










Preview text:
When a pizza maker lists the price of a pizza as $10, this is an example of using money as a: 2/2 store of value. unit of account. medium of exchange. flow of value. Open-market operations are: 2/2
Commerce Department efforts to open foreign markets to international trade.
Central bank purchases and sales of government bonds.
Securities and Exchange Commission rules requiring open disclosure of market trades.
Treasury Department purchases and sales of the U.S. gold stock.
If bread is produced by using a constant returns to scale production function, then if the: 2/2
number of workers is doubled, twice as much bread will be produced.
amount of equipment is doubled, twice as much bread will be produced.
amounts of equipment and workers are both doubled, twice as much bread will be produced.
amounts of equipment and workers are both doubled, four times as much bread will be produced.
If currency held by the public equals $100 billion, reserves held by banks equal $50
billion, and bank deposits equal $500 billion, then the monetary base equals: 2/2 $50 billion. $100 billion. $150 billion. $600 billion.
If the reserves requirement (rr) increases, while the ratio of currency to deposits (cr)
is constant and the monetary base (B) is constant, then: 2/2
it cannot be determined whether the money supply increases or decreases. the money supply increases. the money supply decreases.
the money supply does not change. The money supply consists of: 2/2 currency plus reserves.
currency plus the monetary base. currency plus demand deposits.
the monetary base plus demand deposits.
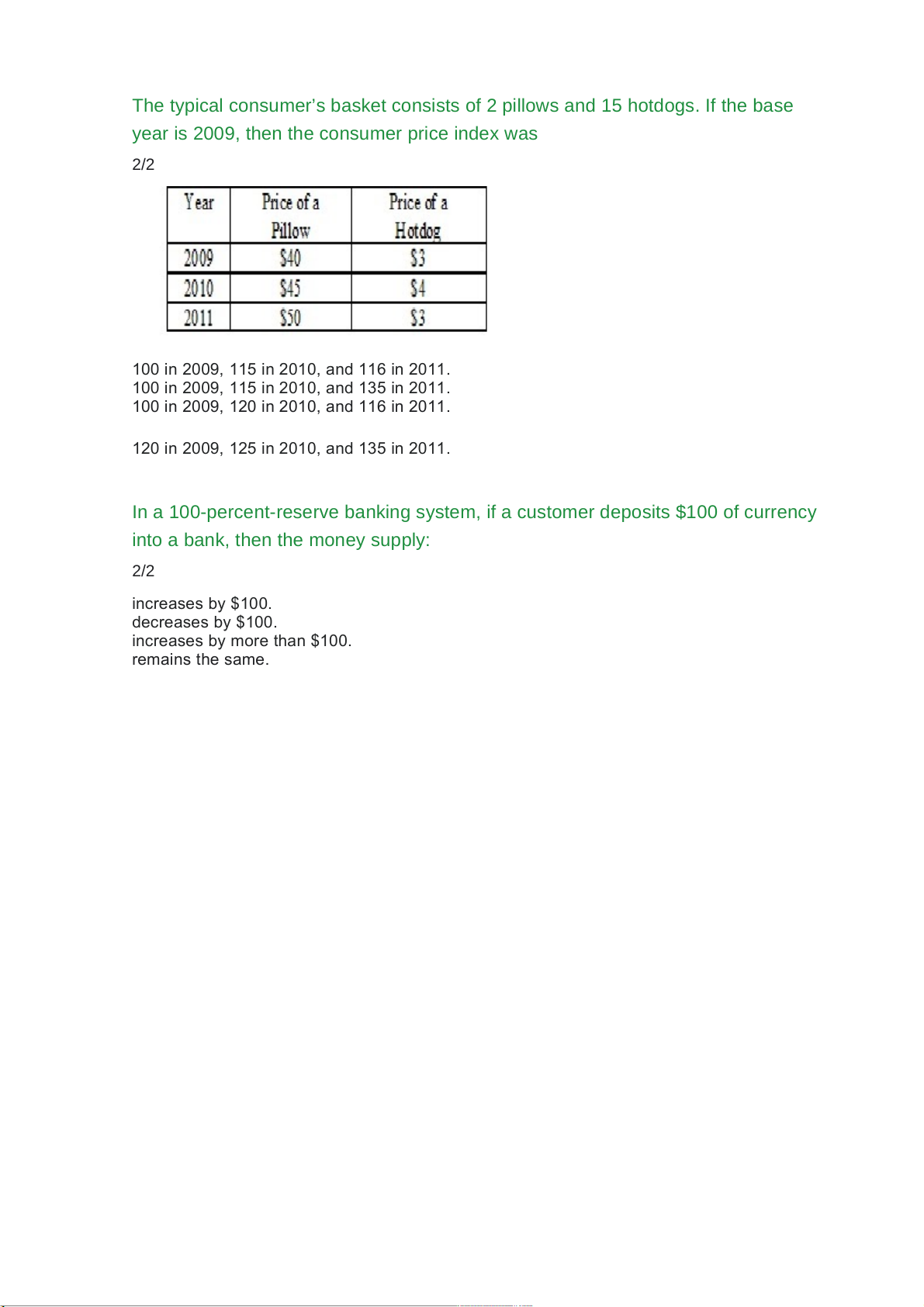
The typical consumer’s basket consists of 2 pillows and 15 hotdogs. If the base
year is 2010, then the consumer price index was 2/2
83.33 in 2009, 100.00 in 2010, and 96.67 in 2011.
85.56 in 2009, 100.00 in 2010, and 102.22 in 2011.
85.56 in 2009, 100.00 in 2010, and 96.67 in 2011.
92.22 in 2009, 99.00 in 2010, and 95.22 in 2011.
Assume that a rancher sells McDonald's a quarter-pound of meat for $1 and that
McDonald's sells you a hamburger made from that meat for $2. In this case, the
value included in GDP should be: 2/2 $0.50. $1. $2. $3.
In calculating the CPI, a fixed basket of goods and services is used. The quantities
of the goods and ser-vices in the fixed basket are determined by 2/2 surveying consumers.
surveying sellers of the goods and services.
working backward from the rate of inflation to arrive at imputed values for those quantities.
arbitrary choices made by federal government employees.
The consumer price index and the GDP deflator are two alternative measures of the
overall price level. Which of the following statements about the two measures is correct? 2/2
The CPI involves a base year; the GDP deflator does not involve a base year.
The CPI can be used to compute the inflation rate; the GDP deflator cannot be used to compute the inflation rate.
The CPI reflects the prices of goods and services produced domestically; the GDP deflator
reflects the prices of all goods and services bought by consumers.
The CPI reflects a fixed basket of goods and services; the GDP deflator reflects current
production of goods and services.
4. Assume that the market basket of goods and services purchased in 2004 by the
average family in the United States costs $14,000 in 2004 prices, whereas the
same basket costs $21,000 in 2009 prices. However, the basket of goods and
services actually purchased by the average family in 2009 costs $20,000 in 2009
prices, whereas this same basket would have cost $15,000 in 2004 prices. Given
this data, a Laspeyres price index of 2009 prices using 2004 as the base year would be: 2/2 1.05. approximately 1.07. approximately 1.33. 1.50.
In addition to the consumer price index, the General Statistic Office also calculates the 2/2 macroeconomic price index. producer price index. rental unit price index. terms of trade.
The two most important factors of production are: 2/2 goods and services. labor and energy. capital and labor. saving and investment.
Which of the following changes in the price index produces the greatest rate of
inflation: 106 to 112, 112 to 118, or 118 to 124? 2/2 106 to 112 112 to 120 118 to 126
All of these changes produce the same rate of inflation.
The market value of all final goods and services produced within an economy in a
given period of time is called: 2/2 industrial production. gross domestic product. the GDP deflator. general durable purchases.
The production function feature called “constant returns to scale” means that if we: 0/2
multiply capital by z1 and labor by z2, we multiply output by z3.
increase capital and labor by 10 percent each, we increase output by 10 percent.
increase capital and labor by 5 percent each, we increase output by 10 percent.
increase capital by 10 percent and increase labor by 5 percent, we increase output by 7.5 percent. Câu trả lời đúng
increase capital and labor by 10 percent each, we increase output by 10 percent.
The basket of goods in the consumer price index changes 2/2
occasionally, as does the group of goods used to compute the GDP deflator.
automatically, as does the group of goods used to compute the GDP deflator.
occasionally, whereas the group of goods used to compute the GDP deflator changes automatically.
automatically, whereas the group of goods used to compute the GDP deflator changes occasionally.
GDP is all of the following except the total: 2/2
expenditure of everyone in the economy.
income of everyone in the economy.
expenditure on the economy's output of goods and services. output of the economy.
To calculate the CPI, the General Statistic Office uses 2/2
the prices of all goods and services produced domestically.
the prices of all final goods and services.
the prices of all consumer goods.
the prices of some consumer goods.
Assume that the adult population of the United States is 191.6 million, total
employment is 117.6 million, and 9.4 million are unemployed. Then the
unemployment rate, as normally computed, is approximately ______ percent. 2/2 4.9 7.4 7.9 9.4
An increase in the price of imported goods will show up in: 2/2
the CPI but not in the GDP deflator.
the GDP deflator but not in the CPI.
both the CPI and the GDP deflator.
neither the CPI nor the GDP deflator.
Assume that total output consists of 4 apples and 6 oranges and that apples cost
$1 each and oranges cost $0.50 each. In this case, the value of GDP is: 2/2 10 pieces of fruit. $7. $8. $10.
The typical consumer’s basket consists of 2 pillows and 15 hotdogs. If the base year is 2011, then the CPI 2/2
increased from 2009 to 2010 and increased from 2010 to 2011.
increased from 2009 to 2010 and decreased from 2010 to 2011.
decreased from 2009 to 2010 and increased from 2010 to 2011.
decreased from 2009 to 2010 and decreased from 2010 to 2011.
The price index was 92 in 2000, and the inflation rate was 13 percent between 1999
and 2000. The price index in 1999 was 2/2 79. 81.4. 103.96. 105.
The typical consumer’s basket consists of 2 pillows and 15 hotdogs. If the base
year is 2009, then the economy’s inflation rate in 2010 is 2/2 20 percent. 25 percent. 30 percent. 120 percent.
The typical consumer’s basket consists of 2 pillows and 15 hotdogs. The cost of the basket 2/2
increased from 2009 to 2010 and increased from 2010 to 2011.
increased from 2009 to 2010 and decreased from 2010 to 2011.
decreased from 2009 to 2010 and increased from 2010 to 2011.
decreased from 2009 to 2010 and decreased from 2010 to 2011. The monetary base consists of: 0/2
currency held by the public, plus reserves held by banks.
all outstanding currency, plus reserves held by banks.
all outstanding currency, plus demand deposits. all bank reserves. Câu trả lời đúng
currency held by the public, plus reserves held by banks.
An increase in the price of goods bought by firms and the government will show up in: 2/2
the CPI but not in the GDP deflator.
the GDP deflator but not in the CPI.
both the CPI and the GDP deflator.
neither the CPI nor the GDP deflator.
If the currency–deposit ratio equals 0.5 and the reserve requirement ratio equals
0.1, then the money multiplier equals: 2/2 0.6. 1.67. 2.0. 2.5.
GDP is the market value of all ______ goods and services produced within an
economy in a given period of time 2/2 used intermediate consumer final
If you hear in the news that the Federal Reserve conducted open-market
purchases, then you should expect ______ to increase. 2/2 reserve requirements the discount rate the money supply the discount rates
If the Federal Reserve increases the interest rate paid on reserves, banks will tend
to hold _____ excess reserves, which will _____ the money multiplier. 2/2 more; increase more; decrease fewer; increase fewer; decrease
If the reserves requirement (rr) ratio is less than one, and the monetary base
increases by $1 million, then the money supply will: 2/2 increase by $1 million. decrease by $1 million.
increase by more than $1 million.
decrease by more than $1 million.
If the Federal Reserve wishes to increase the money supply, it should: 2/2 decrease the discount rate.
increase interest paid on reserves. sell government bonds. decrease the monetary base.
Open-market operations change the ______; changes in interest rate paid on
reserves change the ______; and changes in the discount rate change the ______. 2/2
monetary base; monetary base; monetary base
money multiplier; money multiplier; money multiplier
monetary base; money multiplier; monetary base
money multiplier; monetary base; money multiplier
To increase the monetary base, the Fed can: 2/2 conduct open-market purchases. conduct open-market sales.
raise the interest rate paid on reserves.
lower the required reserve ratio.
Suppose a basket of goods and services has been selected to calculate the
consumer price index. In 2005, the basket of goods cost $108.00; in 2006, it cost
$135.00; and in 2007, it cost $168.75. Which of the following statements is correct? 0/2
Using 2005 as the base year, the economy’s inflation rate was higher in 2007 than it was in 2006.
If 2007 is the base year, then the CPI is 33.75 in 2006.
If the CPI is 156.25 in 2007, then 2005 is the base year.
Using 2005 as the base year, the economy’s inflation rate for 2006 was 27 percent. Câu trả lời đúng
If the CPI is 156.25 in 2007, then 2005 is the base year.
The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is: 2/2 GDP. CPI. GNP. real GDP.
Since GDP includes only the additions to income, not transfers of assets, ______
are not included in the computation of GDP. 2/2 final goods used goods consumption goods goods produced for inventory
Economists use the term money to refer to: 2/2 income. profits. assets used for transactions. earnings from labor.
When the central bank makes an open-market sale, it: 2/2
increases the money multiplier (m).
increases the currency–deposit ratio (cr).
increases the monetary base (MB).
decreases the monetary base (MB). The labor force equals the: 2/2 adult population.
number of employed individuals.
number of unemployed individuals.
number of employed and unemployed individuals.
Unlike the GDP deflator, the CPI includes the prices of: 0/2 goods purchased by firms.
goods purchased by governments. exported goods. imported goods. Câu trả lời đúng exported goods.
All of the following are measures of GDP except the total: 2/2
expenditures of all businesses in the economy.
income from all production in the economy.
expenditures on all final goods and services produced. value of all final production.
Suppose a basket of goods and services has been selected to calculate the CPI
and 2004 has been select-ed as the base year. In 2002, the basket’s cost was $50;
in 2004, the basket’s cost was $52; and in 2006, the basket’s cost was $54.60. The value of the CPI in 2006 was 2/2 91.6. 95.2. 105.0. 109.2.
To increase the money supply, central bank: 2/2 buys government bonds. sells government bonds. buys corporate stocks. sells corporate stocks.
A production function is a technological relationship between: 2/2
factor prices and the marginal product of factors.
factors of production and factor prices.
factors of production and the quantity of output produced.
factor prices and the quantity of output produced.
Assume that apples cost $0.50 in 2002 and $1 in 2009, whereas oranges cost $1 in
2002 and $1.50 in 2009. If 4 apples were produced in 2002 and 5 in 2009, whereas
3 oranges were produced in 2002 and 4 in 2009, then real GDP (in 2002 prices) in 2009 was: 2/2 $5. $6.50. $9.50. $11.
The typical consumer’s basket consists of 2 pillows and 15 hotdogs. If the base
year is 2009, then the consumer price index was 2/2
100 in 2009, 115 in 2010, and 116 in 2011.
100 in 2009, 115 in 2010, and 135 in 2011.
100 in 2009, 120 in 2010, and 116 in 2011.
120 in 2009, 125 in 2010, and 135 in 2011.
In a 100-percent-reserve banking system, if a customer deposits $100 of currency
into a bank, then the money supply: 2/2 increases by $100. decreases by $100. increases by more than $100. remains the same.




