






Preview text:
SECTION 3.5 Applications of Matrices: Leontief Input-Output Models 237 | EXERCISES | 3.5
The following technology matrix for a simple economy
Suppose a primitive economy consists of two indus-
describes the relationship of certain industries to each
tries, farm products and farm machinery. Suppose also
other in the production of 1 unit of product. that its technology matrix is A M F U P M 0.36 0.03 0.10 0.04 Agriculture 0.5 0.1 Products A 0.06 0.42 0.25 0.33 Manufacturing 0.1 0.3 Machinery 0.18 0.15 0.10 0.41 Fuels
If surpluses of 96 units of farm products and 8 units of 0.10 0.20 0.31 0.15 Utilities
farm machinery are desired, find the gross production of each industry.
(a) For each 100 units of manufactured products
12. Suppose an economy has two industries, agriculture
produced, how many units of fuels are
and minerals. Suppose further that the technology required? matrix for this economy is A.
(b) How many units of utilities are required to pro- A M
duce 40 units of agricultural products? 0.3 0.1 Agriculture
2. For the economy in Problem 1, what industry is most A dependent on utilities? 0.1 0.2 Minerals
If surpluses of 60 agricultural units and 70 mineral
The following technology matrix describes the relation-
units are desired, find the gross production for each
ship of certain industries within the economy to each industry.
other. (A&F, agriculture and food; RM, raw materials; M,
13. An economy is based on two industries: utilities and
manufacturing; F, fuels industry; U, utilities; SI, service
manufacturing. The technology matrix for these industries) industries is A. A&F RM M F U SI U M 0.410 0.008 0 0.002 0 0.006 A&F 0.3 0.15 Utilities A 0.025 0.493 0.190 0.024 0.030 0.150 RM 0.3 0.4 Manufacturing 0.015 0.006 0.082 0.009 0.001 0.116 M
If surpluses of 80 units of utilities output and 180 units 0.097 0.096 0.040 0.053 0.008 0.093 F
of manufacturing are desired, find the gross produc- 0.028 0.129 0.039 0.058 0.138 0.409 U tion of each industry. 0.043 0.008 0.010 0.012 0.002 0.095 SI
14. A primitive economy has a mining industry and a
fishing industry, with technology matrix A.
Use this matrix in Problems 3–10. M F
3. For each 1000 units of raw materials produced, how 0.25 0.05 Mining A
many units of agricultural and food products were 0.05 0.40 Fishing required?
4. For each 1000 units of raw materials produced, how
If surpluses of 147 units of mining output and 26 units
many units of service were required?
of fishing output are desired, find the gross production
5. How many units of fuels were required to produce of each industry.
1000 units of manufactured goods?
Suppose the economy of an underdeveloped country
6. How many units of fuels were required to produce
has an agricultural industry and an oil industry, with
1000 units of power (utilities’ goods)? technology matrix A.
7. Which industry is most dependent on its own goods A O
for its operations? Which industry is least dependent 0.4 0.2 Agricultural products on its own goods? A 0.2 0.1 Oil products
8. Which industry is most dependent on the fuels industry?
(a) If surpluses of 0 units of agricultural products
9. Which three industries would be most affected by a
and 610 units of oil products are desired, find the
rise in the cost of raw materials?
gross production of each industry.
10. Which industry would be most affected by a rise in the
(b) Find the additional production needed from each cost of manufactured goods?
industry for 1 more unit of oil products surplus.
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. 238 CHAPTER 3 Matrices
16. Suppose a simple economy with only an agricultural
21. A primitive economy consists of a fishing industry
industry and a steel industry has the following tech-
and an oil industry. A unit of fishing industry output nology matrix.
requires 0.30 unit of fishing industry input and 0.35
unit of oil industry input. A unit of oil industry output A S
requires inputs of 0.04 unit of fishing products and 0.3 0.2 Agriculture A 0.10 unit of oil products. 0.1 0.4 Steel
(a) Write the technology matrix for this primitive economy.
(a) If surpluses of 15 units of agricultural products
(b) If surpluses of 20 units of fishing products and
and 35 units of steel are desired, find the gross
1090 units of oil products are desired, find the production of each industry.
gross production of each industry.
(b) Find the additional production needed from each
22. An economy has a manufacturing industry and a
industry for 1 more unit of agricultural surplus.
banking industry. Each unit of manufacturing output
17. One sector of an economy consists of a mining industry
requires inputs of 0.5 unit of manufacturing and
and a manufacturing industry, with technology matrix A.
0.2 unit of banking. Each unit of banking output M Mfg
requires inputs of 0.3 unit each of manufacturing and 0.2 0.1 Mining banking. A 0.6 0.3 Manufacturing
(a) Write the technology matrix for this economy.
(b) If surpluses of 141 units of manufacturing and
(a) Surpluses of 36 units of mining output and 278
106 units of banking are desired, find the gross
units of manufacturing output are desired. Find production of each industry.
the gross production of each industry.
(b) Find the additional production needed from each
Interdepartmental costs Within a company there is a
industry for 1 more unit of mining surplus.
(micro)economy that is monitored by the accounting
18. An underdeveloped country has an agricultural
procedures. In terms of the accounts, the various depart-
industry and a manufacturing industry, with
ments “produce” costs, some of which are internal and technology matrix A.
some of which are direct costs. Problems 23–26 show A M
how an open Leontief model can be used to determine 0.20 0.20 Agriculture departmental costs. A 0.20 0.45 Manufacturing
23. Suppose the development department of a firm
charges 10% of its total monthly costs to the promo-
(a) Surpluses of 8 units of agricultural products and
tional department, and the promotional department
620 units of manufactured products are desired.
charges 5% of its total monthly costs to the develop-
Find the gross production of each industry.
ment department. The direct costs of the development
(b) Find the additional production needed from
department are $20,400, and the direct costs of the
each industry for 1 more unit of manufacturing
promotional department are $9,900. The solution to surplus. the matrix equation
A simple economy has an electronic components
industry and a computer industry. Each unit of elec- 20,400 0 0.05 x x
tronic components output requires inputs of 0.3 unit of 9,900 0.1 0 y y
electronic components and 0.2 unit of computers. Each
unit of computer industry output requires inputs of 0.6 x for the column matrix gives the total costs for
unit of electronic components and 0.2 unit of computers. y
(a) Write the technology matrix for this simple
each department. Note that this equation can be writ- economy. ten in the form
(b) If surpluses of 648 units of electronic components
D AX X, or X AX D
and 16 units of computers are desired, find the
gross production of each industry.
which is the form for an open economy. Find the total
An economy has an agricultural industry and a textile
costs for each department in this (micro)economy.
industry. Each unit of agricultural output requires
24. Suppose the shipping department of a firm charges
0.4 unit of agricultural input and 0.1 unit of textiles
20% of its total monthly costs to the printing depart-
input. Each unit of textiles output requires 0.1 unit of
ment and that the printing department charges 10%
agricultural input and 0.2 unit of textiles input.
of its total monthly costs to the shipping depart-
(a) Write the technology matrix for this economy.
ment. If the direct costs of the shipping department
(b) If surpluses of 5 units of agricultural products
are $16,500 and the direct costs of the printing
and 195 units of textiles are desired, find the gross
department are $11,400, find the total costs for each production of each industry. department.
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.
SECTION 3.5 Applications of Matrices: Leontief Input-Output Models 239
25. Suppose the engineering department of a firm charges
If surpluses of 24 units of service output, 62 units of
20% of its total monthly costs to the computer depart-
manufactured goods, and 32 units of agricultural
ment, and the computer department charges 25% of
goods are desired, find the gross production of each
its total monthly costs to the engineering department. industry.
If during a given month the direct costs are $11,750
32. Suppose that an economy has the same technology
for the engineering department and $10,000 for the
matrix as the economy in Problem 31. If surpluses of
computer department, what are the total costs of each
14 units of manufactured goods and 104 units of agri- department?
cultural goods are desired, find the gross production
26. The sales department of an auto dealership charges of each industry.
10% of its total monthly costs to the service depart-
ment, and the service department charges 20% of its
Problems 33–38 refer to closed Leontief models.
total monthly costs to the sales department. During
33. Suppose the technology matrix for a closed model of a
a given month, the direct costs are $88,200 for sales simple economy is given by
and $49,000 for service. Find the total costs of each P M H department. 0.5 0.1 0.2 Products
27. Suppose that an economy has three industries, fish- A 0.1 0.3 0 Machinery
ing, agriculture, and mining, and that matrix A is the 0.4 0.6 0.8 Households
technology matrix for this economy.
Find the gross productions for the industries. F A M
34. Suppose the technology matrix for a closed model of 0.5 0.1 0.1 Fishing
a simple economy is given by matrix A. Find the gross A 0.3 0.5 0.2 Agriculture
productions for the industries. 0.1 0.3 0.4 Mining G I H 0.4 0.1 0.3 Government
If surpluses of 110 units of fishing output and 50 units A 0.4 0.3 0.2 Industry
each of agricultural and mining goods are desired, 0.2 0.6 0.5 Households
find the gross production of each industry.
28. Suppose that an economy has the same technology
35. Suppose the technology matrix for a closed model of
matrix as the economy in Problem 27. If surpluses of
a simple economy is given by matrix A. Find the gross
180 units of fishing output, 90 units of agricultural
productions for the industries.
goods, and 40 units of mining goods are desired, find G I H
the gross production of each industry. 0.4 0.2 0.2 Government
29. Suppose that the economy of a small nation has an A 0.2 0.3 0.3 Industry
electronics industry, a steel industry, and an auto 0.4 0.5 0.5 Households
industry, with the following technology matrix.
36. Suppose the technology matrix for a closed model of E S A
an economy is given by matrix A. Find the gross pro- 0.6 0.2 0.2 Electronics ductions for the industries. A 0.1 0.4 0.5 Steel S M H 0.2 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2 Autos Shipping A 0.6 0.5 0.1 Manufacturing
If the nation wishes to have surpluses of 100 units of 0.2 0.4 0.8 Households
electronics production, 272 units of steel production,
and 200 automobiles, find the gross production of
37. A closed model for an economy has a manufacturing each industry.
industry, utilities industry, and households industry.
30. Suppose an economy has the same technology matrix
Each unit of manufacturing output uses 0.5 unit of
as that in Problem 29. If surpluses of 540 units of
manufacturing input, 0.4 unit of utilities input, and
electronics, 30 units of steel, and 140 autos are desired,
0.1 unit of households input. Each unit of utilities
find the gross production for each industry.
output requires 0.4 unit of manufacturing input, 0.5
31. Suppose that a simple economy has three industries,
unit of utilities input, and 0.1 unit of households input.
service, manufacturing, and agriculture, and that
Each unit of household output requires 0.3 unit each
matrix A is the technology matrix for this economy.
of manufacturing and utilities input and 0.4 unit of households input. S M A
(a) Write the technology matrix for this closed model 0.4 0.1 0.1 Service of the economy. A 0.2 0.5 0.2 Manufacturing
(b) Find the gross production for each industry. 0.2 0.1 0.3 Agriculture
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. 240 CHAPTER 3 Matrices
38. A closed model for an economy identifies government,
If an order is received for 10 card tables, 4 legs,
the profit sector, the nonprofit sector, and households as
1top, 1 cover, 6 clamps, and 12 bolts, how many of
its industries. Each unit of government output requires
each primary assembly item are required to fill the
0.3 unit of government input, 0.2 unit of profit sector order?
input, 0.2 unit of nonprofit sector input, and 0.3 unit
41. A sawhorse is made from 2 pairs of legs and a top
of households input. Each unit of profit sector output
joined with 4 nails. The top is a 2 4-in. board 3 ft
requires 0.2 unit of government input, 0.3 unit of profit
long. Each pair of legs is made from two 2 4-in.
sector input, 0.1 unit of nonprofit sector input, and 0.4
boards 3 ft long, a brace, and a special clamp,
unit of households input. Each unit of nonprofit sector The parts-
output requires 0.1 unit of government input, 0.1 unit
listing matrix for the sawhorse is given by
of profit sector input, 0.2 unit of nonprofit sector input, SH T LP 2
and 0.6 unit of households input. Each unit of house- 4 B C N 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Sawhorse
holds output requires 0.05 unit of government input,
0.1unit of profit sector input, 0.1 unit of nonprofit 0 0 0 0 0 0 Top
sector input, and 0.75 unit of households input. 0 0 0 0 0 0 Leg pair
(a) Write the technology matrix for this closed model A 0 0 0 0 0 2 4s of the economy. 0 0 0 0 0 0 Brace
(b) Find the gross production for each industry. 0 0 0 0 0 0 Clamp
39. For the storage shed in Example 6, find the number of 0 0 0 0 0 Nails
each primary assembly item required to fill an order
for 24 sheds, 12 braces, and 96 bolts.
How many of each primary assembly item are required
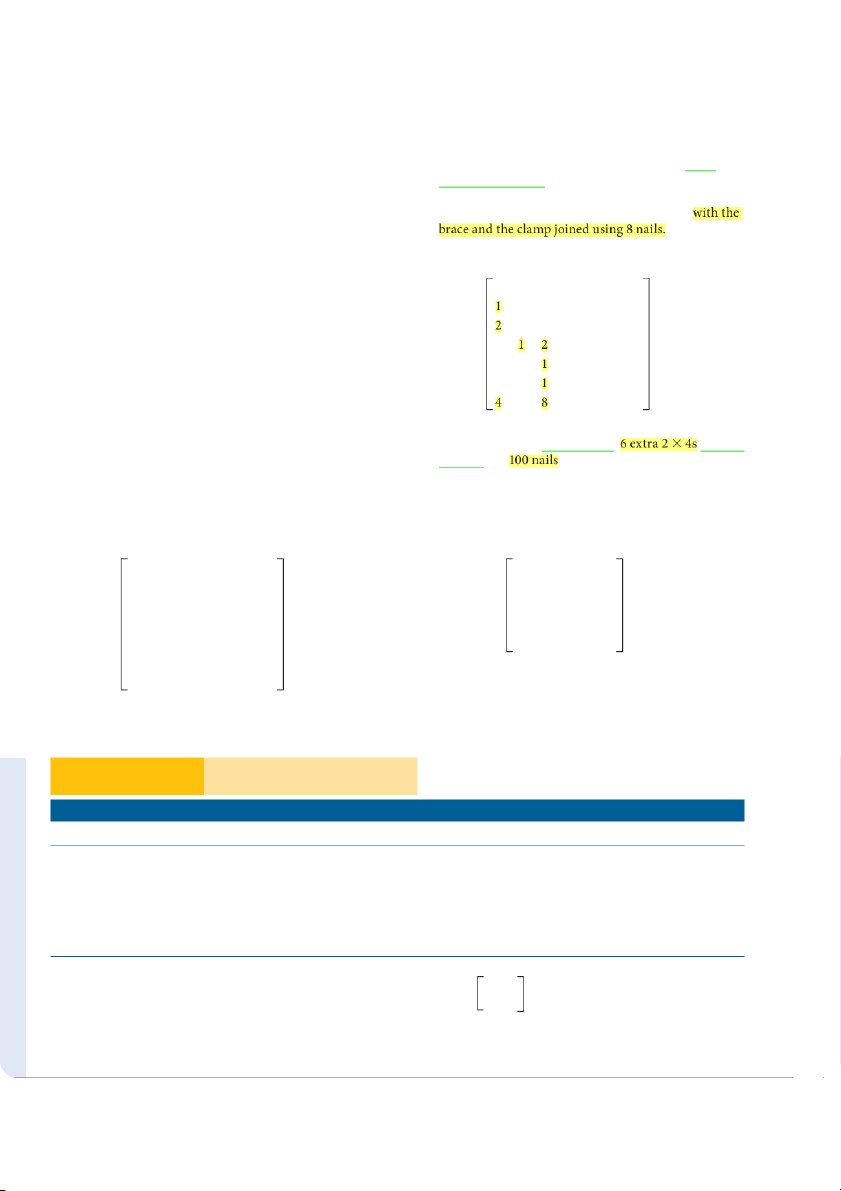
40. Card tables are made by joining 4 legs and a top using
to fill an order for 10 sawhorses, , 6 extra
4 bolts. The legs are each made from a steel rod. The clamps, and ?
top has a frame made from 4 steel rods. A cover and
42. A log carrier has a body made from a 4-ft length of
4special clamps that brace the top and hold the legs are
reinforced cloth having a patch on each side and a
joined to the frame using a total of 8 bolts. The parts-
dowel slid through each end to act as handles. The
listing matrix for the card table assembly is given by
parts-listing matrix for the log carrier is given by CT L T R Co Cl B LC B H C P 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Card table 0 0 0 0 0 Log carrier 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 Legs 1 0 0 0 0 Body 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 Top A 2 0 0 0 0 Handles A 0 1 4 0 0 0 0 Rods 0 1 0 0 0 Cloth 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 Cover 0 2 0 0 0 Patch 0 0 4 0 0 0 0 Clamps
How many of each primary assembly item are required 4 0 8 0 0 0 0 Bolts
to fill an order for 500 log carriers and 20 handles?
C h a p t e r 3 Summary & Review KEY TERMS AND FORMULAS Section 3.1 Matrices (p. 181) Transpose of A (p. 183) Entries AT Order Sum of two matrices (p. 184)
Square, row, column, and zero matrices Negative of a matrix (p. 184) Equal matrices (p. 183) Scalar multiplication (p. 186) Section 3.2 Matrix product (p. 194) Identity matrix (p. 196) 1 0 2 2 is 0 1
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. Re R v e i v e i w e w E xe x r e c r i c s i e s s e s 2 4 2 1 4 Section 3.3 Augmented matrix (p. 203)
Solving systems of equations (p. 204) Coefficient matrix (p. 203) Nonunique solutions (p. 208)
Elementary row operations (p. 204) Solutions summary (p. 210) Equivalent matrices Non-square systems (p. 211) Section 3.4 Inverse matrices (p. 217) Determinants (p. 224) Matrix equations (p. 220) a b a b det ad bc AX B c d c d Section 3.5
Technology matrix A (p. 229)
Technological equation (p. 230)
Leontief input-output model (p. 230) Open
Gross production matrix X (p. 230) (I A)X D Final demands (surpluses) D Closed Leontief model (p. 230) (I A)X 0 REVIEW EXERCISES
Use the matrices below as needed to complete Problems Section 3.3 1–25.
In Problems 26–28, the reduced matrix for a system of 4 4 2 5 2 5 11 8
equations is given. (a) Identify the type of solution for A 6 3 1 0 B 4 0 0 4
the system (unique solution, no solution, or infinitely 0 0 3 5 2 2 1 9
many solutions). Explain your reasoning. (b) For each
system that has a solution, find it. If the system has 4 2 1 1
infinitely many solutions, find two different specific 5 0 3 5 1 1 solutions. C D E 6 0 1 2 4 6 1 0 2 6 1 0 4 0 1 3 0 5 26. 0 1 3 7 27. 0 1 3 0 1 6 2 5 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 F G I 4 11 1 3 0 1 1 0 0 0 Section 3.1 28. 0 1 0 10 0 0 1 14 1. Find a in matrix A. 12 2. Find b in matrix B.
29. Given the following augmented matrix representing a 23
3. Which of the matrices, if any, are 3
system of linear equations, find the solution. 4?
4. Which of the matrices, if any, are 2 4? 1 1 2 5 5. Which matrices are square? 4 0 1 5
6. Write the negative of matrix B. 2 1 1 5
7. If a matrix is added to its negative, what kind of matrix results?
In Problems 30–36, solve each system using matrices.
8. Two matrices can be added if they have the same _____. 4x 4y 3z 4 3x 12y 24
Perform the indicated operations in Problems 9–25. 30. 31. 3x 4y 3z 1 3x 10y 24
9. A B 10. C E 11. DT I 2x 4y 3z 3 12. 3C 13. 4I 14. 2F x y z 3 x y 2z 5
15. 4D 3I 16. F 2D 17. 3A 5B 32. 3x z 1 33. 3x 2y 5z 10 Section 3.2 2x 3y 4z 2 2x 3y 15z 2 18. AC 19. CD 20. DF x y 3 x 3y z 4 21. FD 22. FI 23. IF 34. x y 4z 1 35. 2x 5y z 6 24. DGT 25. (DG)F 2x 3y 2z 7
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. 242 CHAPTER 3 Matrices x x x x 3
and matrix N gives the production for July. Use them in 1 2 3 4 x Problems 47–49. 2x x 4x 5 36. 1 2 3 4 x x x 0 A B A B 1 3 4 x x x 2 150 80 Bookcases 100 60 2 3 4 M N 280 300 Files 200 400 Section 3.4 120 80 1000 800 S P
37. Are D and G inverse matrices if 180 300 600 1200 3 5 2 5 D and G ? Section 3.1 1 2 1 3
47. Production Write the matrix that represents total
In Problems 38–40, find the inverse of each matrix.
production at the two plants for the 2 months. 1 0 2
48. Production If matrix P represents the inventories at the 7 1 38. 39. 3 4 1
plants at the beginning of June and matrix S represents 10 2 1 1 0
shipments from the plants during June, write the matrix 3 3 2
that represents the inventories at the end of June. 40. 1 4 2 Section 3.2 2 5 3
49. Production If the company sells its bookcases to
In Problems 41–43, solve each system of equations by
wholesalers for $100 and its filing cabinets for $120, for using inverse matrices.
which month was the value of production higher: (a) at x 2z 5 plant A? (b) at plant B? 41.
3x 4y z 2 (See Problem 39.)
A small church choir is made up of men and women who x y 3
wear choir robes in the sizes shown in matrix A. 3x 3y 2z 1 Men Women
42. x 4y 2z 10 (See Problem 40.) 1 14 Small 2x 5y 3z 6 A 12 10 Medium x 3y z 0 8 3 Large 43. x 4y 3z 2 S M L 2x y 11z 12 25 40 45 Robes
44. Does the following matrix have an inverse? B 10 10 10 Hoods 1 2 4
Matrix B contains the prices (in dollars) of new robes 2 0 4
and hoods according to size. Use these matrices in 1 0 2 Problems 50 and 51.
50. Cost Find the product BA, and label the rows and In Problems 45 and 46:
columns to show what each entry represents.
(a) Find the determinant of the matrix.
51. Cost To find a matrix that gives the cost of new robes
(b) Use it to decide whether the matrix has an inverse.
and the cost of new hoods, find 4 4 45. 1 BA 2 2 1 1 2 3
52. Manufacturing Two departments of a firm, A and B, 46. 4 1 8
need different amounts of the same products. The fol- 6 3 14
lowing table gives the amounts of the products needed by the two departments. APPLICATIONS Steel Plastic Wood
The Burr Cabinet Company manufactures bookcases Department A 30 20 10
and filing cabinets at two plants, A and B. Matrix M Department B 20 10 20
gives the production for the two plants during June,
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. Re R v e i v e i w e w E xe x r e c r i c s i e s s e s 2 4 2 3 4
These three products are supplied by two suppliers,
and III). Each type A slug requires 1 unit of I, 3 units of
Ace and Kink, with the unit prices given in the follow-
II, and 1 unit of III per day. Each type B slug requires ing table.
1 unit of I, 4 units of II, and 2 units of III per day. Each
type C slug requires 2 units of I, 10 units of II, and Ace Kink 6units of III per day. Steel 300 280
(a) If the daily mixture contains 2000 units of I, 8000 Plastic 150 100
units of II, and 4000 units of III, find the number Wood 150 200
of slugs of each type that can be supported.
(b) Is it possible to support 500 type A slugs? If so,
(a) Use matrix multiplication to find how much these
how many of the other types are there?
two orders will cost at the two suppliers. The
(c) What is the maximum number of type A slugs
result should be a 2 2 matrix.
possible? How many of the other types are there
(b) From which supplier should each department in this case? make its purchase?
56. Transportation An airline company has three types
53. Investment Over the period of time 2006–2015,
of aircraft that carry three types of cargo. The payload
Maura’s actual return (per dollar of stock) was 0.013469
of each type is summarized in the table below.
per month, Ward’s actual return was 0.013543 per
month, and Goldsmith’s actual return was 0.006504. Plane Type including that whatever Units Carried Passenger Transport Jumbo
underlying process generated the past set of observa-
tions will continue to hold in the present and near First-class mail 100 100 100
future, we can estimate the expected return for a stock Passengers 150 20 350
portfolio containing these assets in some combination. Air freight 20 65 35
Suppose we have a portfolio that has 20% of our
(a) Suppose that on a given day the airline must move
total wealth in Maura, 30% in Ward, and 50% in
1100 units of first-class mail, 460 units of air freight,
Goldsmith stock. Use the following steps to estimate
and 1930 passengers. How many aircraft of each
the portfolio’s historical return, which can be used to
type should be scheduled? Use inverse matrices. estimate the future return.
(b) How should the schedule from part (a) be adjusted
(a) Write a 1 3 matrix that defines the decimal
to accommodate 730 more passengers?
part of our total wealth in Maura, in Ward, and in
(c) What column of the inverse matrix used in part Goldsmith.
(a) can be used to answer part (b)?
(b) Write a 3 1 matrix that gives the monthly
returns from each of these companies. Section 3.5
(c) Find the historical return of the portfolio by com-
puting the product of these two matrices.
57. Economy models An economy has a shipping industry
(d) What is the expected monthly return of the stock
and an agricultural industry with technology matrix A. portfolio? S A 0.1 0.2 Shipping Sections 3.3 and 3.4 A 0.2 0.4 Agriculture
54. Investment A woman has $50,000 to invest. She has
(a) Surpluses of 4720 tons of shipping output and
decided to invest all of it by purchasing some shares of
40tons of agricultural output are desired. Find
stock in each of three companies: a fast-food chain that
the gross production of each industry.
sells for $50 per share and has an expected growth of
(b) Find the additional production needed from each
11.5% per year, a software company that sells for $20 per
industry for 1 more unit of agricultural surplus.
share and has an expected growth of 15% per year, and a
58. Economy models A simple economy has a shoe industry
pharmaceutical company that sells for $80 per share and
and a cattle industry. Each unit of shoe output requires
has an expected growth of 10% per year.
inputs of 0.1 unit of shoes and 0.2 unit of cattle products.
Each unit of cattle products output requires inputs of If her goal is 12% growth
0.1unit of shoes and 0.05 unit of cattle products.
per year, how many shares of each stock should she buy?
(a) Write the technology matrix for this simple
55. Nutrition A biologist is growing three different types economy.
of slugs (types A, B, and C) in the same laboratory
(b) If surpluses of 850 units of shoes and 275 units
environment. Each day, the slugs are given a nutrient
ofcattle products are desired, find the gross
mixture that contains three different ingredients (I, II, production of each industry.
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. 244 CHAPTER 3 Matrices
59. Economy models A look at the industrial sector of an
60. Economy models Suppose a closed Leontief model
economy can be simplified to include three industries:
for a nation’s economy has the following technology
the mining industry, the manufacturing industry, and matrix.
the fuels industry. The technology matrix for this sec- G A M H tor of the economy is given by 0.4 0.2 0.2 0.2 Government M Mf F 0.2 0.4 0.1 0.2 Agriculture 0.4 0.2 0.2 A Mining 0.2 0.1 0.3 0.1 Manufacturing A 0.2 0.4 0.2 Manufacturing 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Households 0.1 0.2 0.2 Fuels
Find the gross production of each industry.
Find the gross production of each industry if surpluses
of 72 units of mined goods, 40 units of manufactured
goods, and 220 units of fuels are desired. C h a p t e r 3 TEST
In Problems 1–6, perform the indicated matrix 11. Solve
operations with the following matrices. x y 2z 4 1 2 x 2 4y z 4 2 1 A 3 2 B 2x 3y 3z 8 3 1 5 4 1 12. Solve 1 2 4 3 4 1 C D 3 5 41 x y 3z 4 2 2 1 3 2 3 x 5y 2z 3 2x 4y 5z 8 1. AT B 2. B C 3. CD
13. Use an inverse matrix to solve 4. DA 5. BA 6. ABD x y 2z 4 x 2y z w 4 1 3
7. Find the inverse of the matrix . 2x 5y 4z 2w 10 2 4 2y z 2w 0
8. Find the inverse of the matrix 14. Solve 1 2 4 x y 2z w 4 1 2 2 x 4y z w 4 1 1 4 2x 2y 4z 2w 10 y z 2w 2 9. If AX B and
15. Suppose that the solution of an investment problem 1 2 0 3
involving a system of linear equations is given by A1 3 1 2 and B 1 4 1 1 2
B 75,000 3H and E 20,000 2H find the matrix X.
where B represents the dollars invested in Barton Bank
stocks, H is the dollars invested in Heath Healthcare 10. Solve
stocks, and E is the dollars invested in Electronics Depot stocks. x y 2z 4
(a) If $10,000 is invested in the Heath Healthcare x 4y z 4
stocks, how much is invested in the other two 2x 2y 4z 10 stocks?
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. Chapter 3 Test 245
(b) What is the dollar range that could be invested in
(b) Use matrix multiplication to determine the total the Heath Healthcare stocks?
number of units of each raw material needed.
(c) What is the minimum amount that could be
(c) Write a 4 1 matrix representing the costs of the
invested in the Electronics Depot stocks? How raw materials.
much is invested in the other two stocks in
(d) Use matrix multiplication to find the 1 1 matrix thiscase?
that represents the total investment to fill the orders.
16. In an ecological model, matrix A gives the fractions of
(e) Use matrix multiplication to determine the cost of
several types of plants consumed by the herbivores in
materials for each style of chair.
the ecosystem. Similarly, matrix B gives the fraction of
each type of herbivore that is consumed by the carni-
18. Complete parts (a) and (b) by using the code discussed
vores in the system. Each row of matrix A refers to a type
in Sections 3.2 and 3.4 (where a is 1, . . . , z is 26, and
of plant, and each column refers to a kind of herbivore.
blank is 27), and the coding matrix is
Similarly, each row of matrix B is a kind of herbivore and
each column is a kind of carnivore. 8 5 A 3 2 Herbivores 0.2 0.1 0.4
(a) Encode the message “Less is more,” the motto of 0.3 0.3 0.1 architect Mies van der Rohe.
(b) Decode the message 138, 54, 140, 53, 255, 99, 141, A 0.2 0.1 0.1 Plants 54, 201, 76, 287, 111. 0.1 0.2 0.5 0.4 0.4 0
19. A young couple with a $120,000 inheritance wants
to invest all this money. They plan to diversify their Carnivores
investments, choosing some of each of the following 0.1 0.1 0.2 types of stock. B 0.2 0 0.4 Herbivores 0.1 0.5 0.1 Expected Total
The matrix AB gives the fraction of each plant that is Type Cost/Share Growth/Share consumed by each carnivore. Growth $ 30 $ 4.60 (a) Find AB. Blue-chip 100 11.00
(b) What fraction of plant type 1 (row 1) is consumed Utility 50 5.00 by each carnivore?
(c) Identify the plant type that each carnivore
Their strategy is to have the total investment in growth consumes the most.
stocks equal to the sum of the other investments, and
their goal is a 13% growth for their investment. How
17. A furniture manufacturer produces four styles of chairs
many shares of each type of stock should they purchase?
and has orders for 1000 of style A, 4000 of style B, 2000
of style C, and 1000 of style D. The following table lists
20. Suppose an economy has two industries, agriculture and
the numbers of units of raw materials the manufacturer
minerals, and the economy has the technology matrix
needs for each style. Suppose wood costs $5 per unit,
nylon costs $3 per unit, velvet costs $4 per unit, and Ag M springs cost $4 per unit. 0.4 0.2 Ag A 0.1 0.3 M Wood Nylon Velvet Springs
(a) If surpluses of 100 agriculture units and 140 min- Style A 10 5 0 0
erals units are desired, find the gross production Style B 5 0 20 10 of each industry. Style C 5 20 0 10
(b) How many additional units must each indus- Style D 5 10 10 10
try produce to have 4 more units of agricultural surplus?
(a) Form a 1 4 matrix containing the number of
(c) How many additional units must each industry units of each style ordered.
produce for 1 more unit of minerals surplus?
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. 246 CHAPTER 3 Matrices
21. Suppose the technology matrix for a closed model of
and 0.2 unit of steel. Producing 1 unit of steel requires
a simple economy is given by matrix A. Find the gross
0.1 unit of agricultural products, 0.2 unit of machinery, productions of the industries.
0.3 unit of fuel, and 0.2 unit of steel. P NP H
22. Create the technology matrix for this economy. 0.4 0.3 0.4 Profit A 0.2 0.4 0.2 Nonprofit
23. Determine how many units of each product will give sur- 0.4 0.3 0.4 Households
pluses of 1700 units of agriculture products, 1900units
of machinery, 900 units of fuel, and 300 units of steel.
Use the following information in Problems 22 and 23.
The national economy of Swiziland has four products:
24. A simple closed economy has the technology matrix A.
agricultural products, machinery, fuel, and steel.
Find the total outputs of the four sectors of the economy.
Producing 1 unit of agricultural products requires
0.2unit of agricultural products, 0.3 unit of machinery, Ag S F H Agriculture
0.2 unit of fuel, and 0.1 unit of steel. Producing 1 unit 0.25 0.25 0.3 0.1
of machinery requires 0.1 unit of agricultural products, 0.3 0.25 0.2 0.4 Steel A
0.2unit of machinery, 0.2 unit of fuel, and 0.4 unit of 0.15 0.2 0.1 0.3 Fuel
steel. Producing 1 unit of fuel requires 0.1 unit of agri- 0.3 0.3 0.4 0.2 Households
cultural products, 0.2 unit of machinery, 0.3 unit of fuel,
Copyright 2016 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.




