monetary outlay by the firm, whereas implicit costs do.
C. implicit costs do not require a direct monetary outlay by the firm, whereas explicit costs do.
D. implicit costs are greater than explicit costs.
22. Which of the following is not a condition of the model of perfect competition?
A. Each individual buyer can affect the market price.
B. Within a given market, only one kind of good or service is traded.
C. Producers can freely enter the industry.
D. Producers can freely exit the industry.
E. Sellers all have perfect information. 23.
In a perfectly competitive industry, all firms are price takers. A. True B. False 24. Public goods creates: a. negative externalities. b. positive externalities
c. the problem of unequal income distribution to society
d. imperfect information problems Compute (16 câu) lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 25.
Suppose a firm can sell one unit of product for $50, two units for $45
each, three units for $40 each, or four units for $35 each. When the firm
sells four units, marginal revenues is equal to A. $5. B. $20. C. $25. D. $30. E. $35. 26.
What level of total profit will Handy Hardware make, if it produces 3 lamps? A.
less than $ 0 (that is, a loss) B. between $ 0 and $20 C. between $20 and $50 D. more than $50 E.
Cannot be determined from the information given.
27. Which of the following statements is true regarding the graph shown above? A.
Profits are maximized at point E. lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 B.
The distance from B to C represents profit earned. C.
The distance from B to D represents profit earned. D.
The distance from C to D represents profit earned. E.
At point B, marginal revenue is designated by point D.
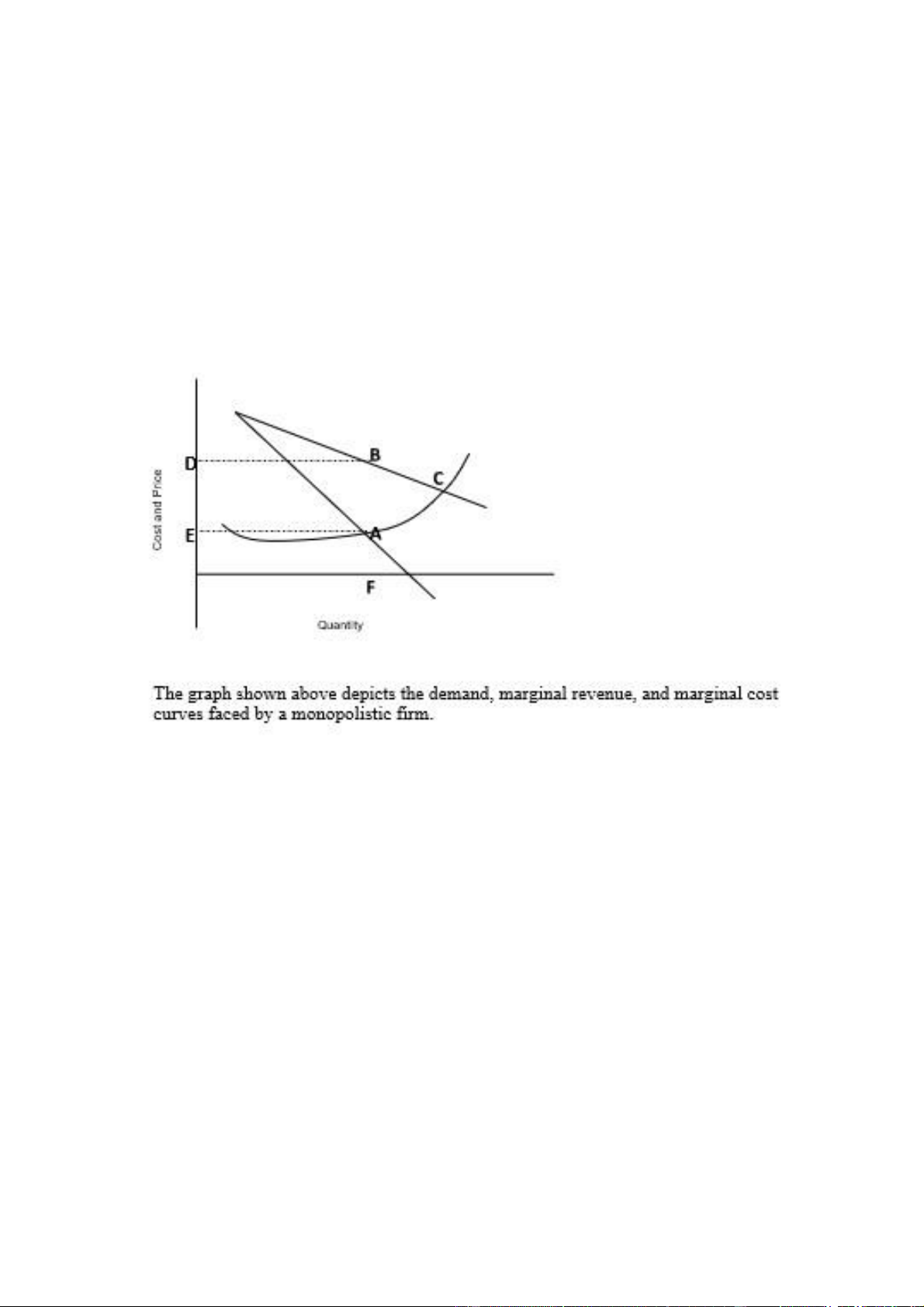
28. The graph shown above depicts the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal
cost curves faced by a monopolistic firm. Point A indicates A. Total cost B. The point where MR=MC. C.
The price buyers are willing to pay at equilibrium. D. The point where MC=P. E. Total revenue.
29. If the government imposes a price ceiling of $120 in this market, then total surplus will decrease by: lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
30. If the government imposes a price floor of $120 in this market, then total
surplus will decrease by A. $0 B. $125 C. $225 D. $600
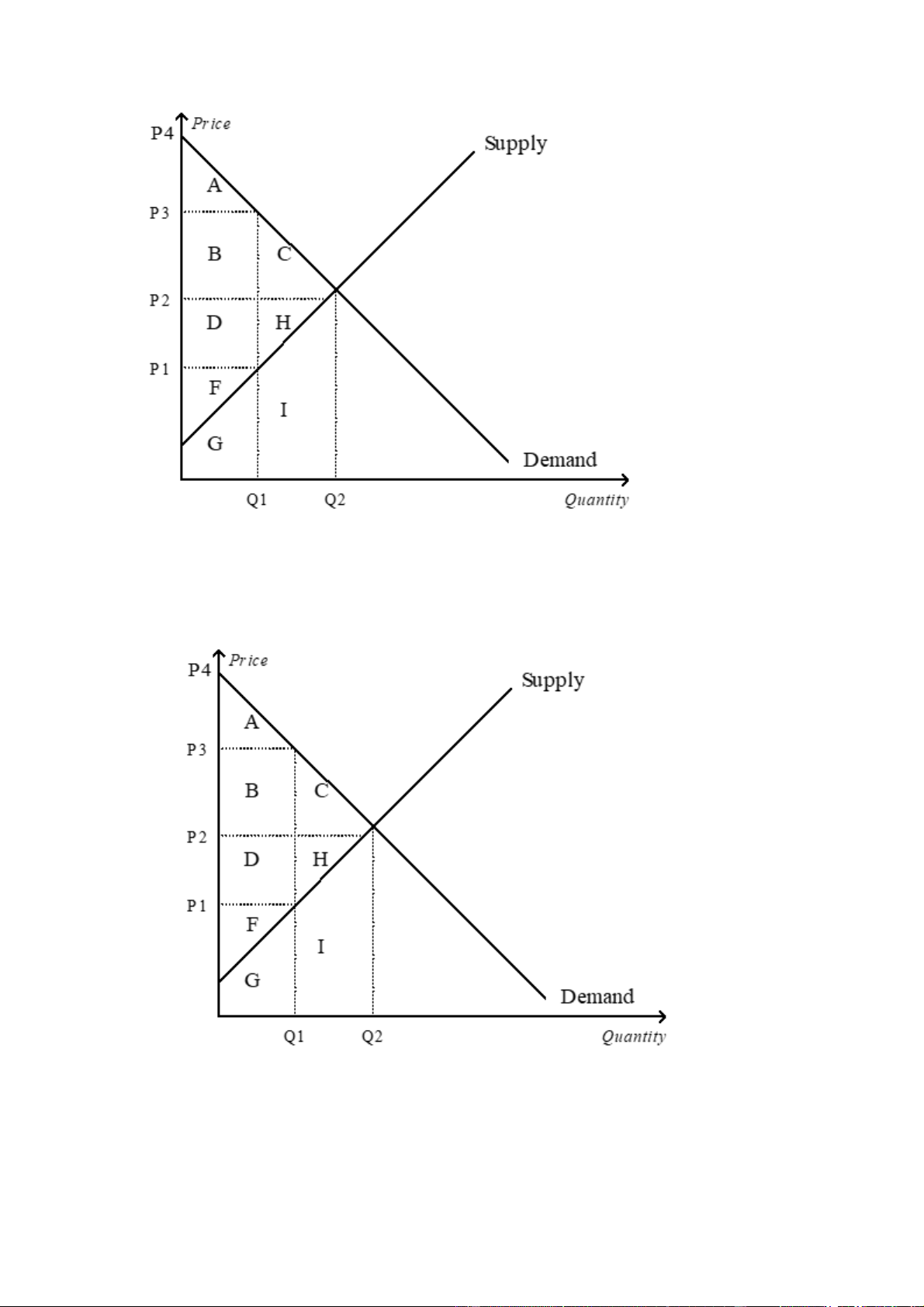
30. At equilibrium, consumer surplus is represented by the area lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 A. A B. A+B+C C. D+H+F D. A+B+C+D+H+F
31. If the price were P3, consumer surplus would be represented by the area A. A B. A+B+C C. D+H+F D. A+B+C+D+H+F lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
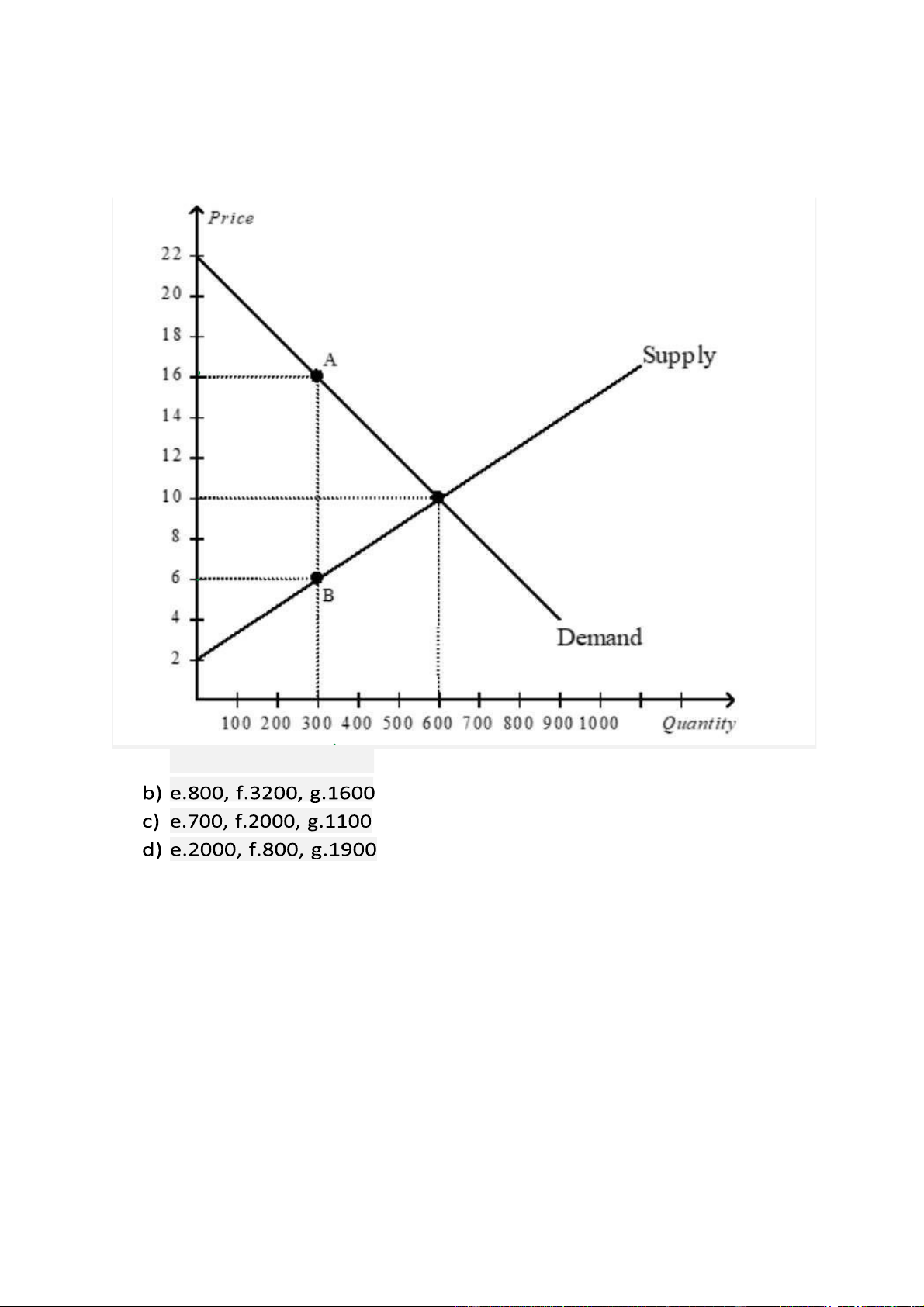
32. Using the graph shown, determine the value of each of the following e: consumer
surplus f: total tax revenue g: deadweight loss a) e.900, f.3000, g.1500
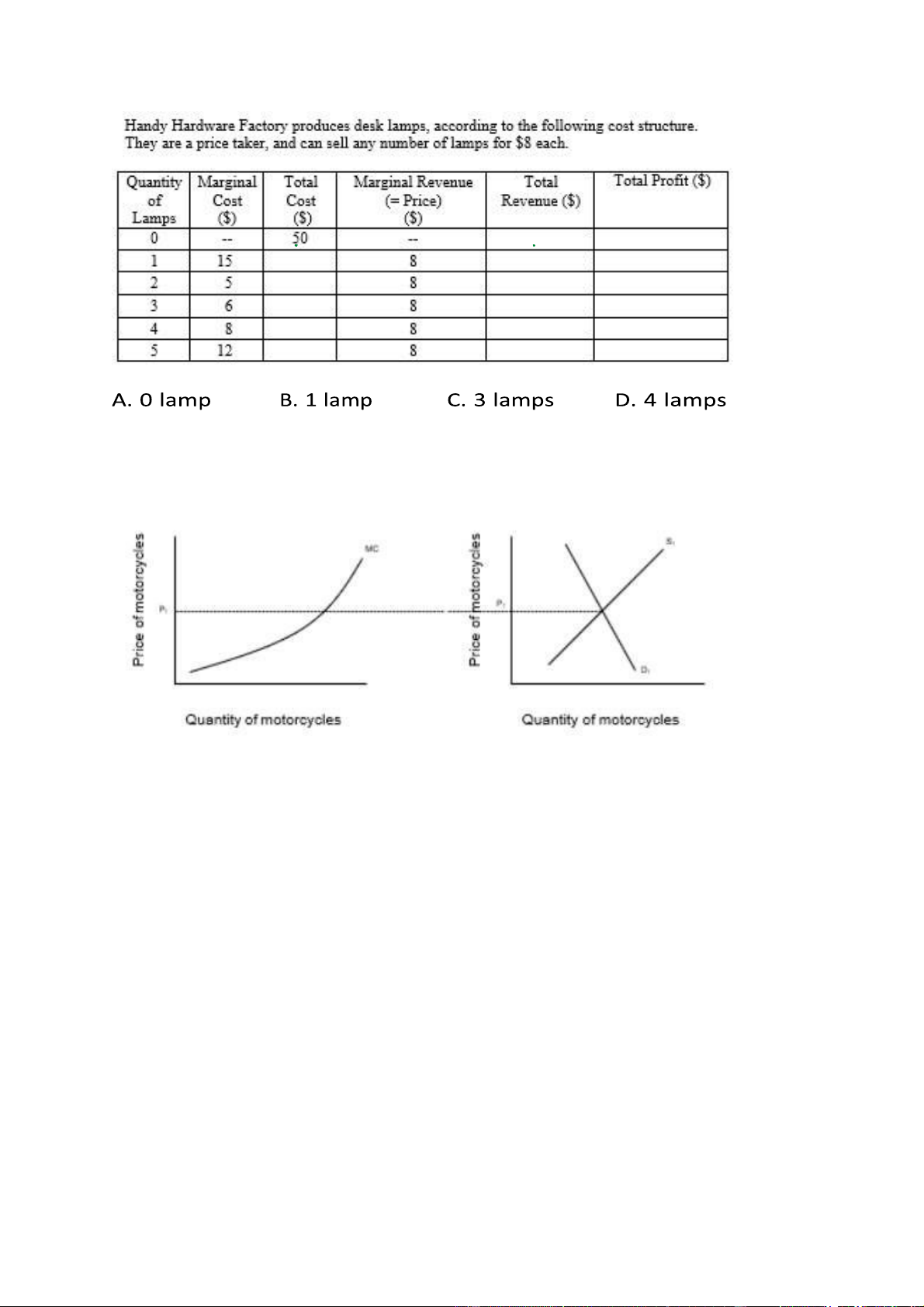
33. What is the profit-maximizing level of output for Handy Hardware? lOMoARcPSD| 49551302
34. Suppose that at price P1, motorcycle manufacturers are making positive economic
profits. Assuming the market in motorcycles is perfectly competitive, which of the
following will occur in the long run? A.
The supply curve will shift to the right. B.
The demand curve will shift to the right. C. Price will rise. D. Price will remain constant. E. Marginal costs will increase.
35. Suppose that competitive pressures drive the price of motorcycles downward.
Which of the following statements is an accurate description of the situation that results? lOMoARcPSD| 49551302 A.
Revenues and profits are reduced. B.
Revenues fall, while profits remain constant. C.
The supply curve shifts to the left. D. Marginal cost rises. E.
The demand curve shifts to the right. 36.
In the market for widgets, the supply curve is the typical upwardsloping
straight line, and the demand curve is the typical downwardsloping straight line. The
equilibrium quantity in the market for widgets is 200 per month when there is no tax.
Then a tax of $5 per widget is imposed. As a result, the government is able to raise
$750 per month in tax revenue. We can conclude that the equilibrium quantity of widgets has fallen by
A.25 per month B. 50 per month
C.75 per month D. 100 per month 37.
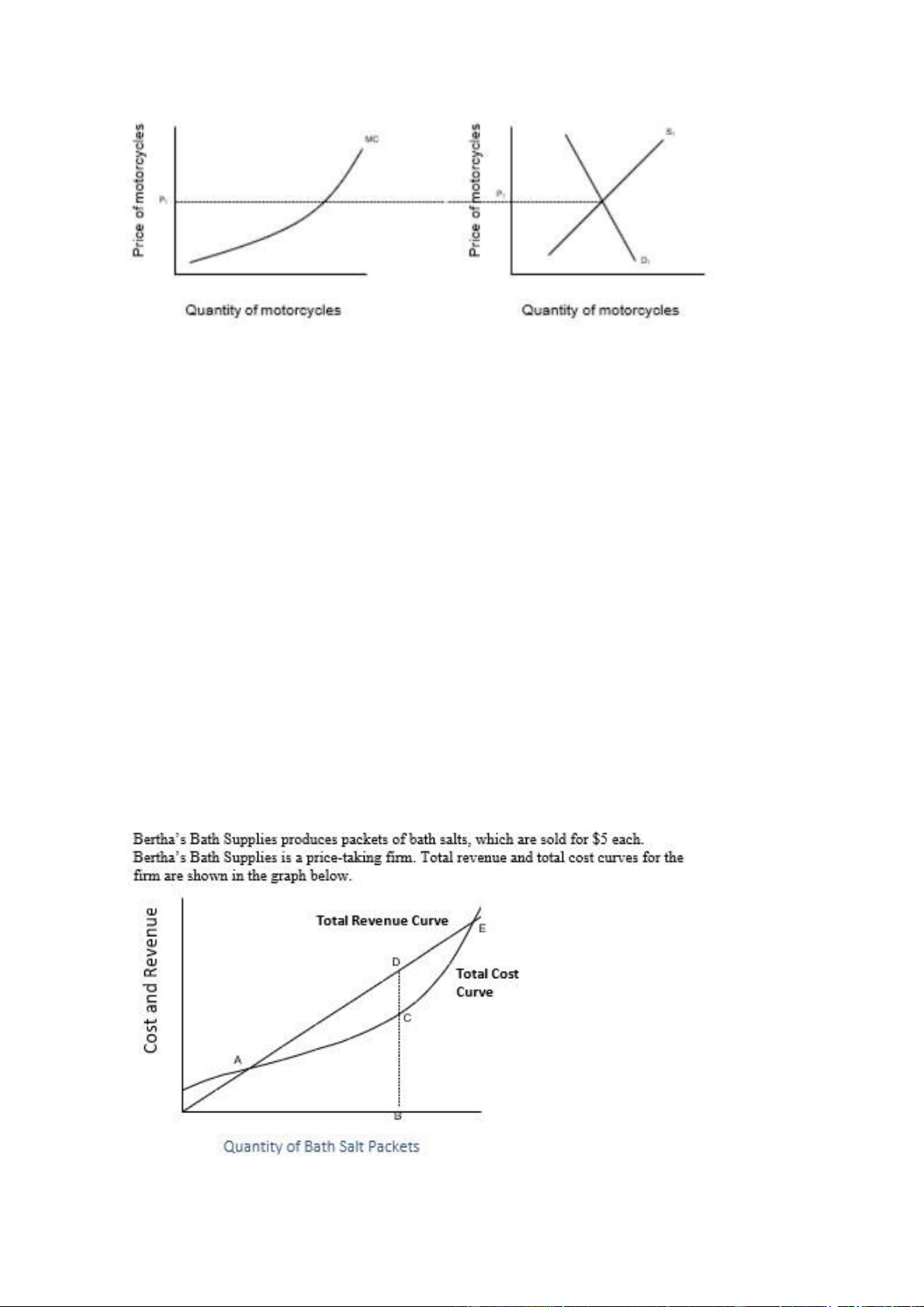
Which of the following statements about Bertha’s Bath Supplies do you know
to be true, based on the information provided above?




