














Preview text:
HCMC UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND EDUCATION
FACULTY FOR HIGH QUALITY TRAINING PROCESS REPORT
RESEARCH AND TESTING ANTI LOCK BRAKING
SYSTEM AND TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM OF
HONDA CIVIC 2020 BY MATLAB AND CARSIM SOFTWARE Student name: BUI TRAN NGUYEN KHOA 19145192 CAO CHI TINH 19145002 NGUYEN MINH KHANG 19145188 Course: SPECIAL PROJECT Advisor: Ph.D. NGUYEN MANH CUONG Ho Chi Minh City, June 2022
HCMC UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND EDUCATION
FACULTY FOR HIGH QUALITY TRAINING PROCESS REPORT
RESEARCH AND TESTING ANTI LOCK BRAKING
SYSTEM AND TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM OF
HONDA CIVIC 2020 BY MATLAB AND CARSIM SOFTWARE Student name: BUI TRAN NGUYEN KHOA 19145192 CAO CHI TINH 19145002 NGUYEN MINH KHANG 19145188 Course: SPECIAL PROJECT Advisor: Ph.D. NGUYEN MANH CUONG Ho Chi Minh City, June 2022
THE SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM
Independence – Freedom– Happiness --------
Ho Chi Minh City, June 12, 2022 PROJECT ASSIGNMENT
Student name: __________________________
Student ID: ___________________
Student name: __________________________
Student ID: ___________________
Student name:___________________________
Student ID: ___________________
Major: ________________________________
Class: ________________________
Advisor: ____________________________
Phone number: _________________
Date of assignment: _____________________
Date of submission: _____________
1. Project title: _________________________________________________________
2. Initial materials provided by the advisor: ___________________________________
3. Content of the project: _________________________________________________
4. Final product: ________________________________________________________ CHAIR OF THE PROGRAM ADVISOR (Sign with full name) (Sign with full name)
THE SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM
Independence – Freedom– Happiness --------
Ho Chi Minh City, June 12, 2022
ADVISOR’S EVALUATION SHEET
Student name:______________________________ Student ID:_____________ Major: Automotive Engineering
Project title: Research and Testing the Anti Lock Braking System and Traction
Control System on Honda Civic 2020 by MATLAB and Carsim Software
Advisor: ............................................................................................................... EVALUATION 1. Content of the project:
......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... 2. Strengths:
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... 3. Weaknesses:
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
4. Approval for oral defense? (Approved or denied)
......................................................................................................................................
5. Overall evaluation: (Excellent, Good, Fair, Poor)
......................................................................................................................................
6. Mark: ………………. (in word.........................................................................)
Ho Chi Minh City, September 19, 2021 ADVISOR (Sign with full name) ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors gratefully acknowledge the valuable supports from Ph.D. Nguyen Manh
Cuong from Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and Education.
CHAPTER I: OVERVIEW OF CAR BRAKE SYSTEM
1. Purpose and meaning of the topic
Currently, cars have become an important means of transporting passengers and goods
for national economic sectors, and at the same time have become a private means of
transport in countries with developed economies. In our country, the number of people
using cars is increasing, along with the growth of the economy, the increasing density of
cars on the road leads to more and more traffic accidents. Therefore, to ensure the safety
of traffic accidents is one of the most necessary solutions, always concerned by the
designers and manufacturers of cars, where the brake system plays a very important
role. Because of that, now the brake system is increasingly improved, the standards for
the design, manufacture and use of the brake system are increasingly strict and strict.
For students majoring in traffic mechanics, the survey and testing of the brake system is
even more practical. That's why I chose the topic "Surveying, calculating and testing the
ABS brake system on Honda Civic 2020". To solve this problem, first of all, we need to
understand the operating principle, structure of details and parts in the brake system.
Thereby creating a premise for the design and improvement of the brake system to
increase braking efficiency, increase directional stability and guideability when braking,
increase working reliability for the purpose of ensuring movement safety and increasing safety. vehicle performance. 2.
Uses, classifications and requirements of the brake system. 2.1 Uses
The brake system is used to slow down the vehicle until it comes to a complete stop or
reaches a certain speed. In addition, the brake system also ensures to keep the vehicle
stationary during stopping, especially when stopping on a slope. For cars, the brake
system is one of the most important systems, because it ensures the car's safe movement
at high speed, allowing the driver to adjust the speed of movement or stop the vehicle in
the middle. dangerous situations, thereby improving transportation productivity and
safety for people and goods during vehicle operation. 2.2 Classifications
- Classification according to use: + Main brake system + Stop brake system
- Classification according to the position of the brake mechanism + Brake at the wheel
+ Brake at drive shaft (after transmission)
- Classification according to the structure of the brake mechanism 1 + Brake clogs + Brakes + Disc brake
- Classification by mode of drive + Mechanical brake drive + Hydraulic brake drive
+ Pneumatic (vapor) brake drive
+ Combined brake drive (hydraulic + pneumatic) + Power-assisted brake drive 2.3 Requirements
The brake system is an important part of the car that performs "active safety" functions,
so the brake system must satisfy the following requirements:
+Has the highest braking efficiency on all wheels under all circumstances
+Quiet operation to ensure the stability of the car when braking
+Smooth control to reduce the driver's labor intensity
+Has high sensitivity to quickly adapt to dangerous situations
+The brake mechanism has no self-tightening phenomenon
+The brake mechanism must have good heat dissipation
+Has a high and stable coefficient of friction
+Keeping the ratio between the force applied to the brake pedal and the braking
force generated by the brake mechanism
+The system must have reliability, durability and long life
+Streamlined layout for easy adjustment of care and maintenance 3.
Structure of disc brakes
Disc brake mechanism is commonly used on passenger cars (mainly on the front
wheels). Recently, this type of brake began to be used on some types of transport and passenger cars.
Disc brakes are of the following types: closed, open, single disc, multi-disc, rotating
housing type, rotating disc, rotating friction ring.
The disc can be a solid disc, a disc with vented slots, a single layer of metal, or a
composite of two dissimilar metals. In automobiles, the main type of open disc is used,
and rarely the rotary shell type is used.
There are two mounting options for clamps: fixed mounting and optional swimming
style mounting. Fixed mounting plan has high rigidity, allowing large driving force to
be used. However, the cooling condition is poor, and the working temperature of the brake mechanism is higher. 2
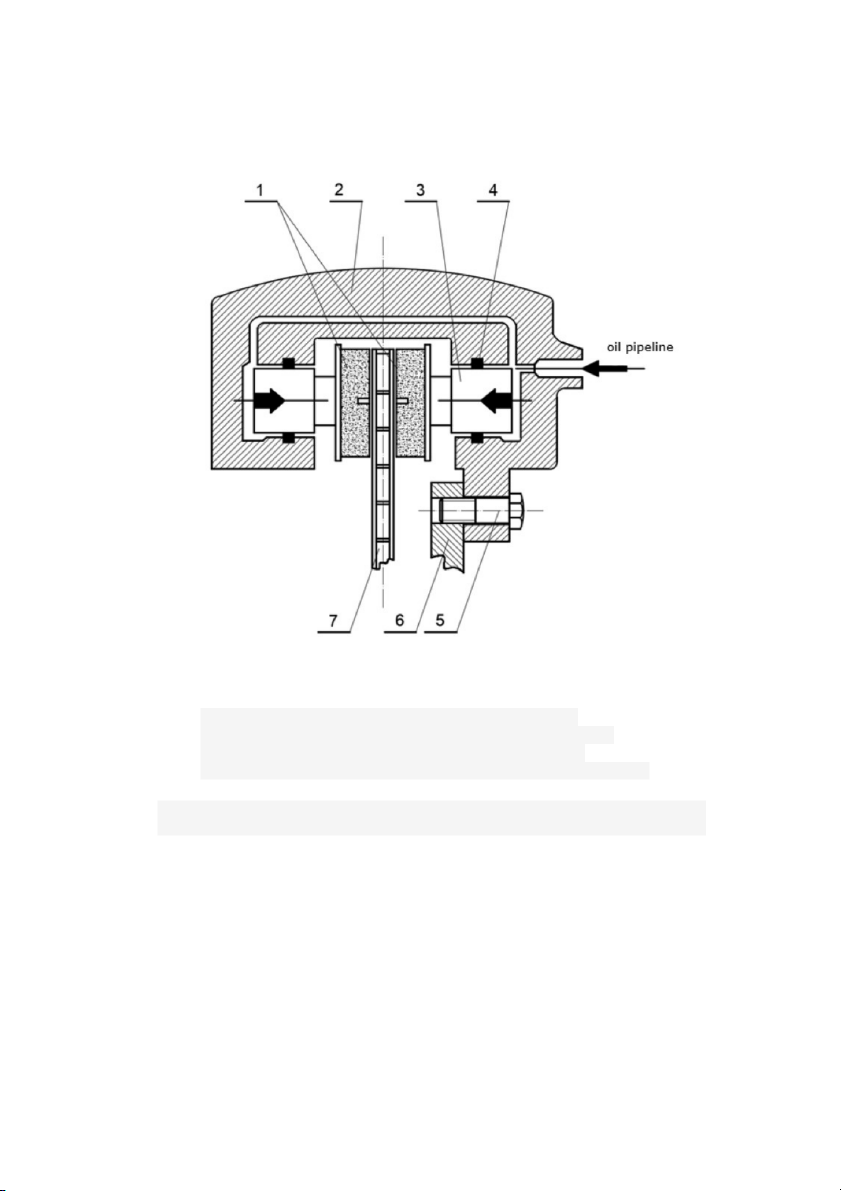
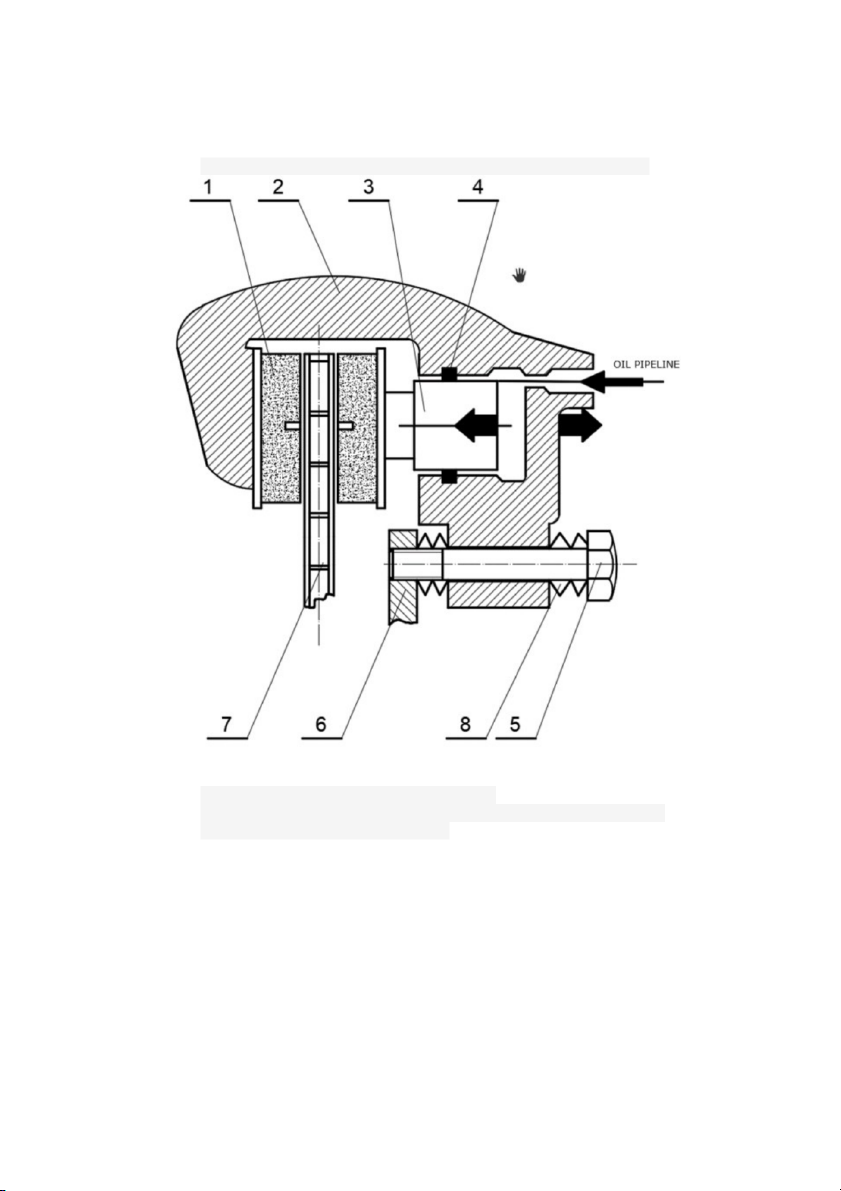
Figure 1 : Structure diagram of disc brake with fixed clamp type. 1. Brake Pads 5. Guide Pin 2. Fixed Clamp 6. Locating Gauze 3. Piston 7. Brake Disc 4. Sealing Ring 8. Shock Absorber Ring
To fix it, you can use the automatic clamp type. The chuck can be split or integrated
with the wheel cylinder and slide on fixed guide pins. Such structures have low 3
stiffness. When the guide pins are deformed, wear and tear will cause the brake pads to
wear unevenly, reduce the braking efficiency and cause vibration. However, it has only
one hydraulic cylinder with twice the length, so the cooling condition is better, the brake
fluid is less hot, the working temperature can be reduced by 30 ÷ 50 ˚C. In addition, it
also allows deep translation of the brake mechanism into the wheel. Thereby reducing
the lever arm acting on the rolling resistance to the vertical cylinder of the guide wheels.
Figure 2: Structural diagram of disc brake with automatic clamp type - fixed cylinder 1. Brake Pads 5. Guide Pin 2. Fixed Clamp 6. Locating Gauze 3. Piston 7. Brake Disc 4 4. Sealing Ring 8. Shock Absorber Ring
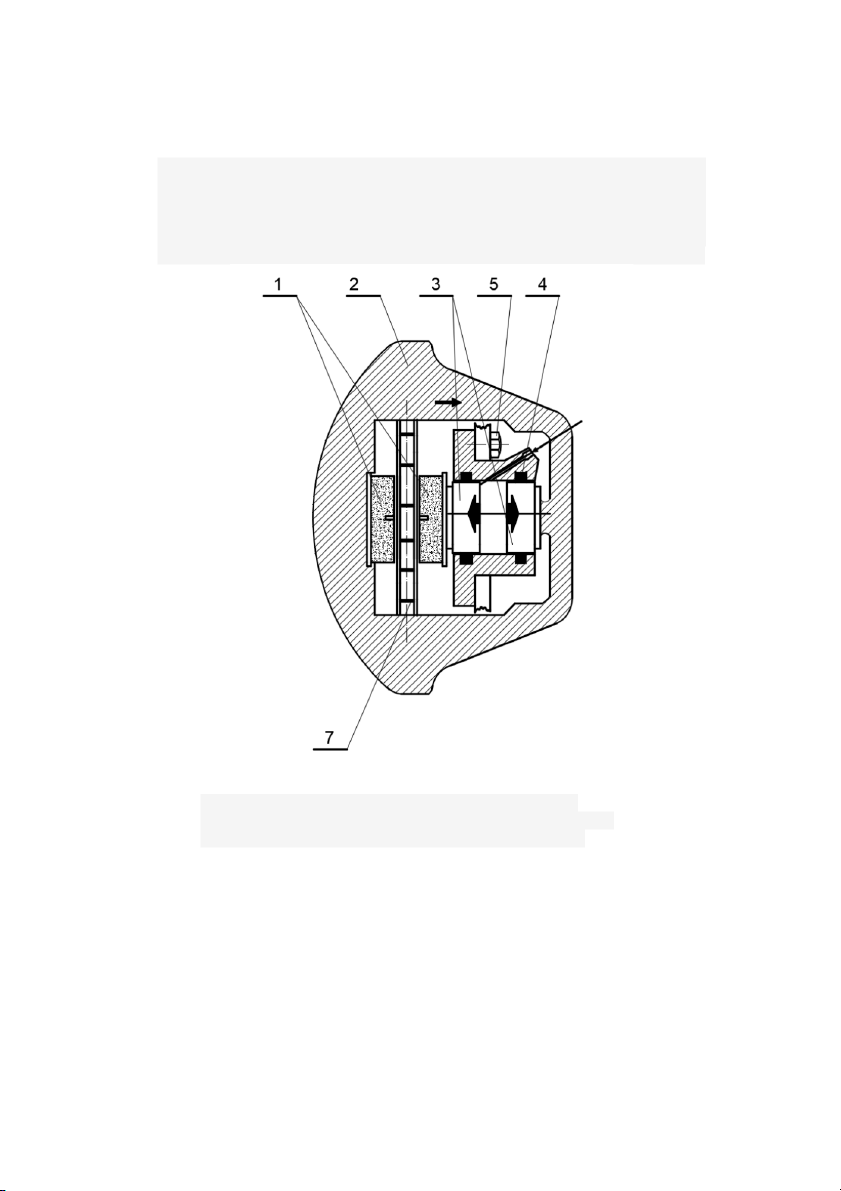
Figure 3: Some causes of brake failure and consequences 1. Brake Pads 5. Hydraulic oil line 2. Fixed Clamp
6. Direction of Displacement Piston and Clamp 3. Piston 7. Guide Pin 5 4. Sealing Ring 8. Ventilation Grooves 9. Brake Disc -
Advantages of disc brake mechanism compared with drum-hoop brake mechanism
+ Able to work with a small gap of 0.05 ÷ 0.15 mm, so it is very sensitive, reduces
the delay time and allows to increase the gear ratio.
+ The pressure is evenly distributed over the surface of the brake pads, so the brake pads wear evenly.
+ Simple maintenance since no clearance adjustment is required.
+ The axial and self-balancing forces should allow their values to be increased to
achieve the required braking effect without being limited by the deformation
conditions of the structure. Therefore, disc brakes are compact in size and easy to arrange in the wheel.
+ The braking effect is independent of rotation direction and more stable.
+ Better cooling conditions, especially with the rotating disc type. -
Disadvantages of disc brake mechanism compared to drum-hoo brake mechanism:
+ Sensitive to dirt and difficult to seal.
+ Open type brake discs are easily oxidized and dirty, causing the brake pads to wear quickly.
+ High working pressure makes the brake pads easy to crack and scratch.
+ It is often necessary to use vacuum boosters to increase driving force, so when the
engine is not working effectively, the brake performance is low and it is difficult
to use them to combine as a stop brake. -
Structural characteristics of the main details and parts:
+ Brake disc: usually made of cast iron. Solid discs are 8 - 13 mm thick. Ventilated
slotted disc 16 - 25 mm thick. The coupling disc can have an aluminum or copper
core and a friction surface – gray cast iron.
+ Clamp: usually cast in wrought iron.
+ Hydraulic cylinders: cast aluminum alloy. To increase wear resistance and reduce
friction, the working surface of the cylinder is chrome plated. When the cylinder is
made of aluminum alloy, it is necessary to reduce the heating temperature of the
brake fluid. One of the ways to reduce the temperature of brake fluid is to reduce
the contact area between the piston and the brake shoe or to use pistons made of non-metallic materials.
+ Brake pad bodies: the place where the piston presses up is made of sheet steel.
+ Friction plate: of open disc brake pads usually have a surface area of about 12 -
16% of the disc surface area, so disc cooling conditions are very favorable. 6
4. Some causes of brake failure and consequences 4.1 Causes
One of the most common causes of “brake failure” accidents is a loss of brake fluid
pressure. The brake is operated by hydraulic pressure inside the system. Therefore, if
there is a leak of brake fluid in the brake fluid line or brake cylinder, the brake system
will not have enough pressure to perform the deceleration. When a serious leak occurs,
the brake fault light will light up to warn you and the vehicle will not be safe to operate in this condition.
Check the brake fluid tank, if the oil level is too low, it means there is a serious brake
fluid leak, need to check the entire brake system to find out where the leak is and fix it.
Leaks have many causes, but if the brake fluid level is too low, it means that the rubber
seal in the brake system is broken or the oil line is rusty.
Figure 4: Brake fluid in hydraulic drive
The brake lines are made of copper and can corrode quickly in some special places,
after a period of time will wear out and have poorer quality than other places on the oil
pipe, so the brake fluid will leak. rust and the vehicle may lose its brakes. 7
If the brake pedal is not effective, there may be air in the system. At this time, it is
necessary to vent the brake system to remove air bubbles. Sometimes it can also be
because the piston inside the master cylinder is damaged.
Figure 5: Low oil pressure indicator light
Another possible cause of brake failure is a faulty ABS controller. Due to the leak, the
internal pressure drops and the brake pressure cannot be transferred when the brake is
applied. Contamination inside the brake fluid can also enter the control unit and prevent
the intake and exhaust valves from opening and closing, causing the brakes to fail. 8
Figure 6: When the ABS controller fails, the light will warn
The cause of brake failure can also be caused by the driver, that is, pressing the brakes
continuously for a long time (usually when the vehicle is going downhill on a pass)
causes the brake pads to burn, leading to ineffective braking. To avoid this, the driver
should not apply the brakes for a long time, instead can use the engine to reduce the
vehicle's speed (by engaging in low gear).
Figure 7: The car goes downhill on the pass 9 4.2 Consequences
Some unexpected accidents related to brake failure, loss of control
Figure 8: The bus lost its brakes and rolled many motorbikes at the red light 10
Figure 9 : Passenger car lost the brake
The brake is the part that helps the vehicle decelerate to reduce motion. However, after
many accidents, the question often arises, why does the brake lose its effect? Is it
because of the driver or the quality of the car?
In theory, the car may not be properly maintained, have technical errors such as lack of
brake fluid, full oil in the master cylinder, broken wheel axles, gas entering the brake
fluid... leading to brake failure. do not eat or lose the effect completely.
But for drivers, the habit of going downhill or going up a high pass, the driver checks
the brakes incorrectly, goes downhill and drifts the throttle... to slow down is extremely
dangerous. This causes the brake pads and brake fluid to heat up. High temperatures can
soften the gasket at the master cylinder, allowing brake fluid to escape when the driver
applies the brake. This causes the braking system to lose its effect or in other words, lose the brakes.
To solve this problem, first of all, we need to understand the operating principle,
structure of details and parts in the brake system. Thereby creating a premise for the
design and improvement of the brake system to increase braking efficiency, increase 11
directional stability and guideability when braking, increase working reliability for the
purpose of ensuring movement safety and increasing safety. vehicle performance. It is
for these reasons that I have chosen this topic.
CHAPTER II: INTRODUCE ABOUT HONDA CIVIC 2020
1. The Overall of Honda Civic 2020
In the Vietnamese market, the Honda Civic model right after its launch has always
received positive feedback from consumers. Over 10 generations, this small sports C-
class sedan has quickly entered the list of Top 10 best-selling cars of all time, Honda
Civic has become a typical representative of Honda, in terms of agility, in terms of
flexibility and especially in terms of reliability.
Figure 10: The exterior appearance of the Honda Civic 2020
Unconventional styling with solid lines but still emotional flexibility along with high-
class details, gives Civic a youthful, modern and sportier appearance than ever. In
particular, the aerodynamic design style also helps to complete the fuel efficiency and quietness of the cabin. 12
This is the most spectacular makeover ever of this small sedan. With an all-new
fastback design, the most powerful turbo engine in the segment, and many safety-
driving assist technologies are notable points in this version.
In Vietnam, Honda Civic is being distributed with 03 versions, which are the standard
Civic 1.8E CVT with naturally aspirated gas, the turbocharged Civic 1.8G CVT and the
high-end Civic 1.5RS CVT Turbo. 2. Honda Civic Overview 2.1
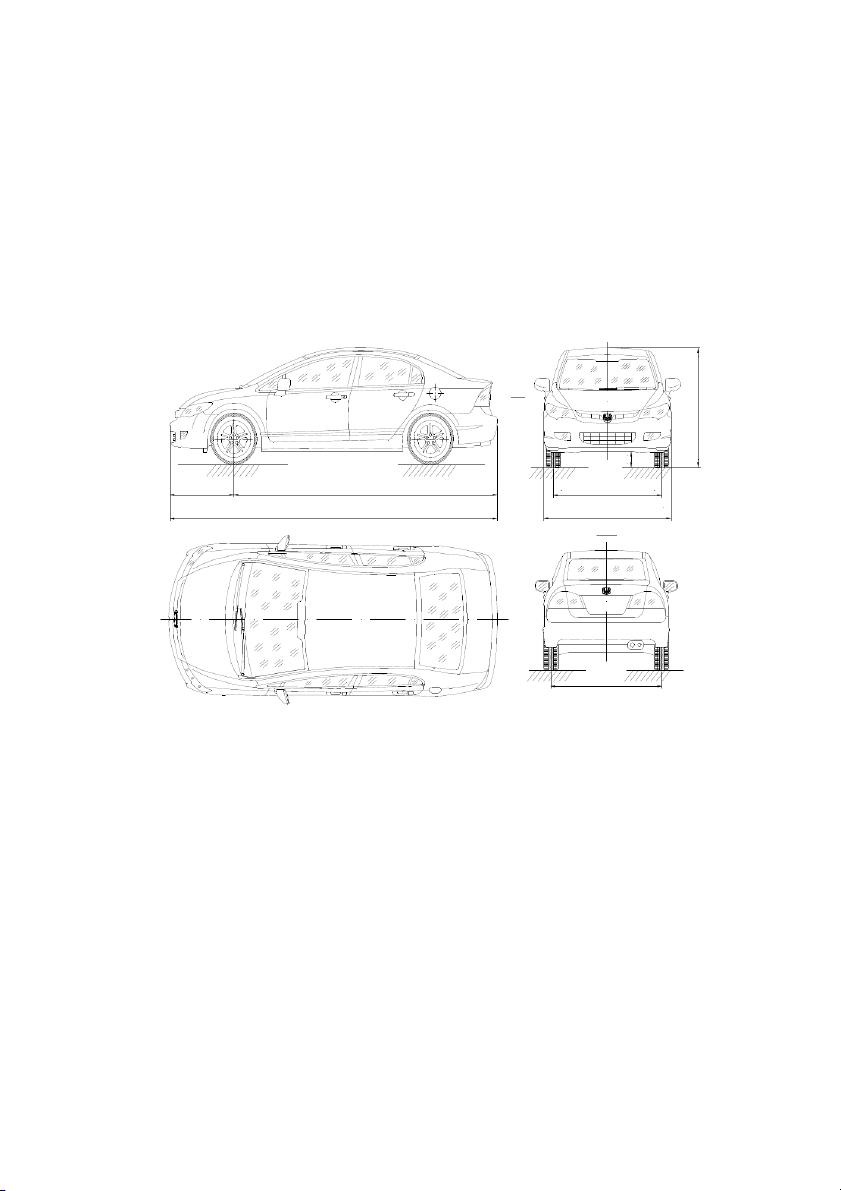
Overview of Honda Civic cars A 6 41 1 33 1 974 2700 1537 4648 1799 Theo A 1553
Figure 11: Overall diagram of Honda Civic car 13
2.2 Technical characteristics of the vehicle
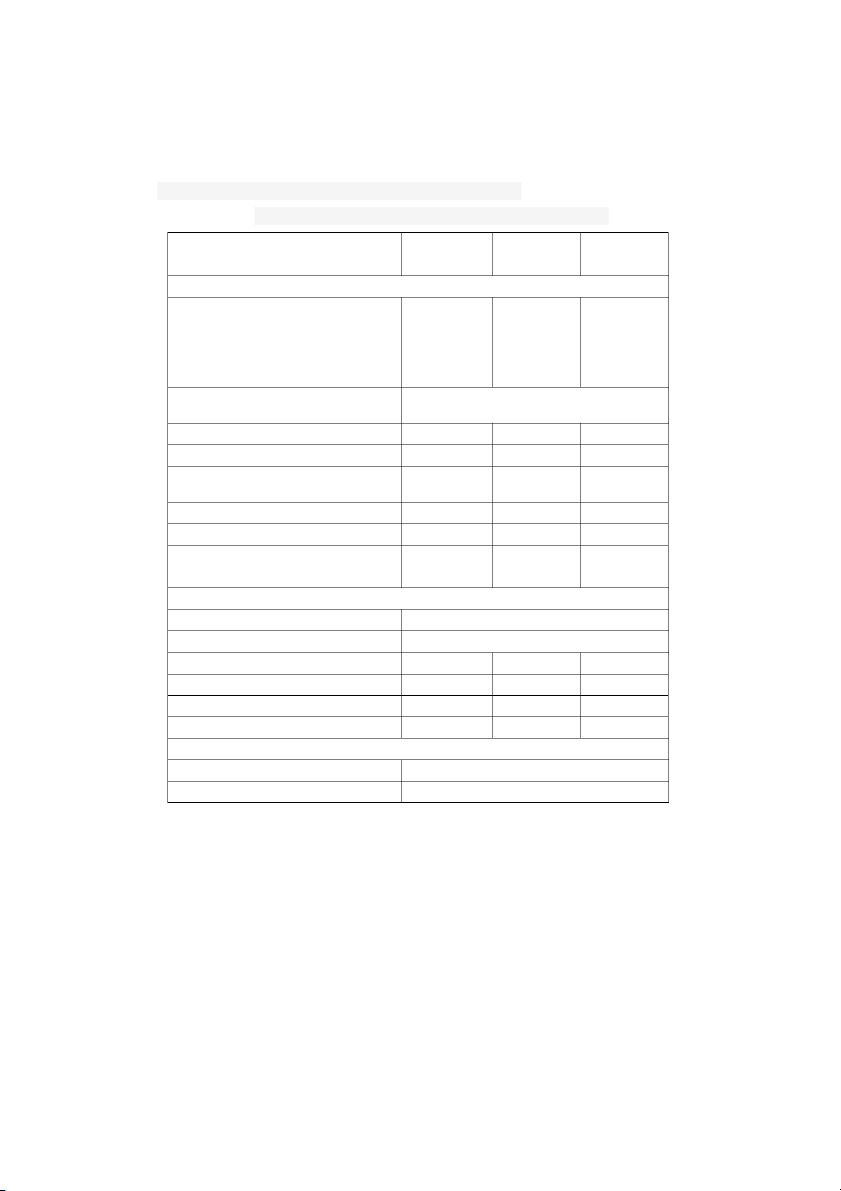
2.2.1 Honda Civic specifications are listed in the table 1
Table 1: Basic technical parameters of Honda Civic 2020 CIVIC 1.8 CIVIC 1.8 CIVIC1.5 CATEGORY E G RS TRANSMISSION ENGINE 1.8 SOHC i- 1.8 SOHC 1.5L VTEC i-VTEC DOHC ENGINE STYLE 4 cylinders 4 cylinders VTEC in line 16 in line 16 TURBO valves valves (CVT) EARTH DREAMS TRANSMISSION TECHNOLOGY Cylinder capacity (cm3) 1.799 1.799 1.498 Maximum power (Hp/rpm) 139/6.500 139/6.500 170/5.500 220/1.700- Maximum torque (Nm/rpm) 174/4.300 174/4.300 5.500 Fuel tank capacity (litre) 47 47 47 Fuel system PGM-FI PGM-FI PGM-FI Acceleration time from 1 to 10 10 8.3 100km/h (giây) SIZE/WEIGHT Length x Width X Height (mm) 4.648 x 1.799 x 1.416 The standard long (mm) 2700 Tire size 215/55R16 215/55R16 235/40R18 Lazang (inch) 16 16 18 Ground clearance (mm) 133 133 133 Minimum turning radius (m) 5.3 5.3 5.3 BRAKING SYSTEM Front brake Disc brake Rear brake Disc brake 2.2.2 Engine 14
Figure 12: Engine on Honda Civic 2020
The first engine block equipped on the standard versions Civic 1.8E & Civic 1.8G is a
naturally aspirated 1.8 SOHC i-VTEC engine, 4 cylinders, 16 valves. This engine block
delivers a maximum power of 139 (hp) at 6,500 rpm (rpm), along with a maximum
torque of 174 (Nm) at 4,300 (rpm). Comes with a CVT automatic transmission using
Honda's Earth Dreams technology. In versions 1.8E & 1.8G naturally aspirated with
electronic fuel injection, Civic will own a maximum speed of 200 (Km/h), with
acceleration time from 0 - 100 (Km/h) within just 10 (seconds), a pretty impressive number.
The second engine block equipped on the two high-end Civic 1.5RS versions is the
famous 1.5L DOHC VTEC TURBO turbocharged engine of the 10th generation. The
maximum power that this machine brings is 170 (hp). at 5,500 rpm (rpm), maximum
torque is 220 (Nm) at 1,700 - 5,500 rpm (rpm). This Honda Civic 1.5RS version is
supported by CVT gearbox, Earth Dreams Technology application. Like the 1.8E and
1.8G versions, the 1.5RS version has a maximum speed of 200 (Km/h), but with faster
acceleration, from 0 to 100 (Km/h) only takes 8.3 (seconds), an impressive number.
VTEC TURBO is a new generation of Honda's breakthrough turbocharged engine that
helps the car achieve two factors simultaneously: strong performance and outstanding
fuel economy - Overcoming the disadvantages of traditional turbocharged engines when 15




