










Preview text:
Chapter 2
Recording business transactions 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 1 Learning objectives
• Explain accounts, journals and ledgers as they relate to recording
transactions, and describe common accounts
• Define debits, credits and normal account balances, and use
double-entry accounting and T-accounts
• List the steps of the transaction recording process
• Post transactions from the journal to the ledger
• Prepare the trial balance from the T-accounts 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 2
2.1. The account, the ledger and the journal
• An account is the detailed record of all the changes that have
occurred in a particular asset, liability or owners’ equity during a period
• The journal is the chronological record of the transactions
• The ledger is the record holding all accounts
• A list of all the ledger accounts, along with their balances, is called a trial balance 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 3
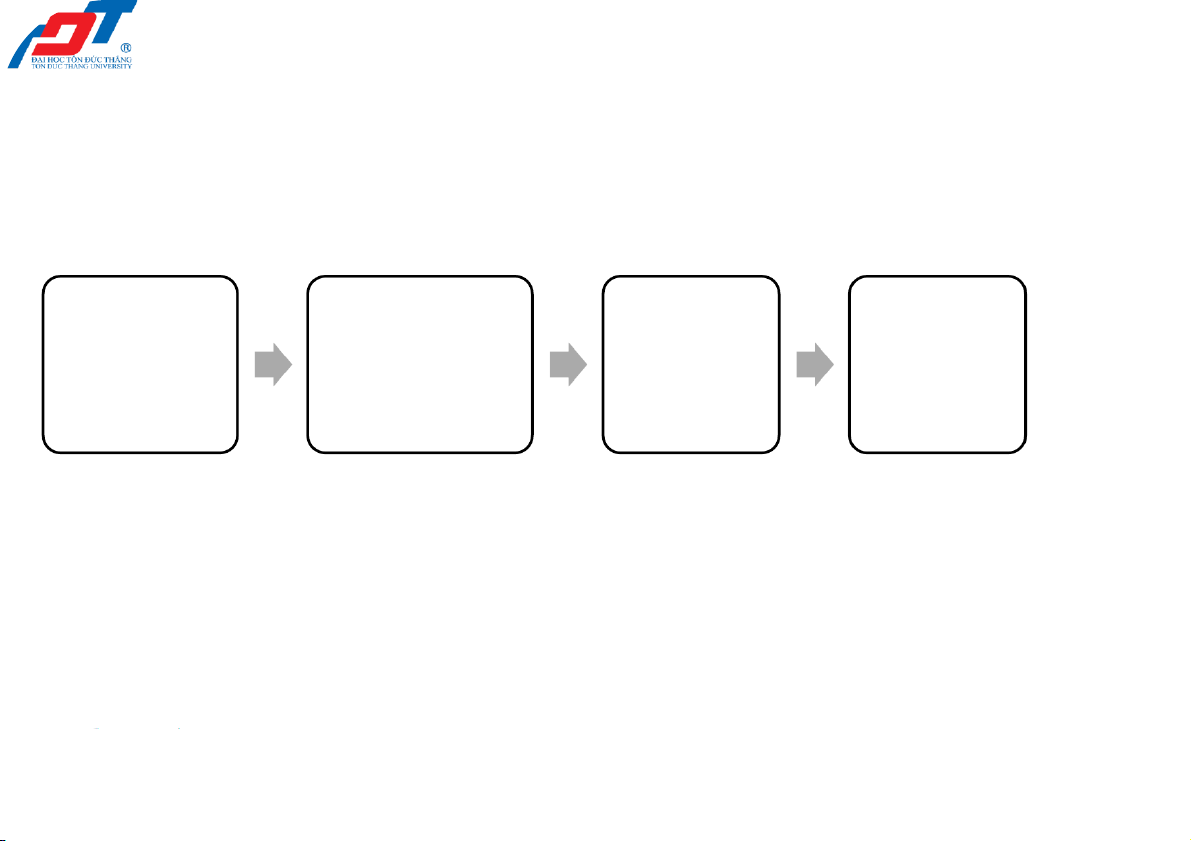
2.1. The account, the ledger and the journal Prepare Collect Record Copy the source of transactions (post) to documents in the journal the ledger trial balance 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 4
2.1. The account, the ledger and the journal Assets
An asset is a resource controlled by an entity as a result of past
events that is expected to provide future economic benefits to the entity in the future • Cash • Prepaid expenses • Accounts receivable • Land • Bills receivable • Buildings • Inventories • Plant and equipment 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 5
2.1. The account, the ledger and the journal Liabilities
A liability is a present obligation of the entity arising from past
events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow
from the entity of resources embodying economic benefits • Accounts payable • Bills payable
• Accrued liabilities (e.g. salary _______, interest _______, electricity ______, etc.) 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 6
2.1. The account, the ledger and the journal Owners’ equity
The financial estimate of owners’ claims to the value in a business
is called owners’ equity. It is the residual interest in the assets of
an entity after deducting all liabilities •Capital •Drawings •Income
•Service revenue/ sale revenue •Expenses 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 7
2.1. The account, the ledger and the journal Chart of accounts 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 8
2.2. Debits, credits and double-entry accounting
• Accounting is based on a double-entry system
• Each transaction affects at least two accounts
• A popular account format is called T-account Debit Account Title Credit 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 9
2.2. Debits, credits and double-entry accounting
• The account category determines how increases and
decreases in the account are recorded as debits and credits
• The pattern of recording debits and credits is based on the accounting equation 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 10 Minigame 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 11
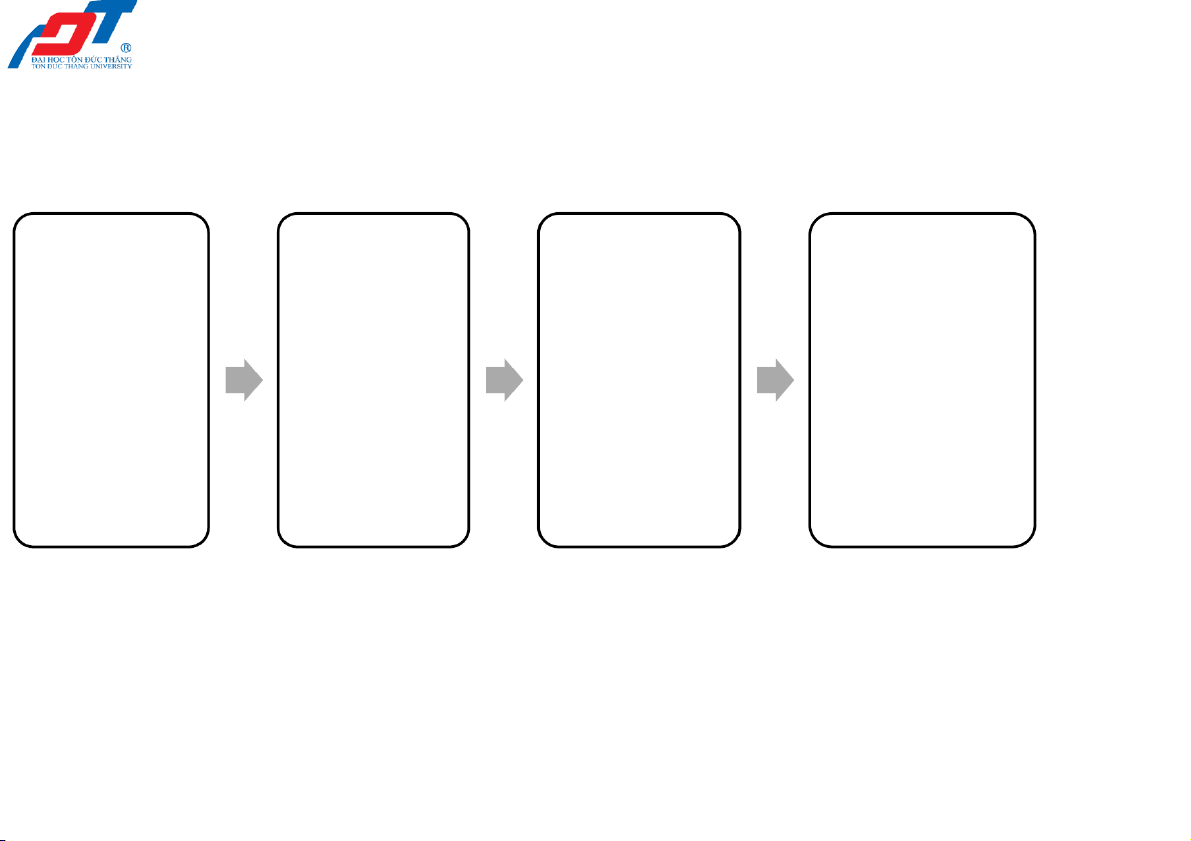
2.3. Recording transactions in the journal Specify Determine each whether Enter the Identify the account each transaction transaction affected by account is in the from the increased journal, source transaction or including a documents and decreased brief classify it by the explanation by type transaction 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 12
2.3. Recording transactions in the journal
Eg: The Smart Touch business received of Sheena Bright’s
$30,000 cash investment in the business.
1. The source documents: ___(1)_________
2. The accounts affected: ____(2)_____________
3. The accounts increased/decreased: ____(3)_________ 4.
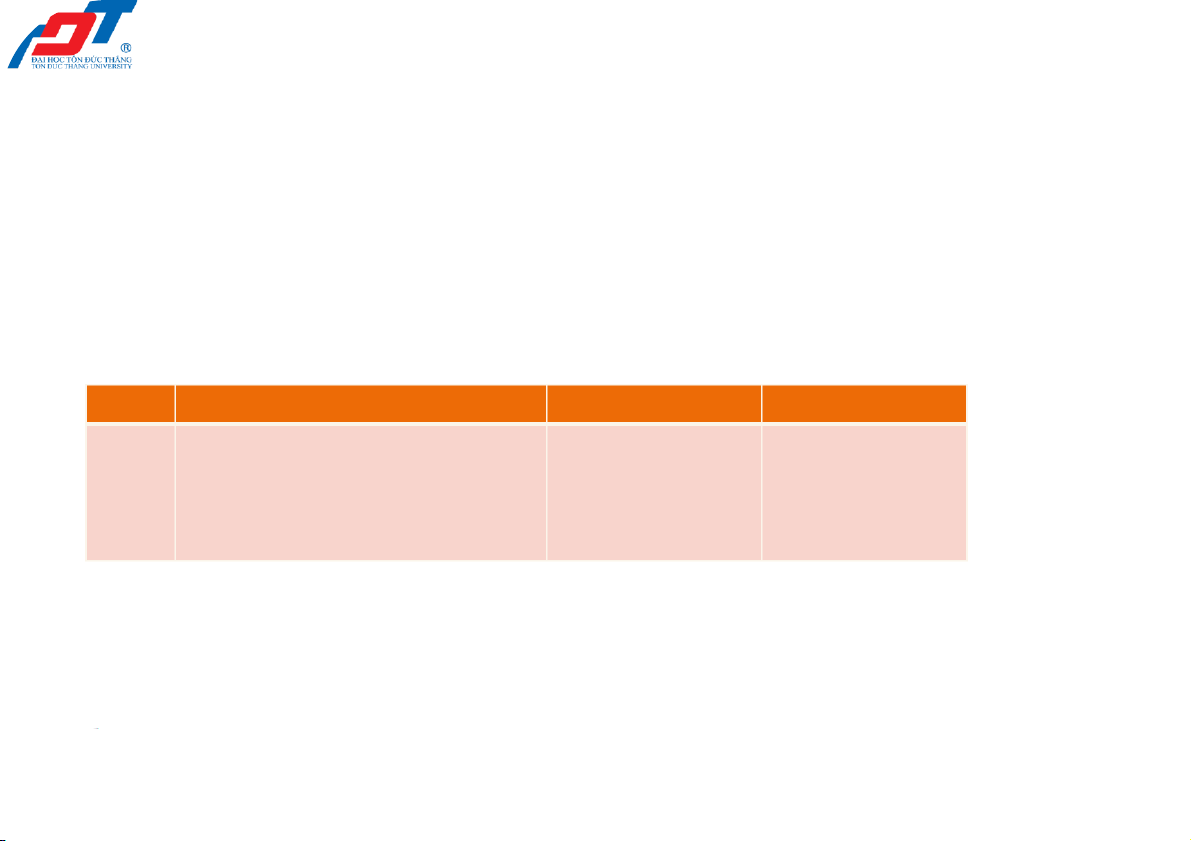
Date Accounts & Explanations Debit (Dr.) Credit (Cr.) 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 13
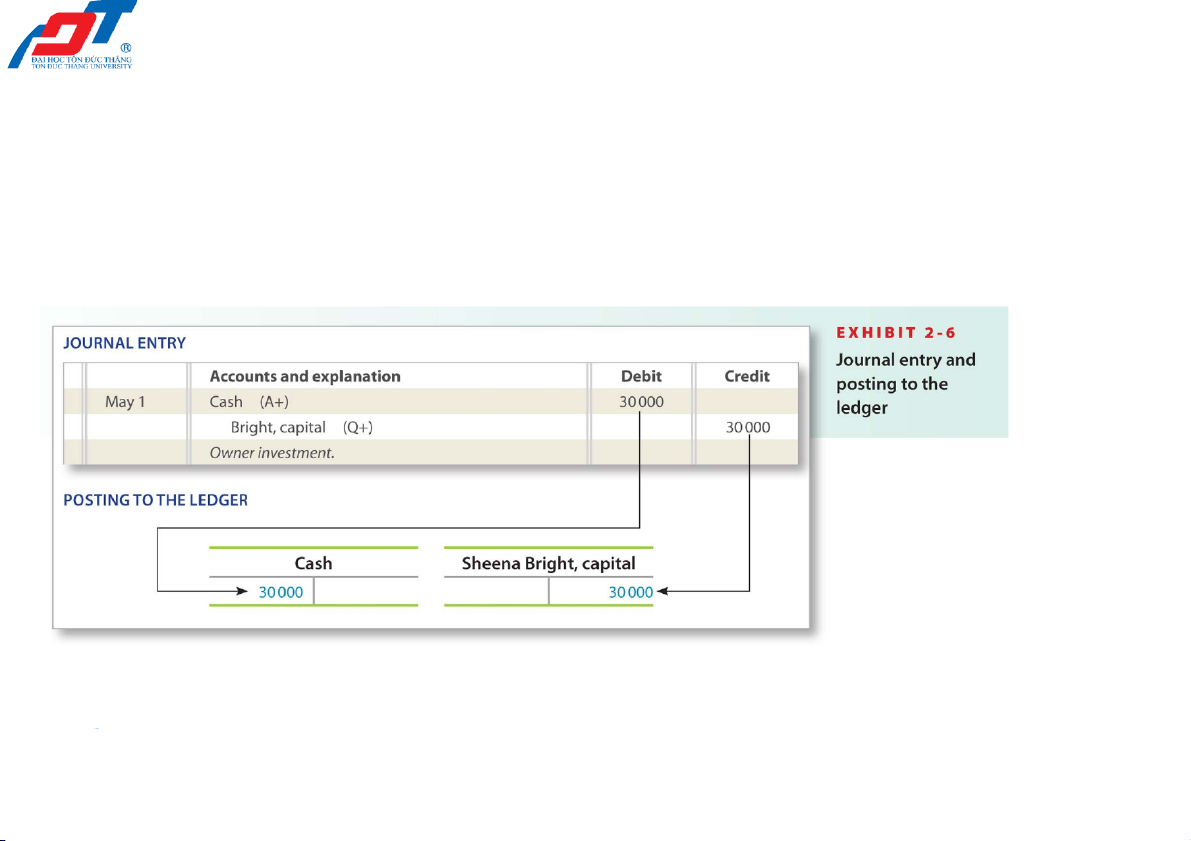
2.4. Transactions analysis, journalizing
and posting to the accounts
Copying information (posting) from the journal to the ledger 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 14
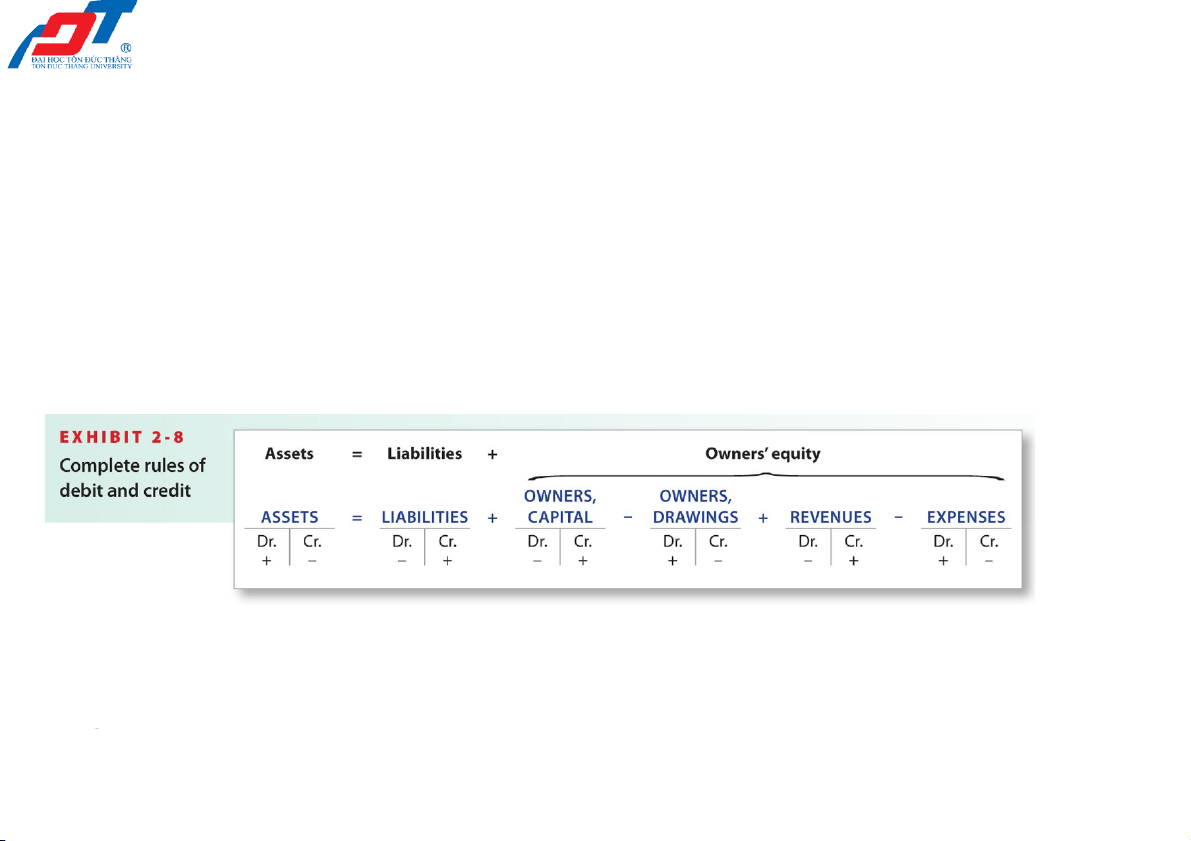
2.4. Transactions analysis, journalizing
and posting to the accounts
The normal balance of an account
(Expanding the accounting equation to
account for revenues and expenses) 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 15
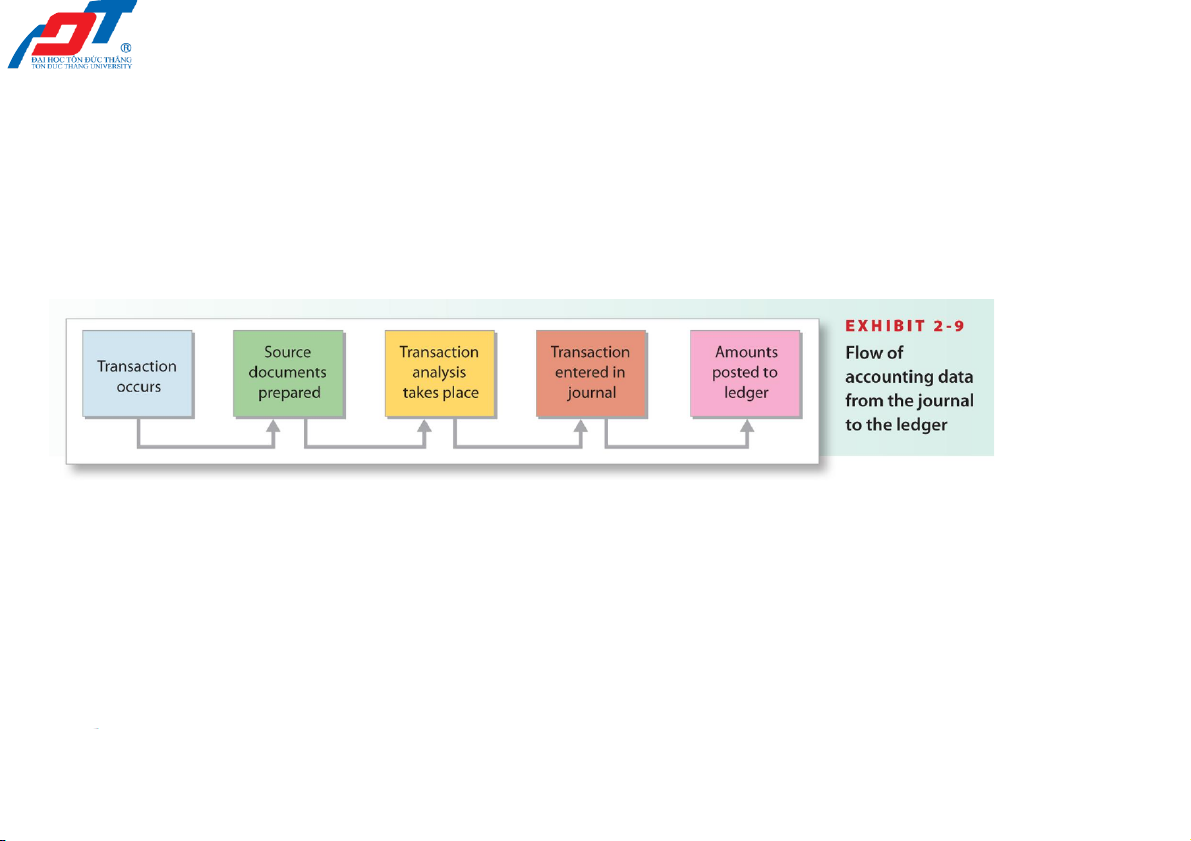
2.4. Transactions analysis, journalizing
and posting to the accounts
Summarise: Flow of accounting information 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 16
2.4. Transactions analysis, journalizing
and posting to the accounts
Eg: Practice journalizing and posting with specific examples:
Details of transactions occurred at Smart Touch business on May 20X2
(1) Sheena Bright invested $30,000 cash in the business.
(2) Paid $20,000 cash for land.
(3) Bought $500 of office supplies on credit.
(4) Received $5,500 cash from clients for service revenue earned.
(5) Performed training service for clients on credit, $3,000.
(6) Paid cash expenses: computer lease, $600; office rent, $1,100;
employee salary, $1,200; electricity and gas, $400. 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 17
2.4. Transactions analysis, journalizing
and posting to the accounts
E.G (Cont.) Practice journalizing and posting with specific examples:
(7) Paid $300 on the account payable created in transaction 3.
(8) Remodelled Sheena Bright’s personal residence. This is not a transaction of the business.
(9) Collected $1,000 on the account receivable created in transaction 5.
(10) Sold land for cash at its cost of $9,000.
(11) Withdrew $2,000 cash for personal expenses. 2/23/2022
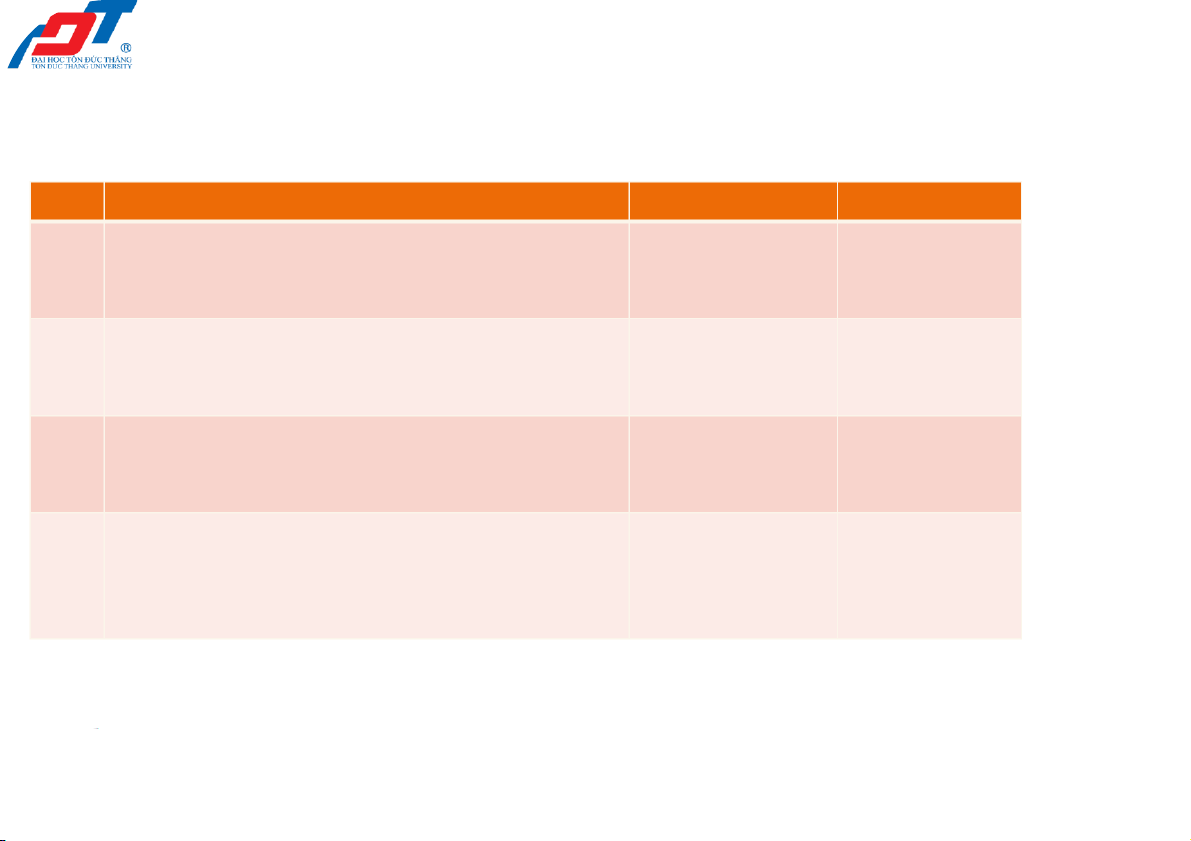
201039 _ Recording business transactions 18 Record to the JOURNAL Smart Touch Learning May 20X2 Journal
No. Accounts & Explanation Debit Credit (1) (2) (3) (4) 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 19
Record to the JOURNAL (Cont.)
No. Accounts & Explanation Debit Credit (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) 2/23/2022
201039 _ Recording business transactions 20




