
Preview text:
Guide for self -study
Guide for exercises(in Vietnamese) – Click vào tên bài để xem clip youtube
Perfectly competitive market Bài 12.
Một hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo có hàm chi phí biến đổi trung bình là: AVC = 2q + 4.
1. Viết phương trình biểu diễn hàm cung của hãng. Tại mức giá nào hãng phải đóng cửa sản xuất?
2. Khi giá bán sản phẩm là 24$ thì hãng bị lỗ 150$. Tính chi phí cố định.
3. Tìm mức giá và sản lượng hòa vốn của hãng?
4. Khi giá thị trường là 104, quyết định của hãng như thế nào?
5. Minh họa các kết quả trên cùng một đồ thị. Monopoly Bài 13.
Một nhà độc quyền có đường cầu P=
15−5 Q , hàm tổng chi phí T C=2,5 Q2+3Q+1
1. Tìm quyết định sản xuất và lợi nhuận kinh tế của hãng độc quyền.
2. Tính thặng dư sản xuất, thặng dư tiêu dùng và tổng thặng dư.
3. Xác định phần mất không do độc quyền gây ra
4. Minh họa bằng đồ thị. Bài 14.
Hãng độc quyền có hàm cầu P =52−2Q , TC=0,5 Q2+2Q+47,5
1. Quyết định sản xuất của hãng là gì, hãng thu được lợi nhuận kinh tế là bao nhiêu
2. Nếu đánh thuế t = 0,5$/sản phẩm, quyết định của hãng thay đổi thế nào? Chính phủ thu thuế bao
3. Nếu chính phủ đánh thuế khoán T = 50$ thì hãng sẽ quyết định thế nào? Bài 15.
Kinh, Tế, Quốc và Dân cùng nhau mở nhà máy sản xuất keo dính chuột duy nhất trong thành phố (tất cả
người đều mua keo dính chuột ở đây). Hàm cầu sản phẩm keo dính chuột trong thành P=5 0 phố 0− Q là: . Hàm
tổng chi phí của nhà máy Tlà: C =Q2+40 Q+8000
Họ đang bàn bạc để quyết định số lượng sản phẩm sẽ sản xuất trong thời gian tới. Có 4 phương án như
Kinh thì muốn tối đa hóa lợi nhuận: MR = MC
Tế thì muốn tối đa hóa doanh thu: MR = 0
Quốc thì muốn tối đa hóa sản lượng mà không bị lỗ: P = ATC
Dân thì muốn tối đa hóa lợi ích ròng của xã hội cho thị trường này: P = MC
Hãy chỉ ra sản lượng, mức giá, tương ứng với mỗi lựa chọn của Kinh, Tế, Quốc và Dân. Minh họa các
trên cùng một đồ thị (chỉ cần vẽ giá và sản lượng)
Monopolistic Competition
Characteristics of the market Many sellers Product differentiation
Free entry and exit ( similar to competitive firm)
Characteristics of a firm Not price takers
Face the downward slope demand curve (i.e., MR < P ) ( similar to monopoly)
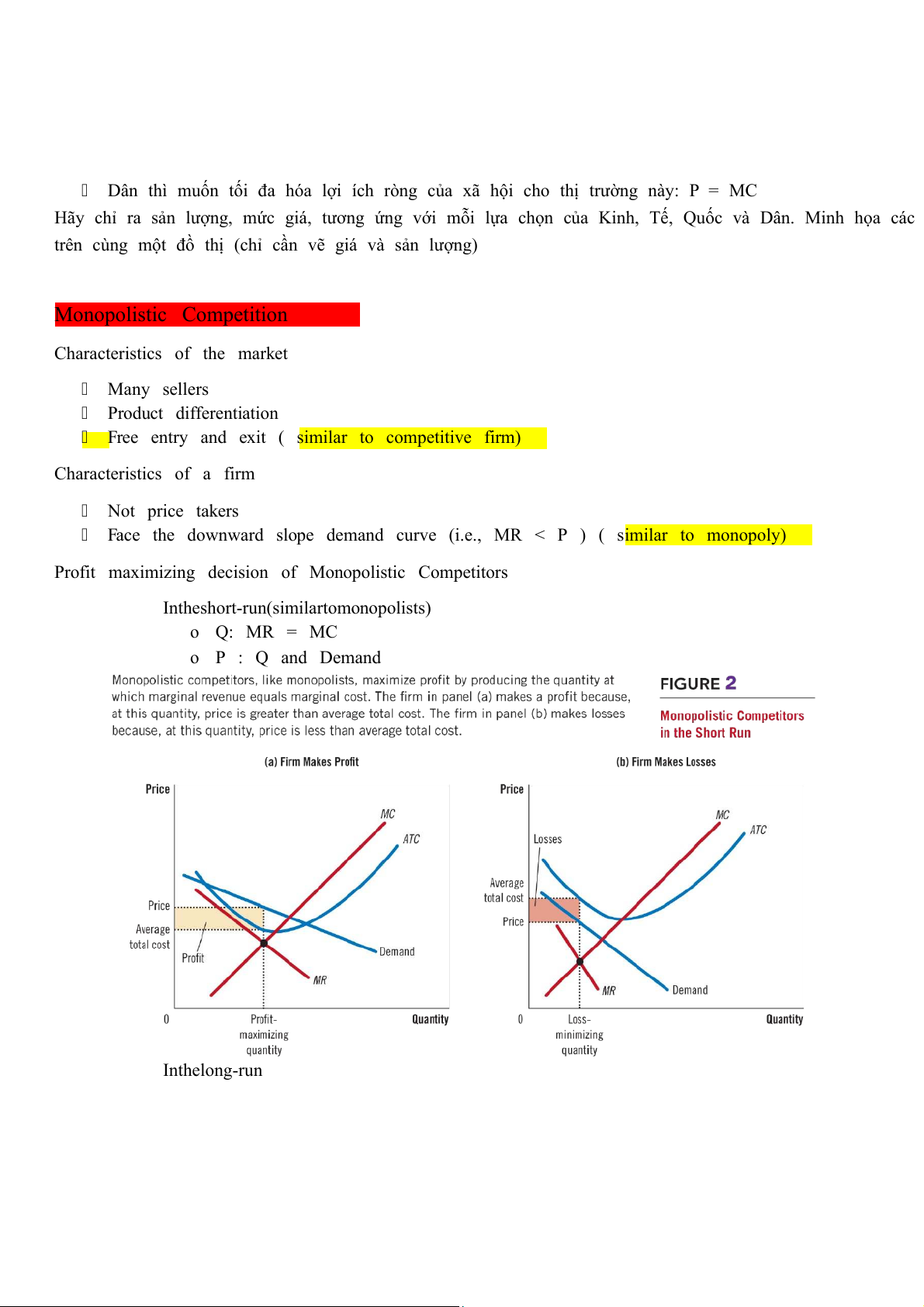
Profit maximizing decision of Monopolistic Competitors
In the short-run (similar to monopolists) o Q: MR = MC o P : Q and Demand
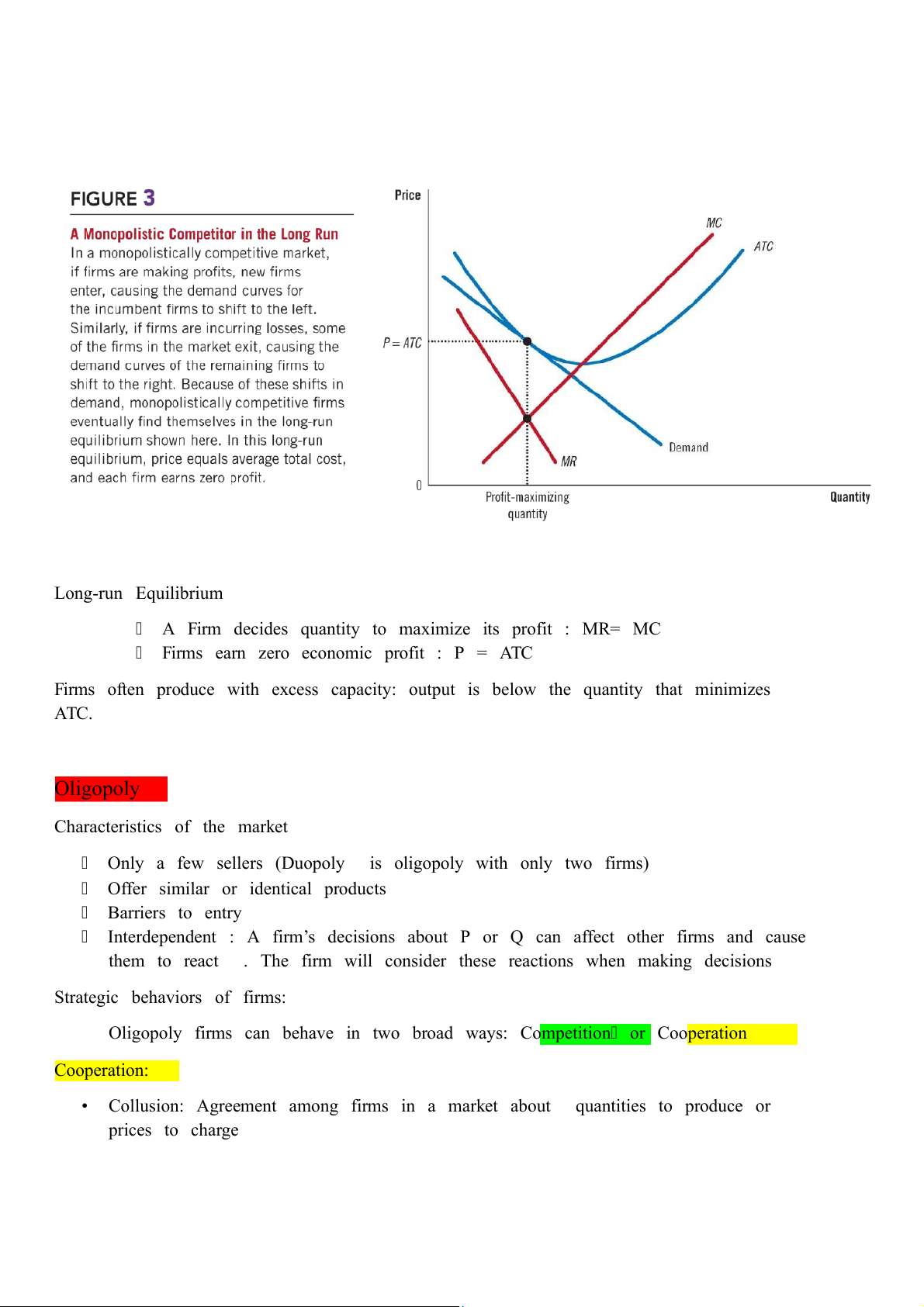
In the long-run Long-run Equilibrium
A Firm decides quantity to maximize its profit : MR= MC
Firms earn zero economic profit : P = ATC
Firms often produce with excess capacity: output is below the quantity that minimizes ATC. Oligopoly
Characteristics of the market
Only a few sellers (Duopoly is oligopoly with only two firms)
Offer similar or identical products Barriers to entry
Interdependent : A firm’s decisions about P or Q can affect other firms and cause
them to react . The firm will consider these reactions when making decisions
Strategic behaviors of firms:
Oligopoly firms can behave in two broad ways: Competition or Cooperation Cooperation: •
Collusion: Agreement among firms in a market about quantities to produce or prices to charge •
Cartel :Group of firms acting in unison (for example : OPEC) HOWEVER:
In most countries, a cartel is illegal under antitrust law.
But cartels are difÏcult to maintain because each firm has an incentive to “cheat.”
(see example of Cell Phone Duopoly in Smalltown in Slides)
The Prisoners’ Dilemma (see in slides), - decision makers as game players
Dominant Strategy: the best strategy regardless others players actions. Nash Equilibrium
o Players interacting with one another.
o Each choose their best strategy, given the strategies that all the other actors have chosen • Oligopolists
– Better off cooperating and reaching the monopoly outcome
– They pursue their own self-interest •
Do not end up reaching the monopoly outcome and maximizing their joint profit •
Each is tempted to raise production and capture a larger share of the market •
Total production rises and price falls
– Produce a quantity of output •
Greater than the level produced by monopoly •
Less than the level produced by competition – The price is • Less than the monopoly price •
Greater than the competitive price (MC) •
If oligopolists form a cartel – Maximize total profit – Produce monopoly quantity – Charge monopoly price
– BUT, difÏcult to reach and enforce an agreement