







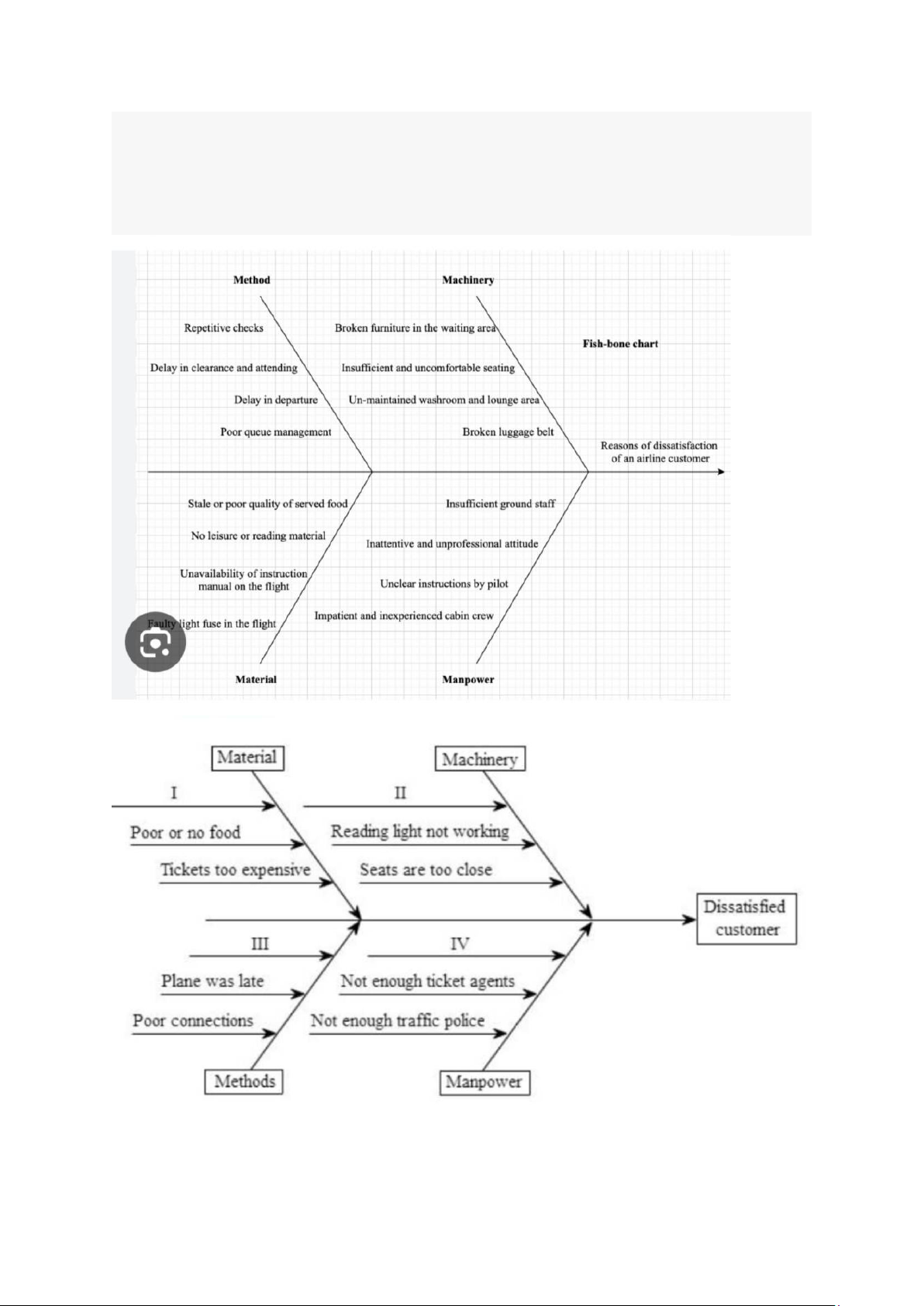
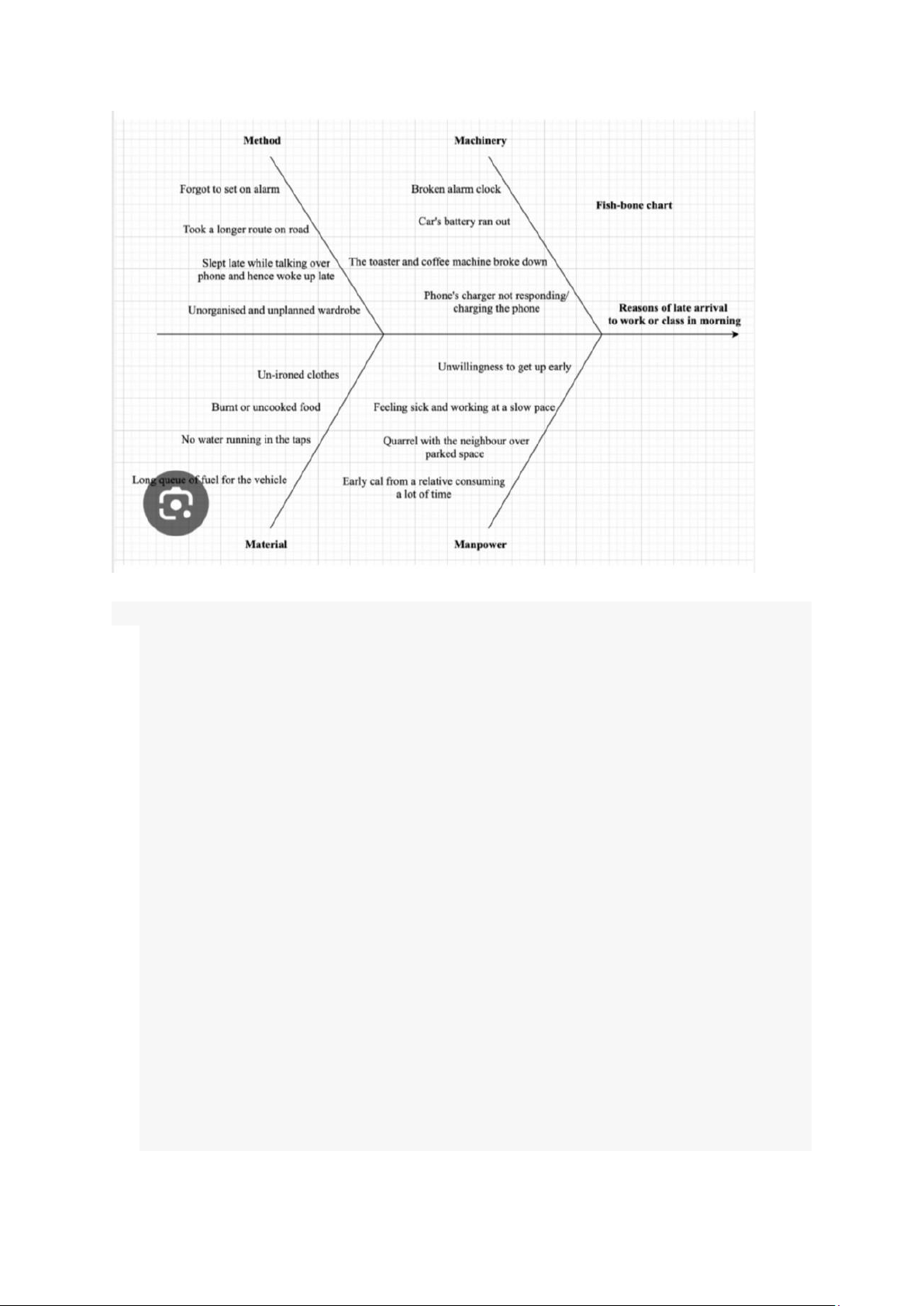

Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
1. Operation —--> organization mission ←→ strategy
( differentiation, responsiveness, cost leadership ) = chap 2
There are 3 primary strategies for operations managers ( cost leadership, differentiation and
response) to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage. Give explanation of these strategies
and suitable examples in the Vietnamese context 1. Cost Leadership:
Cost leadership strategy aims to achieve the lowest operational costs in the industry, allowing
a company to offer products or services at competitive prices. This strategy involves
streamlining operations, optimizing the supply chain, and reducing expenses to drive down
costs. By offering lower prices, companies can attract price-sensitive customers and gain a competitive edge.
-Example: Highlands Coffee is a well-known F&B brand in Vietnam that has implemented a
cost leadership strategy. They focus on offering high-quality coffee products at affordable
prices. Highlands Coffee has established strong relationships with coffee bean suppliers,
allowing them to secure competitive prices for their raw materials. They also emphasize
operational efficiency by optimizing their store layouts, managing inventory effectively, and
implementing cost-saving measures in their supply chain.
-Example in Vietnamese context: VietJet Air is a notable example of a brand in Vietnam that
has adopted a cost leadership strategy. VietJet Air is a low-cost carrier that offers affordable air
travel within Vietnam and other countries in the region. The airline has implemented various
cost-saving measures, such as operating a single aircraft type to reduce maintenance and
training costs and utilizing online platforms for ticket sales, reducing distribution costs. 2. Differentiation:
Differentiation strategy involves creating unique and distinctive products, services, or
experiences that set a company apart from its competitors. This strategy aims to build customer
loyalty and command premium prices by offering something unique and valuable to customers.
-Example: Trung Nguyen Coffee is an example of an F&B brand in Vietnam that has
successfully implemented a differentiation strategy. They focus on producing and serving high-
quality Vietnamese coffee with a unique flavor profile. Trung Nguyen Coffee differentiates
itself by offering a wide range of coffee blends, including special blends made from specific
regions in Vietnam. They also emphasize the cultural aspect of coffee consumption and provide
customers with an immersive coffee experience through their coffeehouses.
-Example: M.O.I Cosmetics is a Vietnamese beauty brand that has successfully implemented
a differentiation strategy. M.O.I Cosmetics focuses on producing natural and organic skincare
products, positioning themselves as providers of clean and sustainable beauty options. They
differentiate themselves by using high-quality, ethically sourced ingredients, and avoiding
harmful chemicals. M.O.I Cosmetics emphasizes their commitment to environmentally
friendly practices and offers a range of products that appeal to consumers seeking natural and
eco-friendly beauty solutions. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008 3. Response:
The response strategy emphasizes flexibility and responsiveness to meet customer needs
quickly and effectively. This strategy involves developing agile operations that can adapt to
changing market conditions and customer demands. Quick response times, efficient supply
chain management, and effective customer service are crucial elements of a response strategy.
-Example: Pizza 4P's is a notable F&B brand in Vietnam that has implemented a response
strategy. They are a pizza restaurant chain that focuses on using high-quality ingredients and
unique flavor combinations. Pizza 4P's emphasizes responsiveness by constantly innovating
and introducing new pizza flavors based on customer feedback and preferences. They also
prioritize customer service by offering personalized dining experiences and engaging with
customers through social media platforms.
-Example: SkinFood Vietnam is a notable beauty and skincare brand that has implemented a
response strategy. SkinFood Vietnam focuses on keeping up with the latest beauty trends and
launching products that address specific customer needs. They actively engage with customers
through social media platforms, seeking feedback and incorporating customer insights into
their product development and marketing strategies. SkinFood Vietnam's responsiveness
allows them to introduce new products and adapt their offerings to meet the evolving demands of their target market.
-Example: Viettel Post, the logistics division of Viettel Group, provides efficient and reliable
delivery services, which demonstrates schedule reliability. Viettel Post ensures precise and fast
delivery throughout Vietnam by running a nationally network of delivery vehicles and
distribution centers. Viettel Post maintains a high degree of schedule reliability by putting in
place cutting-edge tracking technologies and streamlining delivery routes. This reduces delays
and gives clients trust in their logistical skills.
-Example: GHN is a top logistics service provider that provides e-commerce companies with
fast and reliable delivery options. GHN's adaptability is demonstrated by its capacity to scale
operations by adding more delivery staff and streamlining delivery routes at busy times, such
as online shopping festivals or promotional campaigns. Because of its flexibility, GHN can
fulfill client expectations and guarantee on-time delivery even in times of peak demand.
⇒ These examples demonstrate how different brands in Vietnam have adopted various
operations management strategies to achieve sustainable competitive advantage. It is
important for companies to align their chosen strategy with their target market, brand
positioning, and operational capabilities to effectively differentiate themselves and gain a
competitive edge in the industry.
2. Three essential functions of organization?
(MARKETING, FINANCING, OPERATION)- (chap 1)
Marketing: The marketing function is responsible for identifying customer needs and wants,
creating awareness and demand for products or services, and promoting and delivering them lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
to the target market. It involves activities such as market research, product development,
pricing, advertising, sales, and customer relationship management. The marketing function
aims to understand customer preferences, communicate the value of the organization's
offerings, and establish and maintain customer relationships.
Finance: The finance function deals with managing the organization's financial resources and
ensuring their effective utilization. It involves activities such as financial planning, budgeting,
accounting, financial reporting, and risk management. The finance function aims to optimize
the organization's financial performance, maintain financial stability, manage cash flow,
allocate resources efficiently, and provide financial insights for decision-making.
Operations/Production: Operations: Whether the outputs are commodities or services, the
operations function is in charge of creating, overseeing, and improving the systems and
procedures that convert inputs into outputs. It includes tasks like process improvement, supply
chain management, inventory control, quality assurance, and production planning. The
operations department seeks to maximize productivity, cut costs, provide value to consumers,
and assure the efficient and effective production or delivery of goods or services.
=> An organization's performance and ability to operate depend on these three tasks. While
operations ensure the effective execution of procedures to supply goods or services, finance
oversees the financial resources required to support corporate activities. Marketing creates
consumer demand and drives revenue. Organizations may attain their goals, meet client
demands, and sustain a competitive edge in the market by efficiently handling these fundamental activities.
3. How to globally help operations reduce cost: labor cost, taxes, tariffs ? chap 2
Labor Cost Savings: Labor costs can vary significantly between countries due to differences
in wages, benefits, and regulatory requirements. Many countries have lower average wages
compared to developed nations. Moving operations to a location with lower labor costs can
result in substantial savings, especially for labor-intensive industries.
Tax Advantages: Many countries offer tax incentives, exemptions, or lower corporate tax rates
to attract foreign investment. By establishing international operations in jurisdictions with
favorable tax regimes, companies can reduce their overall tax burden and increase profitability.
Tariff Reduction: : Free trade agreements (FTAs), World Trade Organization (WTO), North
American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) can eliminate or significantly reduce tariffs on
imported materials or exported goods. By producing goods or sourcing materials locally in
target markets, companies can avoid or minimize tariff costs, improving competitiveness and profitability. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
4. Risk of outsourcing, What internal issues must managers address when
outsourcing? 1 example in real life of outsourcing (Chap2)
Outsourcing can bring several benefits to organizations, such as cost savings, access to
specialized expertise, and increased flexibility. However, it also carries certain risks and
challenges that managers need to address. Some of the internal issues that managers must
consider when outsourcing include:
1. Loss of Control: Managers may find it difficult to keep control over the activities that
are outsourced when specific services or processes are outsourced. This may give rise
to worries about maintaining the appropriate standard of customer service, complying
to norms and laws, and quality control. To reduce the danger of losing control, managers
must set clear goals, provide performance criteria, and create efficient lines of
communication with the outsourcing partner.
2. Data Security: Sharing private or sensitive information with third parties is a common
element of outsourcing. Risks to data security, and intellectual property protection, and
confidentiality violations may arise from this. Managers are responsible for making
sure that the proper data protection policies, security procedures, and confidentiality
agreements are in place to preserve the company's valuable information and reduce the possibility of data breaches.
3. Changes in Employment Levels: Outsourcing certain functions or processes may lead
to changes in employment levels within the organization. This could involve
downsizing or restructuring existing teams or departments. Managers must carefully
plan and manage the workforce transition, ensuring proper communication, providing
necessary support to affected employees, and complying with labour laws and regulations.
4. Changes in Facilities: Outsourcing may require adjustments to existing facilities. For
example, if manufacturing processes are outsourced, managers may need to repurpose
or downsize production facilities. Similarly, if customer support functions are
outsourced, managers may need to reorganize office spaces. Managers should assess
the impact on facilities, plan for any necessary modifications or reallocations, and
ensure a smooth transition without disrupting operations.
5. Vastly Expanded Logistics Issues: Outsourcing often introduces new logistics
challenges that managers must address. This includes issues related to transportation,
insurance, tariffs, customs, and timing. For instance, when outsourcing production to a
different country, managers need to consider transportation costs, customs regulations,
and potential delays associated with international shipments. They may
also need to navigate insurance and tariff requirements to ensure the smooth movement
of goods and mitigate any potential financial risks. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
An example of outsourcing in real life is the fashion industry's practice of outsourcing
garment production to overseas manufacturers. Many fashion brands outsource their
manufacturing processes to countries with lower labour costs, such as China, Bangladesh, or
Vietnam. This allows them to take advantage of cost savings while focusing on design,
marketing, and brand management.
An example of outsourcing in real life is the ways that several firms outsource their IT.
Businesses frequently contract with specialist IT service providers to handle their software
development, IT infrastructure management, and technical support needs. Through this
approach, companies may use the proficiency of outside IT specialists, save overhead expenses,
and concentrate on their primary business functions. External issues:
6. Financial Attractiveness: It is important for managers to evaluate the financial
feasibility of outsourcing by considering many elements, including labor expenses, tax
benefits, exchange rates stability. To make sure that the financial benefits of outsourcing
outweigh the risks and expenses involved, they should carefully analyze the
outsourcing arrangement's long-term financial sustainability and do a cost-benefit analysis.
7. People Skills and Availability: When it comes to the outsourced activities, managers
must determine whether there is a sufficient supply of skilled workers at the outsourcing
destination and evaluate their experience, knowledge, and abilities. To guarantee a
smooth working relationship with the outsourcing partner, they should also take into
account aspects like language proficiency, fit with culture, and the capacity to operate well in cross-cultural teams.
8. General Business Environment: An important factor in the success of outsourcing is
the overall business climate in the outsourced destination. Political stability, legal and
regulatory frameworks, intellectual property protection, infrastructural quality, and
convenience of conducting business are all important considerations for managers. An
advantageous business environment lowers risks and offers a strong base for outsourced collaboration.
9. Political Backlash: Outsourcing can attract political attention and public scrutiny,
especially when it involves offshoring jobs to other countries. Managers must be aware
of the potential for political backlash, protectionist policies, or changing regulations
that could impact the outsourcing arrangement. They should stay informed about
political developments, engage in proactive communication, and develop contingency
plans to mitigate any negative consequences.
4. . Explain how improving quality can lead to reduced costs? Example = chap 6
Reduced Rework and Scrap: Higher quality products are less likely to have defects or errors,
resulting in fewer instances of rework or scrapping of defective parts or products. This directly
reduces costs associated with labor, materials, and disposal. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Lower Warranty and Liability Costs: Products manufactured with higher quality standards
are less likely to fail prematurely or have defects, leading to fewer warranty claims and liability
issues. This results in reduced costs associated with warranty repairs, replacements, and legal liabilities.
Increased Efficiency: Improving quality often involves optimizing production processes to
minimize errors and defects. Streamlining processes reduces the time and resources required
for production, leading to higher throughput, reduced cycle times, and lower energy
consumption. This efficiency improvement translates into cost savings across various aspects of production.
Enhanced Supplier Relationships: Investing in quality can foster better relationships with
suppliers who provide reliable, defect-free materials and components. As a result, companies
may negotiate better terms, bulk discounts, and reduced inspection requirements, leading to cost savings in procurement.
Improved Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: Higher quality products lead to greater
customer satisfaction and loyalty. Satisfied customers are less likely to return products due to
defects or failures, reducing costs associated with returns, replacements, and customer service.
Additionally, loyal customers are more likely to make repeat purchases and recommend
products to others, reducing marketing and customer acquisition costs.
Reduced Inspection and Testing Costs: As product quality improves, there is less need for
extensive inspection and testing processes to identify defects. This reduces the time and
resources required for quality control activities, resulting in cost savings in terms of labor, equipment, and materials.
Prevention of Costly Errors: Improving quality often involves implementing preventive
measures to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. By detecting and
resolving problems early in the production process, companies can avoid costly errors, delays,
and disruptions that would otherwise result in additional expenses.
Overall, investing in quality not only reduces the direct costs associated with defects and errors
but also contributes to increased efficiency, customer satisfaction, and supplier relationships,
leading to broader cost savings across the entire value chain.
Manufacturing Industry - Electronics Company:
Example: An electronics manufacturing company in Vietnam produces smartphones and
tablets for export markets. Initially, the company faced challenges with product defects, leading
to high rates of rework and scrap, increased warranty claims, and strained relationships with customers and suppliers.
Improvements Implemented:
Implemented stringent quality control measures at each stage of the production process. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Invested in employee training programs to enhance skills and awareness of quality standards.
Enhanced supplier relationships by providing feedback and collaborating on quality improvement initiatives.
Cost Reduction Outcomes:
Reduced rework and scrap costs by 25% due to fewer defects and errors in the manufacturing process.
Decreased warranty claims by 30%, resulting in significant savings in warranty repair expenses.
Improved customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to increased repeat purchases and reduced marketing costs.
Textile Industry - Garment Manufacturing Company:
Example: A garment manufacturing company in Vietnam produces clothing for international
fashion brands. The company struggled with quality issues such as stitching defects, fabric
flaws, and sizing inconsistencies, leading to high levels of rejections and returns. Improvements Implemented:
Implemented comprehensive quality control procedures, including pre-production inspections and in-line quality checks.
Collaborated with suppliers to source higher quality fabrics and materials.
Implemented employee training programs to improve skills and attention to detail. Cost Reduction Outcomes:
Reduced rejections and returns by 20% through improved product quality and consistency.
Negotiated better terms with fabric suppliers, resulting in cost savings on raw materials.
Enhanced brand reputation and customer satisfaction, leading to reduced marketing expenses and increased sales.
Food Industry - Agricultural Processing Company:
Example: An agricultural processing company in Vietnam exports canned fruits and vegetables
to international markets. The company faced challenges with quality control issues such as
inconsistent product quality, packaging defects, and food safety concerns. Improvements Implemented:
Implemented Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) and other food safety management systems.
Upgraded processing equipment and facilities to meet international quality standards.
Enhanced employee training on food safety practices and quality control procedures. Cost Reduction Outcomes:
Reduced product recalls and rejections by 30% due to improved food safety and quality assurance measures. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Enhanced competitiveness in international markets, leading to increased export sales and revenue.
Strengthened relationships with distributors and retailers, resulting in reduced marketing and distribution costs.
These examples illustrate how companies in Vietnam can achieve cost reductions by
investing in quality improvements across various industries, leading to enhanced
competitiveness, customer satisfaction, and long-term profitability. 9. Four considerations
for a goods capacity decision - chap 7
When making capacity decisions for goods production, there are several key considerations to
keep in mind. These considerations help ensure that the chosen capacity level aligns with the
organization's goals and market dynamics. Here are 4 important considerations:
1. Forecast Demand Accurately: Accurate demand forecasting is essential for
determining the appropriate capacity level. Organizations should gather and analyze
data, market trends, customer insights, and other relevant factors to project future
demand. By understanding the expected demand patterns, businesses can avoid
overcapacity or undercapacity situations, optimize resource allocation, and minimize production costs.
2. Match Technology Increments and Sales Volume: Capacity decisions should align
with both anticipated sales volume and technological advancements. Organizations
need to assess their production technology and evaluate whether it can support the
projected sales volume. It is important to consider factors such as production efficiency,
scalability, and flexibility. Matching technology increments to sales volume ensures
that the capacity level remains aligned with market demands while leveraging
technological advancements to improve productivity and cost-efficiency.
3. Find the Optimum Operating Size: Determining the optimum operating size involves
striking a balance between economies of scale and resource utilization. Operating at the
right capacity level allows organizations to benefit from economies of scale, such as
reduced per-unit costs and improved efficiency. However, going beyond the optimal
capacity can result in diminishing returns and increased costs. By analyzing cost
structures, production capabilities, and market conditions, organizations can identify
the capacity level that maximizes operational efficiency and minimizes costs.
4. Build for Change: Flexibility and adaptability are crucial considerations in capacity
decisions. The business environment is dynamic, and market conditions can change
rapidly. Organizations should design their capacity plans with the ability to
accommodate future changes in demand, technology, and business strategies. This may
involve adopting scalable production systems, investing in modular equipment, or
implementing agile manufacturing processes. By building for change,
organizations can respond effectively to shifting market dynamics and avoid the need
for major capacity adjustments in the future. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Overall, considering accurate demand forecasting, aligning technology and sales volume,
finding the optimum operating size, and building for change are critical considerations in
making capacity decisions for goods production. These considerations help organizations
optimize resource allocation, improve operational efficiency, and minimize costs, ultimately
enhancing their competitiveness in the market. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Dưới đây là một số ví dụ về quyết định sản xuất của Toyota và Honda:
1. Lựa chọn công nghệ sản xuất: Cả Toyota và Honda đã đầu tư vào công nghệ sản xuất
tiên tiến để nâng cao hiệu suất và chất lượng sản phẩm. Ví dụ, Toyota đã phát triển công
nghệ Toyota Production System (TPS), một hệ thống sản xuất linh hoạt và hiệu quả.
Honda cũng đã áp dụng công nghệ robot hóa và tự động hóa trong quá trình sản xuất xe của mình.
2. Quyết định về quy mô sản xuất: Toyota và Honda phải đưa ra quyết định về quy mô
sản xuất để đáp ứng nhu cầu thị trường. Ví dụ, khi Toyota quyết định ra mắt một mẫu
xe mới, họ phải xác định quy mô sản xuất hàng nghìn hoặc hàng chục nghìn chiếc mỗi
tháng để đáp ứng nhu cầu của khách hàng trên toàn cầu.
3. Quản lý nguồn lực: Cả Toyota và Honda phải quản lý nguồn lực như lao động, nguyên
liệu và vật liệu một cách hiệu quả. Ví dụ, họ phải đảm bảo rằng có đủ nhân lực chất
lượng cao để vận hành các dây chuyền sản xuất và đủ nguyên liệu để duy trì quá trình sản xuất liên tục.
4. Tối ưu hóa quy trình sản xuất: Cả Toyota và Honda chú trọng vào việc tối ưu hóa quy
trình sản xuất để đạt được hiệu quả cao và chất lượng tốt nhất. Ví dụ, họ sử dụng các
nguyên lý Lean Manufacturing để giảm lãng phí, tăng cường sự linh hoạt và cải tiến quy trình sản xuất.
5. Chiến lược sản xuất toàn cầu: Cả Toyota và Honda có mạng lưới sản xuất toàn cầu để
phục vụ các thị trường khác nhau. Ví dụ, Toyota đã mở các nhà máy sản xuất ở nhiều
quốc gia trên thế giới, bao gồm Nhật Bản, Mỹ, Trung Quốc và các nước châu Âu. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Honda cũng có các nhà máy sản xuất ở nhiều quốc gia như Nhật Bản, Mỹ, Canada và Thái Lan.
Những quyết định này giúp Toyota và Honda duy trì xuất sắc trong việc sản xuất ô tô, đáp ứng
nhu cầu của khách hàng và duy trì cạnh tranh trong ngành công nghiệp ô tô toàn cầu
1. Production Decision (Quyết định sản xuất): Toyota:
Ví dụ về quyết định sản xuất của Toyota là sự đầu tư vào công nghệ sản xuất hybrid và xe điện.
Toyota đã đưa ra quyết định sản xuất hàng loạt các mẫu xe hybrid như Toyota Prius và xe điện
như Toyota Mirai. Điều này phản ánh cam kết của Toyota trong việc phát triển các giải pháp
vận hành xanh hơn và thân thiện với môi trường. Honda:
Honda cũng đã đưa ra quyết định sản xuất liên quan đến công nghệ xanh. Ví dụ, Honda đã phát
triển và sản xuất xe điện Honda Clarity và Honda e. Đây là các mẫu xe điện tiên tiến nhằm
giảm khí thải và tiêu thụ năng lượng.
2. Organizational Focus (Sự tập trung của tổ chức): Toyota:
Toyota tập trung vào sự liên kết và tương tác giữa các phần tử trong tổ chức. Họ thúc đẩy môi
trường làm việc đội nhóm, khuyến khích sự sáng tạo và đề cao sự chia sẻ thông tin. Toyota sử
dụng các công cụ như Hội thảo Kaizen và Hội thảo chất lượng để nâng cao hiệu suất và sự hợp tác trong tổ chức. Honda:
Honda tạo ra một môi trường làm việc năng động và cởi mở, khuyến khích sự đa dạng và sáng
tạo. Họ đặt sự tập trung vào vai trò của cá nhân và khuyến khích nhân viên tham gia vào quyết
định và cải tiến quy trình. Honda cũng có chương trình đào tạo liên tục để phát triển năng lực
và kỹ năng của nhân viên.
3. Customer Focus (Sự quan tâm đến khách hàng): Toyota:
Toyota luôn đặt khách hàng là trung tâm trong mọi quyết định và hoạt động của mình. Họ tiếp
tục nghiên cứu và phát triển các công nghệ mới để cung cấp những sản phẩm an toàn, chất
lượng và tiết kiệm nhiên liệu cho khách hàng. Toyota cũng tạo ra một môi trường dịch vụ
chuyên nghiệp và đáp ứng nhanh chóng đối với các yêu cầu và phản hồi từ khách hàng. Honda:
Honda cũng chú trọng đến sự hài lòng của khách hàng. Họ tập trung vào việc cung cấp các sản
phẩm chất lượng cao và dịch vụ hậu mãi tốt. Một ví dụ là chương trình Honda Care, một dịch
vụ hậu mãi mở rộng bao gồm bảo hành mở rộng, dịch vụ đường dài và dịch vụ cứu hộ để đảm
bảo sự hài lòng và tin tưởng của khách hàng.




