






Preview text:
SECTION A (6 Marks). MCQs 1)
The accompanying graph is the production possibility curve for a three-person economy,
with workers Janna, Drew, and Kari.
Who has the greatest comparative advantage in shoe production? A) None of them B) Janna C) Kari D) Drew 2)
The reason economists consider monopoly to be socially undesirable is that monopolists
A) produce less than the socially optimal level of output.
B) earn too much economic profit.
C) exploit the inelastic nature of demand.
D) can charge any price they want. 3)
One reason the demand curve slopes ______ is that as prices fall ______. Version 1 1
A) downward; more people find that the price is now less than their reservation price.
B) upward; more people find that the price is now less than their reservation price.
C) downward; fewer people find that the price is now less than their reservation price.
D) upward; fewer people find that the price is now less than their reservation price. 4)
When one's performance is judged relative to others' performance and not by an absolute standard
A) players will overinvest in performance enhancements.
B) players will underinvest in performance enhancements.
C) a positional externality is not possible.
D) the incentive to sabotage the other players is lessened. 5)
The responsiveness of the quantity demanded of one good to a change in the price of a
different good is measured by the
A) income elasticity of demand.
B) cross-price elasticity of demand.
C) price elasticity of demand.
D) price elasticity of supply. 6)
The deadweight loss from taxing a good will be smaller for goods
A) that are consumed by a large fraction of the population.
B) whose supply and demand curves are more inelastic.
C) that are relatively expensive.
D) whose supply and demand curves are more elastic. 7)
Unlike economic profit, economic rent Version 1 2 A) can be less than zero.
B) doesn't involve opportunity costs.
C) may not be driven to zero by competition. D) only applies to land. 8)
Suppose the accompanying table describes the demand for a good produced by monopolist. Price Quantity $ 10 1 9 2 8 3 7 4 6 5 5 6 4 7
The total revenue from selling 6 units is ______, and the marginal revenue of selling the 6th unit is ______. A) $30; $0 B) $5; $5 C) $30; $1 D) $24; $5 Version 1 3 9)
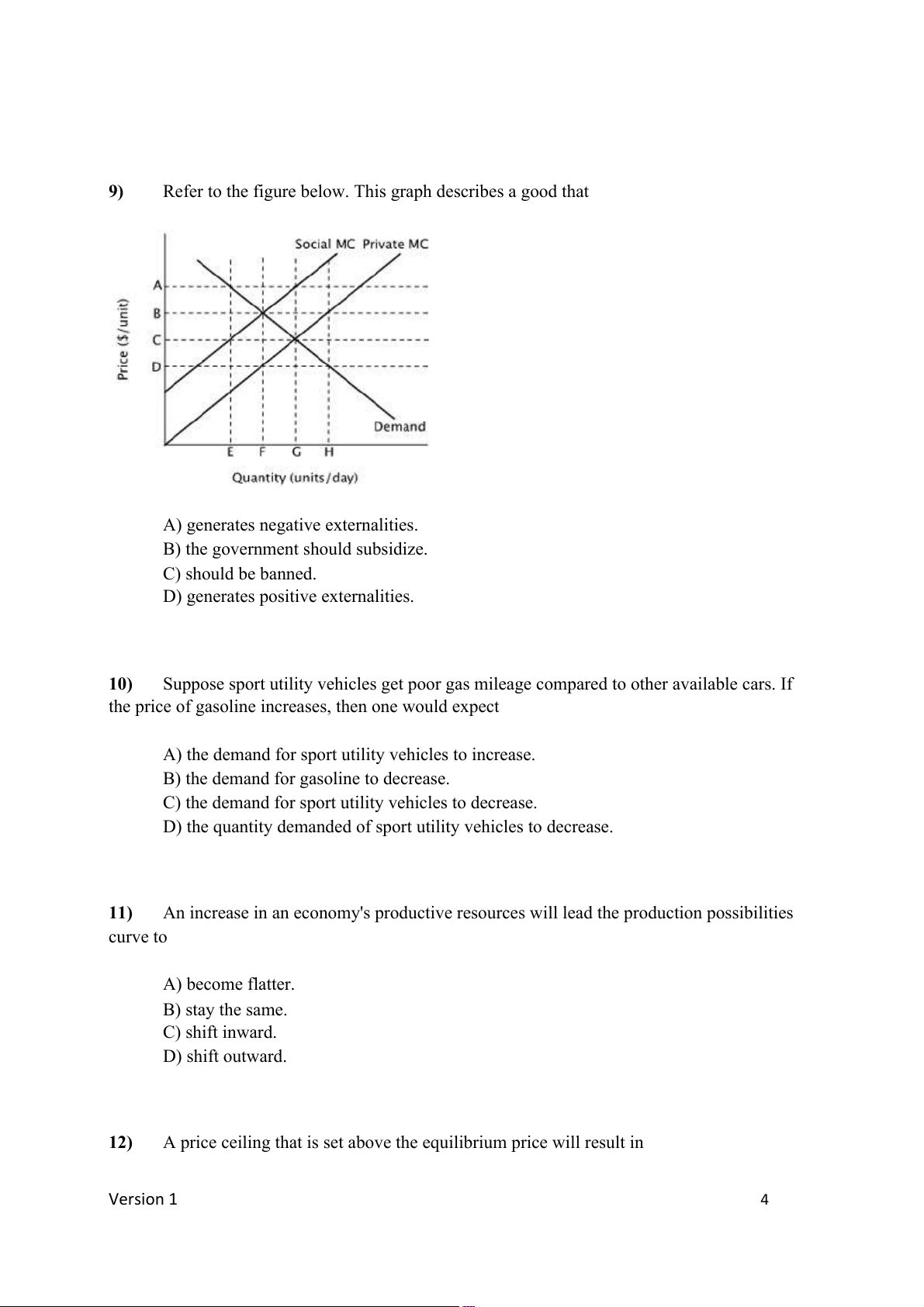
Refer to the figure below. This graph describes a good that
A) generates negative externalities.
B) the government should subsidize. C) should be banned.
D) generates positive externalities. 10)
Suppose sport utility vehicles get poor gas mileage compared to other available cars. If
the price of gasoline increases, then one would expect
A) the demand for sport utility vehicles to increase.
B) the demand for gasoline to decrease.
C) the demand for sport utility vehicles to decrease.
D) the quantity demanded of sport utility vehicles to decrease. 11)
An increase in an economy's productive resources will lead the production possibilities curve to A) become flatter. B) stay the same. C) shift inward. D) shift outward. 12)
A price ceiling that is set above the equilibrium price will result in Version 1 4
A) a loss in total economic surplus.
B) a market price that is above the equilibrium price.
C) an increase in consumer surplus.
D) no change in total economic surplus. 13)
Because of ______, the market will provide ______ the socially optimal level of information. A) moral hazard; more
B) the free-rider problem; less
C) the credibility problem; more
D) the problem of adverse selection; less 14)
The downward slope of the production possibilities curve illustrates the A) Incentive Principle. B) Scarcity Principle.
C) Principle of Comparative Advantage. D) Cost-Benefit Principle. 15)
As price increases, firms in a perfectly competitive market find that it is
A) beneficial to produce more units of output.
B) beneficial to produce fewer units of output.
C) more difficult to sell their product.
D) easier to sell their product. Version 1 5 16)
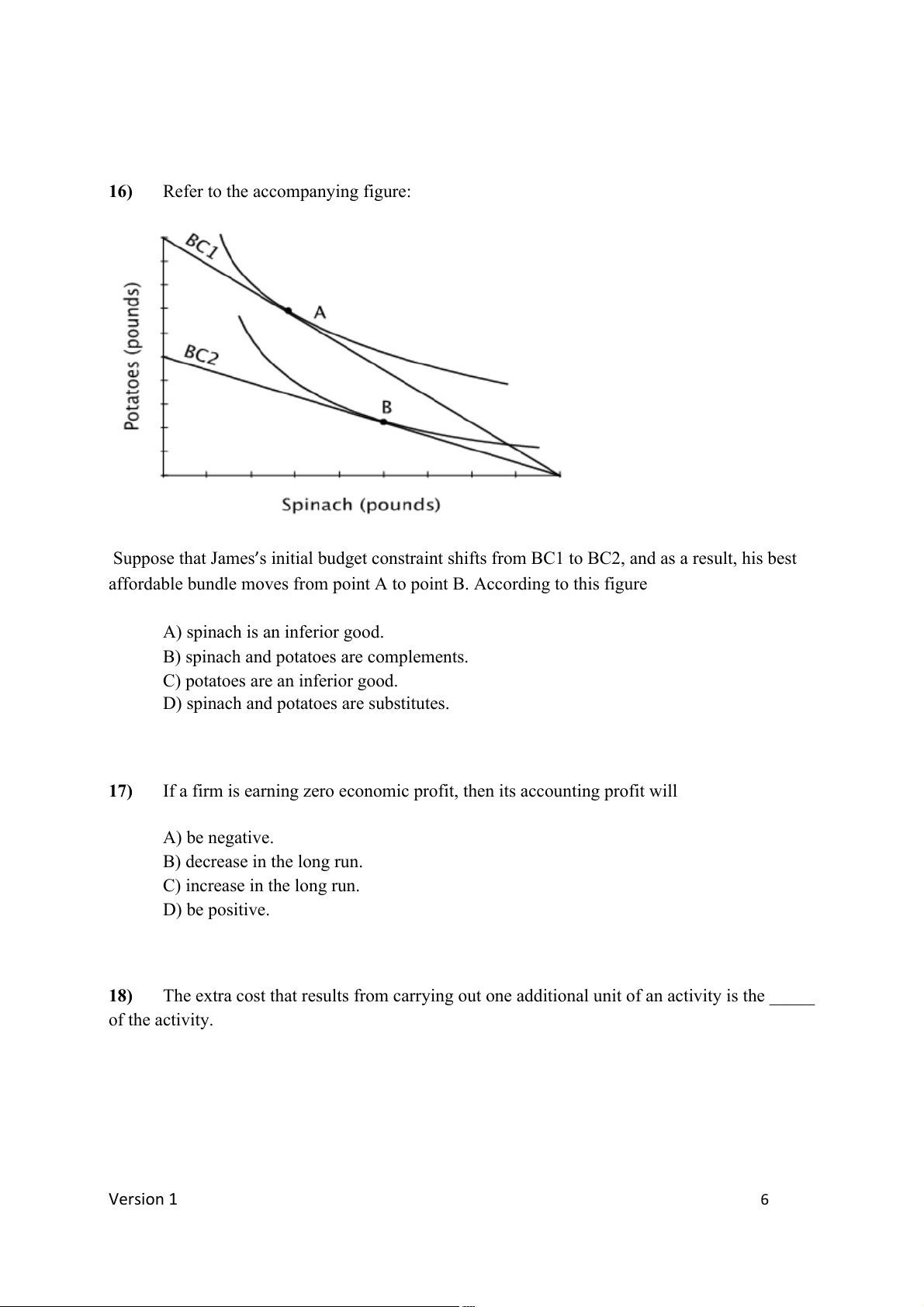
Refer to the accompanying figure:
Suppose that James s initial budget constraint shifts from BC1 to BC2, and as a result, his best ’
affordable bundle moves from point A to point B. According to this figure
A) spinach is an inferior good.
B) spinach and potatoes are complements.
C) potatoes are an inferior good.
D) spinach and potatoes are substitutes. 17)
If a firm is earning zero economic profit, then its accounting profit will A) be negative. B) decrease in the long run. C) increase in the long run. D) be positive. 18)
The extra cost that results from carrying out one additional unit of an activity is the _____ of the activity. Version 1 6 A) reservation cost B) opportunity cost C) marginal benefit D) marginal cost 19)
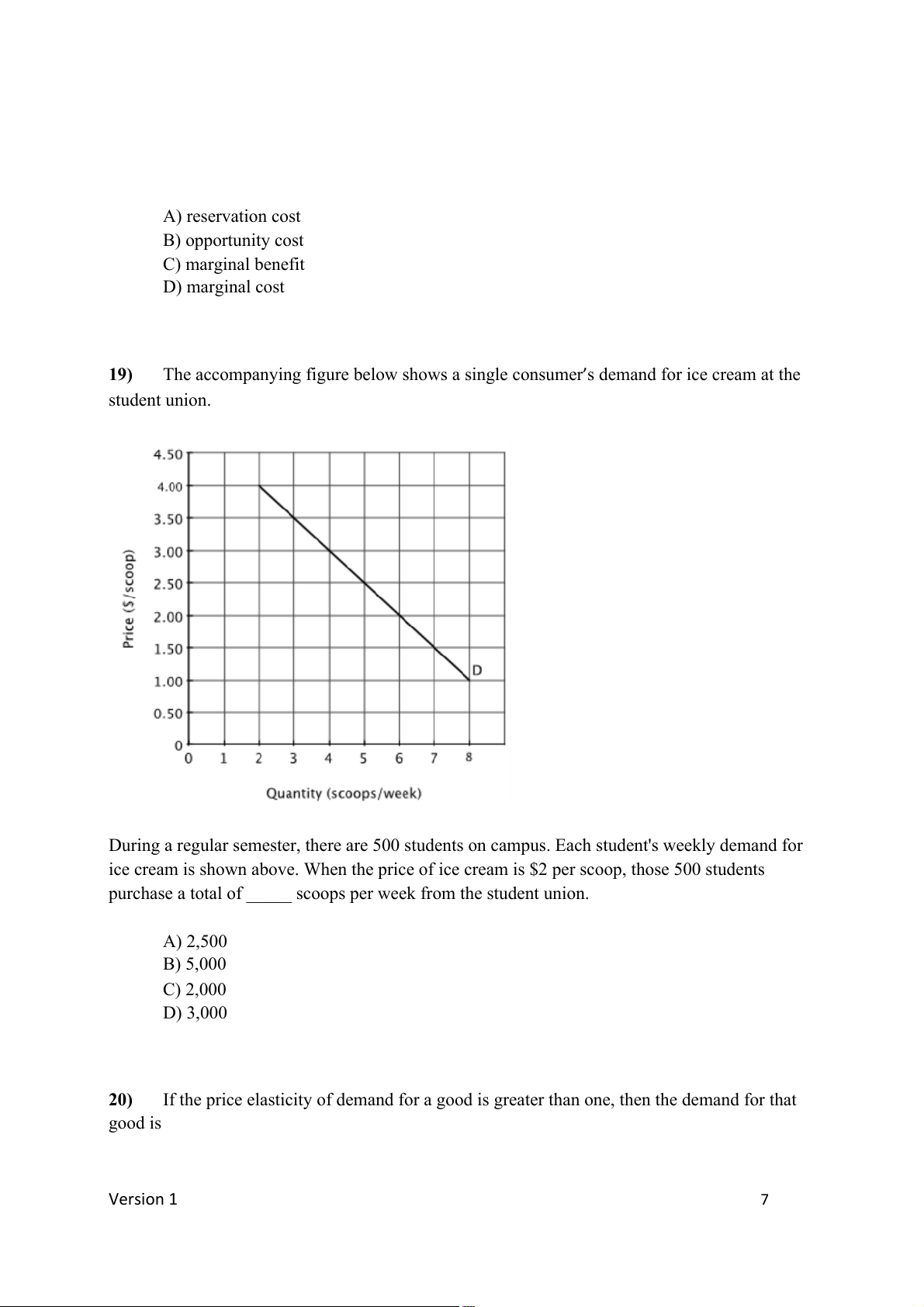
The accompanying figure below shows a single consumer s demand for ice cream at the ’ student union.
During a regular semester, there are 500 students on campus. Each student's weekly demand for
ice cream is shown above. When the price of ice cream is $2 per scoop, those 500 students
purchase a total of _____ scoops per week from the student union. A) 2,500 B) 5,000 C) 2,000 D) 3,000 20)
If the price elasticity of demand for a good is greater than one, then the demand for that good is Version 1 7 A) elastic. B) inelastic. C) perfectly elastic. D) unit elastic. 21)
Janie must choose to either mow the lawn or wash clothes. If she mows the lawn, she will
earn $30, and if she washes clothes, she will earn $45. She dislikes both tasks equally and they
both take the same amount of time. Janie will therefore choose to ______ because it generates a ______ economic surplus. A) mow the law; smaller B) wash clothes; bigger C) wash clothes; smaller D) mow the lawn; bigger 22)
The pattern in which insurance is purchased more frequently by those who are the most
costly for companies to insure is referred to as A) risk aversion.
B) statistical discrimination. C) moral hazard. D) adverse selection. 23)
The demand for cars in a certain country is given by: D = 20,000 – P, where P is the
price of a car. Supply by domestic car producers is: = 5,000 + 0.5 S
P. If this economy opens to
trade while the world price of a car is $6,000, and the government imposes a quota allowing
3,000 cars to be imported, then domestic equilibrium quantity of cars will be A) 10,000. B) 8,000. C) 12,000. D) 6,000. Version 1 8 24)
The marginal cost of providing another viewer with access to HBO is zero. Since only
people who pay for HBO can watch it
A) more than the socially optimal number of people will have access HBO.
B) HBO will not be profitable in the long run.
C) fewer than the socially optimal number of people will have access to HBO.
D) access to HBO is nonexcludable. 25)
Suppose Suzanne allocates her spending on apples and bananas according to the rational
spending rule. If the price of apples is less than the price of bananas, then at Suzanne's optimal
consumption bundle, her marginal utility from apples will be
A) less than her marginal utility from bananas. B) equal to zero.
C) greater than her marginal utility from bananas.
D) equal to her marginal utility from bananas. 26)
If the percentage change in quantity demanded is zero for any percentage change in the
price of the good, demand is classified as A) unit elastic. B) perfectly inelastic. C) perfectly elastic. D) inelastic. 27)
If the market for butter is perfectly competitive, then the demand curve facing a firm that produces butter will be: A) upward sloping. B) unit elastic. C) perfectly elastic. D) perfectly inelastic. Version 1 9 28)
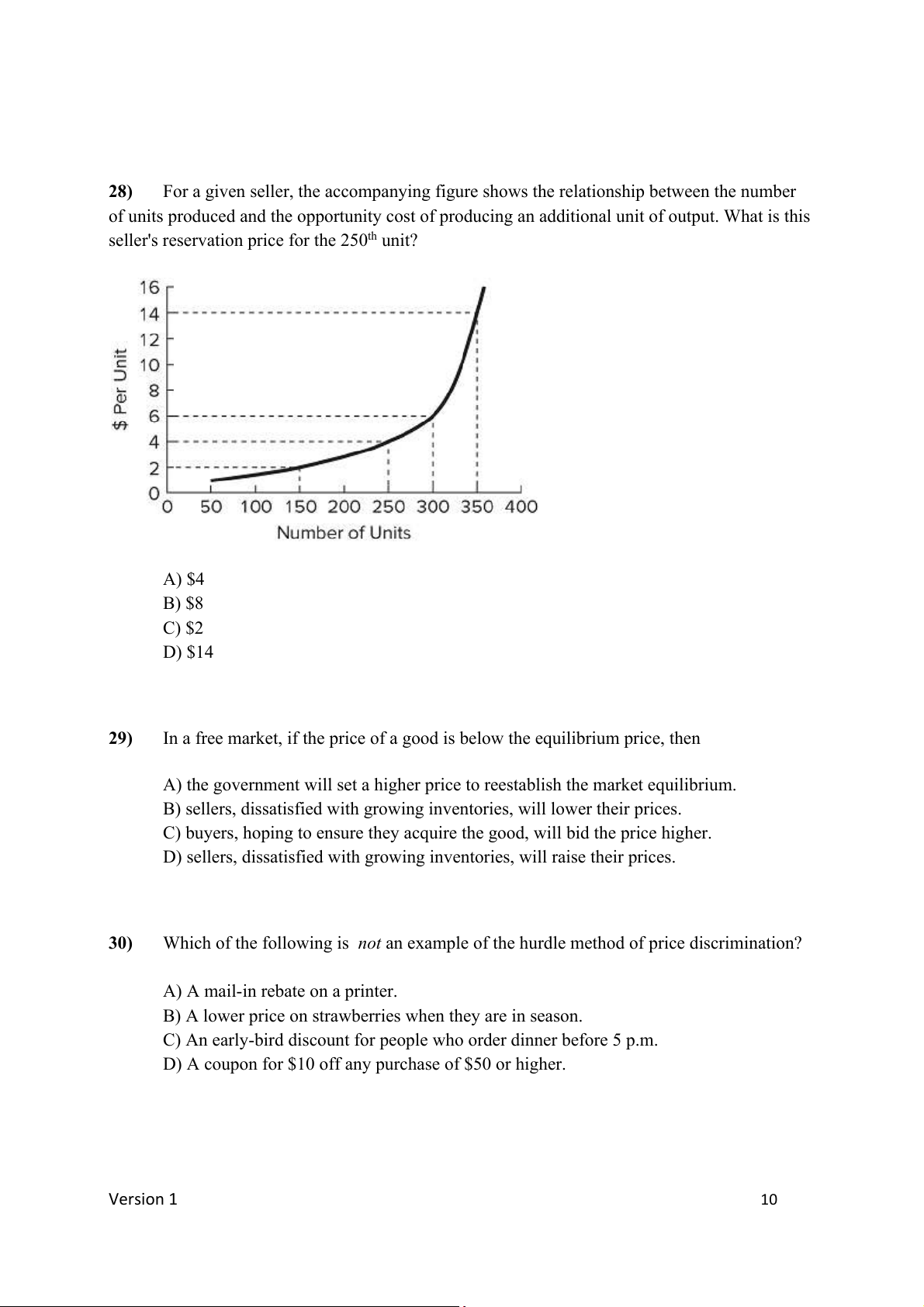
For a given seller, the accompanying figure shows the relationship between the number
of units produced and the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of output. What is this
seller's reservation price for the 250th unit? A) $4 B) $8 C) $2 D) $14 29)
In a free market, if the price of a good is below the equilibrium price, then
A) the government will set a higher price to reestablish the market equilibrium.
B) sellers, dissatisfied with growing inventories, will lower their prices.
C) buyers, hoping to ensure they acquire the good, will bid the price higher.
D) sellers, dissatisfied with growing inventories, will raise their prices. 30)
Which of the following is not an example of the hurdle method of price discrimination?
A) A mail-in rebate on a printer.
B) A lower price on strawberries when they are in season.
C) An early-bird discount for people who order dinner before 5 p.m.
D) A coupon for $10 off any purchase of $50 or higher. Version 1 10 SECTION B (4 Marks)
Problem 1 (1 Mark). How will a new law mandating an increase in required levels of
automobile insurance affect the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for new automobiles? Explain.
Problem 2 (2 Marks). More and more consumers are watching their favorite network television
programs from their computers. Suppose that a network begins to charge a small fee to access
and download an episode of a popular program. For a television network, the marginal cost of
supplying the episode to one more customer is zero.
a) What type of good is this Internet television episode download? Explain.
b) Will the efficient quantity of television downloads be provided? Explain.
Problem 3 (1 Mark). You are a division manager at VinFast. If your marketing department
estimates that the semiannual demand for the VinFast VF8 is Q = 150,000 – 1.5P, what price
should you charge in order to maximize revenues from sales of the VinFast VF8? Version 1 11




