


Preview text:
Xà Tuấn Huy – EBBA 14.3 Group
Problem-solving Exercise assignm Problem 1:
Suppose that a consumer uses $60 to buy ent
2 goods: X and Y. Given that price of the good
X is $3 per unit and the price of the good Y is
$1 per unit. Suppose that the utility function
present of this consumer is TU=XY
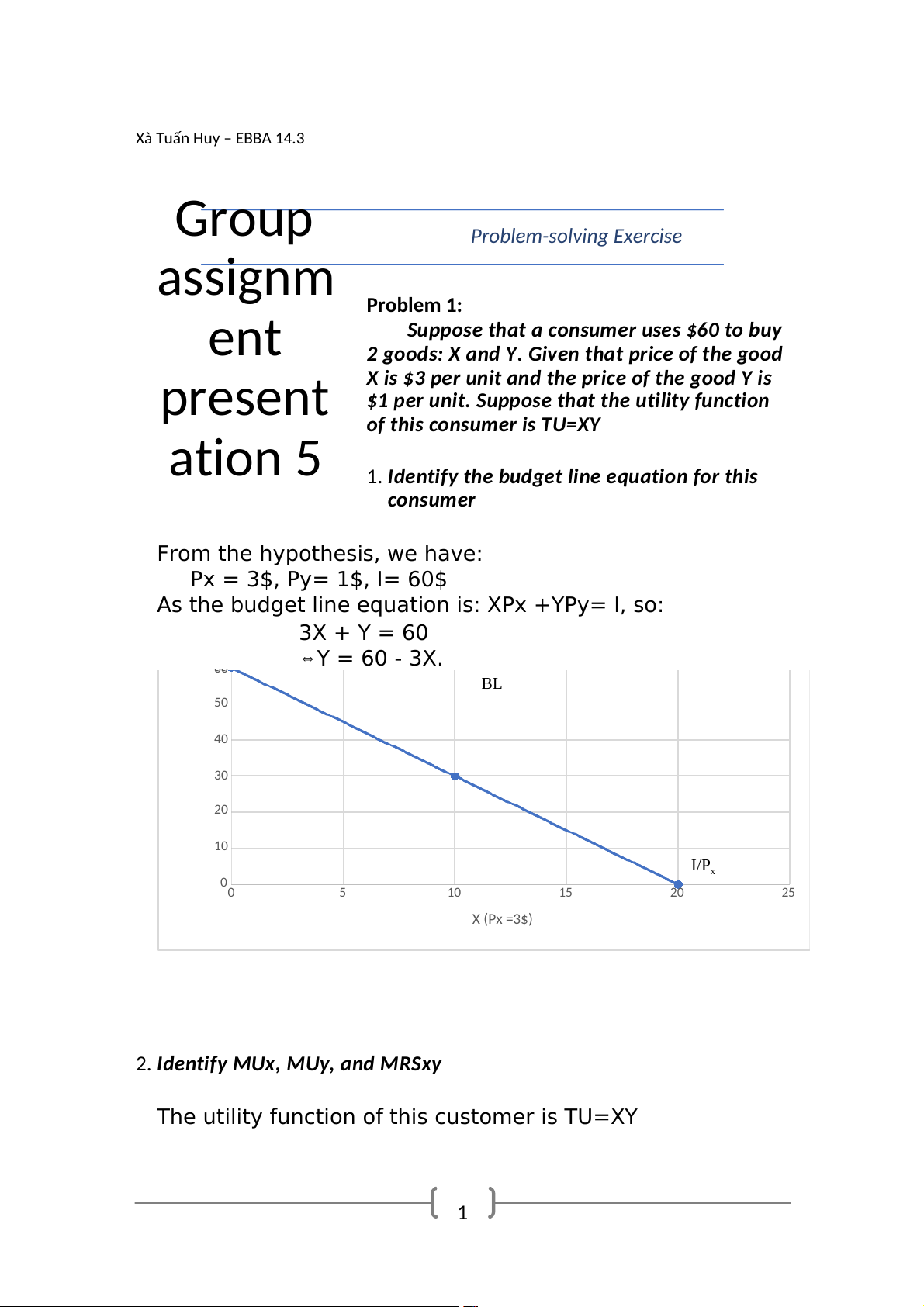
ation 5 1.Identify the budget line equation for this consumer From the hypothesis, we have: Px = 3$, Py= 1$, I= 60$
As the budget line equation is: XPx +YPy= I, so: 3X + Y = 60 ⇔Y = 60 - 3X. 60 BL 50 40 ) 1$ 30 Y (P y= 20 10 I/Px 00 5 10 15 20 25 X (Px =3$)
2. Identify MUx, MUy, and MRSxy
The utility function of this customer is TU=XY 1 Xà Tuấn Huy – EBBA 14.3 ∆ TUx
⇒ MUx = ∆Qx = TUx)’ = Y ( Δ TUy
MUy = ΔQy = (TUy)’= X −ΔY MUx Y MRSxy = = = Δ X MUy X
3. What is the optimal quantity of good X (X*) and the optimal
quantity of good Y (Y*) that he should buy to maximize his utility? Px
To maximize the utility: MU = P ⇒ = MUx =MRSxy Py MUy We have: {MUx MU = y P P x y 3 X +Y =60 = X { Y3 1 3 X +Y =60 { 3 X=Y 3 X +Y =60 {X=10 Y =30
So, optimal quantity of good X (X*) is 10 units
optimal quantity of good Y (Y*) is 30 units Problem 2:
Monthly, Ms. Lan spends 1 million VND for buying meat (X) and
potato (Y). Price of meat is 20,000 dong/kg, and the price of potato is 5000 dong/kg.
a. Identify Lan’s budget line equation and draw that BL curve. From the hypothesis, we have: Px = 20000 dong Py = 5000 dong I = 1000000 dong
As the budget line equation is: XPx +YPy= I, so: 20000X + 5000Y = 1000000 2 Xà Tuấn Huy – EBBA 14.3 ⇔Y = 200 - 4X.
Equation graphed into Budget line curve: 200 150 to)(kg) 100 Y(pota 50 00 10 20 30 40 50 60 X(Meat) (kg)
b. Assume that Lan’s utility function for meat and potato is TU= (X-
2). Y, what is Lan’s optimal choice between meat and potato to
maximize her total utility?
As the assumption above, we have the utility function is: TU = (X-2) Y = XY - 2Y
So, we have the marginal utility for meat and potato are: Δ TUx
MUx = ΔQx = (TUx)’ = (XY -2Y)’ = Y Δ TUy MUy =
= (TUy)’ = ((X-2) Y)’ = X-2 Δ Qy
To calculate the optimal choice of meat and potato to
maximize utility, we use the method base on Budget Line and Indifference Curve Px
To maximize the utility: MU = P ⇒ = MUx =MRSxy Py MUy We have: 3 Xà Tuấn Huy – EBBA 14.3 {MU MU x = y P P x y 4 X +Y =200 = X −2 { Y 20000 5000 4 X +Y =200 (X − )= Y {20000 2 5000 4 X +Y =200 {X=26 Y =96
So, to maximize the utility, Ms. Lan must choose 26kg meats and 96kg potatoes y 200 E INDIFFERENCE CURVE Budget Line 0 50 x 4




