

Preview text:
IAS 21: The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
(AH của sự thay đổi của tỷ giá hối đoái)
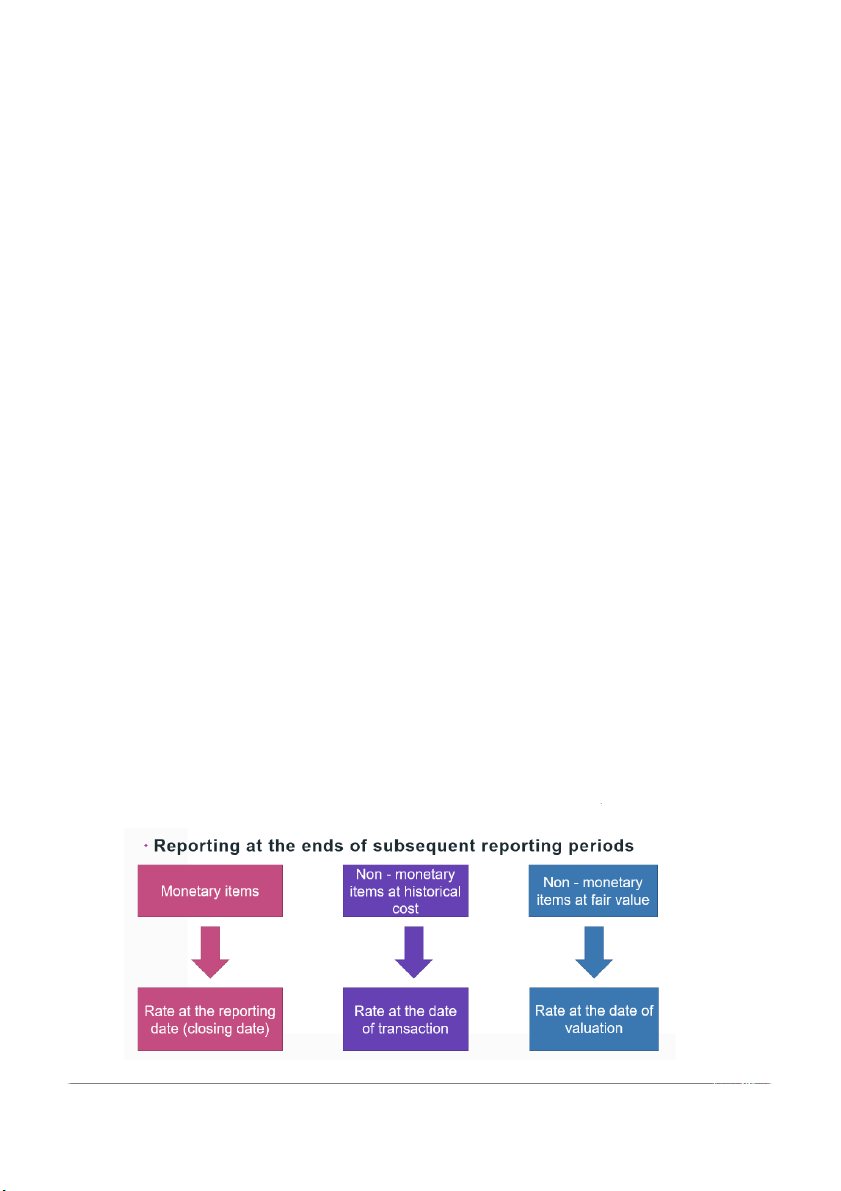
Closing rate: the spot exchange rate at the end of the reporting period
Exchange difference: the difference resulting from translating a
given number of units of one currency into another currency at different exchange rates.
Functional currency: the currency of the primary economic
environment in which the entity operates.
Foreign operation: a subsidiary, associate, joint venture, or
branch whose activities are based in a country or currency other
than that of the reporting entity.
Presentation currency: the currency in which financial statements are presented.
Spot exchange rate: the exchange rate for immediate delivery.
- Determining the functional currency: (xác định đồng tiền chức năng)
IAS 21 provides primary and secondary indicators for
determining the functional currency
* Primary indicators (các chỉ số chính)
The currency that mainly influences sales prices for
goods and services (often the currency in which prices are denominated and settled)
The currency of the country whose competitive forces
and regulations mainly determine the sales prices of its goods and services; and
The currency that mainly influences labour, material and
other costs of providing goods or services
1. The closing exchange rate was €1.5 = $1. The entity’s functional currency is the dollar. 1.
An entity purchases plant from a foreign supplier for €3 million on January
31, 20X6, when the exchange ratewas €2 = $1. At the entity’s year-end of March
31, 20X6, the amount has not been paid. The closingexchange rate was €1.5 = $1.
The entity’s functional currency is the dollar. Which of the followingstatements is correct?
(a) Cost of plant $2 mil ion, exchange loss $0.5 mil ion, trade payable $1.5 mil ion.
(b) Cost of plant $1.5 million, exchange loss $0.6 mil ion, trade payable $2 mil ion.
(c) Cost of plant $1.5 mil ion, exchange loss $0.5 mil ion, trade payable $2 mil ion.
(d) Cost of plant $2 mil ion, exchange loss $0.5 million, trade payable $2 mil ion.
( Doanh nghiệp mua một nhà xưởng từ một nhà cung cấp nước ngoài với giá 3 triệu
EUR vào ngày31/1/20X0, tỷ giá là 2€ = 1$. Vào ngày kết thúc kỳ kế toán
31/12/20X0, DN chưa trả nợ nhà cungcấp. Tỷ giá ngày 31/12/20X0 là 1,5€ = 1$. Đồng
tiền chức năng của DN là $. Xử lý nào sau đây đúng
c. Nguyên giá của nhà xưởng là 1,5 tr $, lỗ chênh lệch tỷ giá 0,5 tr $, khoản phải trả 2 tr $
2. Which of these considerations would not be relevant in determining the entity’s
functional currency? 2. Sự kiện nào sau đầy không phù hợp khi xác định đồng tiền chức năng:
(a) The currency that influences the costs of the entity.
(b) The currency in which finance is generated.
(c) The currency in which receipts from operating activities are retained.
(d) The currency that is the most international y acceptable for trading.
a. Đồng tiền có ảnh hưởng đến chi phí của DN b. Đồng tiền được tạo ra từ hoạt động tài
chính huy động vốn của DN.c. Đồng tiền được phát sinh từ hoạt động kinh doanh của DN và được DN giữ lại.
D. Đồng tiền được chấp nhận rộng rãi trong thương mại quốc tế.
3. An entity has a subsidiary that operates in a foreign country. The subsidiary
sold goods to the parentfor €2.1 million. The functional currency of the
entity is the dollar. The cost of the goods to the subsidiary was €1.2 mil ion. The
goods were recorded by the entity at $1.05 mil ion (€2 = $1) and wereall unsold at the
year-end of December 31, 20X6. The exchange rate at that date was €1.5 = $1.
Whatis the value of the intragroup profit that wil be eliminated at December 31, 20X6?
(a) $205,000 (b) $600,000 (c) $450,000 (d) $350,000
3. Doanh nghiệp có Cty con hoạt động ở nước ngoài. Cty con này bán hàng cho cty mẹ với giá 2,1 tr
€,giá vốn 1,2 tr €. Đồng tiền chức năng của DN là $. Tại cty mẹ ghi nhận giá trị hàng
hóa mua của ctycon là 1,05 tr $ ((€2 = $1) và đấn ngày cuối kỳ kế toán là 31/12/ 20X0 cty mẹ vẫn
chưa bán ra ngoài sốhàng hóa này. Tỷ giá cuối kỳ là €1.5 = $1. Lợi nhuận nội bộ được
loại trừ trên BCTC hợp nhất của tậpđoàn là:(a) $205,000 (b) $600,000 (c) $450,000 (d) $350,000
The following details apply a contract where performance obligations are
satisfied over time at 31 December 20X5 Total contract revenue 120,000 Costs to date 48,000 Estimated costs to completion 48,000 Amounts invoiced 50,400
The contract is agreed to be 45% complete at 31 December 20X5 as a contract asset? Solution
Contract Asset/Liability = Costs incurred to date + Recognized profits – Receivable (amounts invoiced)
Estimated revenue = 120,000 x 45% = 54,000
COGS = (48,000 + 48,000) x 45% = 43,200
Profits = 54,000 – 43,200 = 10,800
Contract asset = 48,000 + 10,800 – 50,400 = 8,400
*IAS 21 provides primary and secondary indicators for
determining the functional currency Primary indicators:
The currency that mainly influences sales prices for goods and
services (often the currency in which prices are denominated and settled)
The currency of the country whose competitive forces and
regulations mainly determine the sales prices of its goods and services; and
The currency that mainly influences labour, material and other costs
of providing goods or services
*If the functional currency is the currency of a hyperinflationary
economy, the entity’s financial statements are restated in
accordance with IAS 29 Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Economies
Reporting foreign currency transactions in the functional currency




