







Preview text:
Câu 1. Christine has a linear demand curve for candy. If she wants to see her consumer surplus………, she
would like to see a …… in the market price of candy. a. increase, decrease b. not change, decrease c. decrease, decrease d. increase, increase Câu 2. Total revenue is:
a. the price effect times the quantity effect.
b. total sales less total cost.
c. the price of a good times the quantity of the good that is sold.
d. the price of a good divided by the amount of the good sold.
Câu 3. The cost of sensors used in making digital cameras falss, while a successful ad campaign makes
digital cameras more fashionable. As a result, the euilibrium price of digital cameras……… and the
equilibrium quantity ……… a. ambiguous; increases b. increases; ambiguous
c. increases, increases d. decreases, increases
Câu 4. The most likely reason the government implements a ………. is because it feels the price is too high for …………… a. price ceiling; producers b. price floor; consumers c. price floor; producers d. ceiling; consumers
Câu 5. Suppose that an increase in the price of a good leads to an increase in total revenue. Ignoring
other factors (such as supply), at its current price the good must be: a. inferior b. price-elastic
c. perfectly price – elastic
d. price – elastic
Câu 6. 6. An inward shift in the U.S. economy's production possibility frontier could represent which statement?
a. U.S. workers moving from New Jersey to Massachusetts
b. U.S, economic growth as workers move to different states
c. U.S. workers moving to Canada d. U.S. economic growth
Câu 7. A competitive market with flexible prices and many buyers and sellers will: a. reach equilibrium. b. eliminate surpluses.
c. eliminate surpluses and shortages and reach equilibrium. d. eliminate shortages.
8. Consumer surplus for an individual buyer is equal to:
a. the consumer's willingness to pay for the good minus the price of the good.
b. the price of the good minus the marginal cost of producing the good.
c. the marginal cost of the good minus the consumer's willingness to pay for the good.
d. the consumer's willingness to pay for the good minus the total cost of producing the good.
Câu 9. Which statement will result in an increased price of milk?
a. a shift to the right of the demand curve for milk
b. a decrease in the number of milk buyers
c. an increase in the number of milk suppliers
d. a shift to the right of the supply arve for milk
Câu 10. The market for lemonade is in equilibrium, and the price of lemons rises. How will this affect the lemonade market?
a. Supply will decrease, increasing the price and decreasing the quantity.
b. Demand will decrease, decreasing the price and decreasing the quantity.
c. Demand will decrease, increasing the price and decreasing the quantity.
d. Supply will increase, decreasing the price and increasing the quantity.
Câu 11. Coffee and tea are substitures in consumption. Assuming that the supply curve for tea is upward
sloping, if there is an increase in the price of coffee, total surplus in the tea market: a. will not change b. will increase c. will decrease d. may fluctuate wildly
Câu 12. The cross-price elasticity of electricity with respect to the price of natural gas has been
estimated as being equal to 0.2. This implies that:
a. natural gas and electricity are both normal goods.
b. electricity and natural gas are substitutes.
c. One of the two goods is inferior and the other is normal, but more information is needed to
determine which of them is normal.
d. electricity and natural gas are complements.
Câu 13. If peanut butter is an inferior good, what would happen to the price and quantity sold of peanut
butter as incomes fall during an economic recession?
a. The price and quantity would both decrease.
b. The price would decrease and the quantity would increase.
c. The price would increase and the quantity would decrease.
d. The price and quantity would both increase.
Câu 14. The burden of a tax that is imposed on a good is said to fall completely on the consumers if the:
a. price paid by consumers for the good increases by the amount of the tax.
b. price paid by consumers does not change.
c. wages received by workers who produce the good increase by the amount of the tax
d. price paid by consumers for the good dedines by the amount of the tax.
Câu 15. Suppose the government decides to fight obesity in America by imposing an excise tax based on
the saturated fat content of food. The most likely effect of this tax would be to:
a. decrease revenue for the government.
b. lower the profits of ice cream suppliers.
c. decrease black market activity.
d. raise the profits of ice cream suppliers.
Câu 16. The consumers' willingness to pay for a good is used to derive the ….. for that good a. producer surplus b, demand curve c. cost of production d. supply curve
Câu 17. Goods are when the cross-price elasticity of demand is positive and price elasticity of demand is negative when the cross
a. substitutes; complements b. complements; substitutes c. inelastic elastic d. elastic inelastic
Câu 18. A utility – maximizing consumer buys so as to make ….. for all pairs of goods a. MUx = Muy b. Px. MUx = Py . Muy c. MUx/Muy = Px/Py d. TUx/TUy = Px/Py
Câu 19. Suppose there is currently a tax of $50 per ticket on airline tickets. Sellers of airline tickets are
required to pay the tax to the government. If the tax is reduced from $50 per ticket to $30 per ticket, then
A. the demand curve will shift upward by $20, and the effective price received by sellers will increase by $20
B. the supply curve will shift downward by $20, and the price paid by buyers will decrease by $20
C. the demand curve will shift upward by $20, and the effective price received by sellers will increase by less than $20
D. the supply curve will shift downward by $20, and the price paid by buyers will decrease by less than $20.
Câu 20. Which is the equation representing perfectly elastic demand curve? a. P = 5 b. Q = 5 c. P + Q = 5 d. P – Q = 5
Câu 21. An indifference curve shows
A) affordable combinations of goods.
B) the relative price of one good relative to another.
C) consumption possibilities that a consumer faces at different prices and income.
D) different combinations of two goods among which the consumer is indifferent.
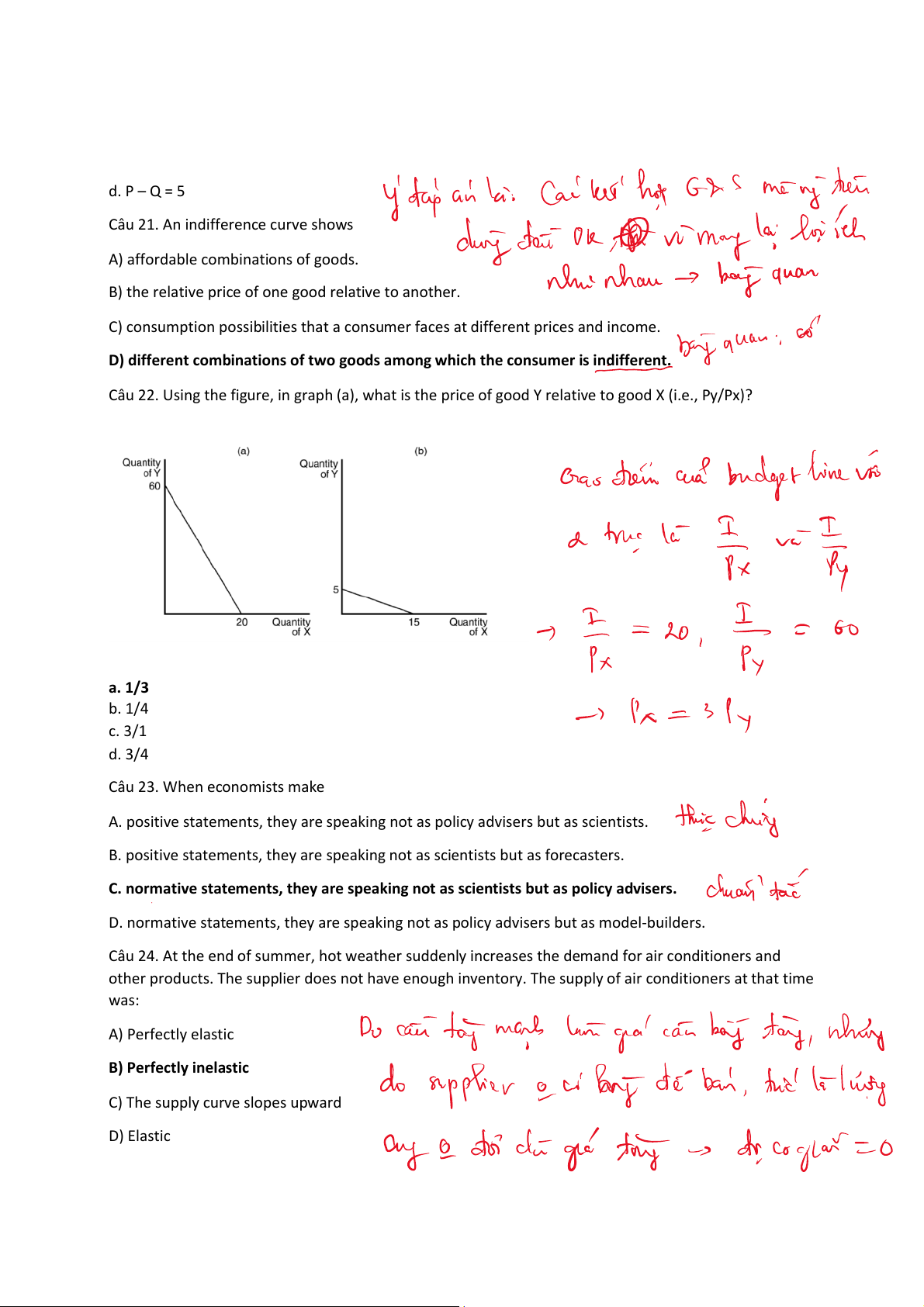
Câu 22. Using the figure, in graph (a), what is the price of good Y relative to good X (i.e., Py/Px)? a. 1/3 b. 1/4 c. 3/1 d. 3/4 Câu 23. When economists make
A. positive statements, they are speaking not as policy advisers but as scientists.
B. positive statements, they are speaking not as scientists but as forecasters.
C. normative statements, they are speaking not as scientists but as policy advisers.
D. normative statements, they are speaking not as policy advisers but as model-builders.
Câu 24. At the end of summer, hot weather suddenly increases the demand for air conditioners and
other products. The supplier does not have enough inventory. The supply of air conditioners at that time was: A) Perfectly elastic B) Perfectly inelastic
C) The supply curve slopes upward D) Elastic
Câu 25. Mai can buy A or B. The price of both A and B is $1. When she spends all her income, Mai's
marginal utility from buying A is 10 and from B is 8. Mai will not be more profitable if: A. buy more A and more B B. buy more A and less B C. buy less of both A and B
D. buy less A and more B
Câu 26. Along any downward sloping straight-line demand curve, the price elasticity varies, but the slope is constant. A. True B. False
Câu 27. Steak and Egg are complementary goods. If the price of steak increases, in egg market
equilibrium price will increase and equilibrium quantity will decrease. A. True B. False
Câu 28. Normal goods have negative income elasticities of demand, while inferior goods have positive
income elasticities of demand. A. True B. False
Câu 29. An example for perfect substitution goods is beer and wine. A. True B. False
Câu 30. An optimizing consumer will select a consumption bundle in which income is maximized and prices are minimized. A. True B. False
Câu 31. (Từ câu 31, điền đáp án dưới dạng số thập phân được làm tròn đến 2 chữ số thập phân nếu cần,
không viết kí tự khác, chỉ viết số, không được viết dưới dạng phân số, dấu chấm cho phần thập phân, ghi
dấu trừ cho số âm nếu có)
A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 + 5Q. What is the equilibrium price? Đáp án: 82
Câu 32. A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 +
5Q. What is the price elasticity of demand in the equilibrium price? Đáp án: -1.28
Câu 33. A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 +
5Q. What is the price elasticity of supply in the equilibrium price? Đáp án: 1.03
Câu 34. A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 +
5Q. What is the consumer surplus in the equilibrium price? Đáp án: 512
Câu 35. A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 +
5Q. If the market price is 18, there is a surplus in the market with …. Units Đáp án: 18
Câu 36. A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 +
5Q. If there exists a price – ceiling of $14, what is the number of product exchanged in the market? (Sản
lượng được giao dịch trên thị trường) Đáp án: 72
Câu 37. A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 +
5Q. If the government imposed a tax of $18 per unit, the new supply function is: P = …. + 5Q Đáp án: 12
Câu 38. A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 +
5Q. If the government imposed a tax of $18 per unit, the new equilibrium price is ….. Đáp án: 72
Câu 39. A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 +
5Q. If the government imposed a tax of $18 per unit, what is the consumer’s tax burden per unit? Đáp án: 10
Câu 40. A market for good X is given by the following functions: Demand: P = 146 – 4Q. Supply: P = 2 +
5Q. If the government imposed a tax of $18 per unit, what is the tax revenue? Đáp án: 252




