


Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220
1. Discount Incremental Cash Flows
A project’s present value depends on the extra cash flows that it produces. So you need to
forecast first the firm’s cash flows if you go ahead with the project. Then forecast the cash flows
if you don’t accept the project. Take the difference and you have the extra (or incremental)
cash flows produced by the project:
Incremental cash flow = cash flow with project − cash flow without project 2. Forget Sunk Costs
They are past and irreversible outflows. Sunk costs remain the same whether or not you accept
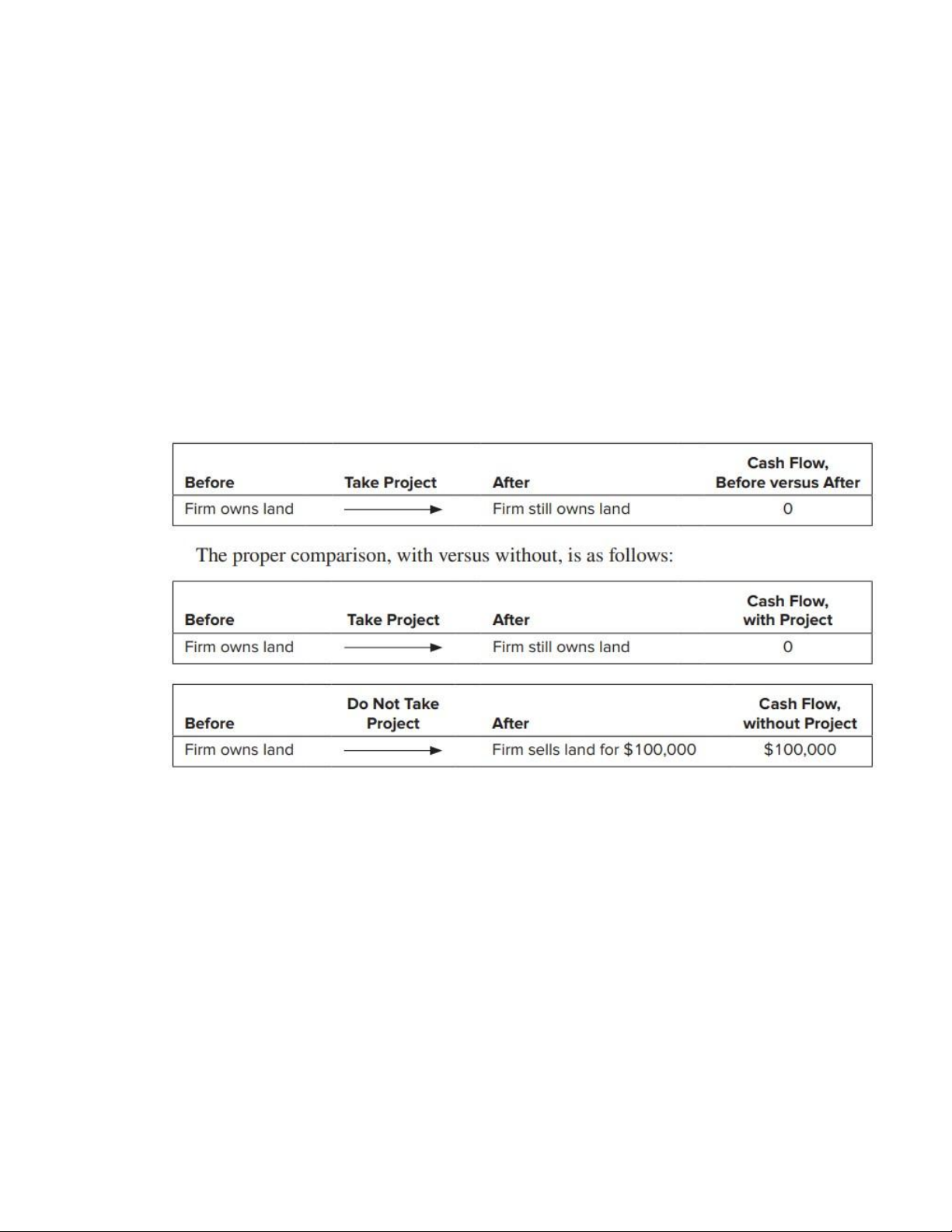
the project. Therefore, they do not affect project NPV. 3. Include Opportunity Costs
Benefit or cash flow forgone as a result of an action
Add (100,000) in the Incremental CF -
Incremental cash flow = cash flow with project − cash flow without project
The opportunity cost equals the cash that could be realized from selling the land now; you lose
that cash if you take the project
4. Recognize the Investment in Working Capital Net working capital (often referred to simply as working capital) -
Current assets minus current liabilities. Often called working capital
5. Beware of Allocated Overhead Costs -
A project may generate extra overhead costs, but then again it may not. We should be cautious
about assuming that the accountant’s allocation of overhead costs represents the incremental
cash flow that would be incurred by accepting the project lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220
The net increase in cash flow equals the after-tax cost savings: (1 − .35) × $30,000 = $19,500
Operating cash flow = revenues − cash expenses – taxes
Operating cash flow = after-tax profit + depreciation
Depreciation tax shield = tax rate × depreciation
Operating cash flow = (revenues − cash expenses) × (1 − tax rate) + (tax rate × depreciation) lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220
Tax PAID = EBDIT*TAX RATE
= (Sale-Cost-Depreciation)*tax rate
Depreciation = (initial cost – salvage value)/year
If depreciation to straight-line = initial cost/year Tax shield on depreciation = depreciation*tax lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220 Definition:
interest tax shield Tax savings resulting from deductibility of interest payments. internal rate of return
(IRR) Discount rate at which project NPV = 0.
depreciation tax shield Reduction in taxes attributable to depreciation.
discounted cash flow (DCF) Method of calculating present value by discounting future cash flows
net working capital Current assets minus current liabilities. Often called working capital