





Preview text:
Exercise 1:
Demand and supply of fridges are shown Group in the table below: Price ($/unit) 10 12 14 16 18 20 assign 0 0 0 0 0 0 Quantity Demanded 10 90 80 70 60 50 (units) 00 0 0 0 0 0 ment Quantity supplied 30 40 50 60 70 80 (units) 0 0 0 0 0 0
presen 1. What are the demand and supply
equations, equilibrium price, and
equilibrium quantity for the fridge? tation
a. Demand equation for the fridges: 2 Qd = f(P) ⇒ Qd = a + b.P (a:
intercept =∆Qd/∆ P)
To solve b, choose 2 points which P=120, Qd=900, and P=140, Qd=800: ∆ Qd 800 900 b = = − = -5 ∆ P 140 120 −
To solve a, choose a point which P=100, Qd=1000: Qd = a +b.P ⇔1000 = a + (-5).100 ⇔a = 1000 - (-500) ⇔a = 1500
Then we have the demand equation: Qd = 1500 - 5. P
b. Supply equation for the fridges: Qs = c + d.P
To solve d, choose 2 points which P=140, Qs=500, and P=160, Qs=600: ∆ Qs 500 600 d = = − = 5 ∆ P 140 160 −
To solve c, choose a point which P=100, Qs=300: Qs = c + d.P ⇒ 300 = c + 5.100 ⇔c = 300 - 500 ⇔c = -200
Then we have the supply equation: Qs = -200 + 5. P
c. The equilibrium price for the fridge:
We have an equilibrium price when Qd = Qs:
⇒ 1500 - 5P = -200 + 5P ⇔10P = 1700 ⇔P = 170
Conclusion: The equilibrium price is 170$
d. The equilibrium quantity for the fridge:
Because the Pe = 170$ and Qd = Qs so we have:
Qe = Qd =Qs = 1500 - 5.170= 650 (units)
Conclusion: The equilibrium quantity is 650 units
2. What are the surpluses and shortages of fridges at
the price of $ 200 and $ 110?
-At the price of $200, we have Qd = 500, Qs = 800
Qd < Qs ⇒ Surplus = 800 -500 = 300 (units)
-At the price of $110, we have:
Qd = 1500 - 5P = 1500 - 5.110 = 950 (units)
Qs = -200 + 5P = -200 + 5.110 = 350 (units)
Qd > Qs ⇒ Shortage: 950 - 350 = 600 (units)
3. Suppose the supply of the fridge is constant, what
happened to the demand for the fridge if the price of
electricity increase? Given that quantity demanded
fridge changed by 300 units at each price level, what
are the new equilibrium price and new equilibrium
quantity for the fridge?
If the price of electricity increase, the demand for fridge will
decrease because electricity and fridge are complementary
goods, we need electricity to use the fridge.
If Qd decreased by 300 units at each price level, we have a new demand equation: Qd = a + b.P
-To solve b, we choose 2 adjacent price levels :P = 100 and P=120: ∆ Q b = = −300 = -15 ∆ P 120 100 −
-To solve a, we choose a point which P =100, Qd = 1000: Qd = a + b.P ⇒1000= a - 15.100 ⇔a = 1000 + 15.100 ⇔a = 2500
Then we have a new demand equation: Qd = 2500 - 15P
-The supply of the fridge is constant, so: Qs = -200 + 5P
-The new equilibrium price of the fridge: Qd = Qs
⇒ 2500 - 15P = -200 + 5P ⇔ 20P = 2700 ⇔P = 135 =Pe
-With Pe = 135, the new equilibrium quantity of the fridge:
Qe= Qd=Qs = 2500 -15.135 = 475 (units)
Conclusion: The new equilibrium quantity of the fridge is 475 units
The new equilibrium price of the fridge is $135
4. Suppose the government imposes a tax of $ 10 per
unit of fridges sold, what are the new equilibrium price
and new equilibrium quantity for fridges? We have:
-The demand equation: Q = 1500 - 5P 1500−Q ⇒P = = 300 - 0,2. Q = Pd 5
-The supply equation: Q = -200 + 5P Q+200 ⇒ P = = 0,2. Q + 40 5
After imposing a tax of $10 per unit of fridge sold, the price of supply will increase:
Ps = 0,2. Q+ 40 + 10 = 0,2. Q + 50
Then we have a new equilibrium quantity: Ps = Pd
⇒0,2. Q + 50 = 300 - 0,2. Q ⇒0,4. Q = 250 ⇒Q = 625 = Qe
With Qe = 625, we have a new equilibrium price:
Pe = Ps = Pd = 300 -0,2. 625 = 175
Conclusion: The new equilibrium price is $175
The new equilibrium quantity is 625 units
5. Suppose government supports the sellers in the
amount of $ 10 per unit of fridge sold, what are the new
equilibrium price and new equilibrium quantity for the fridge?
From the result of the previous task, we have:
-The demand equation: Pd = 300 – 0,2. Q
-The supply equation: Ps = 0,2. Q + 40
When the government supports the sellers at $10 per unit sold,
we have a new supply equation:
Ps’ = 0,2. Q+ 40 - 10 = 0,2. Q + 30
Then we have a new equilibrium quantity: Ps’= Pd
⇒ 0,2. Q + 30 = 300 – 0,2. Q ⇔ 0,4. Q = 270 ⇔ Q = 675 = Qe
With Qe = 675, we have a new equilibrium price:
Pe =Ps’=Pd = 0,2. 675 + 30 = 165
Conclusion: The new equilibrium price is $165
The new equilibrium quantity is 675 units Exercise 2:
With the aid of diagrams, show how each of the following
events affects the supply and/or demand curve for motorcycles.
In each case, show and state the effect on the equilibrium price and quantity.
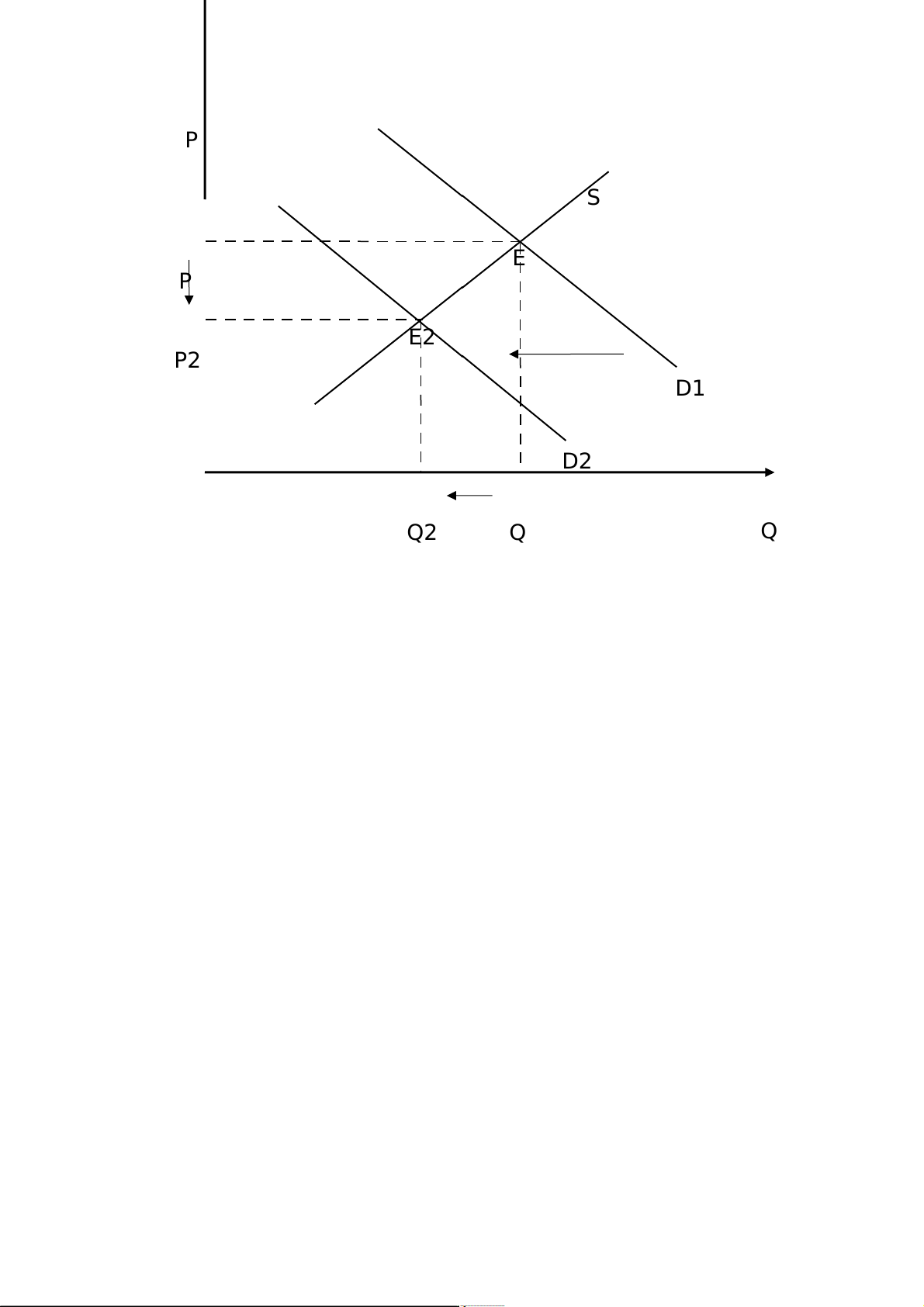
1. An increase in Vietnamese personal income tax rates
The demand curve will shift to the left of the former because
tax is one of the non-price factors. If the personal income tax
rates increase, the demand will fall, equilibrium price and quantity will descrease. P S E P E2 P2 D1 D2 Q2 Q Q
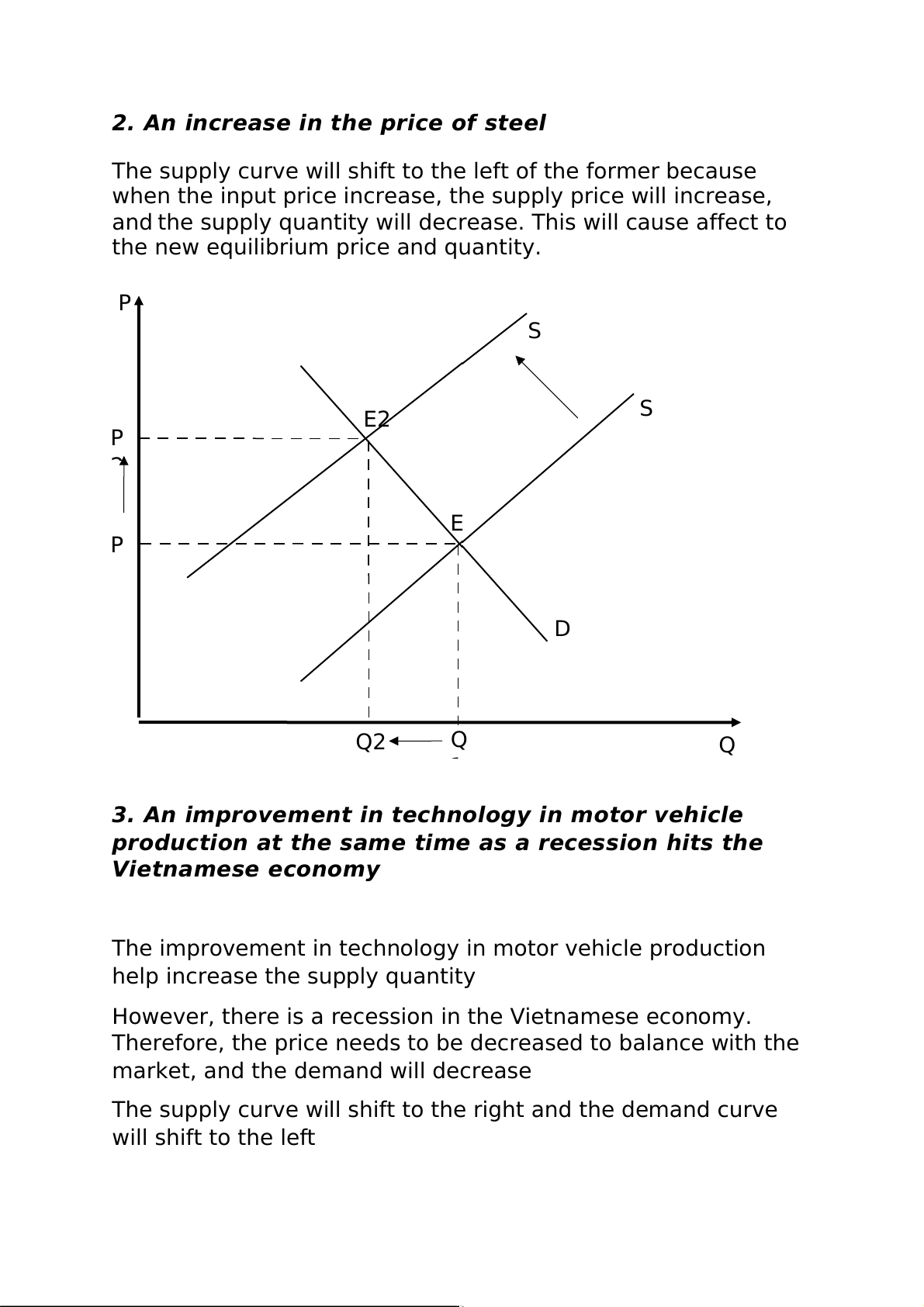
2. An increase in the price of steel
The supply curve will shift to the left of the former because
when the input price increase, the supply price will increase,
and the supply quantity will decrease. This will cause affect to
the new equilibrium price and quantity. P S S E2 P 2 E P D Q2 Q Q
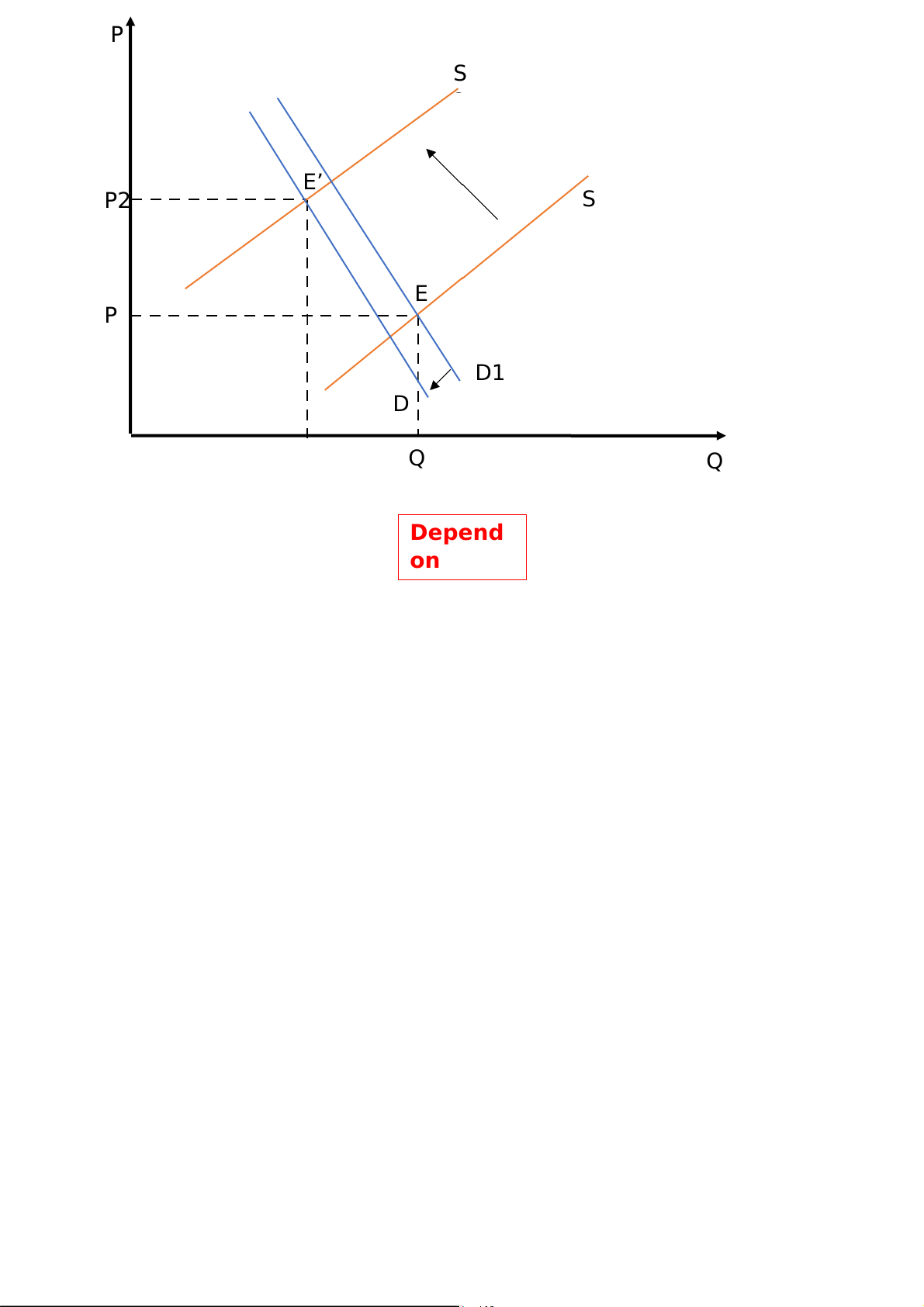
3. An improvement in technology in motor vehicle
production at the same time as a recession hits the Vietnamese economy
The improvement in technology in motor vehicle production
help increase the supply quantity
However, there is a recession in the Vietnamese economy.
Therefore, the price needs to be decreased to balance with the
market, and the demand will decrease
The supply curve will shift to the right and the demand curve will shift to the left
In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity move to the lower left of former one. P S E’ P2 S E P D1 D Q Q Depend on




