









Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Genetic 1 Bui Hong Thuy, Ph.D. SchoolofBiotechnology,
InternationalUniversity
Email: bhthuy@hcmiu.edu.vn lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
1.1 Cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells
Cellular Organization of the Genetic Material
➢A genome can consist of a single DNA molecule
(prokaryotic) or a number of DNA molecules (eukaryotic)
➢DNA molecules in a cell are packaged into chromosomes
➢Somatic cells (nonreproductive cells) have two sets of chromosomes lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
➢Gametes (reproductive cells: sperm and eggs)
have half as many chromosomes as somatic
cells Distribution of Chromosomes During
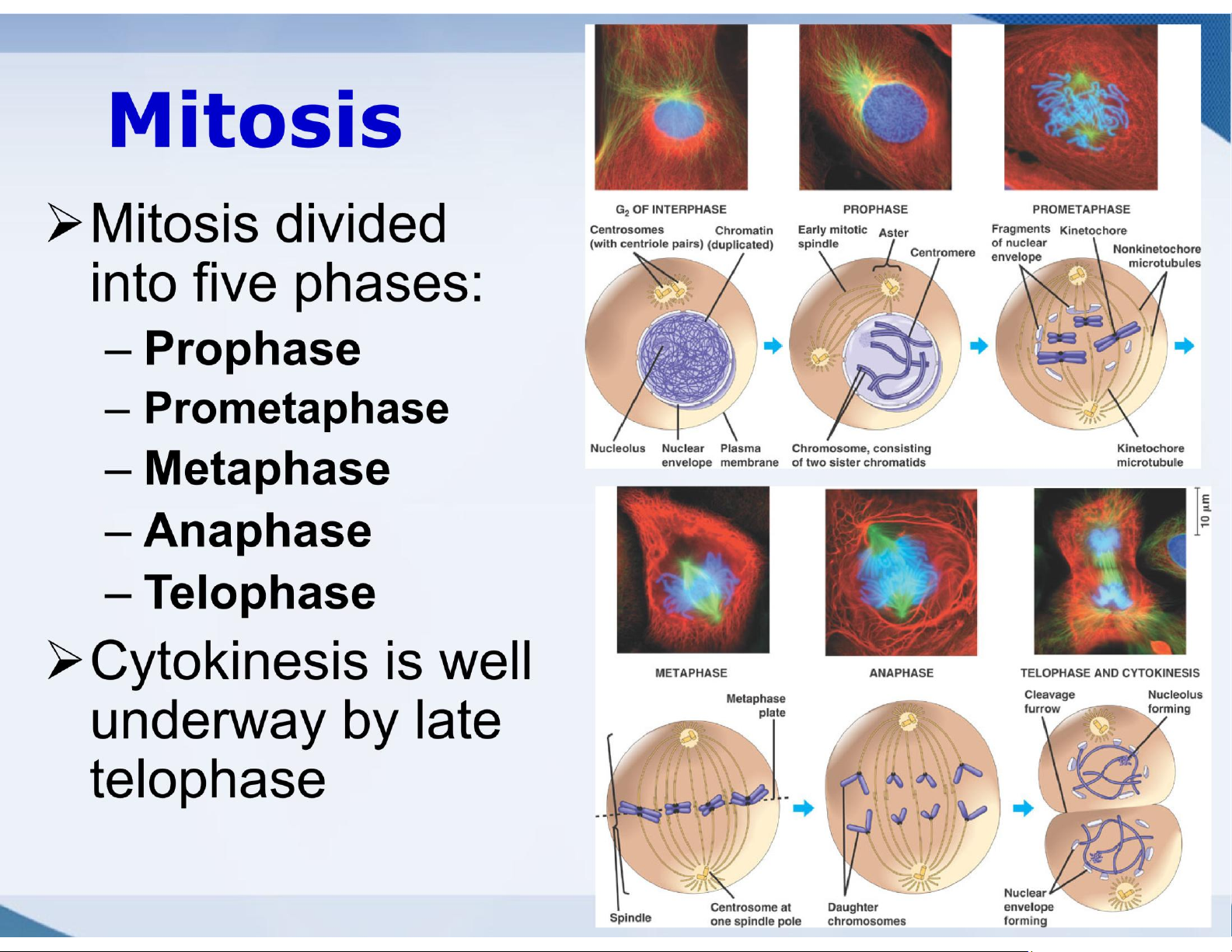
Eukaryotic Cell Division 0.5 m Chromosomes ➢Eukaryotic cell division consists of:
Mitosis, the Chromo-some arm Chromosome division of the
duplication(including DNA nucleus Centromere synthesis)
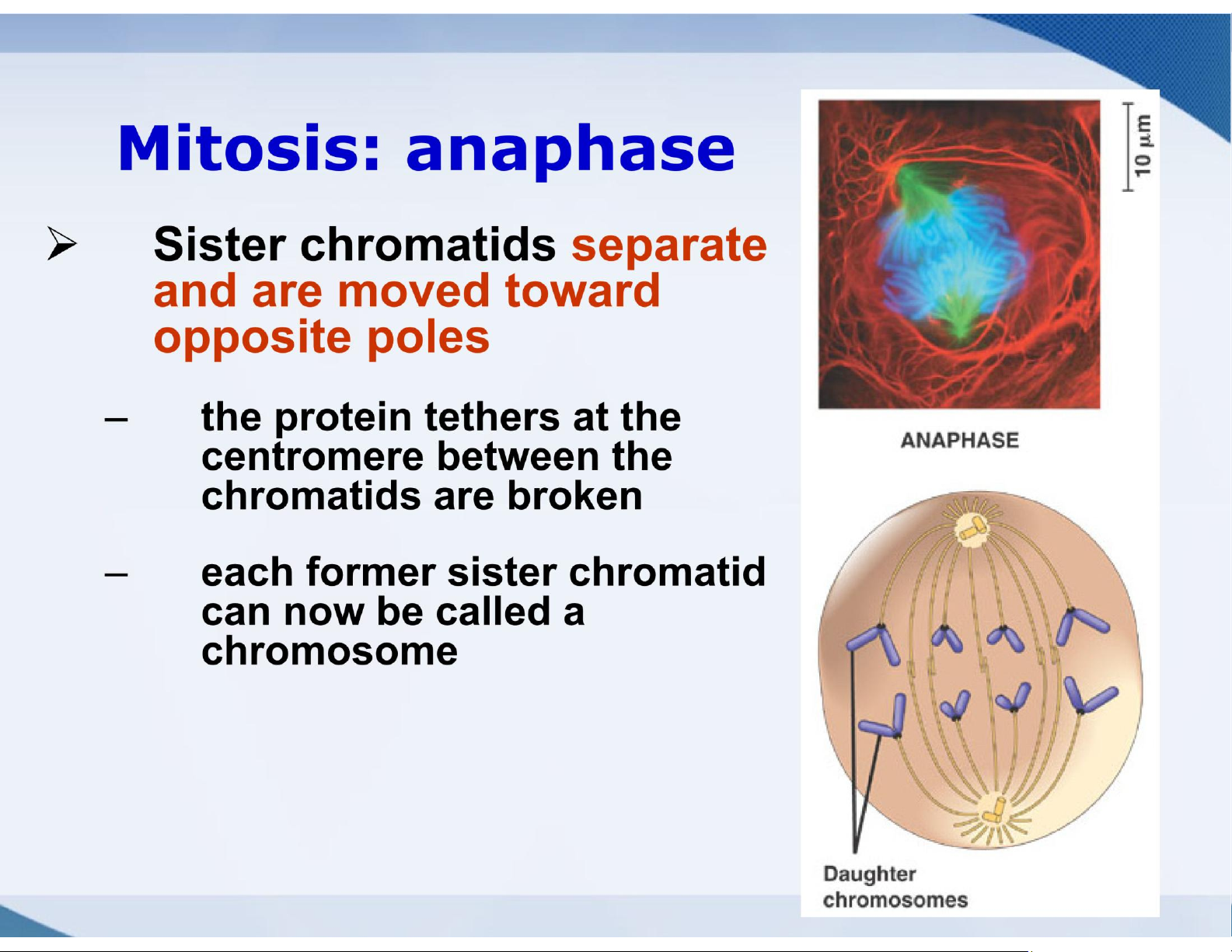
Cytokinesis, Sisterchromatids the division of the cytoplasm Separation of lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
➢Gametes are sister chromatids produced by a Centromere variation of cell Sister chromatids division called
❖ Each duplicated chromosome has two meiosis
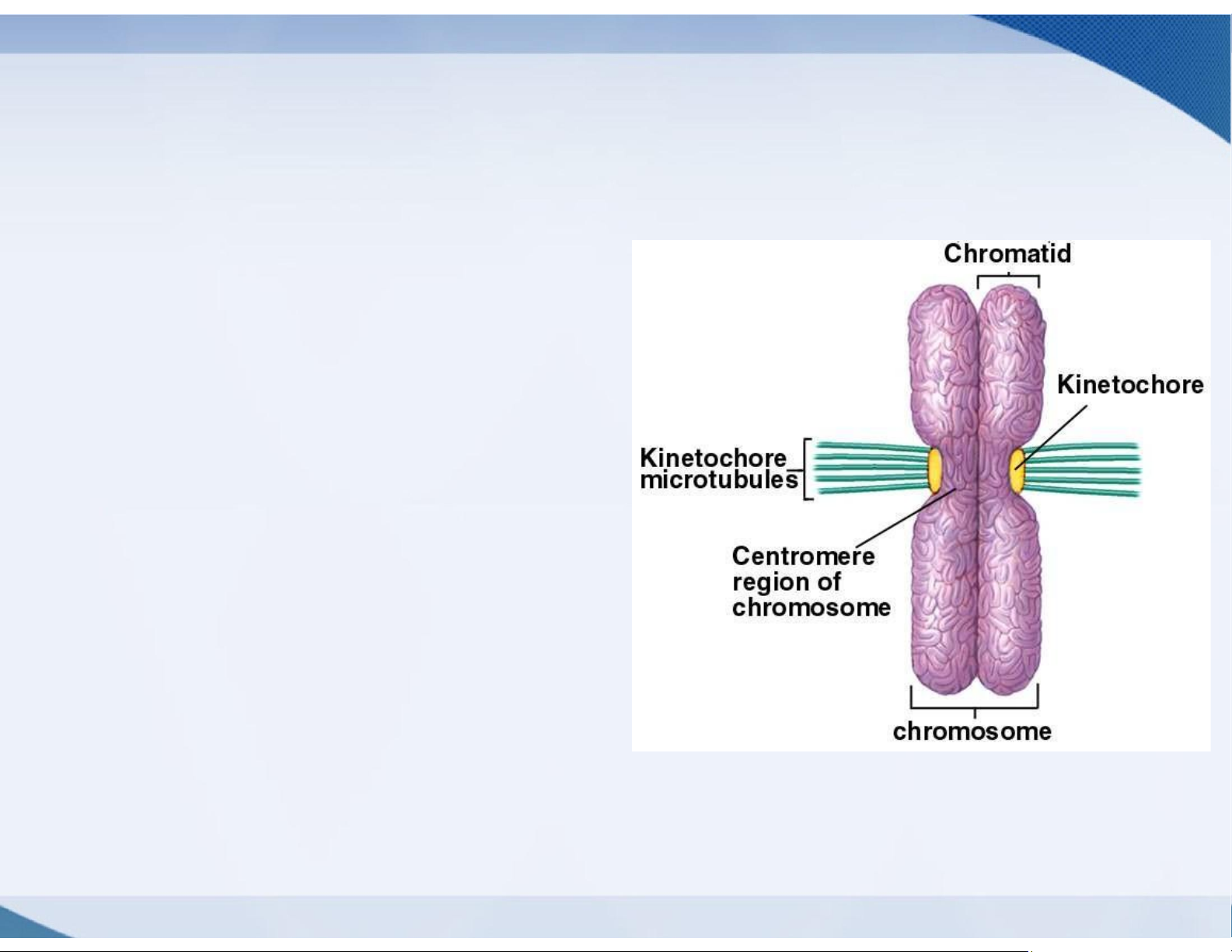
sister chromatids, which separate during cell division lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Mitosis: prophase
Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes ➢ Each chromosome (duplicated during S phase) forms a pair of sister chromatids ➢ Sister chromatids are joined at a centromere by protein tethers ➢ Centromeres contain a kinetochore where microtubules will bind
❖Each sister chromatid has its own kinetochore lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
❖Sister chromatids become attached by their
kinetochores to microtubules from opposite poles lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Mitosis: metaphase
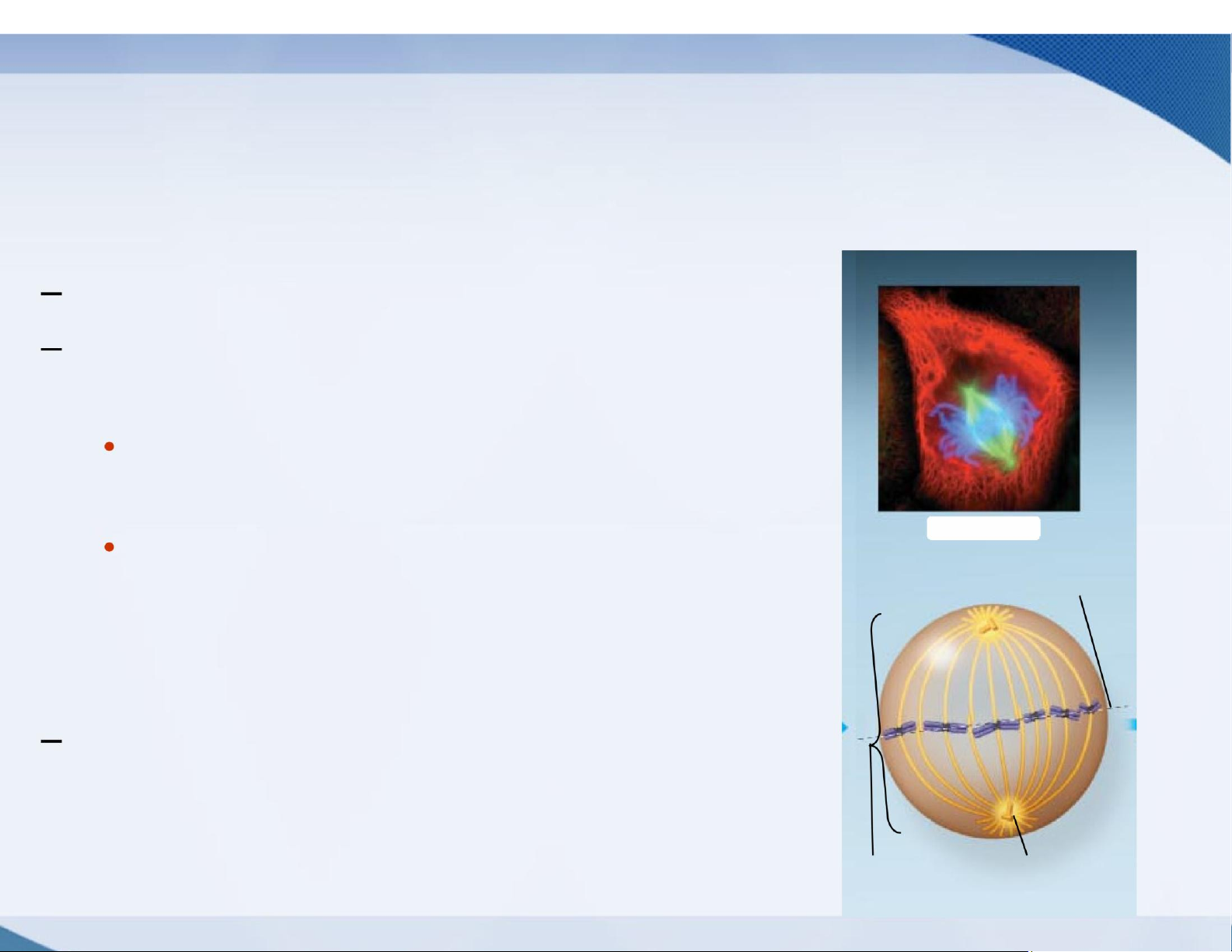
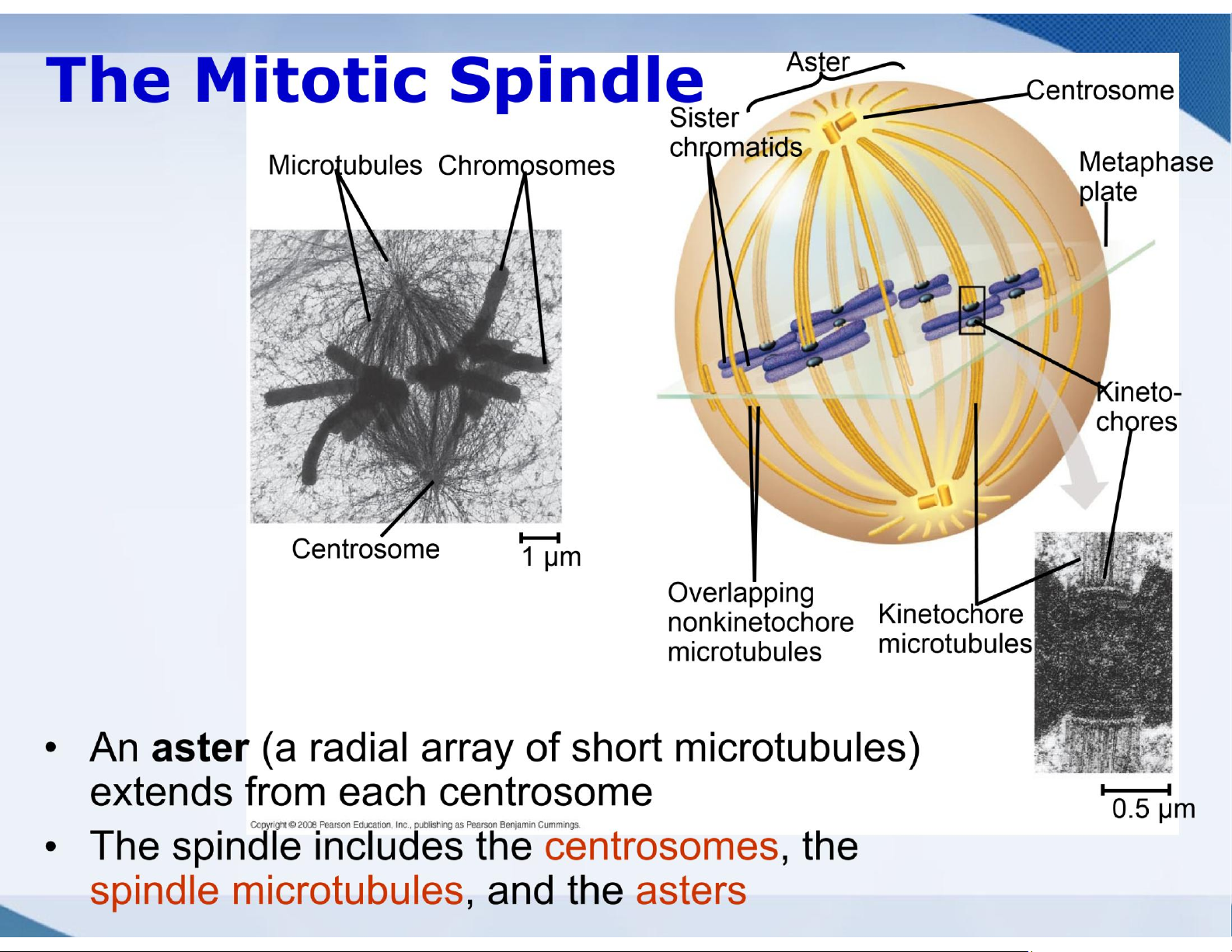
Chromosomes line up along the midplane of
the cell (the metaphase plate)
Chromosomes are highly condensed
The mitotic spindle, now complete, has
two types of microtubules Kinetochore
microtubules extend from a pole to a kinetochore
Polar microtubules extend from a Metaphase pole to
the midplane area, often Metaphaseplate overlapping with
polar microtubules from the other pole The mitosis
checkpoint appears to be here; progress past metaphase
is typically prevented until the
kinetochores are all attached to Spindle Centrosome at one spindle pole microtubules lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
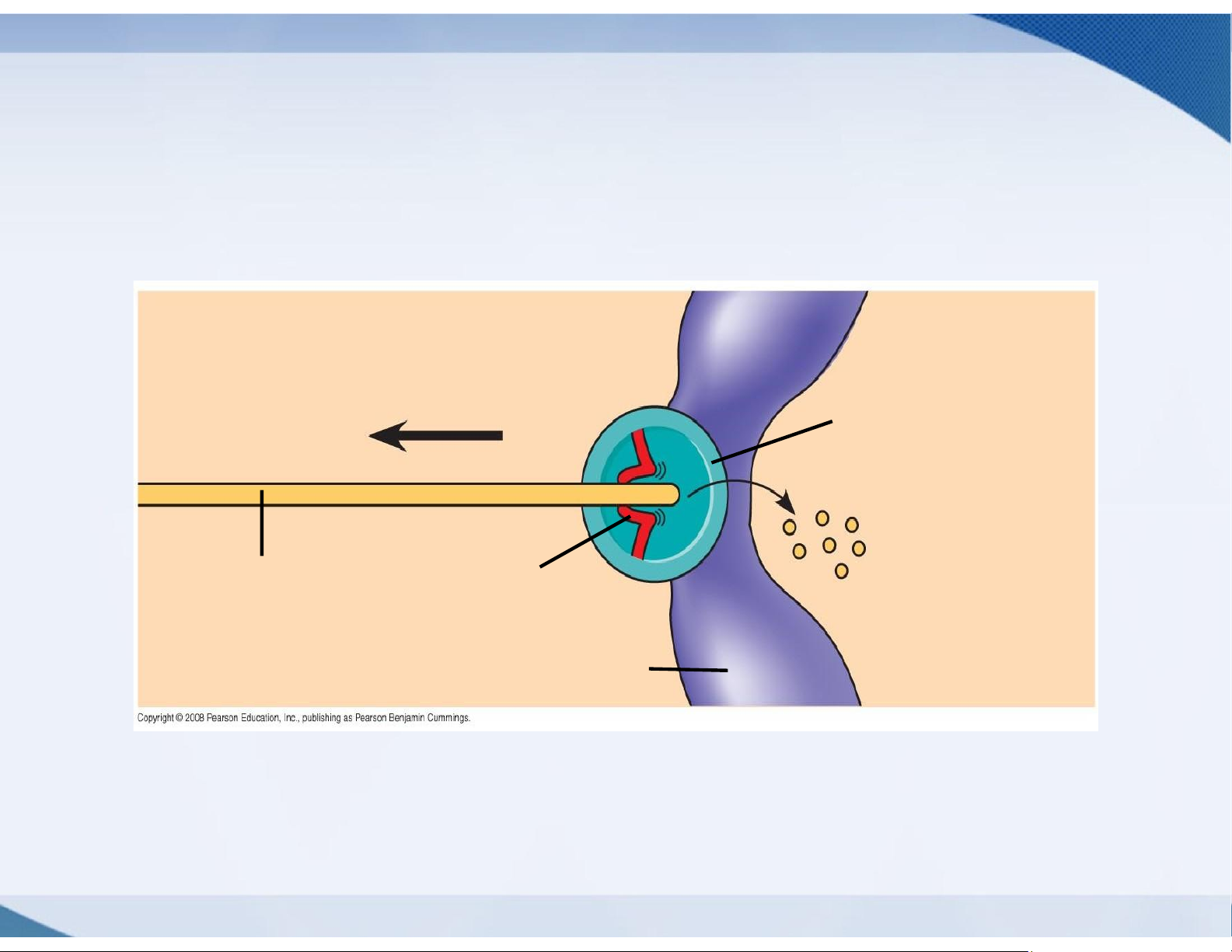
➢Model for the mechanism that moves chromosomes to the poles
❖Motor proteins move the chromosomes towards the
poles along the kinetochores microtubules Chromosome movement Kinetochore Tubulin Motor Microtubule Subunits protein Chromosome
❖This process assures that each daughter cell will
receive one of the duplicate sets of genetic material
carried by the chromosomes lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Cytokinesis ➢
Cytoplasm (and with it most organelles)
is usually distributed randomly but
roughly equally between daughter cells ➢
Sometimes cell division is a highly
regulated polar division that purposefully
distributes some materials unequally lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
➢ In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs by a process
known as cleavage, forming a cleavage furrow
➢ In plant cells, a cell plate forms during cytokinesis Vesicles forming Wall of parent cell 1 m Cleavage furrow 100 m cell plate Cell plate New cell wall Contractile ring of microfilaments Daughter cells Daughter cells (a) Cl
eavage of an animal cell(b) Cell plate formation in a plant cell lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
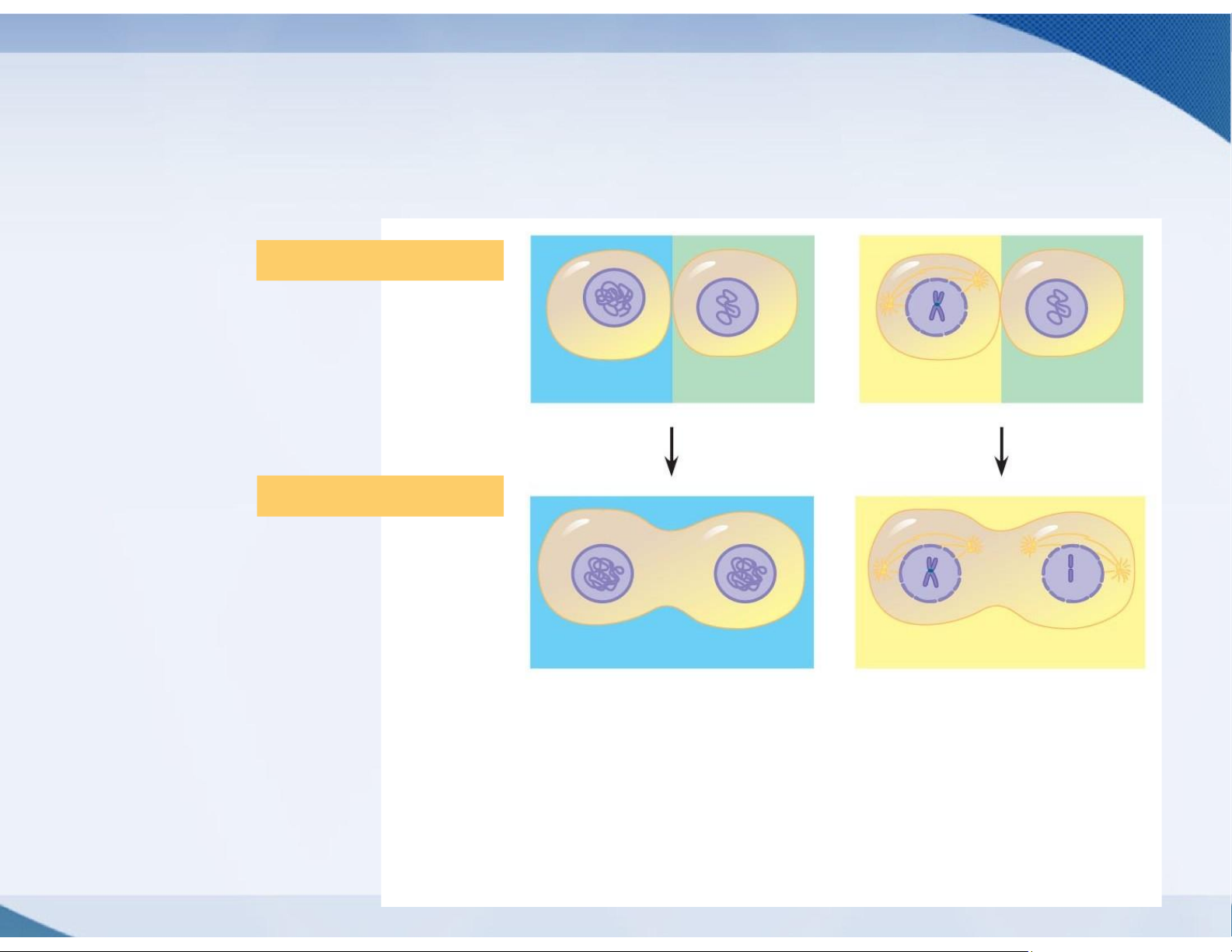
1.3. The eukaryotic cell cycle is regulated by
a molecular control system
Do molecular signals in the cytoplasm regulate the cell cycle? EXPERIMENT S G 1 M G 1 RESULTS S S M M When a cell in the When a cell in the S phase was fused M phase was fused with with a cell in G 1, the G a cell in G , the G 1 1 1 nucleus immediately nucleus immediately entered the S began mitosis a phase DNA was spindle formed and syn thesized. chromatin condensed.




