


Preview text:
MICROECONOMICS
Topic 1: Các vấn đề cơ bản của Microeconomics A. SCARCITY: What is Scarcity?
Scarcity happens when needs & wants are higher than the capacity of resources to satisfy them.
Scarcity always exists because: our needs & wants are unlimited while economic . resources are limited
What are Economic resources?
Economic resources are all the that
natural, human and physical resources
go into the production of goods and services.
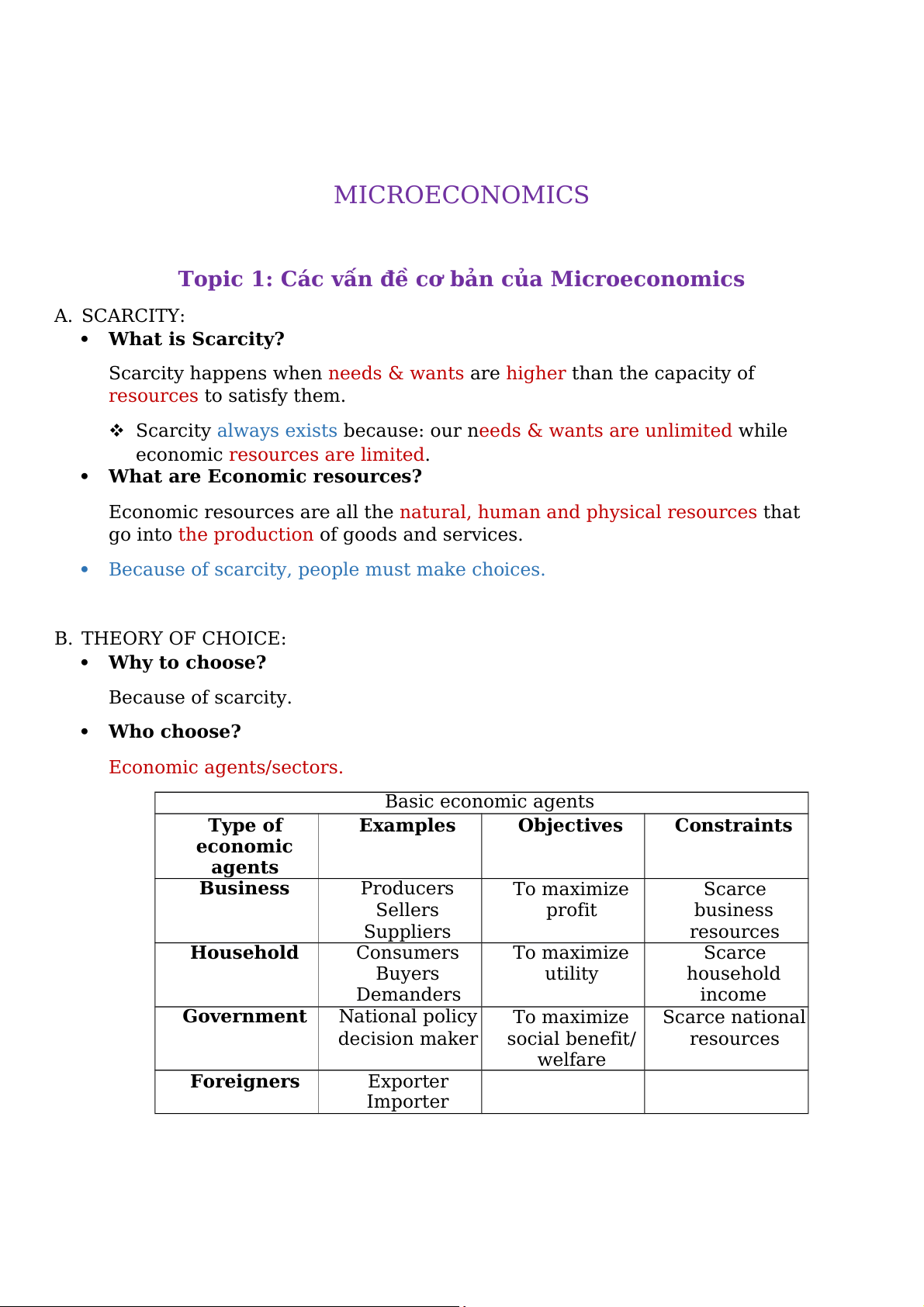
Because of scarcity, people must make choices. B. THEORY OF CHOICE: Why to choose? Because of scarcity. Who choose? Economic agents/sectors. Basic economic agents Type of Examples Objectives Constraints economic agents Business Producers To maximize Scarce Sellers profit business Suppliers resources Household Consumers To maximize Scarce Buyers utility household Demanders income Government National policy To maximize Scarce national decision maker social benefit/ resources welfare Foreigners Exporter Importer What to choose?
Using the Three basic economic issues to determine what to choose. This
question should be solved in the order below. What to produce: Goods and services that to customers.
provide satisfaction or pleasure
Are what the customers' needs and able to afford. How to produce:
Is the best method to produce = the lowest cost method For whom to produce: Based on the economy systems. There are 3 economic systems:
Centrally planned economy (kinh tế kế hoạch hóa tập trung / nền kinh tế quan liêu bao cấp)
Free market economy (kinh tế thị trường tự do, không có sự điều tiết của chính phủ)
Mixed economy (kinh tế hỗn hợp, có sự điều tiết vĩ mô của nhà nước) Vietnam is mixed economy. How to choose? Using - Phân tích cận biên. Marginal Analysis
Marginal Analysis là sự so sánh giữa lợi ích cận biên và chi phí cận biên khi making decision.
Principle: Profit max when MR (marginal revenue) = MC (marginal cost) C. OPPORTUNITIES COST:
Making a choice means when you choose an option, you must give up
another option. => Trade off (đánh đổi)
Opportunity cost is the benefit/the value of things that are being traded off.
Example: Working part-time when in college
=> Opportunity costs are bad grades, have less time for family and friends, … D. PPF MODEL:
Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) model - đường giới hạn khả
năng sản xuất của nền kinh tế. PPF curve is the of different combination maximum quantity of any 2
products in an economy with fixed resources.
It implies: scarcity & the law of increasing opportunity cost
PPF curve exists in situations where: Only 2 goods are produced
Nguồn lực/technology is fixed
The economy uses all resources, with no wastage. PPF questions:
There are 2 goods: clothes & rice. People have 5 alternatives output of the production.
Các điểm A, B, C... is
e => là tập hợp các maximum output on the curv có
thể đạt được với nguồn lực có hạn
H is outside the curve => point impossible
G is inside the curve => Ineffective point – produce with . wastage
Opportunity cost (of increasing clothes quantity) = slope = △ y △ x = △rice △ clothes
Opportunity cost of increasing clothes from A to B: = △ y = 3 = 0.3 △ x 9
=> Opportunity cost of increasing 1 million tons of clothes is to trade off 0.3 million tons of rice.
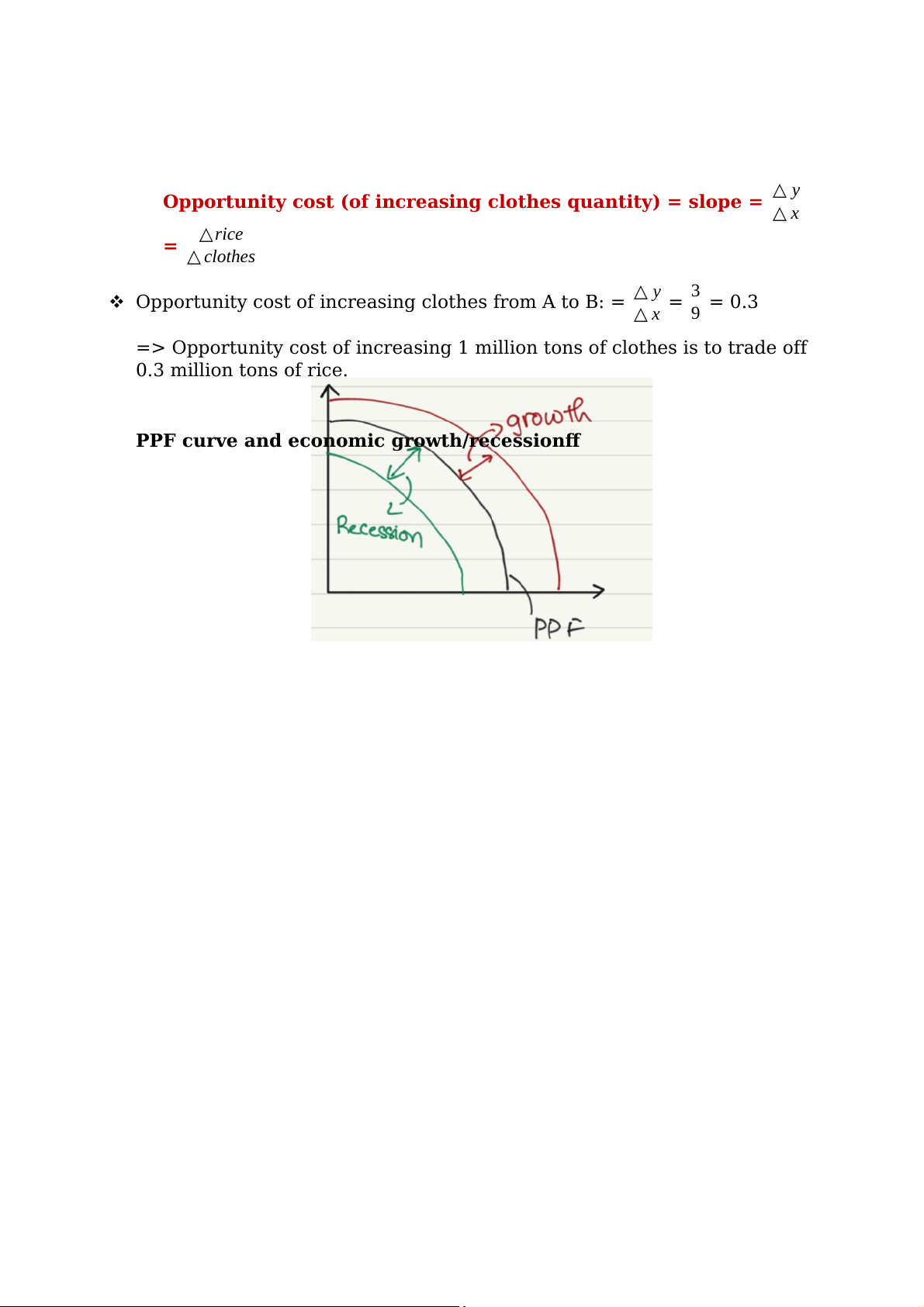
PPF curve and economic growth/recession.




