




















Preview text:
Chapter One Foundations of Information Systems in Business Learning Objectives 1.
Understand the concept of a system and how it relates to information systems. 2.
Explain why knowledge of information systems is important for
business professionals and identify five areas of information systems knowledge they need. 3.
Give examples to illustrate how the business applications of
information systems can support a firm’s business processes,
managerial decision making, and strategies for competitive advantage. 4.
Provide examples of several major types of information systems from
your experiences with business organizations in the real world. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 2 Learning Objectives 5.
Identify several challenges that a business manager might face in
managing the successful and ethical development and use of
information technology in a business. 6.
Provide examples of the components of real-world information
systems. Illustrate that in an information system, people use
hardware, software, data and networks as resources to perform input,
processing, output, storage, and control activities that transform data
resources into information products. 7.
Demonstrate familiarity with the myriad of career opportunities in information systems. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 3 Section 1 Foundation Concepts: Information Systems in Business
Why study Information Systems and Information Technology?
Vital component of successful businesses
Helps businesses expand and compete Businesses use IS and IT
◦ To improve efficiency and effectiveness of business processes
◦ For managerial decision making
◦ For workgroup collaboration 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 5 What is a system? A system
◦ Is a set of interrelated components
◦ With a clearly defined boundary
◦ Working together to achieve a common set of objectives
One system can be made up of other systems or can be part of a bigger system 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 6 What is an Information System? An organized combination of ◦ People ◦ Hardware ◦ Software ◦ Communications networks ◦ Data resources ◦ Policies and procedures
That stores, retrieves, transforms, and disseminates information in an organization 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 7
Information System (IS) versus Information Technology (IT)
IS is all the components and resources necessary to deliver information
and functions to the organization
IT is hardware, software, networking and data management
In theory, IS could be paper based
But we will focus on Computer-Based Information Systems (CBIS) 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 8
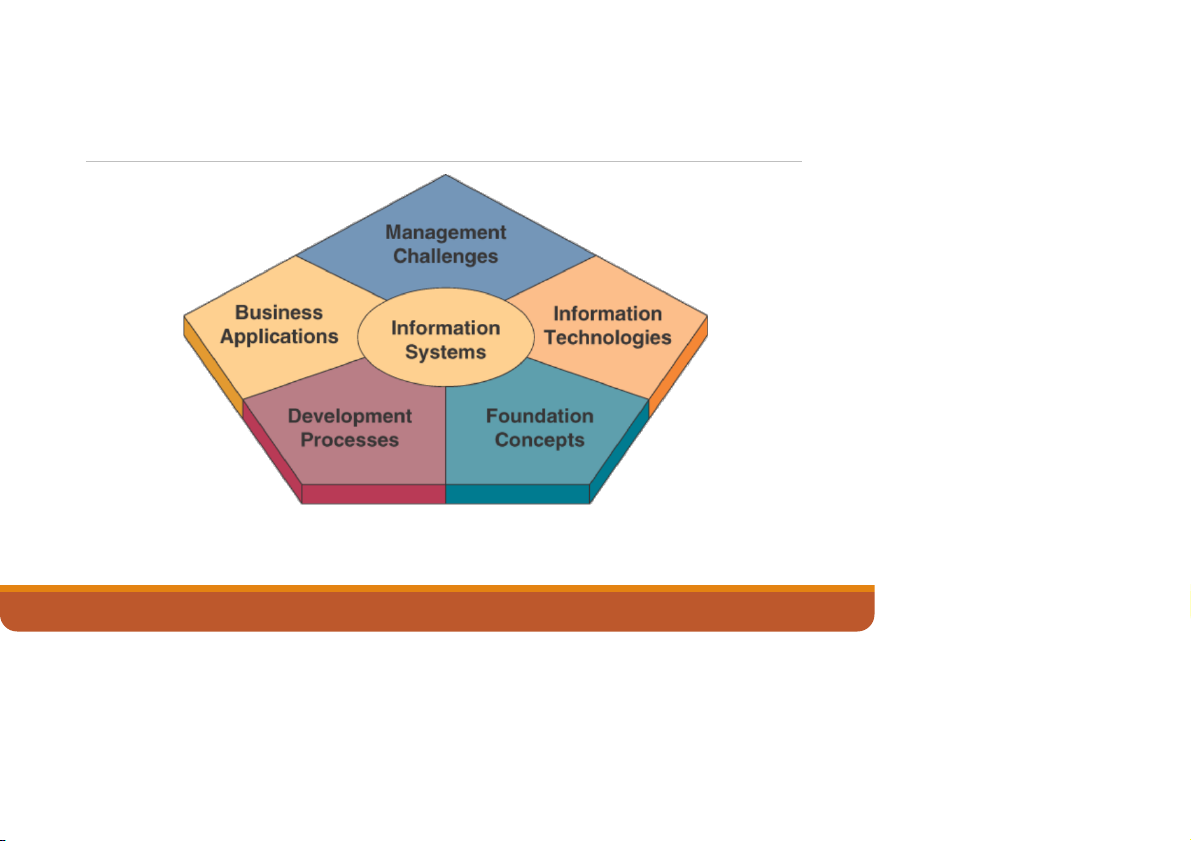
IS Knowledge Framework for Business Professionals
A framework that outlines the major areas of information
systems knowledge needed by business professionals. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 9
What should a Business Professional know about IS?
Foundation Concepts: Fundamental behavioral, technical,
business, and managerial concepts about the components and
roles of information systems. Examples include basic information
system concepts derived from general systems theory or
competitive strategy concepts used to develop business
applications of information technology for competitive advantage
Information Technology: Major concepts, developments, and
management issues in information technology—that is,
hardware, software, networks, data management, and many Internet-based technologies. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 10
What should a Business Professional know about IS?
Business Applications: The major uses of information systems for
the operations, management, and competitive advantage of a business
Development Processes: How business professionals and
information specialists plan, develop, and implement
information systems to meet business opportunities
Management Challenges: The challenges of effectively and
ethically managing information technology at the end-user,
enterprise, and global levels of a business. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 11
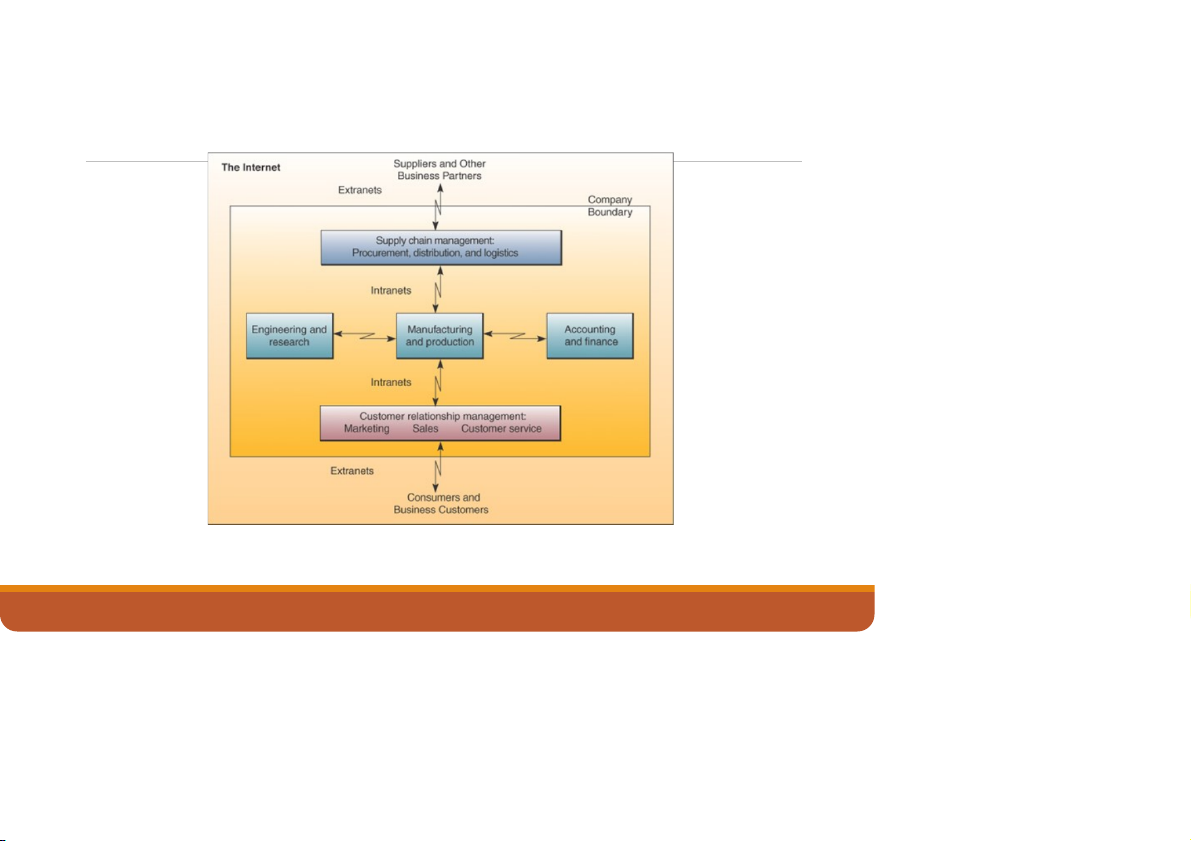
What does IS do for a business?
Interaction among fundamental roles in a typical organization 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 12
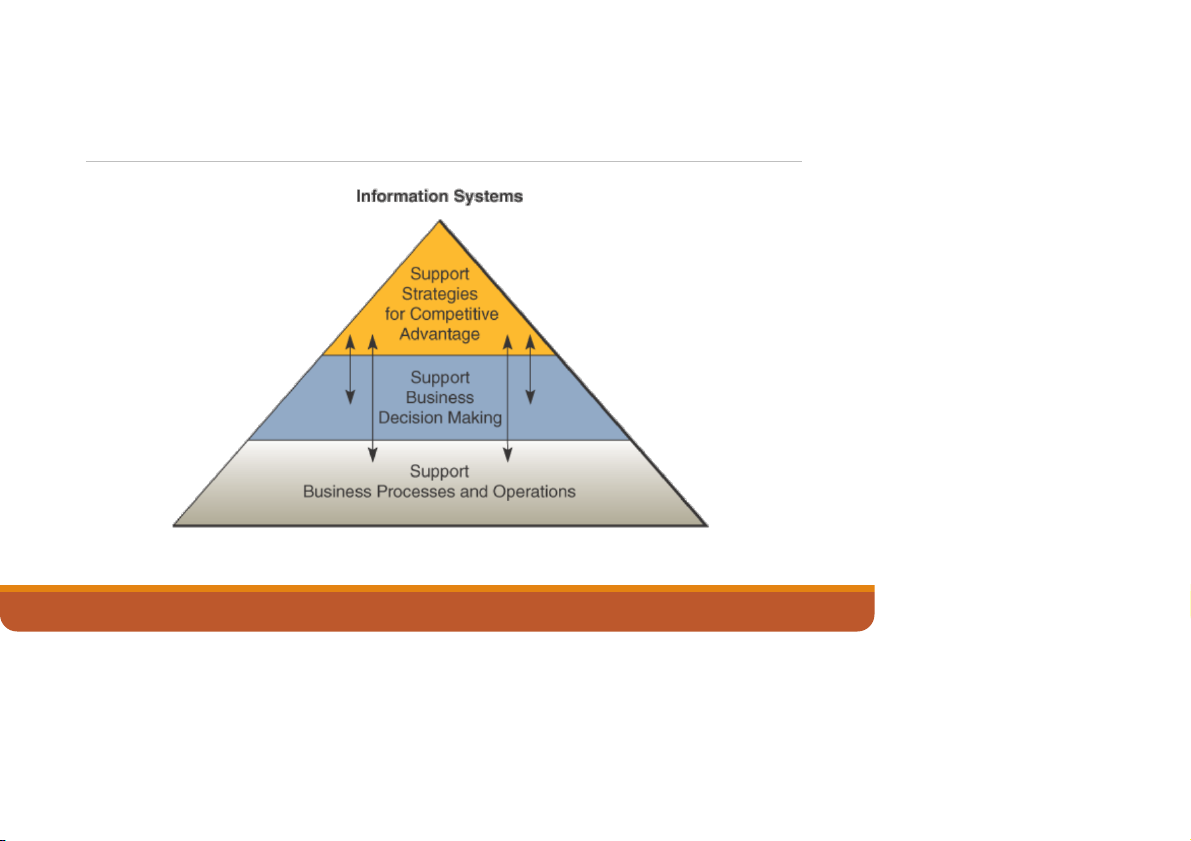
Fundamental Roles of IS in Business
▪Support of business processes and operations.
o As a consumer, you regularly encounter information systems that
support the business processes and operations at the many retail stores where you shop.
▪Support of decision making by employees and managers.
o Information systems also help store managers and other business
professionals make better decisions.
▪Support of strategies for competitive advantage.
o Gaining a strategic advantage over competitors requires the innovative
application of information technologies. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 13 Trends in Information Systems
The expanding roles of the business
applications of information systems. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 14 What is E-business?
The use of Internet technologies
◦ to work and empower business processes, electronic commerce, and enterprise collaboration
◦ within a company and with its customers, suppliers, and other business stakeholders. An online exchange of value.
• Any online exchange of information, money, resources, services,
or any combination there of falls under the e-business umbrella.
• The Internet and Internet-like networks—those inside the
enterprise (intranet) and between an enterprise and its trading
partners (extranet)—are the primary IT infrastructure that
supports the e-business applications of many companies. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 15 How e-business is being used
Businesses today depend on the Internet, intranets, and extranets
to implement and manage innovative e-business applications. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 16 E-business roles
Companies rely on e-business applications to
(1) reengineer internal business processes
(2) implement e-commerce systems with their customers and suppliers
(3) promote enterprise collaboration among business teams and workgroups. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 17 E-business use
Enterprise collaboration systems:
◦ involve the use of software tools to support communication, coordination,
and collaboration among the members of networked teams and workgroups.
◦ A business may use intranets, the Internet, extranets, and other networks to
implement such systems, e.g virtual team
Electronic commerce (e-commerce):
◦ buying, selling, marketing and servicing of products and services over computer networks
◦ Many businesses use the Internet, intranets, extranets, and other networks
to support every step of the commercial process, including everything from
advertising, sales, and customer support on the WWW to Internet security
and payment mechanisms ensuring completion of delivery and payment processes. 12/7/2022
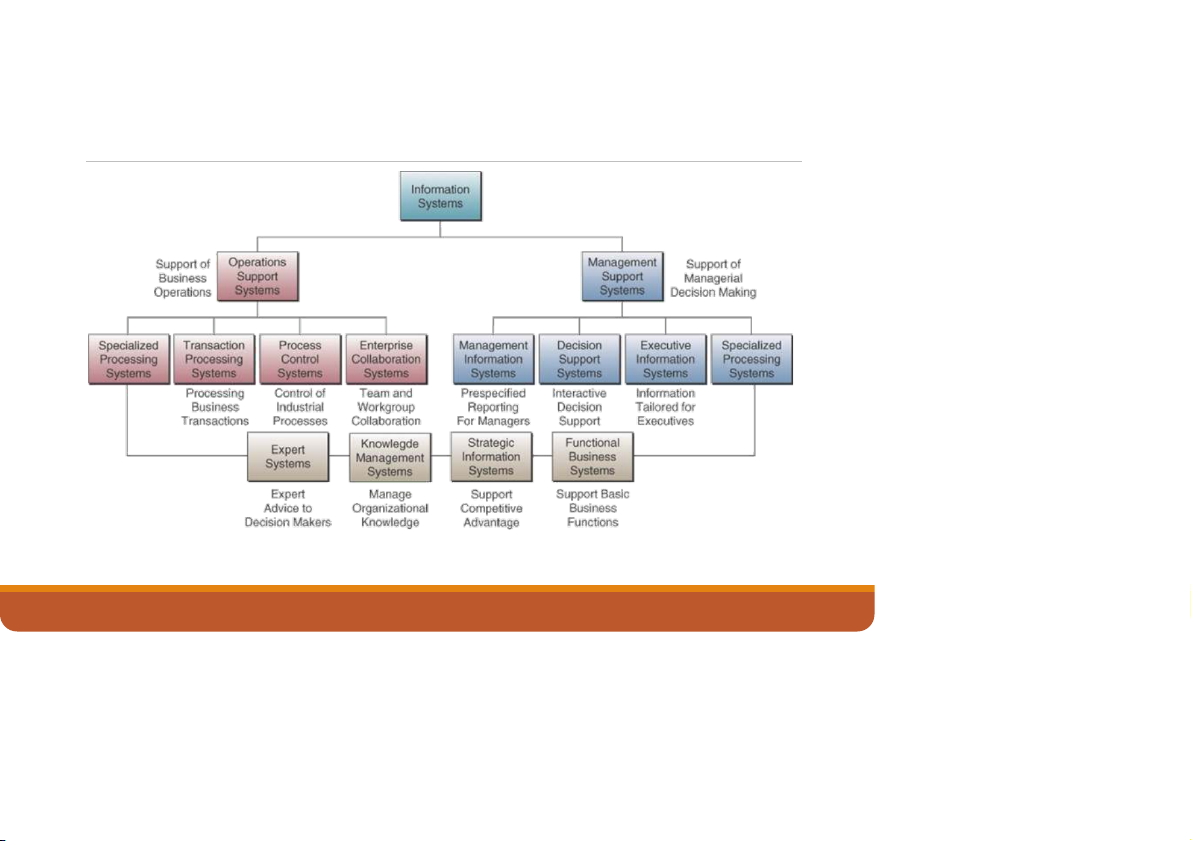
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 18 Types of IS
Operations and management classifications of information systems. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 19 Operations support systems
◦ Efficiently process business transactions
◦ Control industrial processes
◦ Support communications and collaboration ◦ Update corporate databases
A summary of operations support systems with examples. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 20
Types of Operations Support Systems Transaction Processing Systems
◦ Record and process data from business transactions
◦ Examples: sales processing, inventory systems, accounting systems Process Control Systems
◦ Monitor and control physical processes
◦ Example: in a petroleum refinery use sensors to monitor chemical processes
Enterprise Collaboration Systems
◦ Enhance team and work group communications
◦ Examples: e-mail, videoconferencing 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 21
Two ways to handle transactions Batch Processing:
◦ Accumulate transactions over time and process periodically
◦ Example: a bank processes all checks received in a batch at night
Online Processing (real-time processing):
◦ Process transactions immediately
◦ Example: a bank processes an ATM withdrawal immediately 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 22 Management Support Systems What are they?
◦ Provide information and support for effective decision making by managers
A summary of management support systems with examples. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 23
Types of Management Support Systems
Management Information Systems (MIS)
◦ Provide reports and displays to managers
◦ Example: daily sales analysis reports Decision Support Systems (DSS)
◦ Provide interactive ad hoc support for decision making ◦ Example: A what-i -a
f nalysis to determine where to spend advertising dollars
Executive Information Systems (EIS)
◦ Provide critical information for executives and managers
◦ Example: easy access to actions of competitors 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 24
Operational or Management Systems Expert Systems ◦ Provide expert advice
◦ Example: credit application advisor Knowledge Management Systems
◦ Support creation, organization and dissemination of business knowledge throughout company
◦ Example: Intranet access to best business practices 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 25 Classifications of IS by scope Functional business systems
◦ Focus on operational and managerial applications of basic business functions
◦ Examples: support accounting, finance or marketing Strategic information systems
◦ Help get a strategic advantage over its customers by applying IT
◦ Examples: shipment tracking, e-commerce web systems
Cross-functional information systems
◦ Systems that are combinations of several types of information systems
◦ Provide support for many functions 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 26
Challenges and Opportunities of IT 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 27 Measuring success of an IS Efficiency
◦ Minimize cost, time and use of information resources Effectiveness
◦ Support business strategies ◦ Enable business processes
◦ Enhance organizational structure and culture
◦ Increase the customer and business value
What’s the difference between Efficiency and Effectiveness? 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 28 Developing IS Solutions 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 29 Developing IS Solutions
▪Developing IS Solutions – an Information Systems is a Solution to a Business Problem
▪ Investigate (Plan) – recognize the problem exists
▪ Analyze – investigate the current system
▪ Design – designing the new system
▪ Implement – put the new system into effect
▪ Maintain (Use) – use, monitor, and maintain the new system 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 30
Ethical challenges of IT applications
What uses of IT might be considered improper or harmful to other individuals or society?
What is the proper business use of the Internet or a company’s IT resources?
How can you protect yourself from computer crime? 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 31 Challenges of IT Careers
Outsourcing of basic programming
Strong employment opportunities in other areas in IS
Shortage of qualified IS personnel
Long-term job outlook positive and exciting
Among the fastest growing occupations Systems Analyst Database administrators Network specialists Information security 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 32 IS Function represents
Major functional area of business
Important contributor to operational efficiency, employee productivity,
morale, customer service and satisfaction
Major source of information and support for effective decision making
Vital ingredient in developing competitive products and services in the global marketplace
Dynamic and challenging career opportunity
Key component of today’s networked business 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 33 Section 2 Foundation Concepts: The Components of Information Systems What is a system? A system
◦ Is a set of interrelated components
◦ With a clearly defined boundary
◦ Working together to achieve a common set of objectives
◦ By accepting inputs and producing outputs in an organized transformation process 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 35
Systems have three basic functions:
Input involves capturing and assembling elements that enter the system to be processed
Processing involves transformation process that convert input into output
Output involves transferring elements that have been produced by the
transformation process to their ultimate destination 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 36 Cybernetic system
All systems have input, processing and output
A cybernetic system, a self-monitoring, self-regulating
system, adds feedback and control:
◦ Feedback is data about the performance of a system
◦ Control involves monitoring and evaluating feedback to
determine whether a system is moving towards the achievement of its goal 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 37 A Cybernetic system
A common cybernetic system is a home temperature control system. The thermostat
accepts the desired Room temperature as input and sends voltage to open the gas
valve, which fires the furnace.
The resulting hot air goes into the room, And the thermometer in the thermostat
provides feedback to shut the system down when the desired temperature is reached. 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 38 A business as a system 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 39 Information systems model
Basic IS model shows that an information
system consists of five major resources: ▪ people ▪ hardware ▪ software ▪ data ▪ networks 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 40 Components of an IS People Resources
◦ End users: the people who use the IS or the information from the IS
◦ IS specialists: the people who develop and operate IS Hardware Resources
◦ All physical devices used in information processing
◦ Machines, data media, peripherals Software Resources
◦ All information processing instructions including programs and procedures
◦ System software, application software and procedures 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 41 Components of an IS (cont.) Data Resources
◦ Facts about the business transactions
◦ Processed and organized information
◦ Databases of organized data Network Resources ◦ Communications media
◦ Network infrastructure: hardware and software
◦ The Internet, intranets and extranets 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 42 Data versus Information
Data are raw facts about physical phenomena or business transactions
Information is data that has been converted into meaningful and useful context for end users Example:
◦ Sales data is names, quantities and dollar amounts
◦ Sales information is amount of sales by product type, sales territory or salesperson 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 43 IS Activities Inputof data resources ◦ Data entry activities
Processingof data into information
◦ E.g., calculate, compare, sort, classify, summarize Outputof information products
◦ Messages, reports, forms and graphic images Storageof data resources
◦ Data elements and databases Controlof system performance
◦ Monitoring and evaluating feedback 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 44 Recognizing IS
As a business professional, you should be able to look at an IS and identify
◦ The people, hardware, software, data and network resources
◦ The type of information products they produce
◦ The way they perform input, processing, output, storage and control activities 12/7/2022
INTRODUCTION TO IS IN BUSINESS - PHAM TRUNG KIEN 45




