














Preview text:
NATIONAL ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY NEU BUSINESS SCHOOL -----oOo----- MICROECONOMICS
TOPIC: THE BEER MARKET IN VIETNAM
Lecturer: Tran Thi Hong Viet
Subject: Microeconomics Class: EBDB 4 Group 2: Members
Nguyễn Thúy Hiền – 11222231
Trần Châu Giang – 11221833 Hoàng Ngọc Mai – 11224021 Vũ Hồng Nhi – 11224989
Trần Thị Lan Anh – 11220635 Vũ Thanh Tùng – 11226781 June, 2023 Table Of Contents A.
INTRODUCTION......................................................................................3 B.
BODY..........................................................................................................3 I.
Theory - some relevant microeconomic knowledge................................3
1. Definition of the term “Market”, “Demand” and “Supply”......................3
2. Determinants of Supply............................................................................4
a. The price factor of Supply.....................................................................4
b. Non-price factors of Supply..................................................................4
3. Determinants of Demand..........................................................................5
a. The price factor of Demand...................................................................5
b. Non-price factors of Demand................................................................5
4. The market structure: Oligopoly...............................................................6
II. The practical case: Beer market in Vietnam...........................................7
1. Number of brand and market share...........................................................7
2. Product nature...........................................................................................8
3. The structure of the beer market in Vietnam is Oligopoly.......................9
a. Beer market situation in Vietnam..........................................................9
b. Barriers to entry...................................................................................10
c. Non-price competition.........................................................................11
d. Interdependence...................................................................................12
4. The determinants of the supply of the beer in Vietnam..........................13
a. The recent status and quantities.............................................................13
b. The price factor of coffee’s supply in Vietnam.....................................13
c. Some non-price factors of coffee’s supply in Vietnam.........................15
5. The determinants of the demand of the beer in Vietnam........................16
a. The recent status and quantities...........................................................16
b. The price factor of beer’s supply in Vietnam......................................18
c. Some non-price factors of beer’s supply on Vietnam.........................18 C.
CONCLUSION........................................................................................22 D.
LIST OF REFERENCES........................................................................22 2 A. INTRODUCTION
As we know beer is the oldest drink in the world, the history of beer dates
back to 6000 years BC. Since then, the beer market has grown and gradually
become a drink familiar in each of our lives. And it entered the market in
Vietnam at the end of the 19th century as the Hanoi brewery and Saigon beer.
The beer market in Vietnam is currently being likened to a “magnet” that
attracts most beer manufactures big in the world. Every year, the beer industry
contributes hundreds of billions of dollars to the state budget, providing jobs and
creating jobs for hundreds of thousands of direct and millions of indirect
workers in the supply chain from packaging, transportation, storage, wholesale
and retail as well as suppliers of input materials for production, meeting the
needs of the market, serving for export, and competitive products. in the context
of economic integration. Our team write an article about the beer market in Vietnam
This report will analysis about market structures of the beer industry
in Vietnam , based on knowledge of Microeconomics. Additionally, our group
will also identify a number of determinants affecting the supply- demand of the beer industry.
Although thoroughly researched, the report cannot avoid shortcoming.
Our team is looking forward to receiving teacher’s comments and suggestions. Thank you so much! B. BODY I.
Theory - some relevant microeconomic knowledge
1. Definition of the term “Market”, “Demand” and “Supply” - A “ ”
Market can be understood as a place or a system where buyers and
sellers interact to exchange goods or services for a certain price,
depending on the demand and supply conditions. A market can be
physical or virtual, local or global, legal or illegal, competitive or monopolistic.
- “Demand” refers to the various amounts of a product that consumers are
willing and able to buy at various prices, in a given period of time.
- “Supply” is the various amounts of a product that producers are willing
and able to supply at various prices during some specific period. 3
2. Determinants of Supply
a. The price factor of Supply
The amount of a product that is offered depends on how much people are
ready to pay for it, which is called price. This is the most important thing that
affects the availability of a product. The rule of supply says that when an item
becomes more expensive, more of it is supplied, and when it becomes cheaper,
less of it is supplied. This change in price is called the price fluctuation.
b. Non-price factors of Supply - Input price:
This is a very important factor that influences supply. Inputs are the things
that are needed to make a product, such as materials, workers, machines, and
technology. If the inputs are available in large amounts and at low prices, more
products can be made. This would increase the supply of a product in the
market. If the price of flour goes down, the company will have to pay less to
make the same amount of bread. This will decrease its production cost and
increase its profit margin. As a result, the company will be more willing to
supply bread at the same price as before. This will cause an increase in the supply of bread in the market.
- Technology improvement:
Better and more advanced technology helps a company make more
products, which increases the supply of the product. For example, using better
machines and devices can help more productivity.
- Transportation condition:
This means that having a good transportation system helps increase the
supply of a product. Transportation is a problem that can delay the delivery of
the product, because sometimes there are not enough transportation systems to deliver the product on time.
- Government tax policy:
Changes in taxes have the opposite effect on the supply of a company.
When the government increases taxes, the product becomes less profitable. This
reduces the supply of the product by the company. - Production cost:
The cost of making a product and the supply of the product are basically
opposite. If the cost of making a product increases, companies will reduce their
supply of the product to save money. - Natural conditions:
This means that weather has a direct effect on the supply of some
products. Some products depend on the weather to grow. These are called 4
natural products. If there is a good rainfall, the farmer will have more water to
irrigate the orange trees. This will increase the growth and quality of the
oranges. As a result, the farmer will have more oranges to sell in the market. - Calamities:
Natural calamities, such as war or pandemic, also affect the supply of
products. Sometimes there are not enough products because of war or pandemic.
These products are in short supply even if they are very expensive. - Expectation:
What the company wants and aims for. In theory, a company only
increases its supply of a product when the price is high because this meets its
goal of making more money. But sometimes, some companies want to supply
more even if they make less money. The reason for this is that they want to have
more customers and also improve their image and reputation.
3. Determinants of Demand
a. The price factor of Demand
The change in price causes a movement along the demand curve. It
changes the amount of demand. The price of goods and the amount of demand have an opposite relationship.
b. Non-price factors of Demand - Consumer income:
Income affects how much consumers can buy. For most of the normal
goods, income and demand go together. When income goes up, the demand for
normal goods goes up too, and when income goes down, the demand for normal
goods goes down too. But for the inferior goods, it is the opposite. Demand goes
down when income goes up and vice versa. - Price of related goods:
Related goods are either complementary goods or substitute goods.
Complementary goods are goods that are used together. If the price of these
goods goes up, the demand for those goods goes down. Substitute goods are
goods that can replace each other. If the price of these goods goes up, the
demand for those goods goes up too. - Taste and preferences:
These factors have a big effect on demand because they show what consumers like. - Market size:
The demand will go up if there are more customers. 5 - Expectation:
This is the prediction about changes in factors like price, income, or
preferences. They will change the demand now.
4. The market structure: Oligopoly
An oligopoly is a market structure with a small number of firms, none of
which can keep the others from having significant influence. The concentration
ratio measures the market share of the largest firms (The Investopedia Team, 2023).
Some characteristics of oligopoly are:
- Few firms: Under oligopoly, there are a few large firms that dominate the
market and have significant market share. The exact number of firms is
undefined, but it must be low enough that the actions of one firm
significantly influence the others.
- Barriers to entry: There are high barriers to entry in an oligopoly market,
such as economies of scale, brand loyalty, government regulations, and
distribution networks. These barriers prevent new entrants from entering
the market and competing with the existing firms.
- Non-price competiton: Firms in an oligopoly compete on other factors
than price, such as advertising, innovation, quality, and customer service.
This is because price competition can lead to a price war and lower profits
for all firms. Non-price competition can help firms differentiate their
products and gain market share.
- Interdependence: Firms in an oligopoly are interdependent, meaning that
each firm's decision affects the other firms' profits and reactions. Firms
have to anticipate and respond to the moves of their rivals, which can lead
to strategic behavior and game theory analysis.
- Nature of the product: Firms in an oligopoly can produce either
homogeneous or differentiated products. Homogeneous products are 6
identical or very similar, such as gasoline or steel. Differentiated products
are slightly different or have different brand names, such as cars or soft
drinks. The nature of the product affects the degree of competition and the pricing strategy of the firms.
The most prominent feature in this market is the interdependence of the
firms. This means that each firm’s decision affects the other firms’ profits and
reactions, and vice versa. This creates a situation where firms have to anticipate
and respond to the moves of their rivals, which can lead to strategic behavior
and game theory analysis. Interdependence also makes the demand curve and
the price-output determination of the firms indeterminate, as they depend on the
actions and expectations of the other firms. II.
The practical case: Beer market in Vietnam
1. Number of brand and market share
Vietnam has a vibrant and diverse beer industry, ranked in the top 10 in
the world in terms of production and consumption, with revenue expected to
reach 6.53 billion USD expected by 2022 (Nguyen, M. ,2023). The exact
number of beer brands in Vietnam is hard to determine, but it is estimated that
there are over 100 active breweries in Vietnam as of 2020. The beer market in
Vietnam is largely dominated by five big beer brands in 2021: Heineken,
Sabeco, Habeco, Carlsberg and AB InBev. These brands make up more than
94% of the beer market in Vietnam. However, there are also a lot of other
smaller and independent beer brands in Vietnam, especially in the craft beer
segment, such as Pasteur Street Brewing Company, Heart of Darkness Brewery,
Platinum Beer, Furbrew and 7 Bridges Brewing Company.
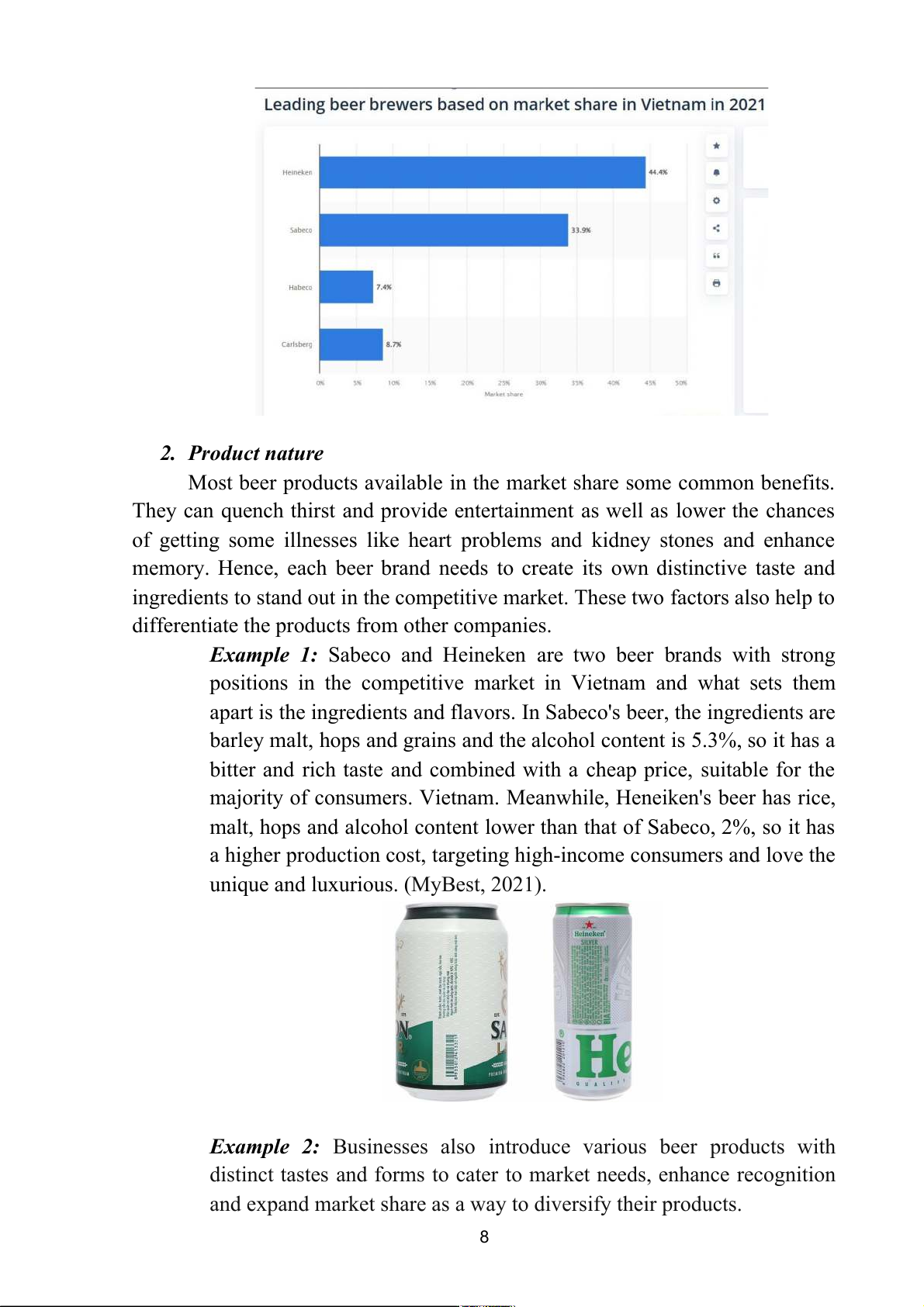
According to the chart that illustrates the market share of Vietnam beer in
2021 below, Heineken, Sabeco, Habeco and Carlsberg made up 44.4%, 33.9%,
7.4% and 8.7% respectively (Statista, 2021). The remaining percentages belong
to smaller firms. Besides selling their products in the local area, these firm also
target export markets that have high standards, such as Europe. The firms have
different levels of market share, with most of it concentrated in the large ones. 7
2. Product nature
Most beer products available in the market share some common benefits.
They can quench thirst and provide entertainment as well as lower the chances
of getting some illnesses like heart problems and kidney stones and enhance
memory. Hence, each beer brand needs to create its own distinctive taste and
ingredients to stand out in the competitive market. These two factors also help to
differentiate the products from other companies.
Example 1: Sabeco and Heineken are two beer brands with strong
positions in the competitive market in Vietnam and what sets them
apart is the ingredients and flavors. In Sabeco's beer, the ingredients are
barley malt, hops and grains and the alcohol content is 5.3%, so it has a
bitter and rich taste and combined with a cheap price, suitable for the
majority of consumers. Vietnam. Meanwhile, Heneiken's beer has rice,
malt, hops and alcohol content lower than that of Sabeco, 2%, so it has
a higher production cost, targeting high-income consumers and love the
unique and luxurious. (MyBest, 2021).
Example 2: Businesses also introduce various beer products with
distinct tastes and forms to cater to market needs, enhance recognition
and expand market share as a way to diversify their products. 8
(Beer products of Heneiken)
(Beer products of Habeco)
3. The structure of the beer market in Vietnam is Oligopoly
a. Beer market situation in Vietnam
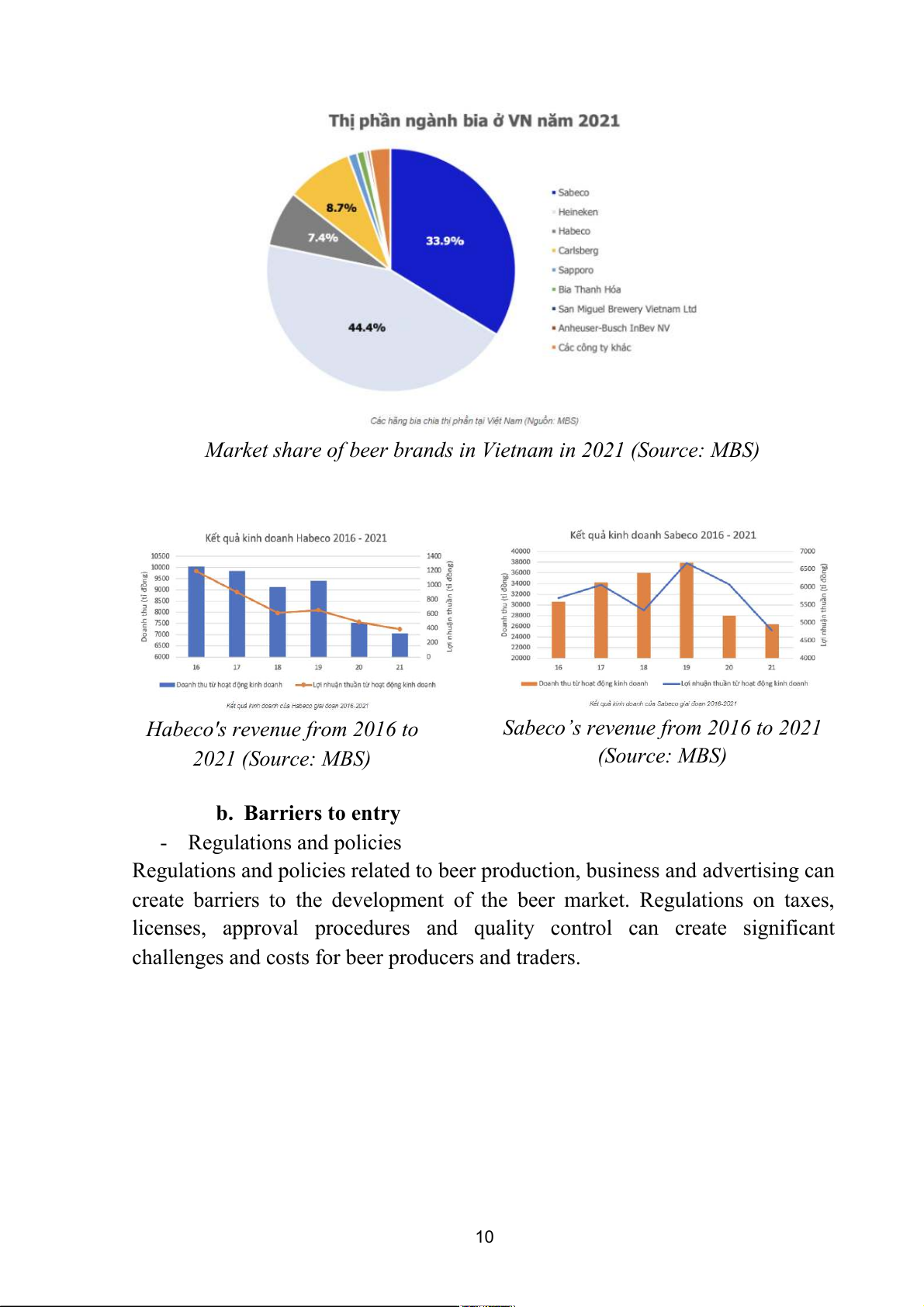
For many years, the beer market has been dominated by a group of four
large companies, namely Heineken, Sabeco, Carlsberg and Habeco. These four
companies accounted for 94.4% of the market share of Vietnam's beer industry
in 2021, of which Heineken and Sabeco alone had a total market share of 78.3%,
overwhelming the other two companies. (MBS)
According to Bloomberg data, Sabeco's after-tax profit margin was
13.49%, higher than Habeco (4.1%). In addition, Sabeco has a much lower
Capex/revenue ratio than other beer industry enterprises, only at 1.25%
compared to the industry average of 3.54%. 9
Market share of beer brands in Vietnam in 2021 (Source: MBS)
Habeco's revenue from 2016 to
Sabeco’s revenue from 2016 to 2021 2021 (Source: MBS) (Source: MBS) b. Barriers to entry - Regulations and policies
Regulations and policies related to beer production, business and advertising can
create barriers to the development of the beer market. Regulations on taxes,
licenses, approval procedures and quality control can create significant
challenges and costs for beer producers and traders. 10
Regulations on prevention and control of harmful effects of alcohol, beer
- Competition from imported beer
Competition from imported beer brands is also an obstacle. Famous beer brands
from abroad often have resources and recognition from customers, making it
difficult to access and compete in the market for domestic beer producers.
- Consumer perception "beer market research"
Some consumers still have limited perception of beer and do not show diversity
in choosing beer. The priority of some consumers is still price and brand rather
than quality and diversity of products. This can limit the access and
consumption of special and craft beers.
- Limitations on distribution and marketing "beer market research"
Beer distribution and marketing also face some challenges. Especially when
accessing rural areas or remote areas, distribution and marketing become
difficult. This can limit market expansion and access to potential customers.
- Health awareness and other consumption trends
With increased health awareness and different consumption trends, some
consumers may reduce beer consumption or switch to other types of drinks. The
increase of trends such as drinking less alcohol, drinking non-alcoholic
beverages or healthy diets can affect the growth of the beer market."
c. Non-price competition
Foreign companies often spend a large sum of money in advertising and
promotion (A & P) to get the consumers’ awareness for their products. The most
typical A & P activities used by them are erecting billboards at crowded
crossroads, commissioning foreign ads agency to develop attractive clips to be
shown on prime time TV, putting large ads in leading newspapers, sponsoring
key sportive and social events, providing free-of-charge name boards to
groceries with their logos, and using promotion girls in restaurants and wedding
parties. As a typical case, Tiger and Heineken brands had made quick and large 11
impacts on the Vietnamese market by a large scale A & P campaign in their
attempt to conquer the market quickly, by using a wide combination of all
means mentioned above. This marketing method has subsequently followed by
other brands like San Miguel, Carlsberg, BGI, but on a much smaller scale.
Creative advertising of Heineken
Advertising cost of Sabeco and
Revenue per one advertising of Sabeco
Habeco (Source: Cafebiz)
and Habeco (Source: Cafebiz) d. Interdependence
Domestic beer producers depend on foreign beer producers for importing
raw materials, such as malt and hops, as well as for accessing advanced 12
technology and management skills. Foreign beer producers depend on domestic
beer producers for expanding their market share, adapting to local tastes and
preferences, and complying with local regulations and standards. Therefore,
both domestic and foreign beer producers have mutual interests and benefits
from cooperating and competing in the beer market in Vietnam.
4. The determinants of the supply of the beer in Vietnam
a. The recent status and quantities
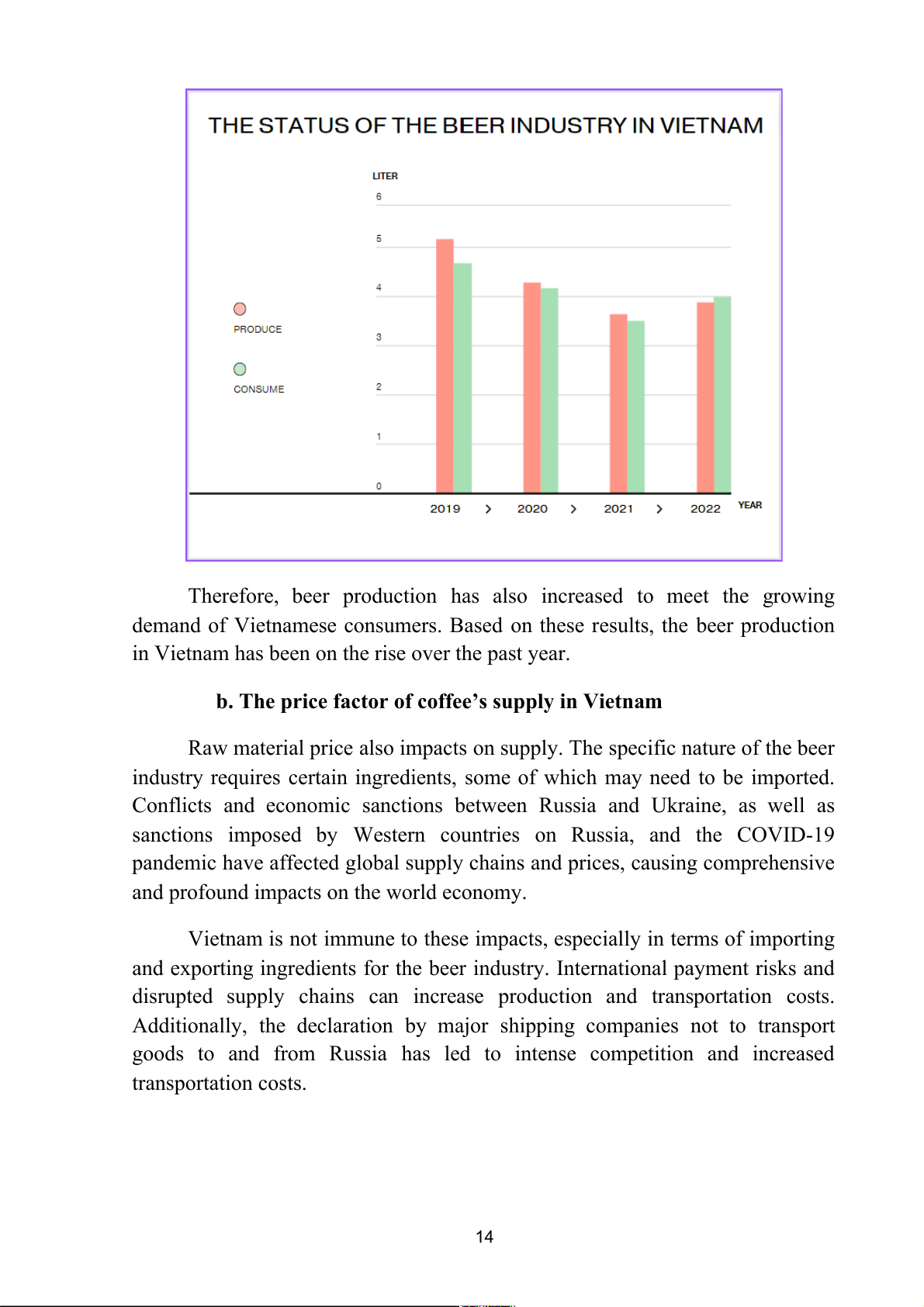
According to CleverAds, Vietnam’s beer market has flutuated between
2019 and 2023. In 2019, the total beer production in Vietnam reached over 5
billion liters, an increase of 22.9% compared to the same period in 2018. The
consumption also reached over 4 billion liters, showing a growth of 29.1%
compared to the previous year. However, due to the prolonged impact of social
distancing measures from the Covid-19 pandemic and additional management
policies imposed by the government, the business operations of beer companies
suffered significant losses. From 2020 to 2021, the beer market experienced a
decline of 20%-30% in consumption.
After successfully controlling the Covid-19 outbreak, various service and
entertainment industries, such as karaoke and bars, resumed their operations. As
a result, the beer consumption market gradually recovered and showed
promising signs. It is predicted that beer consumption in Vietnam will continue
to increase significantly in 2023. 13
Therefore, beer production has also increased to meet the growing
demand of Vietnamese consumers. Based on these results, the beer production
in Vietnam has been on the rise over the past year.
b. The price factor of coffee’s supply in Vietnam
Raw material price also impacts on supply. The specific nature of the beer
industry requires certain ingredients, some of which may need to be imported.
Conflicts and economic sanctions between Russia and Ukraine, as well as
sanctions imposed by Western countries on Russia, and the COVID-19
pandemic have affected global supply chains and prices, causing comprehensive
and profound impacts on the world economy.
Vietnam is not immune to these impacts, especially in terms of importing
and exporting ingredients for the beer industry. International payment risks and
disrupted supply chains can increase production and transportation costs.
Additionally, the declaration by major shipping companies not to transport
goods to and from Russia has led to intense competition and increased transportation costs. 14
Due to icreasing of ingredient prices, some beer manufacturing companies
have had to raise their prices. From the second quarter of 2022, beer prices had
to increase by 15%-30%.Because prices increase dramatically, consumers have
a trend to find a substitute products or limit beer consumption. It led to the
consumption of products falling down causing a reduction in supplying of goods
to avoid surplus. However, some companies may choose to maintain their
original prices in order to meet the demands of their customers. This approach
has limitations as it may result in lower revenue for the company. In the long
term, this can also impact the production process.
c. Some non-price factors of coffee’s supply in Vietnam - Technology
Technology is also one of the factors influencing beer production.
Nowadays, in Vietnam, there are numerous large breweries competing with each
other, not only in terms of price but also in terms of taste, uniqueness, and
meeting the demands of consumers and societal requirements. This necessitates
constant competition among major breweries, utilizing top-of-the-line
machinery and advanced technology to produce delicious beers that hold the
number one position in consumers' hearts.As a result, increased consumption
leads to an increase in production. Additionally, advanced technology helps to
improve productivity by enabling the production of more within the same
timeframe. It saves both time and unnecessary labor costs. 15
For example: Heiniken use new technology to produce new beer. They
has introduced a non-alcoholic beer that retains the delicious taste of Heineken
while containing only 69 calories per 330ml bottle. This caters to the current
consumer trend towards a balanced lifestyle and increased focus on personal
health. As a non-alcoholic beer, Heineken provides consumers with a new
choice for any time of the day. They can enjoy Heineken at their workplace, in
the gym, during lunch breaks, and even before driving, as it is a non-alcoholic beverage. - Government policy.
The government has implemented certain policies that can directly and
significantly impact beer production. The government has issued national
policies to combat the harmful effects of alcohol abuse. As a result, there are
regulations related to the production, business, and consumption of alcoholic 16
beverages, including beer. The Commercial Law restricts the trading of alcohol
as a regulated product. The Investment Law considers alcohol business as a
conditional sector, and the conditions are specified in Government Decree
105/2017/ND-CP regarding alcohol business. These regulations include
prohibitions on selling alcohol to individuals under 18 years old, requirements
for licensing alcohol production activities for individuals under 18 years old, and
regulations for granting licenses for alcohol production, distribution, wholesale,
retail, and on-site consumption. The Road Traffic Law specifies alcohol
concentration limits for drivers of motor vehicles, including cars and trucks.
These government regulations have a significant impact on the beer market and its production processes.
Government policies have significantly impacted the revenue of the beer
industry, leading to a decline in production as the demand has also decreased
due to the implementation of these policies.
For example: Hanoi Beer-Alcohol-Beverage Corporation (Habeco)
experienced a nearly 50% drop in revenue in the first quarter of 2020 compared
to the same period in 2019, resulting in a 55% decrease in profit equivalent to
148 billion Vietnamese dong. Similarly, Sabeco also concluded the first three
months of the year with a 47% decrease in revenue, recording the lowest profit
since the first quarter of 2016.
In particular, beer is subject to special consumption tax with the current
tax rate being 65%. Excessive consumption of beer can have negative health
implications and other serious consequences for society. As a result, sellers have
to increase beer prices to account for the tax and ensure their revenue. This, in
turn, limits beer consumption. Additionally, the production of beer is also affected by these policies.
5. The determinants of the demand of the beer in Vietnam
a. The recent status and quantities
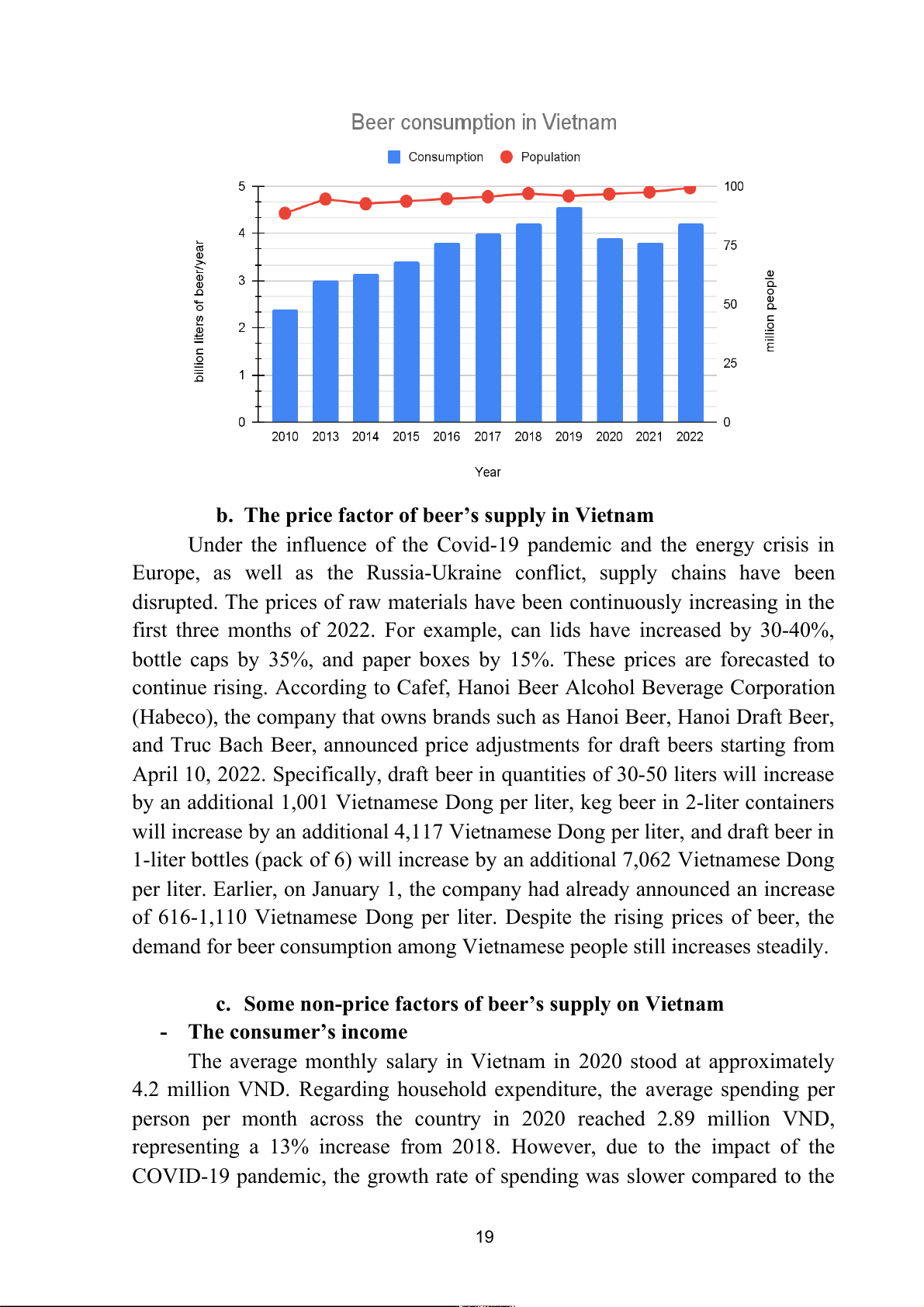
While the beer consumption market in many other countries has reached
saturation, the beer market in Vietnam has continued to grow rapidly, placing it among the top in the world.
According to Euromonitor, in 2010, the total beer consumption in
Vietnam was around 2.4 billion liters. With an estimated population of 88.5
million at that time, on average, each Vietnamese person consumed about 27.1 liters of beer in 2010. 17
By the end of 2018, after nearly a decade, while the population of
Vietnam reached 96.9 million (a 9.5% increase compared to 2010), the
nationwide beer consumption had increased by 62%.
Specifically, the beverage industry analysis report by FPT Securities
Company (FPTS) stated that Vietnam is one of the largest beer markets in the world.
In 2017, the total domestic beer consumption reached 4 billion liters,
accounting for 2.1% of the global beer production and ranking 10th in the world
and 3rd in Asia (after China and Japan).
In 2018, the domestic beer industry had around 110 manufacturing
enterprises with an estimated production volume of 4.3 billion liters and an
estimated consumption volume of 4.2 billion liters, showing a similar growth rate compared to 2017.
Therefore, on average in 2018, each Vietnamese person consumed nearly
43.3 liters of beer. Moreover, if we consider only the working-age population
(15-60 years old), each person in this age group consumed an average of 86.6
liters of beer in the past year.
According to the same report, during the period from 2007 to 2017, the
compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of the Vietnamese beer market was
consistently at 8.3%, which is very high compared to other markets. This led to
Vietnam's market scale rising 15 places, from 25th to 10th in the world.
During the period of 2020-2021, due to the impact of the COVID-19
pandemic, beer consumption also significantly decreased. The total beer
consumption was only around 3.9 billion liters per year.
As of 2022, Vietnam's beer consumption accounted for 2.2% of the global
market, at approximately 3.8 million liters of beer per year. This has made
Vietnam the leader in beer consumption among ASEAN countries.
A recent study published in The Lancet also revealed that Vietnam, India,
and Japan were the three countries with the fastest-growing alcohol consumption from 2010 to 2022.
Compared to 2010, Vietnam's beer consumption in 2022 has increased by
nearly 90%. Vietnam ranks first in the world in terms of this growth rate, with
double the rate of the second-ranked country, India, and 16 times higher than the United States. 18
b. The price factor of beer’s supply in Vietnam
Under the influence of the Covid-19 pandemic and the energy crisis in
Europe, as well as the Russia-Ukraine conflict, supply chains have been
disrupted. The prices of raw materials have been continuously increasing in the
first three months of 2022. For example, can lids have increased by 30-40%,
bottle caps by 35%, and paper boxes by 15%. These prices are forecasted to
continue rising. According to Cafef, Hanoi Beer Alcohol Beverage Corporation
(Habeco), the company that owns brands such as Hanoi Beer, Hanoi Draft Beer,
and Truc Bach Beer, announced price adjustments for draft beers starting from
April 10, 2022. Specifically, draft beer in quantities of 30-50 liters will increase
by an additional 1,001 Vietnamese Dong per liter, keg beer in 2-liter containers
will increase by an additional 4,117 Vietnamese Dong per liter, and draft beer in
1-liter bottles (pack of 6) will increase by an additional 7,062 Vietnamese Dong
per liter. Earlier, on January 1, the company had already announced an increase
of 616-1,110 Vietnamese Dong per liter. Despite the rising prices of beer, the
demand for beer consumption among Vietnamese people still increases steadily.
c. Some non-price factors of beer’s supply on Vietnam - The consumer’s income
The average monthly salary in Vietnam in 2020 stood at approximately
4.2 million VND. Regarding household expenditure, the average spending per
person per month across the country in 2020 reached 2.89 million VND,
representing a 13% increase from 2018. However, due to the impact of the
COVID-19 pandemic, the growth rate of spending was slower compared to the 19
previous year, with average spending in 2018 seeing an 18% increase compared to 2016.
As income levels rise, the demand for most goods tends to increase. This
relationship between income and demand categorizes beer as a normal good,
meaning that as an individual's income increases, their desire for beer also tends to rise. - Substitution effect
Beer often has negative effects on the health of consumers due to its
alcohol and additive content. Excessive beer consumption can lead to health
issues such as liver inflammation, liver fibrosis, weight gain, and can also affect
the nervous system. It can also have social consequences such as traffic
accidents and family conflicts.
Because of these reasons, people in Vietnam often seek alternative
beverages to replace beer. Popular choices include: ● Fresh fruit juice:
Fresh fruit juice is made from pure, fresh fruits without alcohol and
additives. It is a natural source of nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and
antioxidants. Fresh fruit juice can provide refreshment, energy, and a delicious taste.
● Non-alcoholic tea and beverages:
Non-alcoholic teas and beverages are another common choice. They can
have health benefits from natural ingredients such as herbal blends, green tea,
and antioxidants. Additionally, they do not contain alcohol and can provide a
refreshing and revitalizing feeling.
● Filtered water and purified drinking water:
Filtered water and purified drinking water are options that do not contain
alcohol, calories, or additives. They are clean water sources that help maintain
hydration, reduce the risk of negative health impacts, and do not contribute to weight gain.
The benefits of these alternative beverages are that they are not harmful to
health and do not have the negative effects associated with beer. They can
provide natural nutrients, enhance health, and offer a clear and refreshing feeling.
In terms of cost, these alternative beverages may have a higher price
compared to beer, depending on the brand, ingredients, and production process.
However, prices can vary, and there are options available at different price
points to suit the budget of individuals. Consumers may prioritize quality and
health benefits rather than solely considering the price. 20




