







Preview text:
Chapter 6 Retail inventory 201044 - Retail inventory 1 Learning objectives
• Define accounting principles related to inventory
• Define inventory costing methods
• Account for perpetual inventory using the three most common costing methods
• Compare the effects of the three most common inventory costing methods 201044 - Retail inventory 2 4/6/2022
6.2. Inventory costing methods
• The specific-unit-cost method uses the specific cost of each unit
of inventory to determine ending inventory and to determine cost of sales
• The FIFO (first-in, first-out) inventory costing method bases the
cost of sales on the oldest purchases
• Under the average-cost inventory costing method, the business
calculates a new average cost per unit after each purchase
• The different inventory costing methods produce different amounts
for ending inventory and cost of goods sold 201044 - Retail inventory 3 4/6/2022
6.3. Inventory accounting in a perpetual system
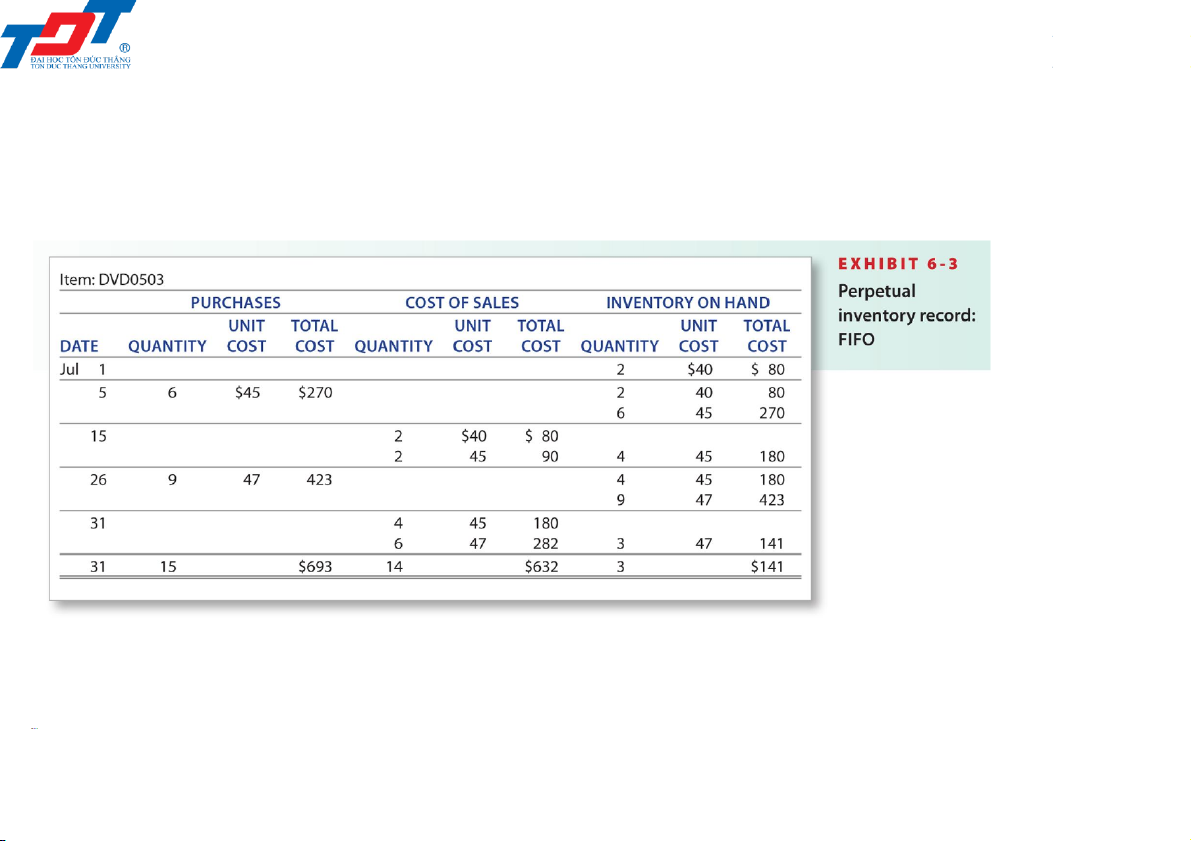
First-in, first-out (FIFO) method 201044 - Retail inventory 4 4/6/2022
6.3. Inventory accounting in a perpetual system
First-in, first-out (FIFO) method Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 5 Inventory (6 × $45) (A+) 270 Accounts payable (L+) 270
Purchased inventory on credit. Jul 15
Accounts receivable (4 × $80) (A+) 320 Sales revenue (R+) 320 Sale on credit. Jul 15
Cost of sales (2 @ $40 + 2 @ $45) (E+) 170 Inventory (A–) 170 Cost of sales. 201044 - Retail inventory 5 4/6/2022
6.3. Inventory accounting in a perpetual system
First-in, first-out (FIFO) method Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 26 Inventory (9 × $47) (A+) 423 Accounts payable (L+) 423
Purchased inventory on credit. Jul 31
Accounts receivable (10 × $80) (A+) 800 Sales revenue (R+) 800 Sale on credit. Jul 31
Cost of sales (4 @ $45 + 6 @ $47) (E+) 462 Inventory (A–) 462 Cost of sales. 201044 - Retail inventory 6 4/6/2022
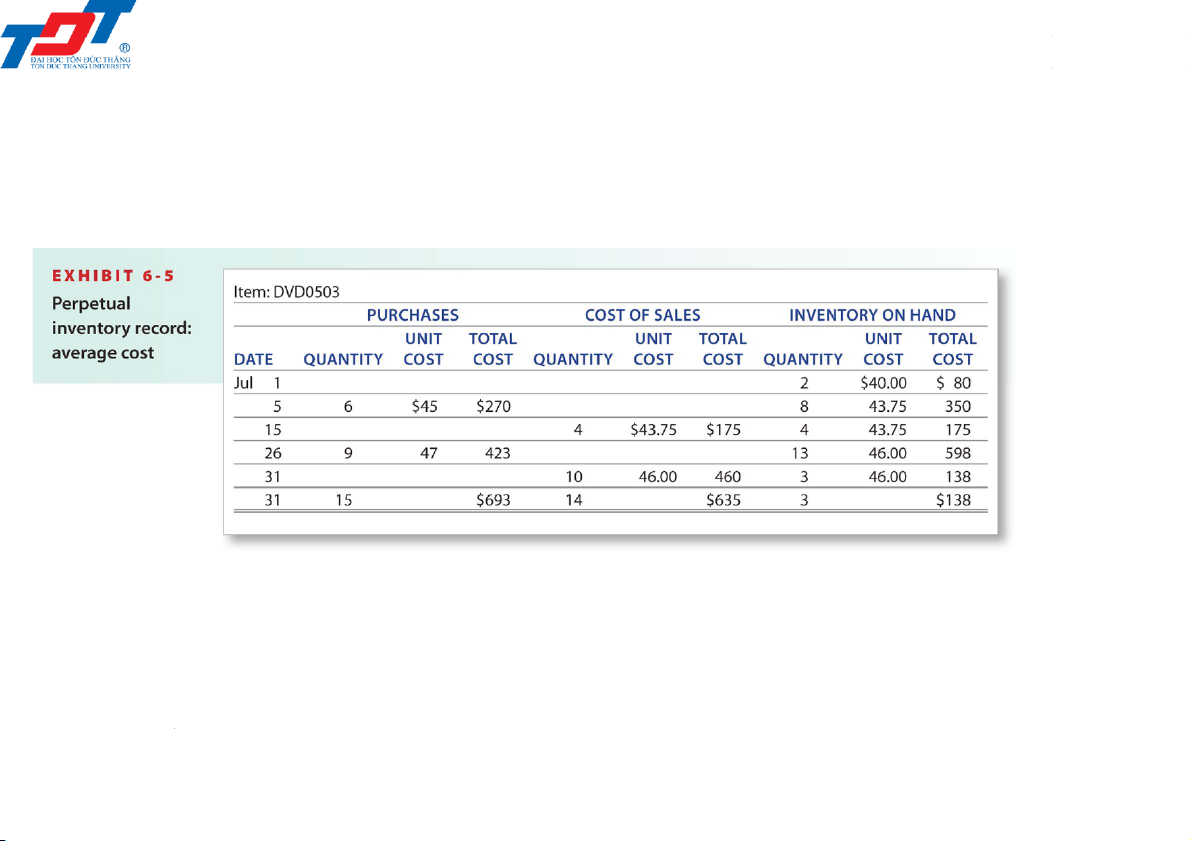
6.3. Inventory accounting in a perpetual system Average-cost method 201044 - Retail inventory 7 4/6/2022
6.3. Inventory accounting in a perpetual system Average-cost method Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 5 Inventory (6 × $45) (A+) 270 Accounts payable (L+) 270
Purchased inventory on credit. Jul 15
Accounts receivable (4 × $80) (A+) 320 Sales revenue (R+) 320 Sale on credit. Jul 15
Cost of sales (4 @ $43.75) (E+) 175 Inventory (A–) 175 Cost of sales. 201044 - Retail inventory 8 4/6/2022
6.3. Inventory accounting in a perpetual system Average-cost method Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 26 Inventory (9 × $47) (A+) 423 Accounts payable (L+) 423
Purchased inventory on credit. Jul 31
Accounts receivable (10 × $80) (A+) 800 Sales revenue (R+) 800 Sale on credit. Jul 31
Cost of sales (10 @ $46.00) (E+) 460 Inventory (A–) 460 Cost of sales. 201044 - Retail inventory 9 4/6/2022
6.4. Comparing FIFO and average cost Average-cost method FIFO Average cost Sales revenue $1 120 $1 120 Cost of sales 632 635 Gross profit $488 $485 201044 - Retail inventory 10 4/6/2022 Summary: Chapter 6
• The accounting principles are the foundations that guide how we record transactions
• Inventory costing methods include specific-unit-cost, FIFO and average cost
• Specific unit identifies the specific cost of each unit of inventory
that is in ending inventory and each item that is in cost of goods sold
• Under LIFO, the cost of goods sold is based on the newest purchases
• Under the average-cost method, the business computes a new
average cost per unit after each purchase 201044 - Retail inventory 11 4/6/2022 Tasks at home 1/ Textbook: Chapter 6 • Quick Check • Starters • Exercises and Problems • Apply 2/ Self-study: Key References [2]: Chapter 11 Key References [3]: Chapter 3 201044 - Retail inventory 12 4/6/2022 The end of Chapter 6 Retail inventory 201044 - Retail inventory 13




