








Preview text:
NATIONAL ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY
ADVANCE EDUCATION PROGRAM -----***----- MACROECONOMIC
Topic: Economic Growth in Vietnam Student name: Le Tuan Dat Student ID: 11211258 Class:
International Business Administration 63B Supervisor: Dinh Mai Huong, M.A Hanoi, June 9th, 2024 TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION..................................................................................3
CHAPTER II: THEORY...............................................................................................4
2.1 Definition of Economic Growth..........................................................................4
2.2 Phases of Economic Growth...............................................................................4
2.3 Economic Growth Rate Calculation....................................................................5
2.3.1 Measuring Economic Growth Rate..............................................................5
2.3.2 Economic Growth Rate Formula..................................................................5
2.4 Factors That Contribute to Economic Growth.....................................................6
2.4.1 Investment....................................................................................................6
2.4.2 Technology...................................................................................................6
2.4.3 Labor Force..................................................................................................6
2.4.4 Economic Policy..........................................................................................6
CHAPTER III: VIETNAM GDP GROWTH RATE FROM 2021 TO 2022................7
3.1 Vietnam GDP Growth Rate in 2021....................................................................8
3.1.1 Economic growth rate..................................................................................8
3.1.2 Factors that impact economic growth...........................................................8
3.2 Vietnam GDP Growth Rate in 2022....................................................................9
3.2.1 Economic growth rate..................................................................................9
3.2.2 Factors that impact economic growth.........................................................10
CHAPTER IV: CONCLUSION..................................................................................10
REFERENCES...........................................................................................................11 2 CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION
Economic growth is a fundamental aspect of macroeconomic analysis, serving as
a key indicator of a nation's economic health and prosperity. It reflects the overall
productivity and efficiency of an economy, influencing various facets of societal well-
being, including employment, income levels, and the standard of living.
Understanding economic growth is crucial because it provides insights into the
effectiveness of economic policies, the health of industries, and the overall economic environment.
The economic growth rate is determined by multiple factors, including physical
capital, human capital, technological advancements, and the size and quality of the
labor force. These elements collectively enhance productivity and drive economic
expansion. Analyzing these factors helps in identifying the strengths and weaknesses
of an economy, enabling targeted strategies to foster sustainable growth.
In the context of Vietnam, the examination of GDP growth from 2021 to 2022 is
particularly meaningful. This period encapsulates the nation's response to the
economic disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and its subsequent recovery
efforts. By studying Vietnam's GDP growth during these years, we gain valuable
insights into the resilience and adaptability of its economy, the impact of various
economic policies, and the broader implications for future economic planning and development.
Thus, the focus on economic growth rate is not merely an academic exercise but
a practical necessity. It aids in understanding the broader economic landscape, guiding
investment decisions, policy formulations, and long-term economic strategies that aim
to improve the quality of life for all citizens. 3 CHAPTER II: THEORY
2.1 Definition of Economic Growth
In simplest terms, economic growth refers to an increase in aggregate production
in an economy, which generally manifests as a rise in national income (Oxford
Reference, n.d.). In many cases, though not always, overall gains in production are
associated with an increase in average marginal productivity. This results in higher
incomes, encouraging consumers to spend more, and boosting the material quality of life and standard of living.
In economics, growth is typically represented as a function of physical capital,
human capital, labor force, and technology. Enhancing the size or quality of the
working-age population, the tools they use, and the methods they have for combining
labor, capital, and raw materials will result in increased economic output. (Lesson
summary: Economic growth, n.d.)
2.2 Phases of Economic Growth
The economy goes through various periods of activity known as the "business
cycle," which includes four phases (Cox, 2022):
Expansion – Employment, income, industrial production, and sales all increase, leading to a rise in real GDP.
Peak – Marks the point where economic expansion reaches its highest level and then turns.
Contraction – The components of expansion begin to decrease, leading to a
recession when there is a widespread decline in economic activity.
Trough – The lowest point of economic contraction.
A business cycle is measured from peak to peak or trough to trough. These cycles are
irregular in duration and can feature periods of contraction within an expansion and vice versa. 4
2.3 Economic Growth Rate Calculation
2.3.1 Measuring Economic Growth Rate
An economic growth rate is the percentage change in the value of all of the
goods and services produced in a nation during a specific period of time, as compared
to an earlier period. The economic growth rate is used to measure the comparative
health of an economy over time. The numbers are usually compiled and reported
quarterly and annually. (CHEN, 2023)
There are three widely recognized methods for measuring economic growth. (CHEN, 2023)
First, the most common method is gross domestic product (GDP), which
calculates the total value of all goods and services produced within a country's
borders during a specified period, such as a year or a quarter.
Second, gross national product (GNP) assesses the overall economic output
generated by a nation's residents, both domestically and internationally. This
metric includes income from foreign investments and activities by a country's
citizens and businesses, offering a broader view of economic performance by
considering international economic interactions.
Third, net domestic product (NDP) is derived by adjusting GDP for
depreciation, accounting for the decline in value of a country's capital assets
due to wear and tear. This measure provides a more accurate representation of
sustainable economic growth by considering the necessity of replacing or
repairing infrastructure and machinery.
2.3.2 Economic Growth Rate Formula
This formula shows how an economic growth rate is calculated based on GDP: GDP 2−GDP 1 Economic Growth = GDP 1
Where GDP = Gross Domestic Product of nation
In the formula mentioned, the numerator represents the difference in GDP
between two periods, typically measured monthly, quarterly, or annually. This 5
difference is then divided by the most recent GDP figure. It's important to note that
economic growth can be negative if a country's GDP declines from one period to the next.
2.4 Factors That Contribute to Economic Growth 2.4.1 Investment
Investment is fundamental to economic growth, encompassing both physical
capital investments like machinery, factories, and infrastructure, as well as human
capital investments through education and training. Physical capital investments boost
productivity, while human capital investments provide the workforce with essential skills. (CHEN, 2023) 2.4.2 Technology
Technological advancements significantly drive economic growth. Innovation
and technological progress improve production processes, lead to the creation of new
products and services, and boost overall productivity. Innovations such as the internet,
automation, and healthcare breakthroughs have profoundly impacted economic
growth by increasing efficiency and generating new industries and job opportunities. (CHEN, 2023)
2.4.3 Labor Force
As mentioned in the 'Investment' section, a skilled and expanding labor force is
crucial for economic growth. A larger workforce boosts production capacity, while a
skilled workforce enhances productivity and fosters innovation. Investing in education
and vocational training is vital for developing a capable labor force that can adapt to
changing industries and technologies, as highlighted in the 'Innovation' section. (CHEN, 2023)
2.4.4 Economic Policy
Effective economic policies are essential for ensuring economic stability and
promoting growth. This encompasses fiscal policies that responsibly manage
government finances, monetary policies that keep inflation low and stable, and
regulatory measures that minimize obstacles to business operations. A stable and 6
predictable policy environment builds confidence among investors and businesses,
fostering long-term investments and economic growth. (CHEN, 2023)
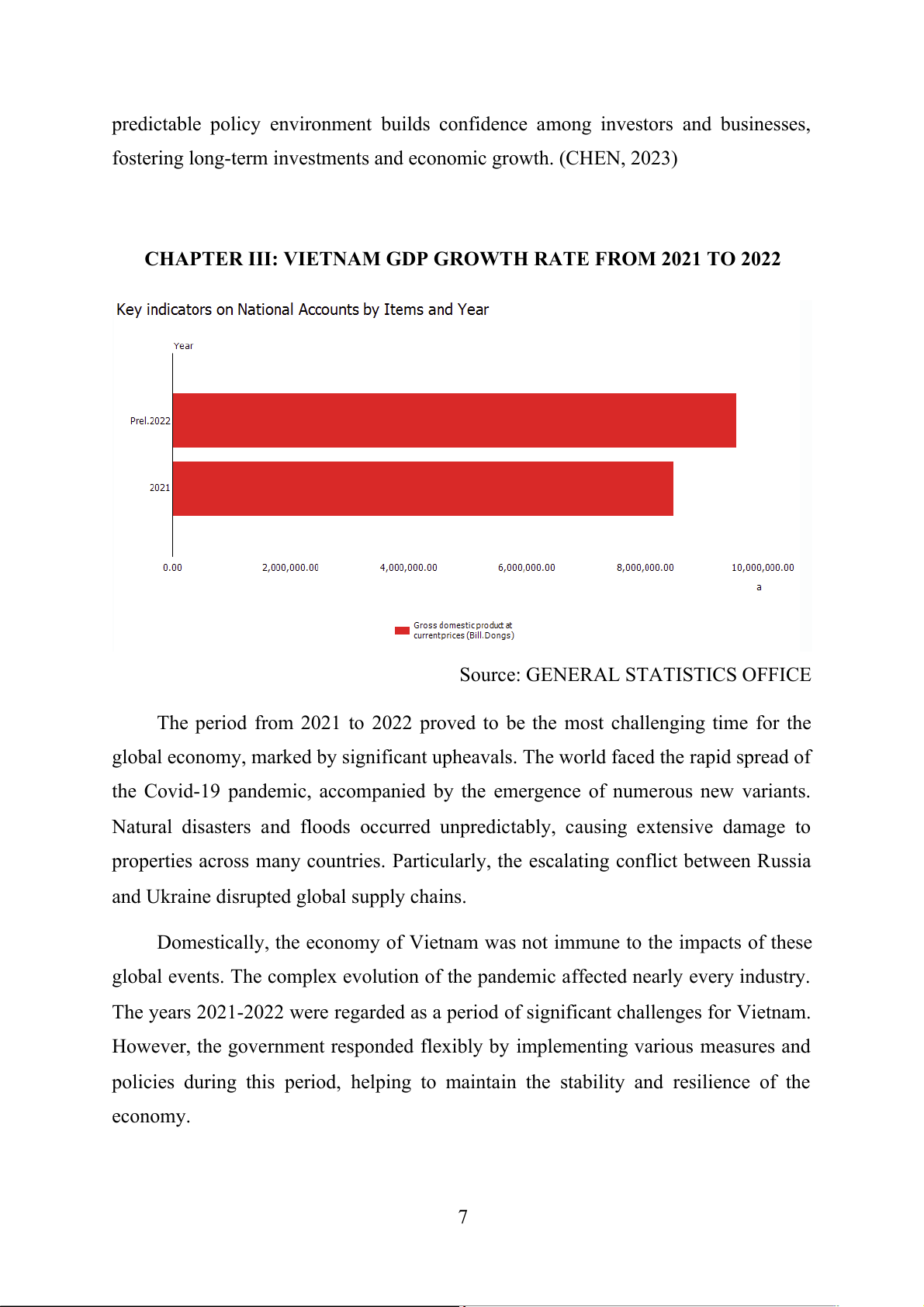
CHAPTER III: VIETNAM GDP GROWTH RATE FROM 2021 TO 2022
Source: GENERAL STATISTICS OFFICE
The period from 2021 to 2022 proved to be the most challenging time for the
global economy, marked by significant upheavals. The world faced the rapid spread of
the Covid-19 pandemic, accompanied by the emergence of numerous new variants.
Natural disasters and floods occurred unpredictably, causing extensive damage to
properties across many countries. Particularly, the escalating conflict between Russia
and Ukraine disrupted global supply chains.
Domestically, the economy of Vietnam was not immune to the impacts of these
global events. The complex evolution of the pandemic affected nearly every industry.
The years 2021-2022 were regarded as a period of significant challenges for Vietnam.
However, the government responded flexibly by implementing various measures and
policies during this period, helping to maintain the stability and resilience of the economy. 7
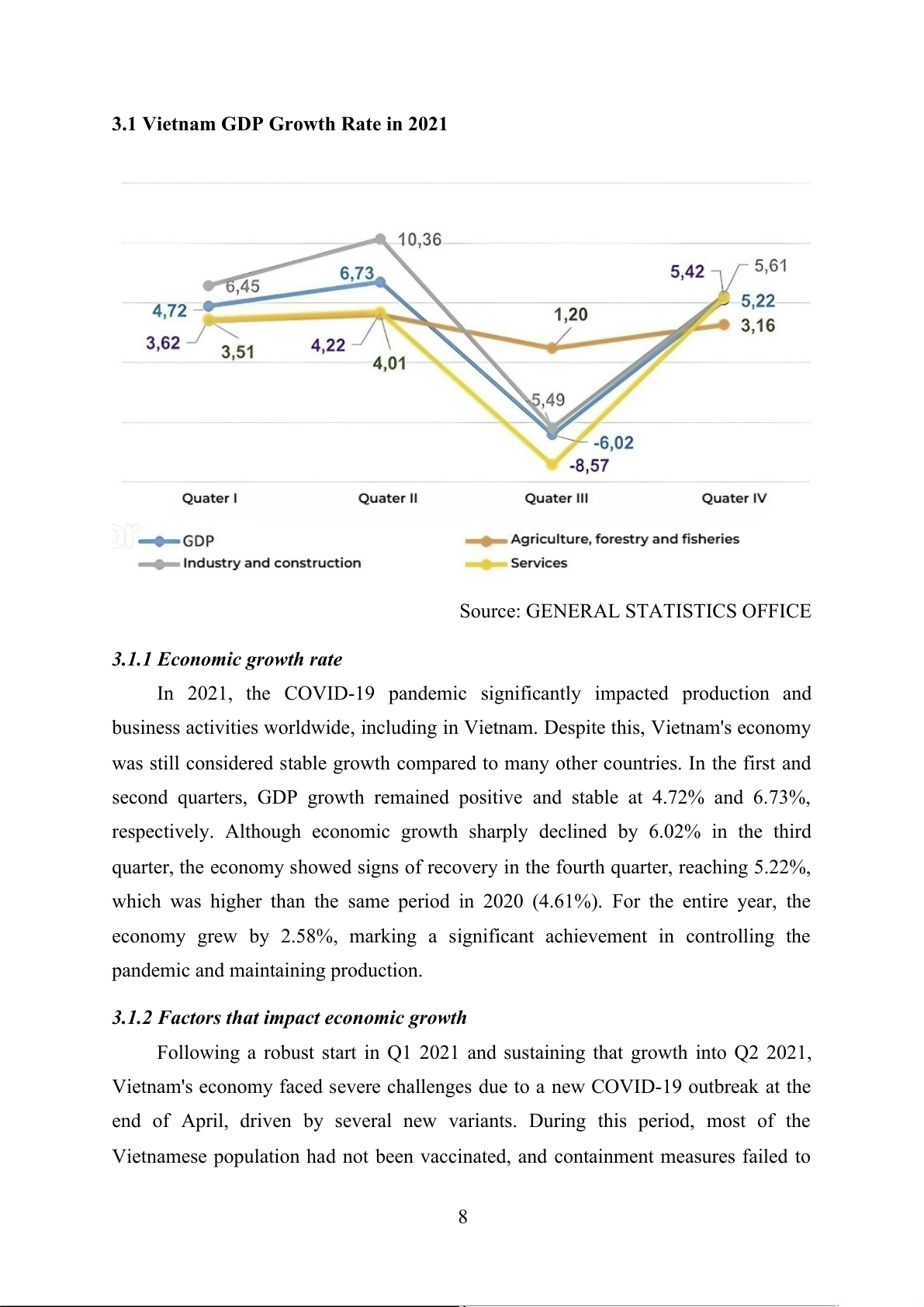
3.1 Vietnam GDP Growth Rate in 2021
Source: GENERAL STATISTICS OFFICE
3.1.1 Economic growth rate
In 2021, the COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted production and
business activities worldwide, including in Vietnam. Despite this, Vietnam's economy
was still considered stable growth compared to many other countries. In the first and
second quarters, GDP growth remained positive and stable at 4.72% and 6.73%,
respectively. Although economic growth sharply declined by 6.02% in the third
quarter, the economy showed signs of recovery in the fourth quarter, reaching 5.22%,
which was higher than the same period in 2020 (4.61%). For the entire year, the
economy grew by 2.58%, marking a significant achievement in controlling the
pandemic and maintaining production.
3.1.2 Factors that impact economic growth
Following a robust start in Q1 2021 and sustaining that growth into Q2 2021,
Vietnam's economy faced severe challenges due to a new COVID-19 outbreak at the
end of April, driven by several new variants. During this period, most of the
Vietnamese population had not been vaccinated, and containment measures failed to 8
curb the virus's spread. This led to severe outbreaks in key industrial areas with high
population densities, such as Ho Chi Minh City and Bac Ninh, significantly disrupting
production and business activities. Consequently, GDP growth dropped sharply from
6.73% in Q2 to a negative 6.02% in Q3. This was the most critical period for
Vietnam's economy in 2021. By the end of Q3 2021, as the pandemic was gradually
brought under control, nationwide vaccination efforts ramped up, lockdowns were
lifted, and businesses started to resume operations. As a result, the economy began to
recover in Q4 2021, achieving a GDP growth rate of 5.22% compared to the negative growth of 6% in Q3.
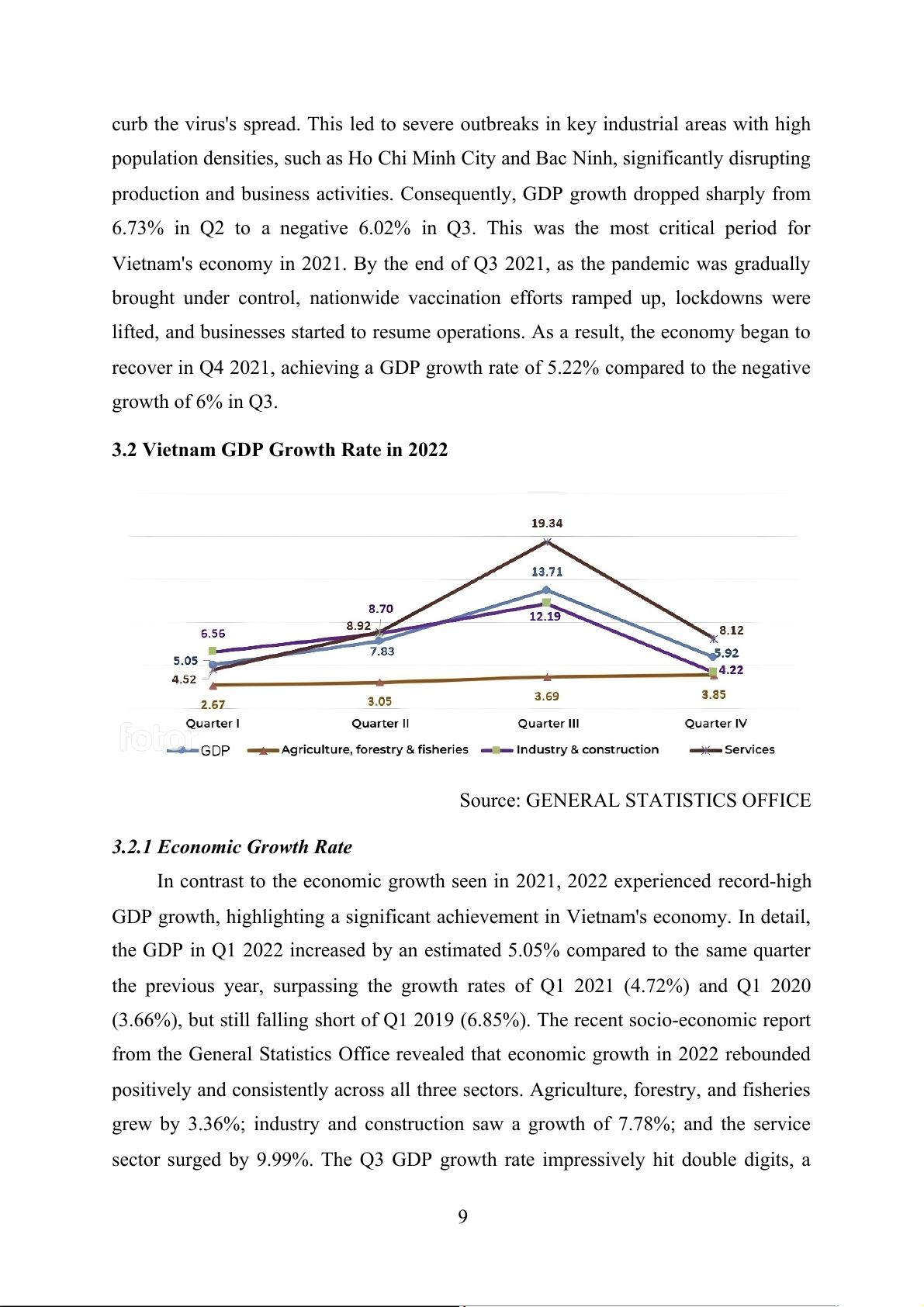
3.2 Vietnam GDP Growth Rate in 2022
Source: GENERAL STATISTICS OFFICE
3.2.1 Economic Growth Rate
In contrast to the economic growth seen in 2021, 2022 experienced record-high
GDP growth, highlighting a significant achievement in Vietnam's economy. In detail,
the GDP in Q1 2022 increased by an estimated 5.05% compared to the same quarter
the previous year, surpassing the growth rates of Q1 2021 (4.72%) and Q1 2020
(3.66%), but still falling short of Q1 2019 (6.85%). The recent socio-economic report
from the General Statistics Office revealed that economic growth in 2022 rebounded
positively and consistently across all three sectors. Agriculture, forestry, and fisheries
grew by 3.36%; industry and construction saw a growth of 7.78%; and the service
sector surged by 9.99%. The Q3 GDP growth rate impressively hit double digits, a 9
commendable improvement over the same period in 2021. In Q4 2022 alone, GDP
grew by an estimated 5.92% year-on-year, a rate higher than the Q4 growth rates of
4.7% in 2020 and 5.17% in 2021, though it remained below the Q4 growth rates from
2011 to 2019. Specifically, agriculture, forestry, and fisheries grew by 3.85%; industry
and construction by 4.22%; and services by 8.12%.
3.2.2 Factors that impact economic growth
This fluctuation is attributed to the strong recovery of Vietnam's economy
following the COVID-19 pandemic. Even though 2022 was a recovery year,
Vietnam's GDP surged, reaching its highest point in 12 years (2011-2022). However,
examining Q4 2022 reveals that despite signs of recovery, the economy had not yet
fully returned to its pre-pandemic state, as the fourth quarter usually represents a
period of economic acceleration. Despite this, the annual GDP growth rate still rose
by 8.02% compared to previous years. This impressive growth was achieved amid
numerous global economic challenges, including competition, the Russia-Ukraine
conflict, and heightened financial risks. Overall, this growth rate is quite remarkable. CHAPTER IV: CONCLUSION
The period from 2021 to 2022 posed significant challenges to both the global
economy and Vietnam's economic landscape. With the rapid spread of the COVID-19
pandemic and the emergence of new variants, coupled with unpredictable natural
disasters and disruptions in global supply chains due to geopolitical tensions,
navigating through this time required resilience and adaptability. Despite these
adversities, Vietnam's economy showcased remarkable stability and growth, thanks to
proactive government interventions and policies.
In 2021, Vietnam experienced a fluctuating GDP growth rate, reflecting the
impact of the pandemic-induced disruptions on production and business activities.
Despite facing severe challenges, including outbreaks and lockdowns, the economy
demonstrated resilience, rebounding from negative growth in the third quarter to
positive growth by the end of the year. This exemplified Vietnam's ability to 10
effectively manage the pandemic's economic fallout while maintaining production levels.
The year 2022 marked a significant turnaround for Vietnam's economy, with
record-high GDP growth rates indicating a robust recovery. Despite lingering global
economic challenges, Vietnam's economy rebounded positively across all sectors,
showcasing its resilience and capacity for growth. While challenges persisted, such as
the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict and heightened financial risks, Vietnam's
economy remained on a trajectory of growth and development.
In conclusion, the period of 2021 to 2022 underscored the importance of
adaptive economic policies and proactive measures in navigating through
unprecedented challenges. Vietnam's ability to maintain stability and achieve
significant economic growth amidst global turmoil highlights its resilience and
potential for continued prosperity. Moving forward, sustained efforts in policy
formulation, investment, and innovation will be crucial in ensuring Vietnam's long-
term economic resilience and prosperity in the face of future uncertainties. REFERENCES (n.d.). Retrieved from Oxford Reference:
https://www.oxfordreference.com/display/10.1093/oi/authority.2011080309574 1367 (n.d.). Retrieved from GENERAL STATISTICS OFFICE:
https://www.gso.gov.vn/tai-khoan-quoc-gia/
CHEN, J. (2023, 09 25). Economic Growth Rate: Definition, Formula, and Example. Retrieved from Investopedia:
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/economicgrowthrate.asp#GeneratedCap tionsTabForHeroSec 11
Cox, J. (2022, 03 16). Federal Reserve approves first interest rate hike in more than
three years, sees six more ahead. Retrieved from cnbc:
https://www.cnbc.com/2022/03/16/federal-reserve-meeting.html
Lesson summary: Economic growth. (n.d.). Retrieved from Khan Academy:
https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance-domain/ap-
macroeconomics/ap-long-run-consequences-of-stabilization-policies/economic-
growth/a/lesson-summary-economic-growth 12




