


















Preview text:
Chương 1: GIÁ TRỊ THỜI GIAN CỦA TIỀN (TIME VALUE OF MONEY)
Ví dụ 1: How much interest do you get if you put $1000 for two years in a savings account that pays
simple interest at a rate of 9% per annum? And if you leave it in the account for only half a year?
(Bạn sẽ nhận được bao nhiêu tiền lãi nếu gửi $1000 trong hai năm vào một tài khoản tiết kiệm tính lãi
đơn với lãi suất 9% mỗi năm? Và nếu bạn gửi trong chỉ nửa năm thì sao?)
Ví dụ 2: How many days does it take for $1450 to accumulate to $1500 under 4% per annum simple
interest? (Mất bao nhiêu ngày để $1450 tích lũy thành $1500 với lãi suất đơn 4% mỗi năm?)
Ví dụ 3: How much do you have after you put $1000 for two years in a savings account that pays
compound interest at a rate of 9% per annum? (Bạn sẽ có bao nhiêu tiền sau khi gửi $1000 trong hai
năm vào một tài khoản tiết kiệm với lãi suất kép 9% mỗi năm?)
Ví dụ 4: Suppose that a capital of $500 dollars earns $150 of interest in 6 years. What was the
interest rate if compound interest is used? (Giả sử một khoản vốn $500 sinh lời $150 tiền lãi trong 6
năm. Lãi suất là bao nhiêu nếu sử dụng lãi kép?)
Ví dụ 5: How long does it take to double your capital if you put it in an account paying compound
interest at a rate of 7.5 %? (Mất bao lâu để nhân đôi số vốn của bạn nếu bạn gửi nó vào một tài khoản
trả lãi kép với lãi suất 7.5%?)
Ví dụ 6: Using the interest rate of 5% compounded annually, find: a.
The future value 6 years from today of 5000 deposited today.
b. The present value of 20000 payable in 15 years.
(Sử dụng lãi suất 5% ghép lãi hàng năm, hãy tìm:
a. Giá trị tương lai sau 6 năm kể từ hôm nay của khoản tiền 5000 được gửi vào hôm nay.
b. Giá trị hiện tại của khoản tiền 20000 sẽ được thanh toán trong 15 năm nữa)
Ví dụ 7: Let the interest rate be 6% and the time interval be [2,3]. Find i[2,3] for a.
compound interest
b. simple interest
(Cho lãi suất là 6% và khoảng thời gian là [2,3]. Tìm i[2,3] cho: a. Lãi kép b. Lãi đơn
Trong đó, i[2,3] có thể hiểu là tỷ suất sinh lời trong khoảng thời gian từ năm thứ 2 đến năm thứ 3)
Ví dụ 8: An investment earns a 6% annual interest rate. Calculate the quarterly (3-month) effective
rates for the period [0.5, 0.75] và [1.5, 1.75] a. at 6% compound interest
b. at 6% simple interest.
(Một khoản đầu tư có lãi suất hàng năm là 6%. Tính lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng quý (3 tháng) cho các
khoảng thời gian [0.5, 0.75] và [1.5, 1.75]: a. Với lãi kép 6%
b. Với lãi đơn 6%.)
Ví dụ 9: On January 31, S borrows 5000 from B and gives B a promissory note. A note states that
the loan will be repaid on April 30 of the same year, with interest at 12% per annum. On March 1 B
sells the promissory note to J, who pays B a sum of money in return for the right to collect the
payment from S on April 30. J pays B an amount such that J’s interest rate earned from March 1 to
the maturity date can be stated as an annual rate of interest of 15%. Assume all calculation are
based on simple interest and a 365 day year.
a. Determine the amount S was to have paid B on April 30.
b. Determine the amount that J paid to B and the interest rate B earned quoted on an annual basis.
(Vào ngày 31 tháng 1, S vay 5000 từ B và đưa cho B một giấy hẹn trả nợ. Giấy hẹn ghi rõ khoản vay sẽ
được hoàn trả vào ngày 30 tháng 4 cùng năm, với lãi suất 12% mỗi năm. Vào ngày 1 tháng 3, B bán giấy
hẹn trả nợ này cho J, người trả cho B một khoản tiền để đổi lấy quyền thu khoản thanh toán từ S vào
ngày 30 tháng 4. J trả cho B một số tiền sao cho lãi suất mà J kiếm được từ ngày 1 tháng 3 đến ngày đáo
hạn có thể được biểu thị là lãi suất hàng năm là 15%. Giả sử tất cả các tính toán đều dựa trên lãi suất
đơn và một năm có 365 ngày.
a. Xác định số tiền S phải trả cho B vào ngày 30 tháng 4.
b. Xác định số tiền mà J đã trả cho B và lãi suất mà B kiếm được được tính theo năm.)
Ví dụ 10: Suppose that interest is earned at a rate of 1% per month, compounded monthly (i.e., a
1% monthly effective rate).
a. What is the nominal annual rate?
b. What is the annual effective rate?
(Giả sử rằng lãi suất là 1% mỗi tháng, được ghép lãi hàng tháng, tức là lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng tháng là
1%. a. Tỷ lệ danh nghĩa hàng năm là bao nhiêu? b. Tỷ lệ hiệu dụng hàng năm là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 11: Interest is convertible semi-annually and results in an annual effective rate of 10.25%.
Find the nominal annual rate convertible semi-annually. (Lãi suất được chuyển đổi nửa năm một lần
và cho ra một tỷ lệ hiệu dụng hàng năm là 10.25%. Tìm tỷ lệ danh nghĩa hàng năm có thể chuyển đổi nửa năm một lần)
Ví dụ 12: Tom is trying to decide between two banks in which to open an account. Bank A offers an
annual rate of 15.25% with interest compounded semi-annually, and Bank B offers an annual rate
of 15% with interest compounded monthly. Which bank should Tom choose? (Tom đang cố gắng
quyết định nên mở tài khoản ở ngân hàng nào trong hai ngân hàng. Ngân hàng A đưa ra lãi suất hàng
năm là 15.25% với lãi kép nửa năm một lần, và Ngân hàng B đưa ra lãi suất hàng năm là 15% với lãi
kép hàng tháng. Tom nên chọn ngân hàng nào?)
Ví dụ 13: Find the annual effective rate of discount that is equivalent to a nominal annual rate of
discount of 8% convertible quarterly. (Tìm tỷ lệ chiết khấu hiệu dụng hàng năm tương đương với tỷ lệ
chiết khấu danh nghĩa hàng năm là 8% có thể chuyển đổi hàng quý)
Ví dụ 14: Find the nominal annual rate of discount convertible monthly that is equivalent to an
annual effective rate of discount of 6%. (Tìm tỷ lệ chiết khấu danh nghĩa hàng năm có thể chuyển đổi
hàng tháng tương đương với tỷ lệ chiết khấu hiệu dụng hàng năm là 6%)
Ví dụ 15: Find the rate of discount convertible semi-annually that is equivalent to a nominal rate of
interest of 8% convertible monthly. (Tìm tỷ lệ chiết khấu có thể chuyển đổi nửa năm một lần tương
đương với tỷ lệ lãi suất danh nghĩa 8% có thể chuyển đổi hàng tháng)
Ví dụ 16: In order to receive $600 at the end of 8 years, you agree to pay $100 at once, $200 at the
end of the fifth year and to make a final payment X at the end of the tenth year. For a nominal rate
of interest of 8% convertible semiannually, what is the value of X? (Để nhận được $600 vào cuối năm
thứ 8, bạn đồng ý trả $100 ngay lập tức, $200 vào cuối năm thứ năm và một khoản thanh toán cuối cùng
là X vào cuối năm thứ mười. Với lãi suất danh nghĩa 8% có thể chuyển đổi nửa năm một lần, giá trị của X là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 17: You deposit 1000 into an account at t = 0 and an amount X one year later. The account
earns an annual effective rate of 6%. What value of X will result in an account balance of 2000 at
the end of two years? (Bạn gửi 1000 vào một tài khoản tại thời điểm t = 0 và một khoản tiền X một năm
sau đó. Tài khoản này có lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 6%. Giá trị của X là bao nhiêu để số dư tài
khoản đạt 2000 vào cuối năm hai?)
Ví dụ 18: An amount of 3000 is deposited into an account at time 0. The account earns of 6%
annual effective rate. At the end of 2 years, 500 is withdrawn from the account. What is the account
balance at the end of three years? (Một khoản tiền 3000 được gửi vào tài khoản tại thời điểm 0. Tài
khoản này có lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 6%. Vào cuối năm thứ 2, 500 được rút ra khỏi tài khoản. Số
dư tài khoản vào cuối năm thứ ba là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 19: Bob puts 10000 into a bank account that has monthly compounding with interest credited
at the end of each month. The monthly interest rate is 1% for the first 3 months of the account and
after that the monthly interest rate is 0.75%. Find the balance in Bob’s account at the end of 12
months just after interest has been credited (Bob gửi 10000 vào một tài khoản ngân hàng có lãi kép
hàng tháng, lãi được ghi có vào cuối mỗi tháng. Lãi suất hàng tháng là 1% trong 3 tháng đầu tiên của tài
khoản và sau đó lãi suất hàng tháng là 0.75%. Tìm số dư trong tài khoản của Bob vào cuối 12 tháng
ngay sau khi lãi đã được ghi có)
Ví dụ 20: Jeff deposits 10 into a fund today and 20 fifteen years later. Interest is credited at a
nominal discount rate of d compounded quarterly for the first 10 years, at at a nominal interest
rate of 6% compounded semi-annually thereafter. The accumulated balance in the fund at the end
of 30 years is 100. Calculate d. (Jeff gửi $10 vào một quỹ hôm nay và $20 vào mười lăm năm sau đó.
Lãi được ghi có theo tỷ lệ chiết khấu danh nghĩa là d, ghép lãi hàng quý trong 10 năm đầu tiên, và theo tỷ
lệ lãi suất danh nghĩa là 6% ghép lãi nửa năm sau đó. Số dư tích lũy trong quỹ vào cuối 30 năm là 100. Tính d)
Ví dụ 21: Bruce and Rob each open new bank account at time 0. Bruce deposits 100 into his bank
account, and Rob deposits 50 into his. Each account earns the same annual effective rate. The
amount of interest earned in Bruce’s account during the 11th year is equal to X. The amount of
interest earned in Rob’s account during the 17th year is equal to X. Calculate X. (Bruce và Rob mỗi
người mở một tài khoản ngân hàng mới tại thời điểm 0. Bruce gửi 100 vào tài khoản của mình, và Rob
gửi 50 vào tài khoản của mình. Mỗi tài khoản đều có cùng một lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm. Số tiền lãi
mà Bruce kiếm được trong năm thứ 11 là X. Số tiền lãi mà Rob kiếm được trong năm thứ 17 là X. Tính X)
Ví dụ 22: Eric deposits X into a saving account at time 0, which pays interest at a nominal rate of i,
compounded semiannually. Mike deposits 2X into a different savings account at time 0, which pays
simple interest at an annual rate of i. Eric and Mike earn the same amount of interest during the
last 6 months of the 8 th year. Calculate i (Eric gửi X vào một tài khoản tiết kiệm tại thời điểm 0, tài
khoản này trả lãi suất danh nghĩa là i, ghép lãi nửa năm một lần. Mike gửi 2X vào một tài khoản tiết
kiệm khác tại thời điểm 0, tài khoản này trả lãi đơn với lãi suất hàng năm là i. Eric và Mike kiếm được
cùng một số tiền lãi trong 6 tháng cuối năm thứ 8. Tính i)
Ví dụ 23: Derive an expression for δt if accumulation is based on
a. simple interest at annual rate i.
b. compound interest at annual rate i.
(Hãy thiết lập biểu thức cho δt nếu sự tích lũy dựa trên:
a. Lãi suất đơn với tỷ lệ hàng năm là i.
b. Lãi suất kép với tỷ lệ hàng năm là i.)
Ví dụ 24: Let a(t)=(t+1)2 . Find the expression for δt . 2
Ví dụ 25: Given δt=1+t . Find an expression for a(t).
Ví dụ 26: A customer is offered an investment where interest is calculated according to the
following force of interest δt
The customers invest 1000 at time 0. Find the accumulated value at time 4.
(Một khách hàng được đề nghị một khoản đầu tư mà lãi suất được tính theo lực lãi suất trên. Khách hàng
đầu tư 1000 vào thời điểm 0. Tìm giá trị tích lũy tại thời điểm 4)
Ví dụ 27: Ernied makes deposits of 100 at time 0, and X at time 3. The fund grows at a force of t2
interest δt=
t>0. The amount of interest earned from time 3 to time 6 is also X. Find X. (Ernied 110
thực hiện các khoản tiền gửi 100 vào thời điểm 0 và X vào thời điểm 3. Quỹ tăng trưởng theo lực lãi suất
như trên. Số tiền lãi kiếm được từ thời điểm 3 đến thời điểm 6 cũng là X. Tìm X)
Ví dụ 28: Bruce deposits 100 into a bank account. His account is credited interest at a nominal rate
of interest of 4% convertible semi-annually. At the same time, Peter deposits 100 into a separate
account. Peter’s account is credited interest at a force of interest of δ. After 7.25 years, the value of
each account is the same. Calculate δ. (Bruce gửi 100 vào một tài khoản ngân hàng. Tài khoản của anh
ấy được tính lãi theo lãi suất danh nghĩa 4% ghép lãi nửa năm một lần. Cùng lúc đó, Peter gửi 100 vào
một tài khoản riêng biệt. Tài khoản của Peter được tính lãi theo lực của lãi suất δ. Sau 7.25 năm, giá trị
của mỗi tài khoản là như nhau. Tính δ)
Ví dụ 29: Two deposits are made into an account: 100 at time 0, and 300 twelve years later. For the
first 8 years interest are credited at a nominal annual rate of 6% convertible quarterly. For the next
8 years the account accumulates at a force of interest δ. At the end of 16 years the account balance
is 656. Find δ. (Hai khoản tiền gửi được thực hiện vào một tài khoản: 100 tại thời điểm 0 và 300 mười
hai năm sau đó. Trong 8 năm đầu tiên, lãi suất được tính theo tỷ lệ danh nghĩa hàng năm là 6% ghép lãi
hàng quý. Trong 8 năm tiếp theo, tài khoản tích lũy theo lực lãi suất δ. Vào cuối 16 năm, số dư tài khoản là 656. Tìm δ)
Chương 2: NIÊN KIM
Ví dụ 1: Calculate the present value and future value of an annuity-immediate of amount $100 paid
annually for 5 years at the rate of interest of 9% (Tính giá trị hiện tại và giá trị tương lai của một niên
kim trả trước với khoản thanh toán $100 hàng năm trong 5 năm với lãi suất 9%)
Ví dụ 2: A man wants to save $100000 to pay for his son’s education in 10 years’ time. An education
fund requires the investors to deposit equal installments annually at the end of each year. If interest
of 7.5% is paid, how much does the man need to save each year in order to meet his target? (Một
người đàn ông muốn tiết kiệm $100000 để chi trả cho việc học hành của con trai mình trong 10 năm tới.
Một quỹ giáo dục yêu cầu nhà đầu tư gửi các khoản tiền bằng nhau hàng năm vào cuối mỗi năm. Nếu lãi
suất là 7.5%, người đàn ông cần tiết kiệm bao nhiêu mỗi năm để đạt được mục tiêu của mình?)
Ví dụ 3: A loan for 15000 is to be repaid by 9 year-end payments with interest at an annual effective
rate of 10%. What is the amount of the annual payment? (Một khoản vay 15000 sẽ được hoàn trả
bằng 9 khoản thanh toán vào cuối mỗi năm với lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 10%. Giá trị của khoản
thanh toán hàng năm là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 4: You have a 6000 balance in an account earning a 5% annual effective rate. You want to
increase your balance to 20000 at the end of 10 years by making a level deposit of X at the end of
each of the next 10 years. Find X (Số dư hiện tại trong tài khoản của bạn là 6000, tài khoản này đang
hưởng lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 5%. Bạn muốn tăng số dư của mình lên 20000 vào cuối 10 năm
bằng cách gửi một khoản tiền đều đặn là X vào cuối mỗi năm trong 10 năm tới. Tìm X)
Ví dụ 5: You want to accumulate at least $30000 in an account earning a 6% annual effective rate.
You will make a level deposit of $1000 at the beginning of each year for n years. What is the value
of n? What is the account balance after n year? (Bạn muốn tích lũy ít nhất $30000 trong một tài khoản
có lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 6%. Bạn sẽ thực hiện một khoản tiền gửi đều đặn là $1000 vào đầu
mỗi năm trong n năm. Giá trị của n là bao nhiêu? Số dư tài khoản sau n năm là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 6: You will make 3 deposits of 10000 each into a bank account, at the beginning of this year
and th following 2 years. You then plan to withdraw a level payment X starting at the beginning of
year 4 and continuing for 5 years. The account pays interest at an annual effective rate i = 8%.
What is the amount of the level payment X? (Bạn sẽ thực hiện 3 khoản tiền gửi, mỗi khoản 10000, vào
một tài khoản ngân hàng, vào đầu năm nay và 2 năm tiếp theo. Sau đó, bạn dự định rút một khoản tiền
đều đặn X bắt đầu từ đầu năm thứ 4 và kéo dài trong 5 năm. Tài khoản trả lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm
là i = 8%. Giá trị của khoản thanh toán đều đặn X là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 7: Based on a 5% annual effective interest rate, find the present value of a 10-year annuity
with level annual payments of 100, where the first payment will occur 4 years from now. (Dựa trên
lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 5%, hãy tìm giá trị hiện tại của một niên kim 10 năm với các khoản thanh
toán hàng năm đều nhau là 100, trong đó khoản thanh toán đầu tiên sẽ diễn ra sau 4 năm nữa)
Ví dụ 8: Bob wants to purchase a perpetuity paying 1000 per year with the first payment due at the
end of year 11. He can purchase it by either:
• paying 900 per year at the end of each year for 10 years; or
• pay K per year at the end of each year for the first 5 years and nothing for the next 5 years. Calculate K.
(Bob muốn mua một niên kim vĩnh viên trả 1000 mỗi năm, với khoản thanh toán đầu tiên đến hạn vào
cuối năm thứ 11. Anh ấy có thể mua nó bằng một trong hai cách sau:
• Trả 900 mỗi năm vào cuối mỗi năm trong 10 năm; hoặc
• Trả K mỗi năm vào cuối mỗi năm trong 5 năm đầu tiên và không trả gì trong 5 năm tiếp theo. Tính K)
Ví dụ 9: An annuity pays 200 at the end of each of the next four years and 300 at the end of the four
following years. Based on a 5% annual effective interest rate, what is the present value of this
annuity? (Một niên kim trả 200 vào cuối mỗi năm trong bốn năm tới và 300 vào cuối bốn năm tiếp theo.
Dựa trên lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 5%, giá trị hiện tại của niên kim này là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 10: An annuity-immediate has 5 annual payments of 100, followed by a perpetuity of 200
starting in the 6 th year. Find its present value at 6.5% annual interest of rate. (Một niên kim trả
trước có 5 khoản thanh toán hàng năm, mỗi khoản 100, tiếp theo là một niên kim vĩnh viễn trả 200 bắt
đầu từ năm thứ 6. Tìm giá trị hiện tại của nó với lãi suất hàng năm là 6.5%)
Ví dụ 11: Calculate the present value of an annuity-immediate of amount 100 payable quarterly for
10 years at the annual rate of interest of 8% convertible quarterly. Also calculate its future value at
the end of 10 years. (Tính giá trị hiện tại của một niên kim trả trước với khoản thanh toán 100 trả hàng
quý trong 10 năm với lãi suất hàng năm là 8% ghép lãi hàng quý. Đồng thời, tính giá trị tương lai của nó vào cuối 10 năm)
Ví dụ 12: A saver deposits 200 into a bank account at the end of every month for 15 years. If the
account earns interest at an annual effective rate of 5%, what is the saver’s balance at the end of 10
years? (Một người tiết kiệm gửi 200 vào tài khoản ngân hàng vào cuối mỗi tháng trong 15 năm. Nếu tài
khoản hưởng lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 5%, số dư của người tiết kiệm vào cuối 10 năm là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 13: A man turns 40 today and wishes to provide supplemental retirement income of 2000 at
the beginning of each month starting on his 65th birthday. Starting today, he makes monthly
contributions of X to a fund for 25 years. The fund earns a nominal rate of 8% compounded
monthly. Each 1000 will provide for 9.85 of income at the beginning of each month starting on his
65th birthday until the end of his life. Calculate X. (Hôm nay một người đàn ông tròn 40 tuổi và muốn
có thêm thu nhập hưu trí là 2000 vào đầu mỗi tháng bắt đầu từ sinh nhật lần thứ 65 của mình. Bắt đầu từ
hôm nay, ông ấy đóng góp hàng tháng một khoản tiền X vào một quỹ trong 25 năm. Quỹ này sinh lời theo
lãi suất danh nghĩa 8% ghép lãi hàng tháng. Cứ mỗi 1000 sẽ cung cấp 9.85 thu nhập vào đầu mỗi tháng
bắt đầu từ sinh nhật lần thứ 65 của ông ấy cho đến cuối đời. Tính X)
Ví dụ 14: For a given interest rate i > 0, the present value of a 20-year continuous annuity of one
dollar per year is equal to 1.5 times the present value of a 10-year continuous annuity of one dollar
per year. Calculate the accumulated value of a 7-year continuous annuity of one dollar per year.
(Với một lãi suất i > 0 cho trước, giá trị hiện tại của một niên kim liên tục 20 năm với mức thanh toán 1
đô la mỗi năm bằng 1.5 lần giá trị hiện tại của một niên kim liên tục 10 năm với mức thanh toán 1 đô la
mỗi năm. Tính giá trị tích lũy của một niên kim liên tục 7 năm với mức thanh toán 1 đô la mỗi năm)
Ví dụ 15: An account pays interest at a continuously compounded rate of 0.06 per year. Continuous
deposits are made to the account at a rate of 1000 per year for 6 years, and then at a rate of 1400
per year for the next 4 years. What is the present value of this payment stream? (Một tài khoản ghép
lãi liên tục là 0.06 mỗi năm. Các khoản tiền gửi liên tục được thực hiện vào tài khoản 1000 mỗi năm
trong 6 năm, và sau đó 1400 mỗi năm trong 4 năm tiếp theo. Giá trị hiện tại của dòng tiền này là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 16: P borrows 20000 at an annual effective rate of 8%, and agrees to repay the loan over 20
years with level payments at the end of every second year. What is the amount of P’s biennial
payment? (P vay 20000 với lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 8%, và đồng ý trả nợ trong 20 năm với các
khoản thanh toán đều nhau vào cuối mỗi hai năm. Khoản thanh toán hai năm một lần của P là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 17: Joe is saving for retirement. Because he receives a large bonus every 3 years, he plans to
contribute to his retirement savings at the end of every third year for the next 30 years. He
estimates that his retirement savings account will accumulate at the 7% annual effective rate. If
Joe’s retirement saving goal is 1000000, how much should he deposit every 3 years? (Joe đang tiết
kiệm cho nghỉ hưu. Vì anh ấy nhận được một khoản thưởng lớn cứ sau 3 năm, anh ấy dự định đóng vào
khoản tiết kiệm hưu trí của mình vào cuối mỗi 3 năm trong 30 năm tới. Anh ấy ước tính rằng tài khoản
tiết kiệm hưu trí của mình sẽ tích lũy với lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 7%. Nếu mục tiêu tiết kiệm hưu
trí của Joe là 1000000, anh ấy nên gửi bao nhiêu sau mỗi 3 năm?)
Ví dụ 18: A perpetuity paying 1 at the beginning of each 6–month period has a present value of 20.
A second perpetuity pays X at the beginning of every 2 years. Assuming the same annual effective
interest rate, the two present values are equal. Determine X. (Một niên kim vĩnh viễn trả 1 vào đầu
mỗi kỳ 6 tháng có giá trị hiện tại là 20. Một niên kim vĩnh viễn thứ hai trả X vào đầu mỗi 2 năm. Giả sử
cùng một lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm, hai giá trị hiện tại bằng nhau. Xác định X)
Ví dụ 19: A principal of 5000 generates income of 500 at the end of every year at an effective rate of
interest of 4.5% for as long as possible. Find the number of full withdrawals and the final
withdrawal a year later which completely exhausts the fund. (Một khoản vốn 5000 tạo ra thu nhập
500 vào cuối mỗi năm với lãi suất hiệu dụng là 4.5% trong thời gian dài nhất có thể. Tìm số lần rút tiền
đầy đủ và khoản rút cuối cùng một năm sau đó để làm cạn kiệt hoàn toàn quỹ)
Ví dụ 20: A borrower takes out a loan of 4000 at an annual effective interest rate of 6%. Starting at
the end of the fifth year, the loan is repaid by annual payments, each of which equals 600 except for
a final balloon payment that is less than 1000. Calculate the final balloon payment. (Một người vay
một khoản vay 4000 với lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 6%. Bắt đầu từ cuối năm thứ năm, khoản vay
được trả bằng các khoản thanh toán hàng năm, mỗi khoản bằng 600 ngoại trừ một khoản thanh toán
cuối cùng nhỏ hơn 1000. Tính khoản thanh toán cuối cùng này)
Ví dụ 21: A principal of 5000 generates income of 500 at the end of every year for 15 years. What is
the effective rate of interest? (Một khoản vốn 5000 tạo ra thu nhập 500 vào cuối mỗi năm trong 15 năm.
Lãi suất hiệu dụng là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 22: An annuity immediate has semi-annual payments of 100 for 10 years. Find its present
value at an interest of 6% convertible monthly. (Một niên kim trả trước có các khoản thanh toán nửa
năm một lần là 100 trong 10 năm. Tìm giá trị hiện tại của nó với lãi suất 6% ghép lãi hàng tháng)
Ví dụ 23: John can save 125 a month and invest it at 5% compounded semi-annually. Find the
number of full deposits and the final one month later in order to have 10000 in the fund. (John có
thể tiết kiệm 125 mỗi tháng và đầu tư với lãi suất 5% ghép lãi nửa năm một lần. Tìm số lần gửi tiền đầy
đủ và khoản gửi cuối cùng một tháng sau đó để có 10000 trong quỹ)
Ví dụ 24: Jim began saving money for his retirement by making monthly deposits of 200 into a fund
earning 6% interest compounded monthly. The first deposit occurred on January 1, 2020. Jim
became unemployed and missed making deposits 60 through 72. He then continued making
monthly deposits of 200. How much did Jim accumulate in his fund on December 31, 2030? (Jim bắt
đầu tiết kiệm tiền cho nghỉ hưu bằng cách gửi hàng tháng $200 vào một quỹ có lãi suất 6% ghép lãi hàng
tháng. Khoản tiền gửi đầu tiên diễn ra vào ngày 1 tháng 1 năm 2020. Jim bị thất nghiệp và bỏ lỡ các
khoản tiền gửi từ tháng thứ 60 đến tháng thứ 72. Sau đó, anh ấy tiếp tục gửi hàng tháng $200. Jim đã tích
lũy được bao nhiêu tiền trong quỹ của mình vào ngày 31 tháng 12 năm 2030?)
Ví dụ 25: A loan of 10 000 is to be amortized in 10 annual payments beginning 6 months after the
date of the loan. The first payment, X, is half as large as the other payments. Interest is calculated
at an annual effective rate of 5% for the first 4.5 years and 3% thereafter. Determine X. (Một khoản
vay $10 000 sẽ được hoàn trả dần trong 10 khoản thanh toán hàng năm, bắt đầu sau 6 tháng kể từ ngày
vay. Khoản thanh toán đầu tiên, X, bằng một nửa các khoản thanh toán còn lại. Lãi suất được tính theo
lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 5% trong 4.5 năm đầu tiên và 3% sau đó. Xác định X)
Ví dụ 26: Susan invests Z at the end of each year for seven years at an annual effective interest rate
of 5%. The interest credited at the end of each year is reinvested at an annual effective rate of 6%.
Compute the accumulated value at the end of seven years. (Susan đầu tư Z vào cuối mỗi năm trong
bảy năm với lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 5%. Lãi suất được ghi có vào cuối mỗi năm được tái đầu tư
với lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 6%. Tính giá trị tích lũy vào cuối bảy năm)
Ví dụ 27: Sally lends 5000 to Tim. Tim agrees to pay back the loan over 5 years with monthly
payments payable at the end of each month. Sally can reinvest the monthly payments from Tim in a
savings account paying interest at 6%, compounded monthly. The yield rate earned on Sally’s
investment over the five-year period turned out to be 7.45%, compounded semi-annually. What
nominal rate of interest, compounded monthly, did Sally charge Tim on the loan? (Sally cho Tim vay
$5000. Tim đồng ý trả lại khoản vay trong 5 năm bằng các khoản thanh toán hàng tháng vào cuối mỗi
tháng. Sally có thể tái đầu tư các khoản thanh toán hàng tháng từ Tim vào một tài khoản tiết kiệm trả lãi
suất 6%, ghép lãi hàng tháng. Tỷ suất lợi nhuận mà Sally kiếm được từ khoản đầu tư của mình trong
khoảng thời gian năm năm là 7.45%, ghép lãi mỗi nửa năm. Sally đã tính lãi suất danh nghĩa, ghép lãi
hàng tháng, là bao nhiêu cho Tim đối với khoản vay?)
Ví dụ 28: A 10-year annuity-immediate has a first-year payment of 500. The subsequent payments
increase by 100 each year. Find the present value of this annuity at the annual effective interest rate
of 5%. (Một niên kim trả trước trong 10 năm có khoản thanh toán năm đầu tiên là $500. Các khoản
thanh toán sau đó tăng thêm $100 mỗi năm. Tìm giá trị hiện tại của niên kim này với lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 5%)
Ví dụ 29: J bought an increase perpetuity-due with annual payments starting at amount 5 and
increasing by 5 each year until the payment amount reaches 100. The payments remain at 100
thereafter. The effective annual interest rate is 8%. Determine the present value of this perpetuity.
(J mua một niên kim vĩnh viễn trả trước tăng dần với các khoản thanh toán hàng năm bắt đầu ở mức $5
và tăng thêm $5 mỗi năm cho đến khi khoản thanh toán đạt $100. Các khoản thanh toán sau đó giữ
nguyên ở mức $100. Lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 8%. Xác định giá trị hiện tại của niên kim vĩnh viễn này)
Ví dụ 30: Calculate the present value of a 25-year annuity-immediate with the first payment of 2500
and decreasing by 100 each year thereafter. Assuming an annual effective interest rate of 10%.
(Tính giá trị hiện tại của một niên kim trả trước trong 25 năm với khoản thanh toán đầu tiên là $2500 và
giảm dần $100 mỗi năm sau đó. Giả sử lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 10%)
Ví dụ 31: Olga buys a 5–year increasing annuity for X. Olga will receive 2 at the end of the first
month, 4 at the end of the second month, and for each month thereafter the payment increases by 2.
The nominal interest rate is 9% convertible monthly. Calculate X. (Olga mua một niên kim tăng dần
trong 5 năm với giá X. Olga sẽ nhận được $2 vào cuối tháng đầu tiên, $4 vào cuối tháng thứ hai, và cứ
mỗi tháng sau đó khoản thanh toán tăng thêm $2. Lãi suất danh nghĩa là 9% ghép lãi hàng tháng. Tính X)
Ví dụ 32: A 15-year annuity-immediate makes payments continuously at a rate of 10 the first year,
20 the second year, increasing to 150 in year 15. Find its present value at the effective annual
interest rate of 8%? (Một niên kim trả trước trong 15 năm thực hiện các khoản thanh toán liên tục với
$10 trong năm đầu tiên, $20 trong năm thứ hai, tăng dần đến $150 trong năm thứ 15. Tìm giá trị hiện tại
của nó với lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng năm là 8%?)
Ví dụ 33: Claire is receiving a 25 year continuous annuity with payments of 1234t at time t. Using a
force of interest of 6%, calculate the present value of Claire’s annuity. (Claire đang nhận một niên
kim liên tục trong 25 năm với các khoản thanh toán là 1234t tại thời điểm t. Sử dụng lực của lãi suất là
6%, hãy tính giá trị hiện tại của niên kim của Claire)
Ví dụ 34: Simon wishes to purchase a 20-year annuity with annual payments beginning one year
from now. The annuity will be valued at an effective annual rate of 12%. Simon anticipates an
effective annual inflation rate over the next 20 years of 5% per year, so he would like each payment
after the first to be 5% larger than the previous one. If Simon’s first payment is to be 23000, what is
the present value the the annuity? (Simon muốn mua một niên kim 20 năm với các khoản thanh toán
hàng năm bắt đầu sau một năm kể từ bây giờ. Niên kim này sẽ được định giá theo lãi suất hiệu dụng hàng
năm là 12%. Simon dự đoán tỷ lệ lạm phát hiệu dụng hàng năm trong 20 năm tới là 5% mỗi năm, vì vậy
anh ấy muốn mỗi khoản thanh toán sau khoản đầu tiên lớn hơn 5% so với khoản trước đó. Nếu khoản
thanh toán đầu tiên của Simon là $23000, thì giá trị hiện tại của niên kim là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 35: A loan is amortized over five years with monthly payments at a nominal interest rate of
9% compounded monthly. The first payment is 1000 and is to be paid one month from the date of
the loan. Each succeeding monthly payment will be 2% lower than the prior payment. Calculate
the outstanding loan balance immediately after the 40th payment is made. (Một khoản vay được trả
dần trong năm năm bằng các khoản thanh toán hàng tháng với lãi suất danh nghĩa là 9% ghép lãi hàng
tháng. Khoản thanh toán đầu tiên là $1000 và sẽ được thanh toán một tháng sau ngày vay. Mỗi khoản
thanh toán hàng tháng tiếp theo sẽ thấp hơn 2% so với khoản trước đó. Tính số dư nợ còn lại ngay sau
khi thực hiện khoản thanh toán thứ 40)
Ví dụ 36: A 5-year annuity makes continuous payments at a rate of 1000+50t per year. Calculate 1
the present value of this annuity at a continuously varying force of interest δ(t)=
. (Một niên 20+t
kim 5 năm thanh toán liên tục với tốc độ 1000+50t mỗi năm. Tính giá trị hiện tại của niên kim này với 1
lực của lãi suất là δ(t)= ) 20+t
Ví dụ 37: Payments are made to an account at a continuous rate of (8k+tk), where 0≤t≤10. 1
Interest is credited at a force of interest δt=8+t . After 10 years, the account is worth 20000.
Calculate k. (Các khoản thanh toán được thực hiện vào một tài khoản với tốc độ (8k+tk), với 1
0≤t≤10. Lãi suất được ghi có theo lực của lãi suất δt=8+t. Sau 10 năm, tài khoản có giá trị 20000. Tính k)
Ví dụ 38: Dylan is receiving a continuous annuity that pays at a rate of 1000+500t at time t for 25
years. Calculate the present value at δ=0.09. (Dylan đang nhận một niên kim liên tục trả với tốc độ
1000+500t tại thời điểm t trong 25 năm. Tính giá trị hiện tại với δ=0.09)
CHƯƠNG 3: THANH TOÁN KHOẢN VAY
Ví dụ 1: A debt of 5000 with interest rate 5% compounded semiannually is to be amortized by equal
semi-annual payments over the next 3-years, the first due in 6 months. Construct an amortization
for the debt. (Một khoản nợ trị giá 5000 với lãi suất 5% tính lãi kép, nửa năm một lần sẽ được hoàn trả
bằng các khoản thanh toán bằng nhau mỗi nửa năm trong vòng 3 năm tới, với khoản thanh toán đầu tiên
đến hạn sau 6 tháng. Hãy lập bảng kế hoạch trả nợ cho khoản nợ này)
Ví dụ 2: A loan of amount 1000 at a nominal annual interest rate of 6% compounded monthly is
repaid by 6 monthly payments, starting one month after the loan is made. The first three payments
are amount X each and the final three payment are amount 2X each. Construct the amortization
schedule for this loan. (Một khoản vay trị giá 1000 với lãi suất danh nghĩa hằng năm là 6%, ghép lãi
mỗi tháng, được hoàn trả bằng 6 khoản thanh toán hằng tháng, bắt đầu một tháng sau khi khoản vay
được cấp. Ba khoản thanh toán đầu tiên có giá trị X mỗi tháng, và ba khoản thanh toán cuối có giá trị 2X
mỗi tháng. Hãy lập bảng kế hoạch trả nợ cho khoản vay này)
Ví dụ 3: A loan of amount 1000 is repaid by 6 equal monthly payments, starting one month after the
loan is made. The interest rate for the first three months is a nominal annual rate of 6%
compounded monthly, and the interest rate for the next three month is at 12% compounded
monthly. Construct the amortization schedule for this loan. (Một khoản vay trị giá 1000 được hoàn
trả bằng 6 khoản thanh toán hằng tháng bằng nhau, bắt đầu một tháng sau khi khoản vay được cấp. Lãi
suất trong ba tháng đầu là lãi suất danh nghĩa hằng năm 6%, ghép lãi mỗi tháng; lãi suất trong ba tháng
tiếp theo là 12%, ghép lãi mỗi tháng. Hãy lập bảng kế hoạch trả nợ cho khoản vay này)
Ví dụ 4: A loan of 3600 at an effective quarterly interest rate of j = 0.02 is amortized by means of 4
quarterly payments, beginning one quarter after the loan is made. Each payment consists of a
principal repayment of 900 plus interest due on the previous quarter’s outstanding balance.
Construct the amortization schedule. (Một khoản vay trị giá 3600 với lãi suất hiệu dụng mỗi quý là j =
0.02 được hoàn trả bằng 4 khoản thanh toán hằng quý, bắt đầu một quý sau khi khoản vay được cấp. Mỗi
khoản thanh toán bao gồm phần trả nợ gốc là 900 cộng với tiền lãi phát sinh từ số dư nợ của quý trước.
Hãy lập bảng kế hoạch trả nợ cho khoản vay này.)
Ví dụ 5: A borrower would like to borrow 30000 at 8% for 5 years, but wishes to pay only 2000 for
the first two years and then catch up with a higher payment for the final three years. Construct the
amortization schedule for this loan. (Một người vay muốn vay 30.000 với lãi suất 8% trong vòng 5
năm, nhưng chỉ muốn trả 2.000 mỗi năm trong hai năm đầu, sau đó sẽ trả phần còn lại bằng các khoản
thanh toán cao hơn trong ba năm cuối. Hãy lập bảng kế hoạch trả nợ cho khoản vay này)
Ví dụ 6: A loan for 40000 at a 7% annual effective rate has an annual payment of 9755.63. Find the
balance after the fourth payment. (Một khoản vay trị giá 40.000 với lãi suất hiệu dụng hằng năm là 7%
có khoản thanh toán hằng năm là 9.755,63. Hãy tìm dư nợ còn lại sau khoản thanh toán thứ tư)
Ví dụ 7: A loan with an annual effective interest of 6.5% has 7 remaining annual payments of 1050.
The next payment is due in one year. Find the loan balance today? (Một khoản vay với lãi suất hiệu
dụng hằng năm là 6,5% còn lại 7 khoản thanh toán hằng năm trị giá 1050. Khoản thanh toán tiếp theo
đến hạn sau một năm. Hãy tìm dư nợ khoản vay tại thời điểm hôm nay)
Ví dụ 8: Peter borrows X for four years at an annual effective interest rate of 8%, to be repaid with
equal payments at the end of each year. The outstanding loan balance at the end of the third year is
559.12. Calculate the principal repaid in the first payment. (Peter vay một khoản tiền X trong 4 năm
với lãi suất hiệu dụng hằng năm là 8%, được hoàn trả bằng các khoản thanh toán bằng nhau vào cuối
mỗi năm. Dư nợ khoản vay vào cuối năm thứ ba là 559,12. Hãy tính phần tiền gốc được trả trong khoản thanh toán đầu tiên)
Ví dụ 9: A loan is repaid with level annual payments based on annual effective interest rate of 7%.
The 8th payment consists of 789 of interest and 211 of principal. Calculate the amount of interest
paid in the 18th payment. (Một khoản vay được hoàn trả bằng các khoản thanh toán hằng năm bằng
nhau, dựa trên lãi suất hiệu dụng hằng năm là 7%. Khoản thanh toán thứ 8 bao gồm 789 tiền lãi và 211
tiền gốc. Hãy tính số tiền lãi được trả trong khoản thanh toán thứ 18.)
Ví dụ 10: A housing loan of 400000 was to be repaid over 20 years by monthly installments of an
annuity-immediate at the nominal rate of 5% per year. After the 24th payment was made, the bank
increased the interest rate to 5.5%. If the borrower was required to repay the loan within the same
period, how much would be the increase in the monthly installment? If the installment remained
unchanged, how much longer would it take to pay back the loan? (Một khoản vay mua nhà trị giá
400.000 được hoàn trả trong 20 năm bằng các khoản thanh toán hàng tháng theo hình thức chuỗi trả nợ
thường xuyên (annuity-immediate) với lãi suất danh nghĩa 5% mỗi năm. Sau khi thanh toán khoản thứ
24, ngân hàng đã tăng lãi suất lên 5,5%. Nếu người vay vẫn phải hoàn trả khoản vay trong cùng một
khoảng thời gian, thì khoản thanh toán hàng tháng sẽ tăng bao nhiêu? Nếu khoản thanh toán không thay
đổi, thì người vay sẽ mất thêm bao lâu để trả hết khoản vay?)
Ví dụ 11: A housing loan is to be repaid with a 15-year monthly annuity-immediate of 2000 at a
nominal rate of 6% per year. After 20 payments, the borrower requests for the installments to be
stopped for 12 months. Calculate the revised installment when the borrower starts to pay back
again, so that the loan period remains unchanged. What is the difference in the interest paid due to
the temporary stoppage of installments? (Một khoản vay mua nhà được hoàn trả bằng chuỗi trả nợ
thường xuyên hàng tháng trong 15 năm trị giá 2.000 với lãi suất danh nghĩa 6% mỗi năm. Sau 20 khoản
thanh toán, người vay yêu cầu dừng thanh toán trong 12 tháng. Tính toán lại khoản thanh toán khi người
vay bắt đầu trả nợ lại, sao cho thời gian vay không thay đổi. Chênh lệch lãi suất phải trả do việc tạm
dừng thanh toán là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 12: A loan at a 10% annual effective interest rate has an initial payment of 120, and 9 further
payments. The payment amount increases by 3% each year. Find the loan balance after the 4 th
payment. (Một khoản vay với lãi suất hiệu dụng hằng năm là 10% có khoản thanh toán ban đầu là 120,
và 9 khoản thanh toán tiếp theo. Mỗi năm, khoản thanh toán sẽ tăng 3%. Hãy tìm dư nợ của khoản vay
sau khoản thanh toán thứ 4)
Ví dụ 13: A 20-year loan is to be repaid by installments of 100 at the end of year 1, 200 at the end of
year 2, and so on, increasing by 100 each year, up to 600 at the end of the sixth year. From then
onwards,a level installment of 600 will be paid. The rate of interest charged is 6%. Calculate the
loan amount. What is the interest and the principal reduction in the 3rd and the 12th payments?
(Một khoản vay 20 năm sẽ được hoàn trả bằng các khoản thanh toán lần lượt là 100 vào cuối năm thứ 1,
200 vào cuối năm thứ 2, và cứ mỗi năm tăng thêm 100, cho đến 600 vào cuối năm thứ 6. Từ đó trở đi,
khoản thanh toán sẽ cố định ở mức 600. Lãi suất được tính là 6%. Tính số tiền vay ban đầu. Số tiền lãi và
tiền gốc trả trong khoản thanh toán thứ 3 và thứ 12 là bao nhiêu?)
Ví dụ 14: A loan is being repaid with 25 annual payments of 300 each. With the 10th payment, the
borrower pays an extra 500, and then repays the balance over 10 years with the revised annual
payment. The annual effective interest rate is 8%. Calculate the amount of the revised annual
payment. (Một khoản vay được hoàn trả bằng 25 khoản thanh toán hằng năm, mỗi khoản thanh toán là
300. Với khoản thanh toán thứ 10, người vay trả thêm 500, sau đó trả phần còn lại trong 10 năm với
khoản thanh toán hằng năm đã điều chỉnh. Lãi suất hiệu dụng hằng năm là 8%. Tính toán khoản thanh
toán hằng năm đã điều chỉnh)
Ví dụ 15: A 30-year loan has level annual payments. The principal repaid in the 5 th payment is
1489.40. The principal repaid in the 15th payment is 2795.81. What total amount of interest will be
paid over the term of the loan? (Một khoản vay 30 năm có các khoản thanh toán hằng năm cố định. Số
tiền gốc được trả trong khoản thanh toán thứ 5 là 1489,40. Số tiền gốc được trả trong khoản thanh toán
thứ 15 là 2795,81. Tổng số tiền lãi sẽ được trả trong suốt thời gian vay là bao nhiêu?)
CHƯƠNG 4: TRÁI PHIẾU VÀ ĐỊNH GIÁ TRÁI PHIẾU
Ví dụ 1: The following shows the results of a government bond auction:
Type of Bond: Government bond
Issue Date: February 15, 2010
Maturity Date: February 15, 2040
Coupon Rate: 4.500 % payable semiannually
Yield Rate: 4.530% convertible semiannually
Assume that the redemption value of the bond is the same as the face value, which is $100. Find the
price of the bond.
(Dưới đây là kết quả từ một cuộc đấu giá trái phiếu chính phủ:
Loại trái phiếu: Trái phiếu chính phủ
Ngày phát hành: Ngày 15 tháng 2, 2010
Ngày đáo hạn: Ngày 15 tháng 2, 2040
Lãi suất coupon: 4,500% trả lãi nửa năm một lần
Lãi suất sinh lời (Yield Rate): 4,530% tính lãi nửa năm một lần
Giá trị hoàn lại của trái phiếu là giống với giá trị mệnh giá, là 100 USD. Hãy tìm giá của trái phiếu)
Ví dụ 2: The following shows the information of a government bond
Type of Bond: Government bond
Issue Date: June 15, 2015
Maturity DateL June 15, 2030
Coupon Rate: 4.200 % payable semiannually
Assume that the redemption value of the bond is the same as the face value, which is $100. Find the
purchase price of the bond immediately after its 8th coupon payment (on June 15, 2019) if the yield
rate is 4.0% convertible semiannually.
(Dưới đây là thông tin về một trái phiếu chính phủ:
Loại trái phiếu: Trái phiếu chính phủ
Ngày phát hành: Ngày 15 tháng 6, 2015
Ngày đáo hạn: Ngày 15 tháng 6, 2030
Lãi suất coupon: 4,200% trả lãi nửa năm một lần
Giá trị hoàn lại của trái phiếu là giống với giá trị mệnh giá, là 100 USD.
Hãy tính toán giá mua của trái phiếu ngay sau khi thanh toán lãi lần thứ 8 (vào ngày 15 tháng 6, 2019),
nếu lãi suất sinh lời là 4,0% tính lãi nửa năm một lần)
Ví dụ 3: A 1000 par value 20–year bond with annual coupons and redeemable at maturity at 1050 is
purchased for P to yield an annual effective rate of 8.25%. The first coupon is 75. Each subsequent
coupon is 3% greater than the preceding coupon. Determine P (Một trái phiếu có giá trị mệnh giá
1000 USD, kỳ hạn 20 năm với lãi suất coupon hằng năm và có thể được hoàn lại vào thời điểm đáo hạn
với giá 1050 USD, được mua với giá P để có lãi suất hiệu dụng hằng năm là 8,25%. Khoản coupon đầu
tiên là 75 USD. Mỗi khoản coupon tiếp theo sẽ lớn hơn 3% so với khoản coupon trước đó. Hãy xác định
giá P của trái phiếu)
Ví dụ 4: A 3-year 1000 par value (same as the redemption value) bond pays semi-annual coupons at
a 5% annual rate. It is sold to yield 6% convertible semi-annually. Construct the amortization
schedule for the bond over its term. (Một trái phiếu có mệnh giá 1000 USD (bằng với giá trị hoàn lại)
kỳ hạn 3 năm, trả lãi coupon nửa năm một lần với lãi suất hằng năm là 5%. Trái phiếu được bán với mức
sinh lời là 6%, ghép lãi nửa năm một lần. Hãy lập bảng kế hoạch trả nợ (amortization schedule) cho trái
phiếu này trong suốt thời hạn của nó.)
Ví dụ 5: A 10,000 par value 10-year bond with 8% annual coupons is bought at a premium to yield
an annual efective rate of 6%. Calculate the interest portion of the 7th coupon. (Một trái phiếu có
mệnh giá 10.000 USD, kỳ hạn 10 năm với lãi suất coupon 8% hằng năm được mua với giá cao hơn mệnh
giá (mua với giá premium) để đạt được lãi suất hiệu dụng hằng năm là 6%. Hãy tính phần tiền lãi trong
khoản thanh toán coupon thứ 7.)
Ví dụ 6: A 1000 par value 5–year bond with 8.0% semiannual coupons was bought to yield 7.5%
convertible semiannually. Determine the amount of premium amortized in the 6-th coupon
payment. (Một trái phiếu có mệnh giá 1000 USD, kỳ hạn 5 năm với lãi suất coupon 8,0% trả nửa năm
một lần được mua để đạt mức sinh lời 7,5% ghép lãi nửa năm một lần. Hãy xác định phần premium được
khấu hao (premium amortized) trong khoản thanh toán coupon thứ 6)
Ví dụ 7: A 1000 par value 18–year bond with annual coupons is bought to yield an annual effective
rate of 5%. The amount for amortization of premium in the 10th year is 20. The book value of the
bond at the end of year 10 is X. Calculate X. (Một trái phiếu có mệnh giá 1000 USD, kỳ hạn 18 năm,
trả lãi coupon hằng năm được mua để đạt mức lãi suất hiệu dụng hằng năm là 5%. Khoản khấu hao
phần ưu đãi trong năm thứ 10 là 20. Giá trị sổ sách (book value) của trái phiếu vào cuối năm thứ 10 là X. Hãy tính X)
Ví dụ 8: Laura buys two bonds at time 0. Bond X is a 1000 par value 14-year bond with 10%
annual coupons. It is bought at a price to yield an annual effective rate of 8%. Bond Y is a 14-year
par value bond with 6.75% annual coupons and a face amount of F. Laura pays P for the bond Y to
yield an annual effective rate of 8%. During year 6, the principal paid on bond X is equal to the
discount amortized on bond Y. Calculate P. (Laura mua hai trái phiếu tại thời điểm 0. Trái phiếu X có
mệnh giá 1000 USD, kỳ hạn 14 năm với lãi suất coupon 10% hằng năm. Trái phiếu được mua với giá sao
cho lãi suất hiệu dụng hằng năm là 8%. Trái phiếu Y là một trái phiếu 14 năm với lãi suất coupon 6,75%
hằng năm và mệnh giá F. Laura trả số tiền P để mua trái phiếu Y sao cho nó mang lại lãi suất hiệu dụng
hằng năm là 8%. Trong năm thứ 6, số tiền gốc được trả trên trái phiếu X bằng với khoản chiết khấu được
khấu hao trên trái phiếu Y. Hãy tính P)
Ví dụ 9: Matt purchased a 20-year par value bond with an annual nominal coupon rate of 8%
payable semiannually at a price of 1722.25. The bond can be called at par value X on any coupon
date starting at the end of year 15 after the coupon is paid. The lowest yield rate that Matt can
possibly receive is a nominal annual interest rate of 6% convertible semiannually. Calculate X (Matt
mua một trái phiếu có mệnh giá, kỳ hạn 20 năm, với lãi suất coupon danh nghĩa hằng năm là 8%, trả lãi
nửa năm một lần, với giá 1722,25 USD. Trái phiếu có thể bị gọi hoàn trả (called) tại mệnh giá X vào bất
kỳ ngày thanh toán coupon nào, bắt đầu từ cuối năm thứ 15, sau khi coupon được trả. Mức lãi suất thấp
nhất mà Matt có thể nhận được là lãi suất danh nghĩa hằng năm 6%, ghép lãi nửa năm một lần. Hãy tính giá trị X)
Ví dụ 10: Sue purchased a 10-year par value bond with an annual nominal coupon rate of 4%
payable semiannually at a price of 1021.50. The bond can be called at par value X on any coupon
date starting at the end of year 5. The lowest yield rate that Sue can possibly receive is an annual
nominal rate of 6% convertible semiannually. Calculate X (Sue mua một trái phiếu có mệnh giá, kỳ
hạn 10 năm, với lãi suất coupon danh nghĩa hằng năm là 4%, trả lãi nửa năm một lần, với giá mua là
1021,50 USD. Trái phiếu có thể bị gọi hoàn trả tại mệnh giá X vào bất kỳ ngày thanh toán coupon nào,
bắt đầu từ cuối năm thứ 5. Mức lãi suất thấp nhất mà Sue có thể nhận được là lãi suất danh nghĩa hằng
năm 6%, ghép lãi nửa năm một lần. Hãy tính giá trị X)
Ví dụ 11: Toby purchased a 20-year par value bond with semiannual coupons of 40 and a
redemption value of 1100. The bond can be called at 1200 on any coupon date prior to maturity,
starting at the endof year 15. Calculate the maximum price of the bond to guarantee that Toby will
earn an annual nominal interest rate of at least 6% convertible semiannually. (Toby mua một trái
phiếu có mệnh giá, kỳ hạn 20 năm, với các khoản thanh toán coupon nửa năm một lần là 40 USD và giá
trị hoàn lại là 1100 USD. Trái phiếu có thể bị gọi hoàn trả với giá 1200 USD vào bất kỳ ngày thanh toán
coupon nào trước khi đáo hạn, bắt đầu từ cuối năm thứ 15. Hãy tính giá tối đa mà Toby có thể trả để đảm
bảo rằng anh ấy sẽ nhận được mức lãi suất danh nghĩa hằng năm ít nhất 6%, ghép lãi nửa năm một lần)
CHƯƠNG 5: QUẢN LÝ DÒNG TIỀN,
DANH MỤC ĐẦU TƯ VÀ TÀI SẢN - NỢ
Ví dụ 1: An investor is asked to invest 1100 and is promised in return a payment of 500 in one year
and 700 at the end of second year. Find the IRR (Một nhà đầu tư được đề nghị đầu tư 1100 USD và
được hứa sẽ nhận lại khoản thanh toán 500 USD sau 1 năm và 700 USD vào cuối năm thứ hai. Hãy tìm
tỷ suất hoàn vốn nội bộ (IRR) cho khoản đầu tư này)
Ví dụ 2: A company deposits 1000 at the beginning of the first year and 150 at the beginning of each
subsequent year into perpetuity. In return the company receives payments at the end of each year
forever. The first payment is 100. Each subsequent payment increase by 5%. Calculate the
company’s rate of return for this transaction. (Một công ty gửi 1000 USD vào đầu năm thứ nhất và
150 USD vào đầu mỗi năm tiếp theo, kéo dài vĩnh viễn. Đổi lại, công ty nhận được các khoản thanh toán
vào cuối mỗi năm cũng kéo dài mãi mãi. Khoản thanh toán đầu tiên là 100 USD. Mỗi khoản thanh toán
sau đó tăng thêm 5%. Hãy tính tỷ suất sinh lời của công ty đối với giao dịch này)
Ví dụ 3: A corporation is considering two alternative projects. Project A requires an initial
investment of 1000000 at time 0 and is expected to generate returns of 2000000 per year (at the end
of each year) for 9 years. Project B also requires an initial investment of 1000000 at time 0 and is
expected to generate returns of 3000000 per year for 5 years. Which project the corporation should
choose? (Một tập đoàn đang xem xét hai dự án thay thế. Dự án A yêu cầu đầu tư ban đầu 1.000.000 USD
tại thời điểm 0 và dự kiến tạo ra lợi nhuận 2.000.000 USD mỗi năm (vào cuối mỗi năm) trong vòng 9
năm. Dự án B cũng yêu cầu đầu tư ban đầu 1.000.000 USD tại thời điểm 0 và dự kiến tạo ra lợi nhuận
3.000.000 USD mỗi năm trong vòng 5 năm. Tập đoàn nên chọn dự án nào?
Ví dụ 4: An investor pays 100000 today for a 4-year investment that returns cash flows of 60000 at
the end of each of years 3 and 4. The cash flows can be reinvested at 4% per annum effective. If the
rate of interest at which the investment is to be valued is 5%, what is the net present value of this
investment today? (Một nhà đầu tư bỏ ra 100.000 USD hôm nay cho một khoản đầu tư kéo dài 4 năm,
mang lại dòng tiền 60.000 USD vào cuối năm thứ 3 và năm thứ 4. Các dòng tiền này có thể được tái đầu
tư với lãi suất hiệu dụng 4% mỗi năm. Nếu lãi suất dùng để định giá khoản đầu tư là 5% mỗi năm, thì giá
trị hiện tại ròng (NPV) của khoản đầu tư này tại thời điểm hôm nay là bao nhiêu?)
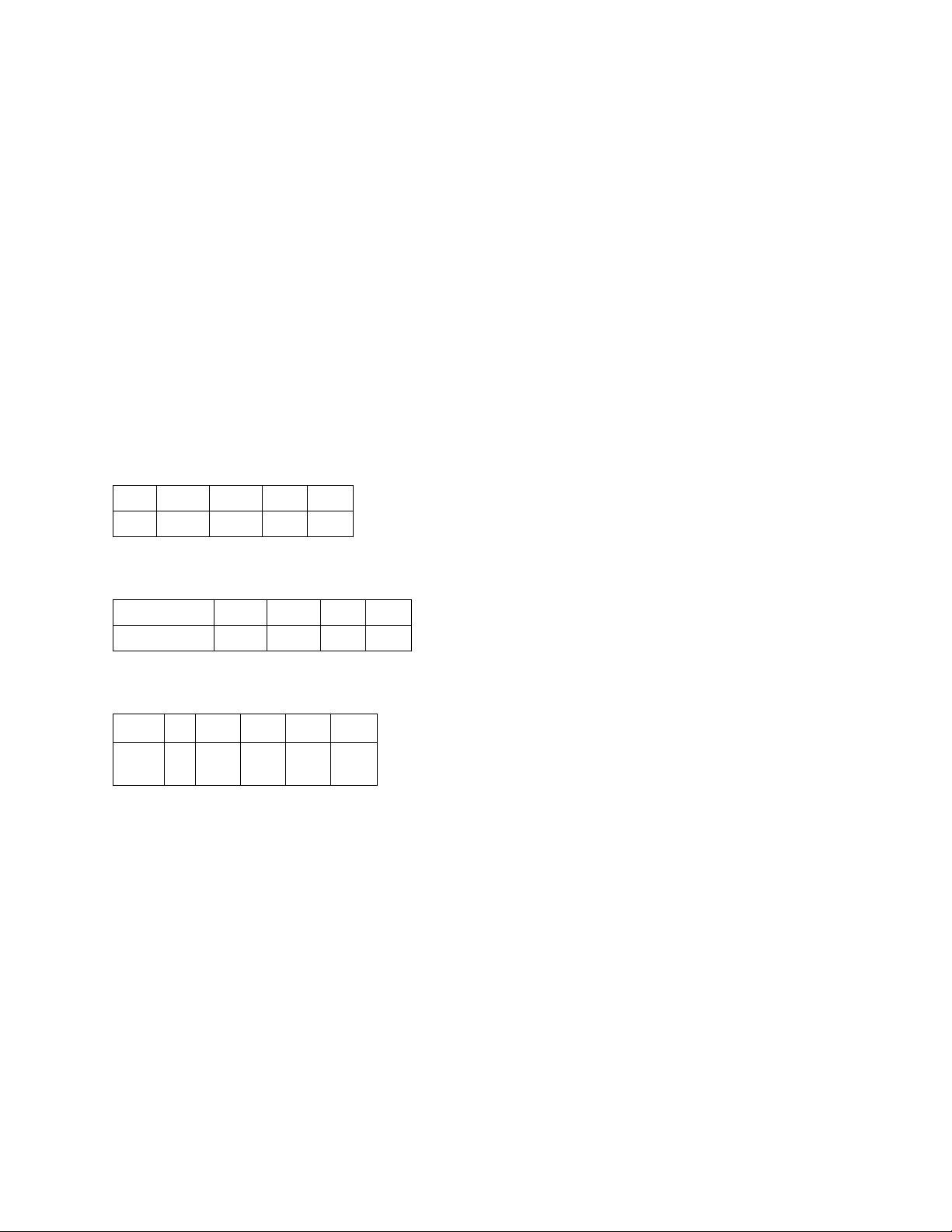
Ví dụ 5: The following are prices of 1−, 2−, 3− and 4−year bonds. All of the bond have a face value
(and maturity value) of 100 and pay 4% annual coupons. Find the spot rate for 1, 2, 3, and 4 years. Term 1 2 3 4
Price 101.50 101.00 99.70 99.00
(Bảng dưới đây là giá của các trái phiếu có kỳ hạn 1, 2, 3 và 4 năm. Tất cả các trái phiếu đều có mệnh
giá (và giá trị đáo hạn) là 100 và trả lãi coupon hằng năm 4%. Hãy tìm lãi suất giao ngay (spot rate) cho
các kỳ hạn 1, 2, 3 và 4 năm) Kỳ hạn (năm) 1 2 3 4 Giá
101.50 101.00 99.70 99.00
Ví dụ 6: Given the following forward rates, calculate the spot rate for terms of 1 to 5 years. (Cho
bảng lãi suất kỳ hạn (forward rates) sau đây, hãy tính lãi suất giao ngay (spot rate) cho các kỳ hạn từ 1 đến 5 năm) Term 1 2 3 4 5 i
5% 6.2% 6.8% 7.3% 7.7% n−1,n
Ví dụ 7: The yield curve’s spot rates are based on the following formula sk
=0.085+0.003k−0.0015k2. Calculate the 1-year forward rate, deferred 3 years, implied by this
yield curve. (Đường cong lợi suất (yield curve) có các lãi suất giao ngay (spot rate) được xác định theo
công thức trên. Hãy tính lãi suất kỳ hạn (forward rate) trong 1 năm, trì hoãn 3 năm (tức là từ năm thứ 3
đến năm thứ 4), được ngụ ý từ đường cong lợi suất này)
Ví dụ 8: A zero-coupon matures in 20 years for 1500. The nominal interest is at 5% compounded
semiannually. Calculate the modified duration of the bond. (Một trái phiếu zero-coupon đáo hạn sau
20 năm với giá trị 1.500. Lãi suất danh nghĩa là 5%, ghép lãi mỗi nửa năm. Hãy tính modified duration
(kỳ hạn hiệu dụng điều chỉnh) của trái phiếu này)



