Preview text:
MICROECONOMICS Individual Assignment Full name: Nguyen Ha Chi Student ID: 11220995 Class: EBBA 14.1
------------------------------------------ Exercise 1:
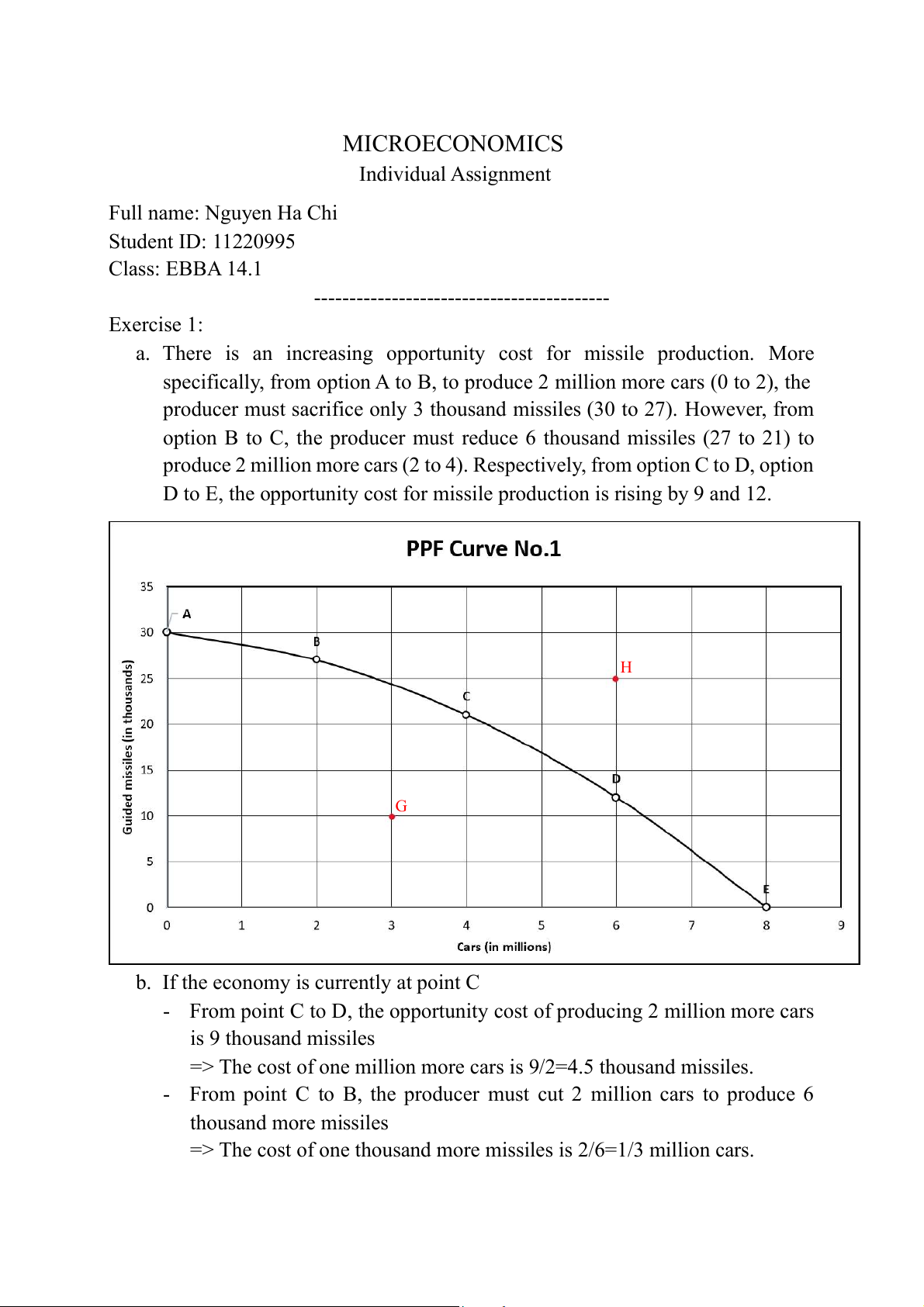
a. There is an increasing opportunity cost for missile production. More
specifically, from option A to B, to produce 2 million more cars (0 to 2), the
producer must sacrifice only 3 thousand missiles (30 to 27). However, from
option B to C, the producer must reduce 6 thousand missiles (27 to 21) to
produce 2 million more cars (2 to 4). Respectively, from option C to D, option
D to E, the opportunity cost for missile production is rising by 9 and 12. H G
b. If the economy is currently at point C
- From point C to D, the opportunity cost of producing 2 million more cars is 9 thousand missiles
=> The cost of one million more cars is 9/2=4.5 thousand missiles.
- From point C to B, the producer must cut 2 million cars to produce 6 thousand more missiles
=> The cost of one thousand more missiles is 2/6=1/3 million cars.
c. Point G indicates that the producer’s output is 3 million cars and 10 thousand
missiles. This means that resources are not used efficiently. If the producer
increased one of its factors of production, it would be able to move towards point C or D.
d. Point H indicates that the producer’s output is 6 million cars and 25 thousand
missiles. This point is currently unattainable with the current resources
available. To achieve that level of production, more resources should be
allocated. For example, technological advancements can improve certain
aspects of producing cars and missiles. If the producer applies modern
technology, it can increase production level to point H.
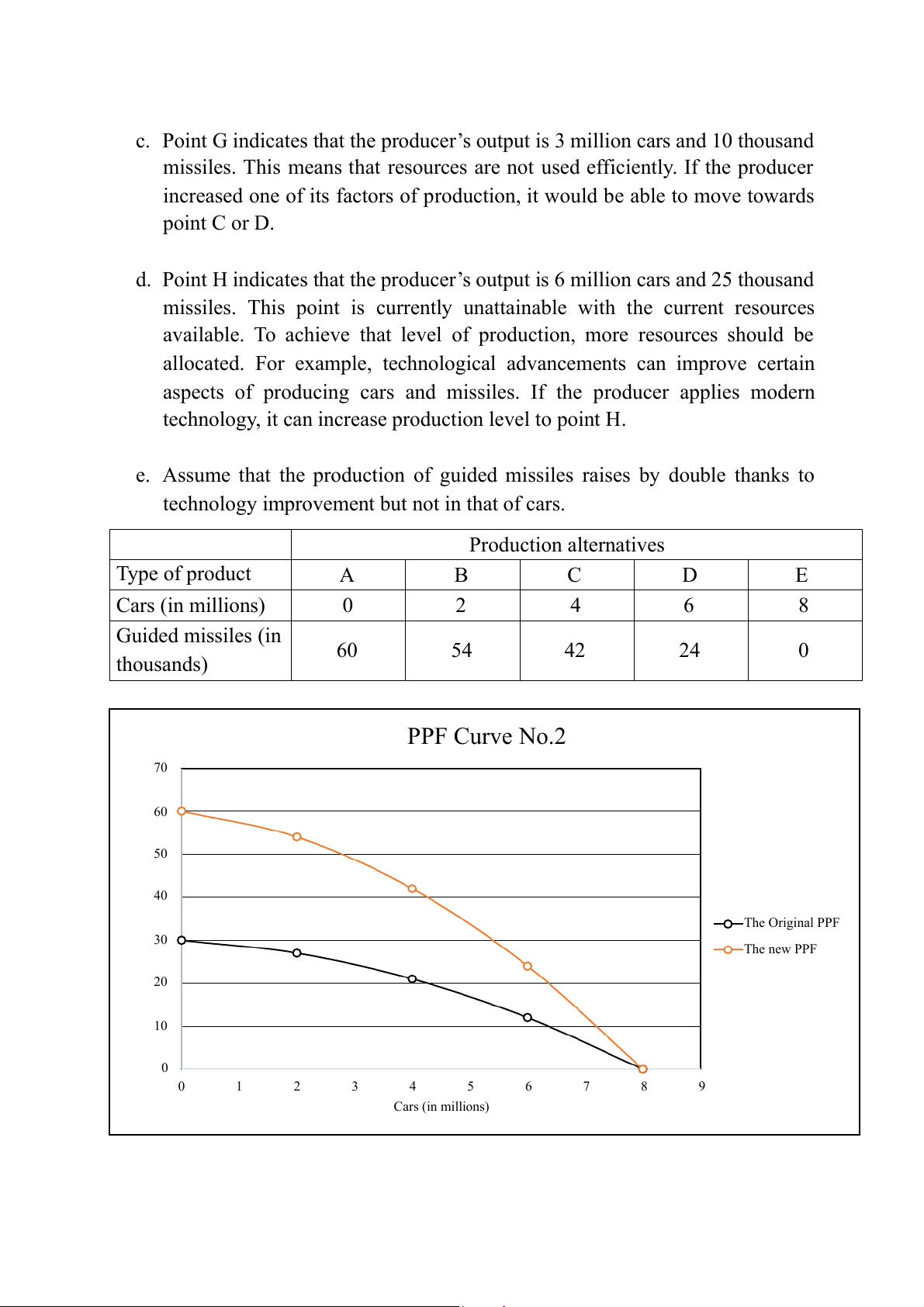
e. Assume that the production of guided missiles raises by double thanks to
technology improvement but not in that of cars. Production alternatives Type of product A B C D E Cars (in millions) 0 2 4 6 8 Guided missiles (in 60 54 42 24 0 thousands) PPF Curve No.2 70 60 ds) 50 40 The Original PPF 30 The new PPF 20 Guided missiles (in thousan 10 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Cars (in millions)
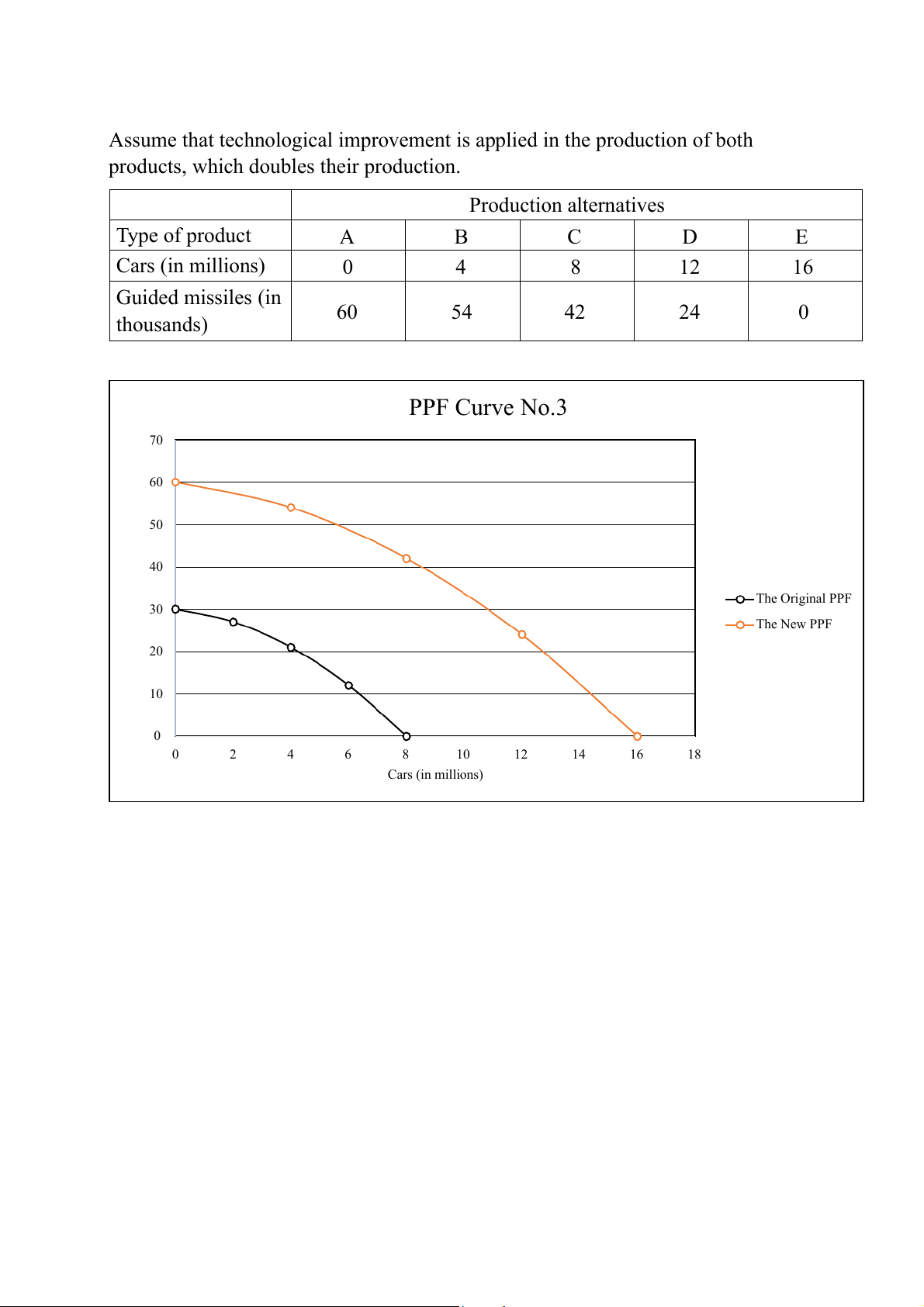
Assume that technological improvement is applied in the production of both
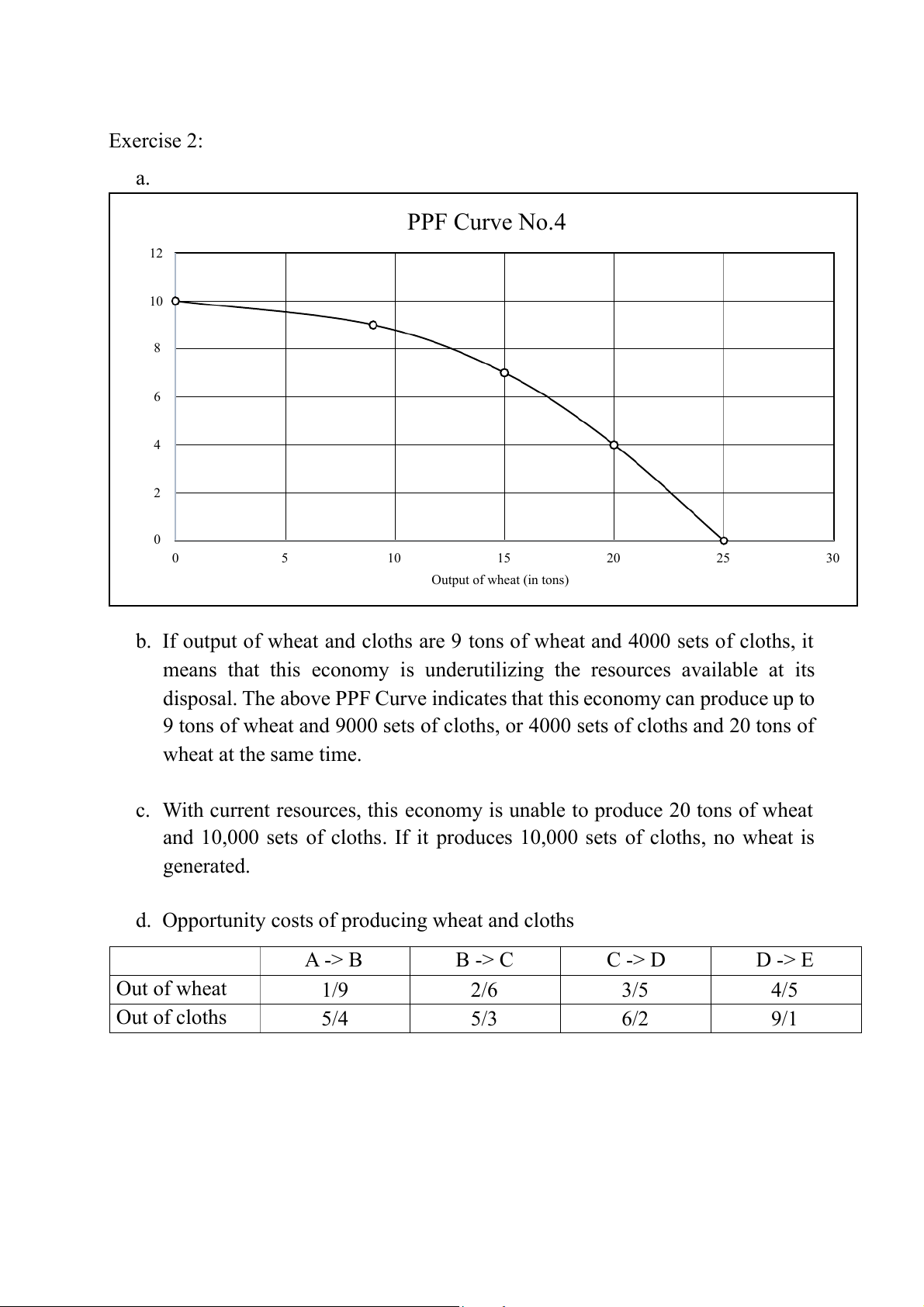
products, which doubles their production. Production alternatives Type of product A B C D E Cars (in millions) 0 4 8 12 16 Guided missiles (in 60 54 42 24 0 thousands) PPF Curve No.3 70 60 ds) 50 40 The Original PPF 30 The New PPF 20 Guided missiles (in thousan 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Cars (in millions) Exercise 2: a. PPF Curve No.4 12 10 8 s (1000 set) 6 4 Output of cloth 2 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Output of wheat (in tons)
b. If output of wheat and cloths are 9 tons of wheat and 4000 sets of cloths, it
means that this economy is underutilizing the resources available at its
disposal. The above PPF Curve indicates that this economy can produce up to
9 tons of wheat and 9000 sets of cloths, or 4000 sets of cloths and 20 tons of wheat at the same time.
c. With current resources, this economy is unable to produce 20 tons of wheat
and 10,000 sets of cloths. If it produces 10,000 sets of cloths, no wheat is generated.
d. Opportunity costs of producing wheat and cloths A -> B B -> C C -> D D -> E Out of wheat 1/9 2/6 3/5 4/5 Out of cloths 5/4 5/3 6/2 9/1




