


Preview text:
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 1 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY REPORT
EXPERIMENT 3: REDOX TITRATION Semester: 2 Year: 2023 - 2024 Group: 1 Session: 3 Date: 03/04/2024 Group members: No. Full name Student ID
% Contribution Signature Score (Total = 100%) 1 Lam Na BEBEIU23079 25
2 Ho Huu Hanh Nguyen BEBEIU23080 25 3 Phan Do Dang Khoa BEBEIU23058 25 4 Le Pham Anh Thu BEBEIU23067 25 Total score:________/100 I. Introduction
Potassium permanganate is a potent oxidizing agent that finds its use in various chemical reactions. Its
strong oxidizing properties are evident when it participates in a redox reaction. During this reaction,
the dark purple solution of potassium permanganate turns colorless and then changes to a brown or pink
solution. This reaction can be conducted in both acidic and basic mediums. Oxalic acid has a
polymorphic structure and appears as a white crystalline solid. When it is dissolved in water, it becomes
a colorless solution. It is a reducing agent that is often used as a chelating agent with oxalate as its
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 2 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
conjugate base. In today's experiment, we will perform a precise chemical process called titration. We
will titrate the KMnO4 solution with the H2C2O4 standard solution by slowly adding potassium
permanganate into the mixed solution according to the instructions, then shake well until the solution
has a light pink color that does not disappear, then titrate the H2C2O4 solution of unknown concentration
with the standard KMnO4 solution and similar to the above process, we shake the mixture well until
there is a pale pink color that does not disappear. This process will allow us to determine the exact
concentration of the unknown H2C2O4 solution. The experiment requires extreme precision and attention
to detail, and the results will be important for understanding the chemistry of the solutions involved. II. Experimental
The chemicals and equipments that are used in the experiment: Chemicals Equipments 0.05 N H2C2O4 Burette Distilled water Beakers 6N H2SO4 Flasks Unknown H2C2O4 Cylinder KMnO4 Pipette
Before commencing the experiment, our instructor provided comprehensive guidance on how to handle
the burette. After the training session, we washed our tools and began practicing the procedures.
First we will clean the burette and prepare for the experiment:
Step 1. Rinse the burette thrice with distilled.
Step 2. Rinse the burette 3 times with ~5mL KMnO4.
Step 3. Fill the burette with KMnO4 and let it run through the tip to (Remove air bubbles). Step
4. Record the initial point and start doing the experiment.
1. TITRATION OF KMnO4 SOLUTION WITH STANDARD H2C2O4 SOLUTION
Step 1. Add 10mL of 0.05 N H2C2O4 into the flask.
Step 2. Add 40mL distilled water into the flask above.
Step 3. Add 20mL of 6N H2SO4 to the mixture above. Step
4. Heat the flask to ~85-90oC.
Step 5. Record the first point.
Step 6. Add KMNO4 slowly and rotate the flask continuously until the solution turns light pink.
Step 7 .Record the final results.
Step 8. Calculate the volume of KMnO4.
Repeat the above steps with the remaining 2 flasks and compare them with each other.
The report must be typed and handed in together with the signed data sheet by the deadline.
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 3 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
2. TITRATION OF UNKNOWN CONCENTRATION H2C2O4 SOLUTION WITH
STANDARD KMnO4 SOLUTION
Step 1. Add 10mL of unknown H2C2O4 to the flask.
Step 2. Pour 40mL distilled water into the flask above.
Step 3. Add 20 mL of 6N H2SO4 to the liquid above.
Step 4. Heat the flask to around 85-90oC.
Step 5. Record the first point.
Step 6. Slowly add KMNO4 and constantly swirl the flask until the solution turns light pink. Step
7. Record the final results.
Step 8. Calculate the volume of KMnO4.
III. Results and Discussions
1. TITRATION OF KMnO4 SOLUTION WITH STANDARD H2C2O4 SOLUTION Calculation:
Normality of the standard H2C2O4 solution, N(H2C2O4) = 0.05 N
Volume of the standard H2C2O4 solution used, V(H2C2O4) = 25 mL
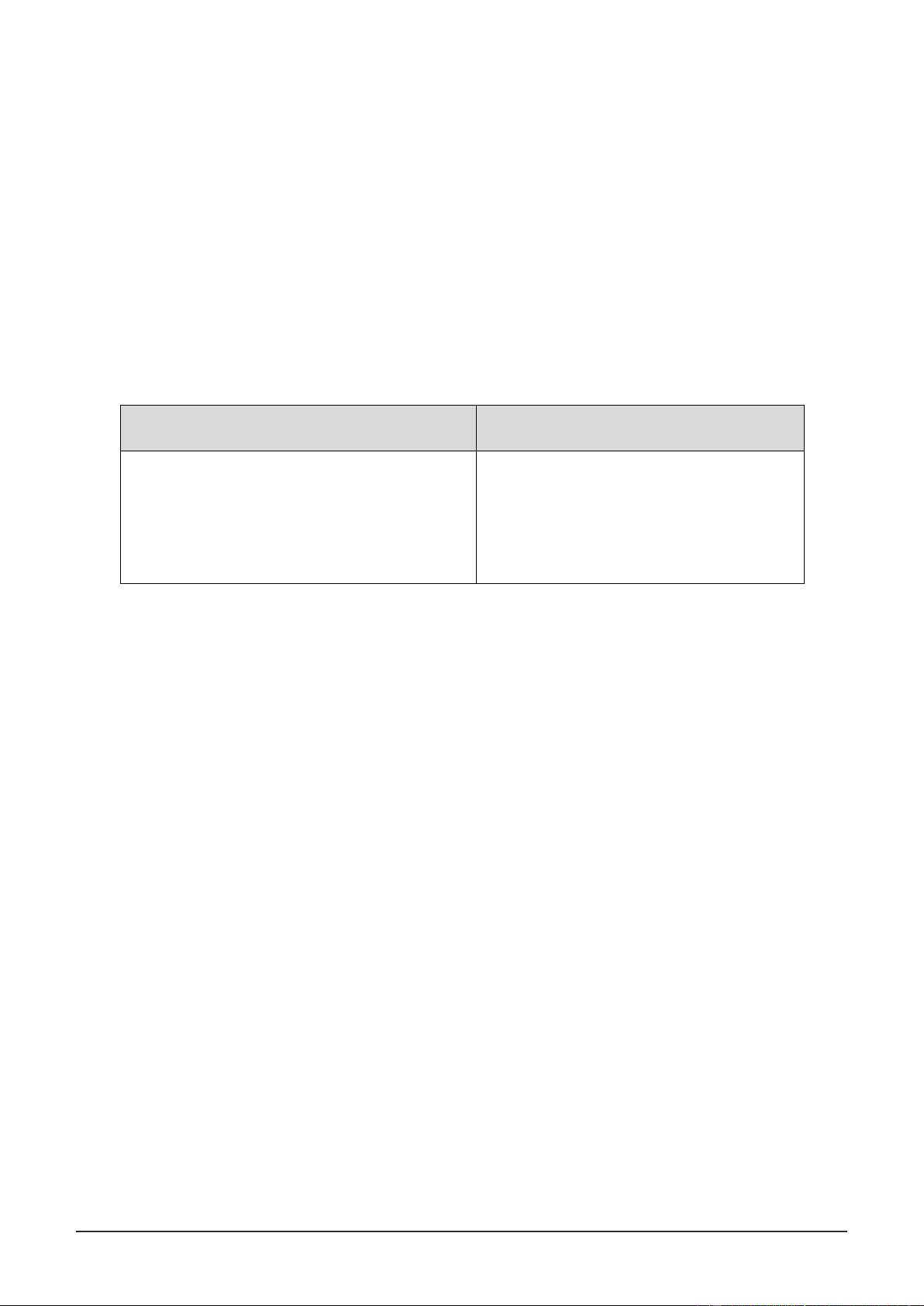
Trial # Burette reading Volume of Normality of Images (mL) KMnO 4 (mL) KMnO4 (N) 1 29.69 – 22.45 7.24 0.069 2 37.20 – 29.69 7.51 0.066
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 4 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY 3 26.30 – 19.00 7.30 0.068
Average Normality of KMnO4 = 0.067 N Comment:
To calculate the normality of KMnO4 for 3 trials, we first need to calculate the volume of KMnO4 by
subtracting the initial volume from the current volume. ((initial and final volume data are recorded during measurement)
Trial 1: Vf – Vi = 29.69 – 22.45 = 7.24 mL
Trial 2: Vf – Vi = 37.20 – 29.69 = 7.51 mL
Trial 3: Vf – Vi = 26.30 – 19.00 = 7.30 mL
Using the equation Voxidizing × Noxidizing = Vreducing × Nreducing.
So we have Nreducing = Normality of KMnO4 = 𝑉𝑜𝑥𝑖𝑑𝑖𝑧𝑖𝑛𝑔×𝑁𝑜𝑥𝑖𝑑𝑖𝑧𝑖𝑛𝑔
𝑁𝑟𝑒𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑖𝑛𝑔
Voxidizing = 25 mL (Volume of H2C2O4)
Noxidizing = 0.05 N (Normality of H2C2O4)
Vreducing = Volume of KMnO4 ( These data were calculated in the above step for 3 experiments)
Trial 1: Normality of KMnO4 = = 0.069 N
Trial 2: Normality of KMnO4 = = 0.066 N
Trial 3: Normality of KMnO4 = = 0.068 N 0.069+0.066+0.068 Average Normality of KMnO4 = = 0.067 N 3 Discussion:
The report must be typed and handed in together with the signed data sheet by the deadline.
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 5 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
In the second test, it is clear to observe the solution's color is darker than the others. This happened
because during practice, in the KMNO4 measuring stage, we did not watch carefully and left a few drops
of KMnO4 behind, causing the solution to become darker in color.
2. TITRATION OF UNKNOWN CONCENTRATION H2C2O4 SOLUTION WITH STANDARD KMnO4 SOLUTION Calculation:
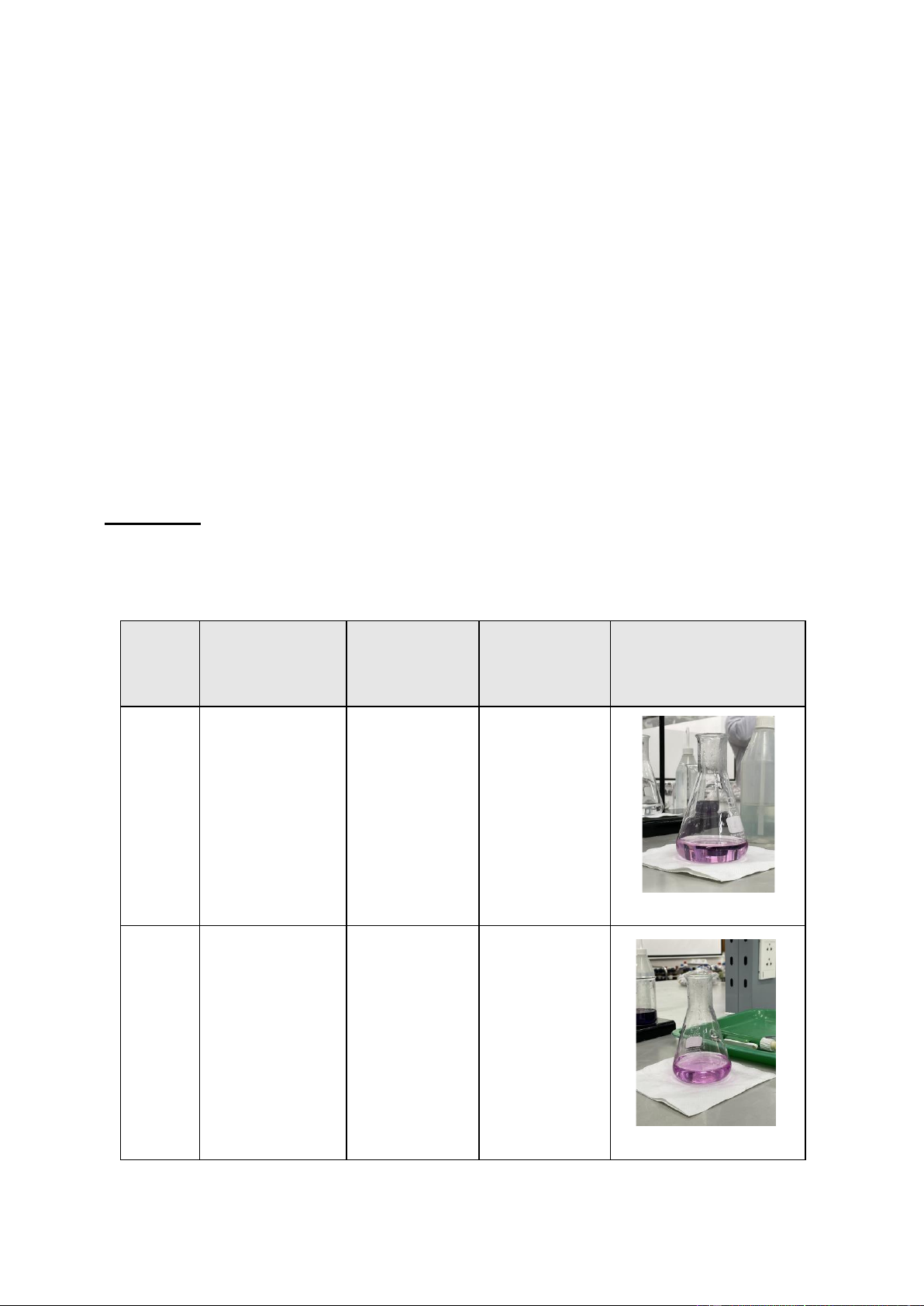
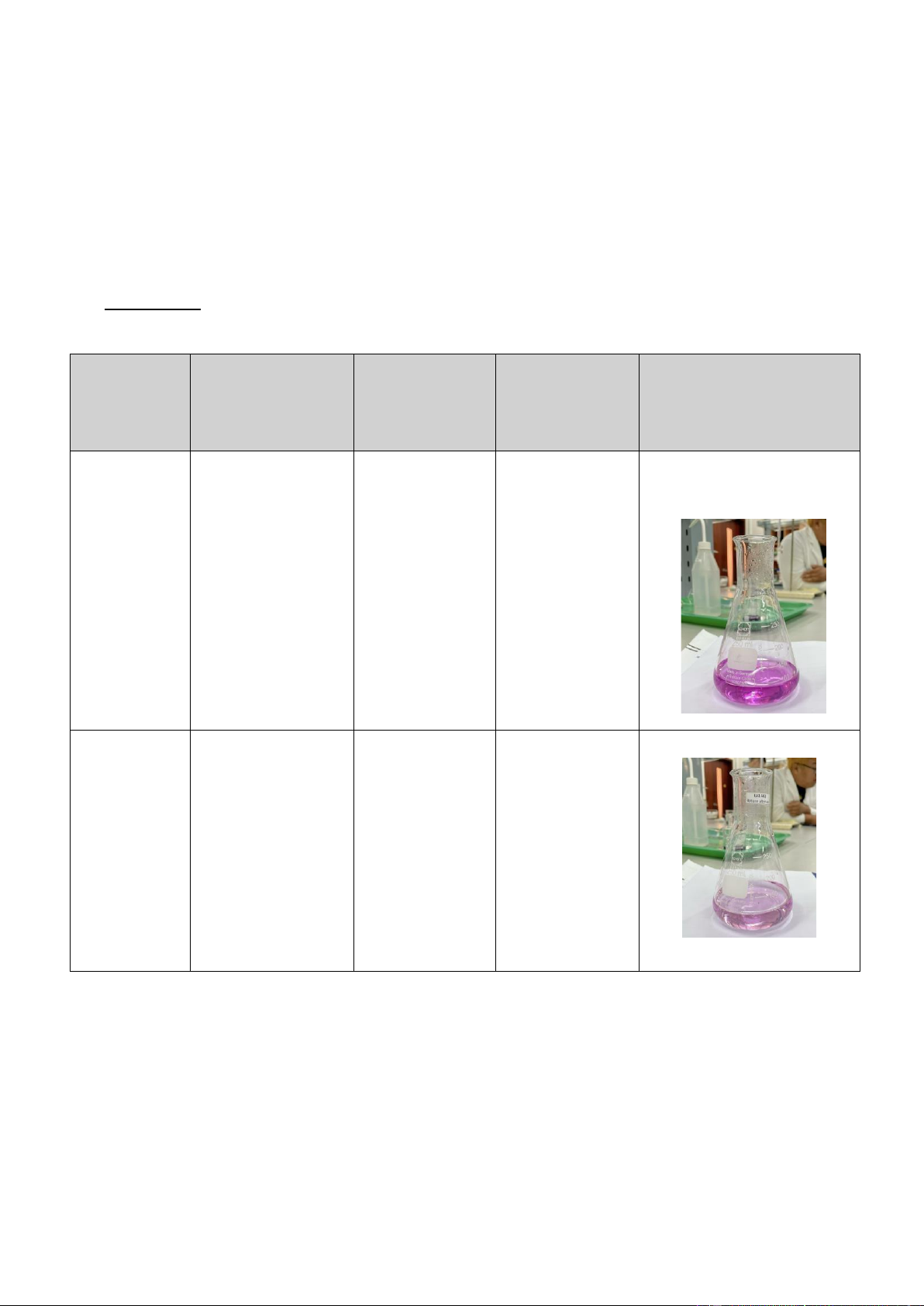
Normality of the standard KMnO4 solution, N(KMnO4) = 0.067 N Trial Burette reading Volume of Normality of Image (mL) KMnO4 (mL) H2C2O4 (N) 1 16.20 – 12.50 3.70 0.02479 2 19.65 – 16.20 3.45 0.023115
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 6 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY 3 23.20 – 19.65 3.55 0.023785
Volume of the unknown H2C2O4 solution used, V(H2C2O4) = 10 mL.
Average Normality of H2C2O4 = 0.0239 N Average Normality of KMnO4 = 0.067 N
For the calculation of the unknown normality of H2C2O4, we calculate the difference between the first
value and the final value of the volume of KMnO4 after each titration. After that, applying the formula:
Voxidizing x Noxidizing = Vreducing x Nreducing.
Trial 1: 3.70 x 0.067 = 10 x Nreducing -> N(H2C2O4) = 0.02479 N.
Trial 2: 3.45 x 0.067 = 10 x Nreducing -> N(H2C2O4) = 0.023115 N.
Trial 3: 3.55 x 0.067 = 10 x Nreducing -> N(H2C2O4) = 0.023785 N.
To calculate the average normality of H2C2O4, we have: (0.02479 + 0.023115 + 0.023785)/3 = 0.0239 N. Comment:
In the end of the titration experiment, the light or pale pink solution appears instead of the clear solution
during the first period of the process. One problem needs to be mentioned is the color of trial 1, it is
darker than the two remaining trials. The reason for this is our team is careless of controlling the faucet of the burette.
The results of this titration may be different from the published literature because the concentration and
the amount of many solutions that we use are not the same as others. Furthermore, there are a lot of
causes that affect the procedure. IV. Conclusion
To summarize today's experiments, we conducted two experiments. In the first part, we titrated the
solution of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) with the standard solution of oxalic acid (H2C2O4) We
slowly added potassium permanganate to the mixed solution as per the instructions given. Then, we
shook the solution well until it had a light pink color that did not disappear. In the second experiment,
The report must be typed and handed in together with the signed data sheet by the deadline.
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 7 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
we titrated the solution of oxalic acid with an unknown concentration using the standard solution of
potassium permanganate. We followed a similar procedure as in the first experiment and shook the
mixture well until a light pink color did not disappear. After conducting the experiments and recording
the parameters, we used the formulas to calculate the normality and volume of the substances, as shown
in part III. By coordinating with each other, our team quickly completed the experiments quickly and carefully.