
Preview text:
Accounting books
Source Documents: Represent all documents in business which contains financial records and act as
evidence of the transactions which have taken place
These kinds of resources can collect from Checks, Invoices, Receipts, Credit memos,
Employee timecards, Deposit slips, Purchase orders.
Depend on the time when the information has been collected, they can be divided into
Journal in short time and ledger accounts in long time
Book Of Original (Journal): These are books which are used in recording the transactions for the
first time. The books are maintained for memorandum purpose only and will not form part of the double entry system. Type of Journal
General Journal - To record the transactions not recorded in special journals
Special Journals - Special journals include further sub-journals; as given below:
Sales journal - To record sales invoices issued by the firm when selling goods on credit
Purchases journal - To record purchases invoices received by the business from suppliers, when buying goods on credit
Return inwards journal - To record sales returns from customers
Return outwards journal - To record purchases returns to suppliers
Cash book - To record receipts or payments
Components of Books of Original Date of transaction
Details relating to transactions, i.e., the second aspect of transactions, e.g., name of
trade receivable in the sales journal
Monetary amount of the transactions
References to the relevant ledger accounts (often called folio)
References to original source documents, e.g., invoice number
Ledger accounts: These form part of double entry system and used to record the transactions for
the period. These are accounts where the information relating to particular asset, liability, capital,
income and expenses and recorded.
There are 3 types of Ledgers – Sales Ledger lOMoAR cPSD| 41487872 Purchase Ledger General Ledger
1. Sales Ledger – Sales Ledger is a ledger in which the company maintains the transaction of selling
the products, services or cost of goods sold to customers. This ledger gives the idea of sales revenue and income statement.
2. Purchase Ledger – Purchase Ledger is a ledger in which the company organizes the transaction of
purchasing the services, products, or goods from other businesses. It gives the visibility of how
much amount the company paid to other businesses.
3. General Ledger – General Ledger is divided into two types – Nominal Ledger and Private Ledger. Nominal
ledger gives information on expenses, income, depreciation, insurance, etc. And Private ledger gives private
information like salaries, wages, capitals, etc. Private ledger is not accessible to everyone.
Ledger Account Examples: Ledger Account Examples Assets Cash Land lOMoAR cPSD| 41487872 Accounts receivable Equipment Liabilities Debt Accounts Payable Loans Accrued expenses Stock Stockholders Equity Common Stocks Retained Earnings Operative Revenues Sales Services Fees Operating Expenses Salaries and wages Office Expenses Depreciation Expense Ledger Posting
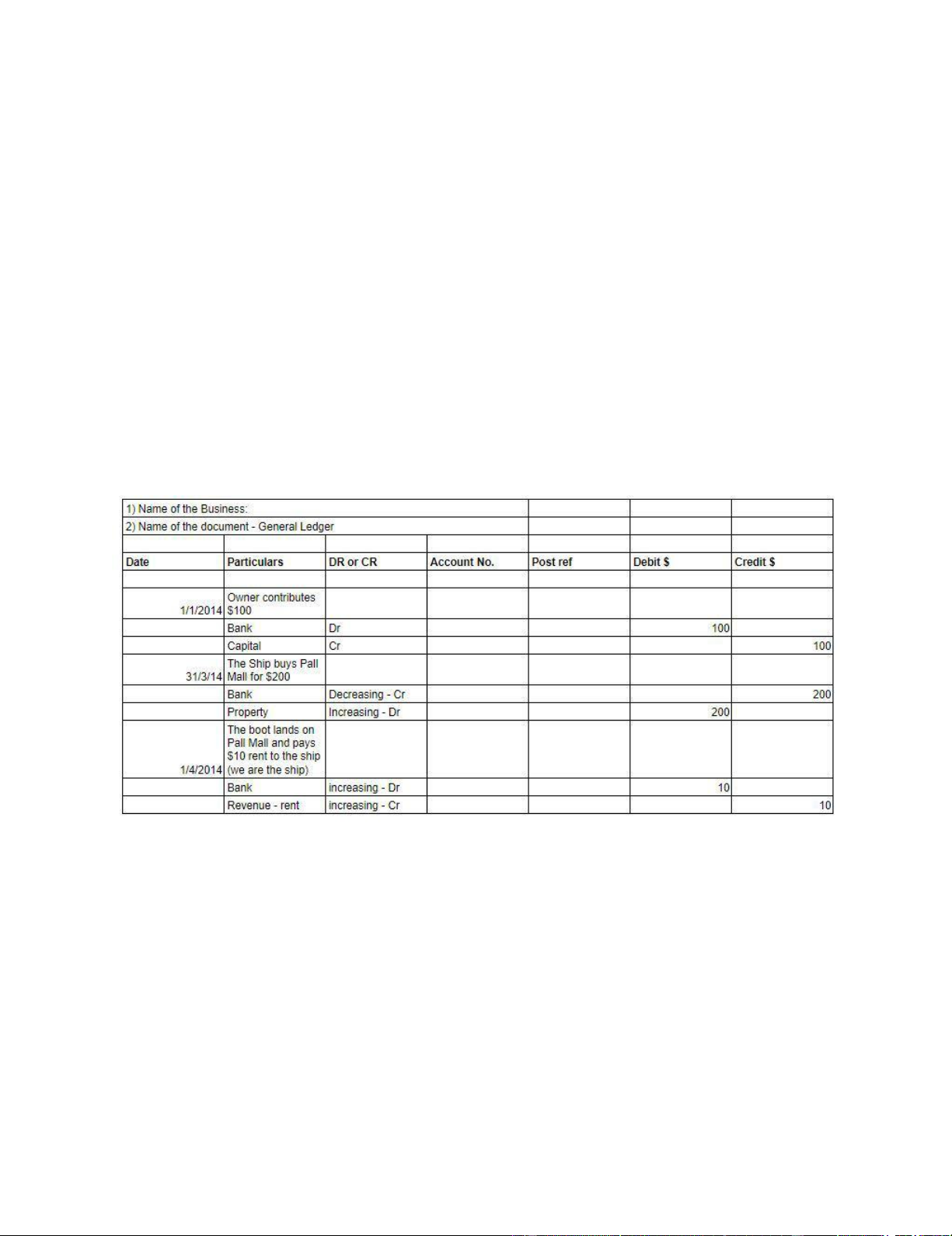
Whenever a transaction takes place it is denoted and recorded in the journal in the form of the
journal entry. Furthermore, this entry is posted again in their respective journal accounts.
This is done from the journal under the double entry principle. This is known as the ledger posting. There are
some rules which you have to adhere to while writing the journal entries for the following accounts.
Rules for writing Journal Entries in Ledger Account
Liabilities: This decreases on the side of debt and increases on the credit side.
Assets: In assets, the figure increases on the left side or you can say the debit side. While this
decreases on the credit size or the right side.
Capitals: This follows the same rule as liabilities.
Gains or Income: In this, there is a decrease on the debit side. Also, there is an increase in the credit side. lOMoAR cPSD| 41487872
Expenses: The expense in the ledger decreases on the credit side while increases on the debit side.
There are some rules that students should understand according to the nature of debit and credit. Debits and Credits Credit
For properties and goods, the credit represents that the value and stock of goods and
properties have decreased. This is moreover related to real accounts.
In the case of different accounts like dividend or interest or commission received, or the
discount to be gained, it is reported that the firm has made again. This is moreover related to the nominal account. Debit
For goods or properties, the value and use of such goods have been increased. This is related to real accounts.
Also, there is a case in which a person has received some benefit against some service given by
him or will be rendered by him in the future. Thus, when a person is liable to do something for
a firm, the fact is mentioned using that person’s account. This is moreover related to the personal account.
For other accounts like expenses or losses, a certain expense has been incurred by the firm
or has lost money. This can be related to the nominal account.
Mr. John Wick wants to start a new clothing business. He has a total sum of $100,000 in his savings
that can be invested. In addition, he owns a small shop at a primary location that can be used to start a
retail clothing outlet. He purchased furniture, including shelves, a counter desk, and other equipment
for the store for $15,000. He also hires a staff of two for customer support and other office work for $5,000 each.
Mr. Wick decided to start with men’s clothing and purchased a complete range of clothes from the
wholesale market, which cost him around $75,000. The initial purchase got sold in not more than one month for $95000.
Mr. Wick wants to journalize these transactions and create ledger accounts for April 2019.