











Preview text:
DESIGN AND CALCULATE THE MANUAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM OF TOYOTA INNOVA
Chapter 1: Fundametal of theory
1. History and Development of Automotive Industry
1.1 History of automotive industry
1.2 Development of automotive industry
2. Manual Transmission overview 2.1 Mission
2.2 classification of manual transmission 2.3 Technical requirements 2.4 Transmission selection
2.4.1 Selecting for transmission placement position 2.4.2 Selecting gearbox
chapter 2 calculation of a 3 shaft 5 speed manual transmission design
1. Introduction to the basic parameters of toyota innova 2020
2. structure diagram,operate principle of a 3-shaft 5-speed manual transmission
2.1 Structure diagram and technical drawing of a 3-shaft 5-speed manual transmission
2.2 operate principle of a 3-shaft 5-speed manual transmission
3. identify the basic sizes and detail design
3.1 Selection transmission ratio
3.2 Selection the distance of axles
3.3 Selection normal module of transmission gears
3.4 Selection number of teeth of gear
4. strength of gearbox's components
4.1 gearbox's teeth calculation
4.2 Preliminary selection of gearbox shaft dimensions
4.3 Calculation of the sliding gears of the gearbox shaft
4.4. Selection shaft bearing gearbox Conclusion Chap1
1. History and Development of Automotive Industry
1.1 History of automotive industry
The world's first gasoline-powered car was built by Carl Benz, a German engineer and
automotive pioneer, in 1885 in the city of Mannheim, Germany. He patented it on
January 20, 1886, and became the first automobile manufacturer in 1888 shortly after his
wife, Bertha Benz, made the first successful long-distance trip (from Mannheim to
Pforzheim and return) in August of the same year. Indeed, her journey proved to everyone
that the horse-drawn carriage was perfectly suitable for daily use. Since 2008, the Bertha
Benz Memorial Route, an avenue has been named after her in memory of the event.
Not long after, in 1889 in Stuttgart, Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach designed an
automobile from a miscellaneous vehicle, resembling a horse-drawn carriage with an
engine. They are often considered the inventors of the first automobile in 1886. However,
from 1892 an Italian at the University of Padua, Enrico Bernardi, applied for a patent for
a single-cylinder engine. petrol engine, power 0.024 hp (17.9 W) 122 cc. This engine he
attached to his son's tricycle, and made it a candidate product for the world's first car and
first motorcycle. In 1892, Bernardi expanded the tricycle to accommodate two people.
The history of the automobile industry, though brief compared with that of many other
industries, has exceptional interest because of its effects on history from the 20th century.
Although the automobile originated in Europe in the late 19th century, the United States
completely dominated the world industry for the first half of the 20th century through the
invention of mass production techniques. In the second half of the century the situation
altered sharply as western European countries and Japan became major producers and exporters.
1.2 Development of automotive industry
2. Manual Transmission overview 2.1 Mission
2.2 classification of manual transmission
Manual transmission cars include two types of structure: Transaxle and transmission. • Transaxle
A transaxle is a single unit that combines the transmission, axle, and differential. It’s a
smaller version of a transmission, found mainly in FWD vehicles with automatic
transmissions. Most vehicles with a transaxle have a transverse engine layout. This means
the engine is mounted with the crankshaft running left to right. Transaxles usually contain
automatic transmissions, though they can be manual or continuously variable.
Transaxles have the axle integrated into its assembly for a much smaller package. Instead
of having the differential in the rear of the vehicle, it’s located in the transaxle housing
that’s mounted parallel to the transmission. This simplifies the vehicle's driveline as the
driveshaft doesn't have to connect to a differential before power is sent to the wheels.
Cars with transaxles often weigh less as they have fewer drivetrain components.
Transaxles are usually found on vehicles with a front engine and FWD or a rear engine
and RWD. But the transaxle can also be integrated into the rear axle on cars with a front
engine and rear-wheel drive. The transaxle is in the rear where the differential would be rather than beside the engine.
Front-engine RWD cars aren't as common, but some performance cars use this setup for
better weight balance and handling. Porsche, Corvette, and Mercedes have all used
transaxles in a few of their vehicles. - Operation
The transmission part of a transaxle operates the same as any other transmission.
However, rather than connecting to the rear axle via the driveshaft, a transaxle contains
both the transmission and the differential. When power is applied, the transmission’s
output shaft rotates a pinion gear that connects to the ring gear on the differential. Power
is transferred to the wheels through two axle shafts, or half shafts, connecting the transaxle and the wheels.
Transaxles use a torque-splitting differential so the axle shafts can operate at different
speeds. This allows the car to corner effectively.
Differentials inside a transaxle often use four or more gears, with one gear attached to
each axle and two more connected to the differential pinion shaft. • Transmission
A transmission is a series of gears that transmit power from the engine to the wheels.
Most RWD vehicles with a longitudinal engine will have a transmission. Longitudinal
engines mount down the center of the vehicle so the crankshaft faces front to back. This
creates a straight line from the crankshaft to the transmission, driveshaft, and rear differential.
There are a few different types of transmissions available. They can either be manual,
automatic, continuously variable (CVT), or semi-automatic. - Operation
Transmissions connect to the engine crankshaft through a flywheel and clutch, torque
converter, or system of pulleys. Transmissions usually have one output shaft. The output
shaft connects to the rear axle via the driveshaft.
Each type of transmission works differently, but they all control the speed and torque
available on the drive wheels. Most transmissions, whether automatic or manual, do this
through the use of gears. Continuously variable transmissions use pulleys or rollers rather than gears.
2.3 Technical requirements
+ Size/dimension: ensure the shafts’ diameter, shaft distance, gears’ thickness, bề rộng
then, bearing diameter, shift forks’ sizes, flange size.
+ Surface’s gloss: N5 for machining gears, N6 for shaft surface, and N7, N10 for grears and bearings.
+ Stiffness: after thermal treatment gears surface have to reach 55HRc and shaft is 60HRc.
+ Thermal treatment: quenching and tempering.
Technical requirements for components: + Gears: •
Ensures steady transmission of torque. •
No unsual noise during operation. • Accurate meshing. •
Good strength of material for working condition. + Shafts:
Size and materials of the shafts are the two important components that can affect the
working ability of gears and bearings in the long terms. Kinematic diagram of gearbox
affect the size and load of the shafts.
The stiffer of the shaft will increase the gears’ durabilty and reduce noise during
operation, while avoiding gear wrap.
Ensuring the durability and accuracy of axial and radial dimensions reaching the requirements. + Bearings:
Bearings are selected according to the working ability of manual transmission so the
sizes and durability need to reach the requirements.
+ Manual transmissions’ cover:
. Light weight and good rigidity to make protect the shafts and bearings from deformation during operation.
. Sizes and shape depend on the kinematic diagram of gearbox and the arrangement of shafts and gears.
. For lubrication the cover must have oil filling hold, level checker, and button to drain
the old oil. Oil filling hole need to be placed at lowest position of the cover.
Overall technical requirement:
+ Suitable ratio to improve dynamic and economical features of car.
+ High transmission efficiency, no unsual noise, and shifting smoothly.
+ Compact structure, easy to control and maintain when damaged
2.4 Transmission selection
The Toyota Innova line is one of the most popular car models for household segment.
Innova is highly appreciated for its durability and stable operation. It is a multi-purpose
vehicle commonly used for families, with the flexibity in switching between carrying
people and carrying goods. And because of that, front engine rear drive (FR) with 5-speed
gears are a suitable choice for Toyota Innova.
2.4.1 Selecting for transmission placement position a. Structure diagram
According to the structural diagram in the figure, the internal combustion engine (ICE) is
connected to clutch then transmission. The transmission has the function of converting
power from the engine, converting the torque generated from the engine into torque with
a speed and magnitude suitable for driving conditions. There is a support transmit power
component called propeller shaft. The propeller shaft is attached to the differential. Then
the two output ways is connect to drive axle shaft and final is tires. b. Working principles
When the crankshaft rotate, torque from ICE will go to the flywheel then go through the
clucth to the input shaft of transmission. When the driver needs to engage any gear
(depend on driving condition), the clutch is disengaged which brings the rotating parts to
a complete stop. The gear shifter is then pushed to the gear driver want, which pushes the
shift rod. The shift rod makes the fork move the synchronizer towards the gear. The
blocker ring rubs against the straight cut teeth to lock on to the gear and sync the
speed.When the driver engages the clutch again, the blocker ring causes the synchronizer
sleeve to rotate along with it and the speed of the rotating parts are matched. Then the
matched speed delivery to output shaft. By The propeller shaft, the power is transmitted
from the gearbox’s output shaft to the differential c. Advantages and disavantages
Toyota Innova is a 7 seater car so it is relatively high load capacity. Therefore, FR layout
is appropriate. It has a better weight distribution. The longitudinal transmission can be
placed in the center of the vehicle, helping to distribute weight more evenly between the
two axles. This helps improve the vehicle's performance, especially handling and traction force.
Next is more spacious interior space. Longitunal transmission saves space under the
hood, helping to increase space in the passenger compartment and luggage compartment.
Moreover it is increase slightly the steering angle which also increase safety for customer
and propitious for suspension arrangement.
Beside the advantages of FR drivetrain, it also have its background. First is ability to take
advantage of adhesive weight when in low load state will lead to decrease traction force
when drive in a low adhesion coefficient road. Next is the power transmission efficieny
of power decrease due to the loss in long line power transmitting. Finally, because of
large weight of vehicle will cause overload for braking system in front wheel. 2.4.2 Selecting gearbox
After choosing the engine placement position, the next part is select the number of speed
for the Toyota Innova. A four gear box gives you long gearing, which makes for good
highway economy. Futher more, 4-speed gearbox taking up little space in the engine
compartment. but since each gear has to cover a wider range of speeds, either you
accelerate slower or use more power to get up to speed which lead to poor fuel economy and it is not good selection.
A five gear box gives shorter spacing between the ratios, so you can accelerate more
quickly at the same revs. A 5-speed gearbox has more gears than a 4-speed gearbox,
helping the vehicle operate more effectively in many different road conditions. The 5-
speed gearbox helps the car achieve higher speeds and more speed.
About a 6-speed gearbox, it have one more gear, so the shifting will be smoother and you
will achieve higher speed very fast. But adding one more gear speed that’s mean more
component such as shifting rod, add more synchronizer,.... which is made the struture
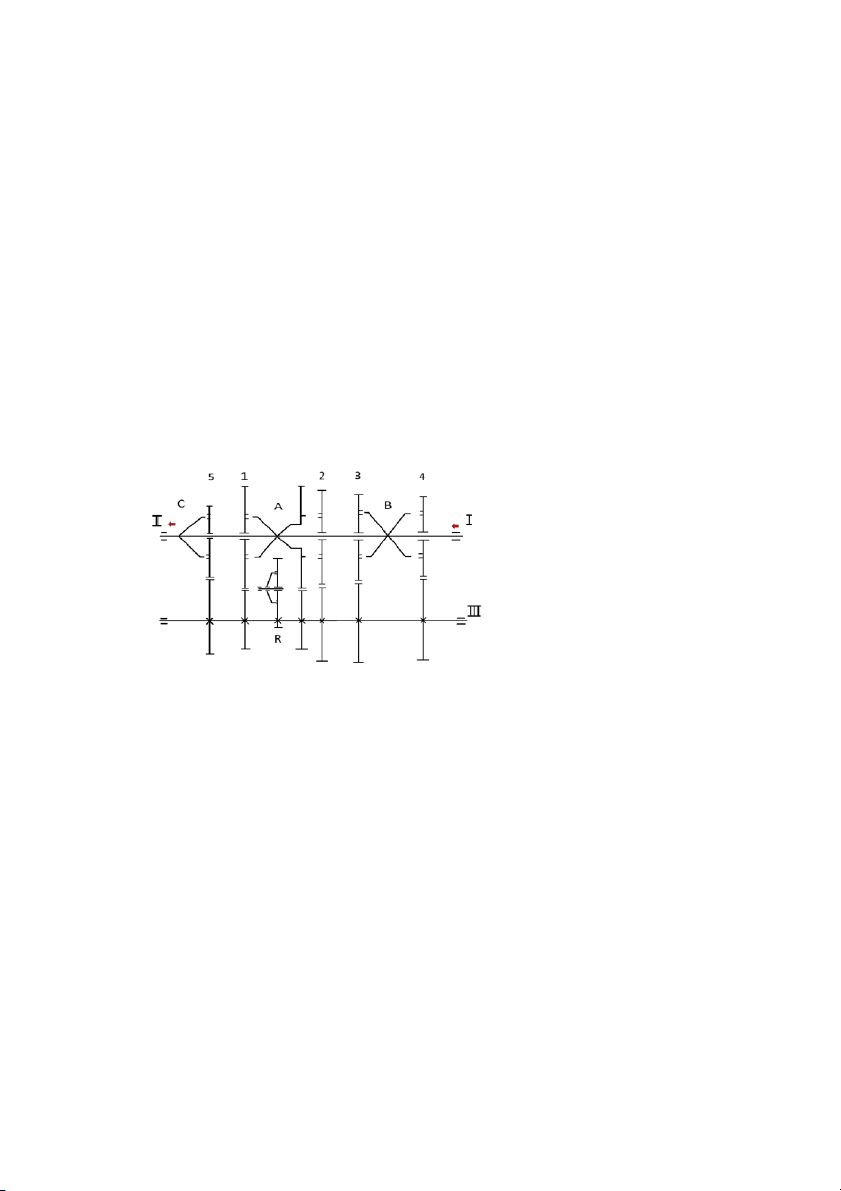
more complex and increase the weight of the vehicle. So choosing 5-speed gearbox is suitable for Toyota Innova. a. Structure Diagram *FR Drive Train
I - Primary shaft ( Input shaft)
II - Secondary shaft (Output shaft) III - Intermediate shaft A - 1th/2nd Synchronizer B - 3th/4th Synchronizer C - 5th/ Reverse Synchronizer R – Reverse Gear b. Working priciples
The intermediate shaft is the shaft attach with driven gears. Gears in primary shaft match
with the driven gears of intermediate shaft. The alignment of these two gears is shown in
the fact that when the primary shaft rotates and the driving gear rotates, the driven gear
also rotates, causing the intermediate shaft to rotate as well.
The output shaft is the component that carries the power out of the transmission to the
wheels. When the power is transmitted from input shaft to intermediate shaft, the driving
gears of intermediate shaft match with gears of output shaft. When the intermediate shaft
rotate, it allow power transmitt to the Output shaft and transmit to the drive wheels
When shifting gears, the driver will press the brake pedal and move the gear shift lever
to the desired gear position. The shift fork will move in the direction of the gear shift
lever. The synchronizer ring will be pushed against the cone of the gear. The friction
between the synchronizer ring and the cone of the gear will synchronize the speed of the
gear with the speed of the shift fork. When the speed of the gear and the shift fork are
equal, the synchronizer ring will begin to rotate slightly in the direction of the gear
rotation. At this time, the shift fork will lock the gear into position.
Reverse requires an additional gear in the gear train. A reverse idler gear is used to
change the direction of the output shaft for reverse. The reverse gear is a straight cut spur
gear and does not have a synchronizer.
c. Advantages and Disavantages
About the advantage of 5-speed transmission, it has better fuel eefficiency. Manual
transmissions are generally more fuel-efficient than automatic transmissions, especially at
highway speeds. This is because manual transmissions have fewer moving parts and less
parasitic drag. More over gear shifting process in 5-speed gearbox is smoother,
minimizing vibration and noise.
In the other side, the design of 5-speed transmission is complex and it need mis-shift
prevention mechanism to protect the gearbox.




