









Preview text:
Chapter 5 Retailing operations 201044 - Retailing operations 1 Learning objectives
• Describe retailing operations, perpetual and periodic inventory
systems and understand how to account for GST
• Account for the purchase of inventory using a perpetual system
• Account for the sale of inventory using a perpetual system
• Adjust and close the accounts of a retailing business
• Prepare a retailer’s financial statements
• Use gross profit percentage, inventory turnover and days in
inventory to evaluate a business 201044 - Retailing operations 2 4/6/2022
5.1. What are retailing operations?
• Retailing consists of buying and selling goods rather than services
• Retailers have some new balance sheet and income statement
items, for example Inventory, Sales revenue, and Cost of sales
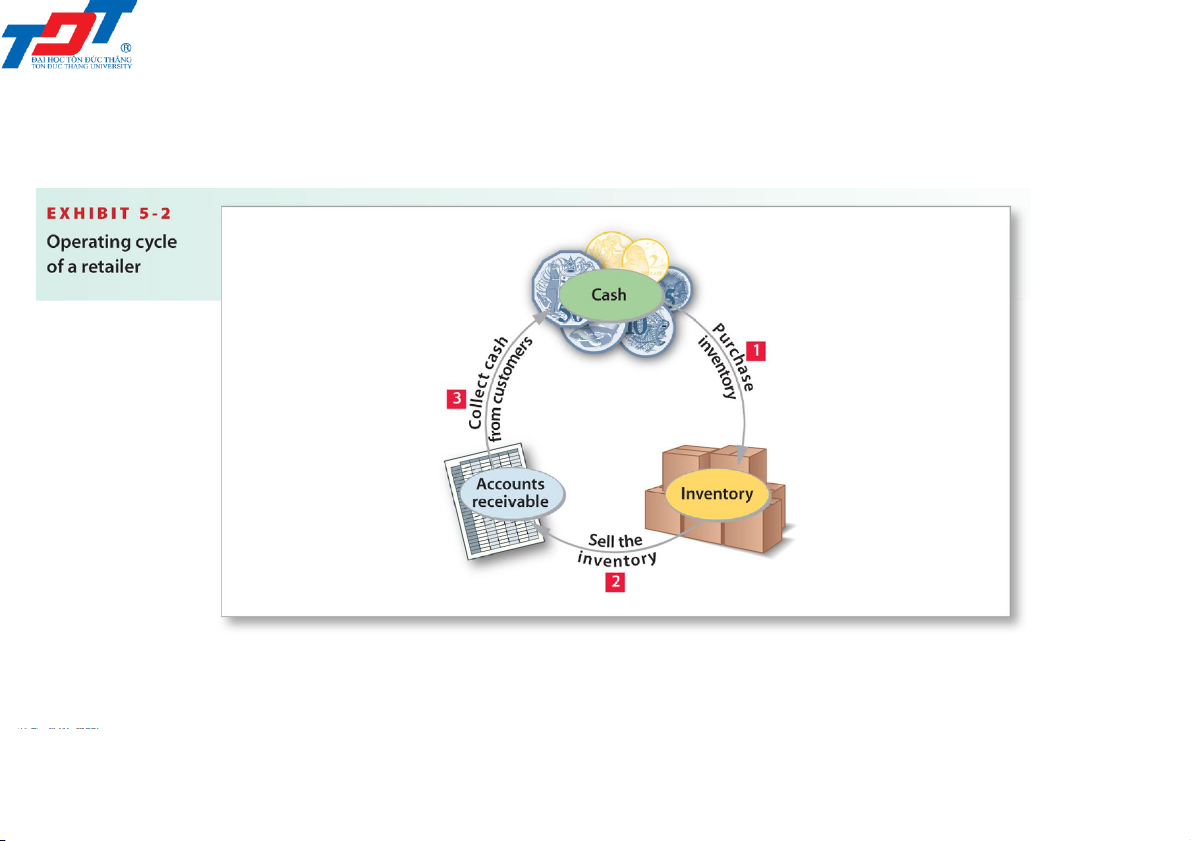
• The operating cycle of a retailing business begins when the business
purchases inventory from a vendor. It then sells the inventory to a
customer. Finally, the business collects cash from customers 201044 - Retailing operations 3 4/6/2022
5.1. What are retailing operations? 201044 - Retailing operations 4 4/6/2022
5.1. What are retailing operations?
Goods and services tax (GST)
• GST is a tax levied on the supply of goods and services
• The tax is a flat percentage charge
• Each firm registered for GST collects tax on the goods and services
it supplies and pays tax on the goods and services it buys
• The firm then deducts the tax it pays on purchases from the tax it
charges on sales and pays the balance to the Australian Taxation Office 201044 - Retailing operations 5 4/6/2022
5.1. What are retailing operations?
Inventory systems: Perpetual and Periodic
• The periodic inventory system is normally used for relatively inexpensive goods
• Goods are counted periodically to determine quantity
• The perpetual inventory system keeps a running computerised record of inventory
• The number of inventory units and the dollar amounts are
perpetually (constantly) updated
• It records units purchased and cost amount, units sold and sales
and cost amounts, and the quantity of inventory on hand and its cost 201044 - Retailing operations 6 4/6/2022
5.2. Accounting for inventory in the perpetual system 201044 - Retailing operations 7 4/6/2022
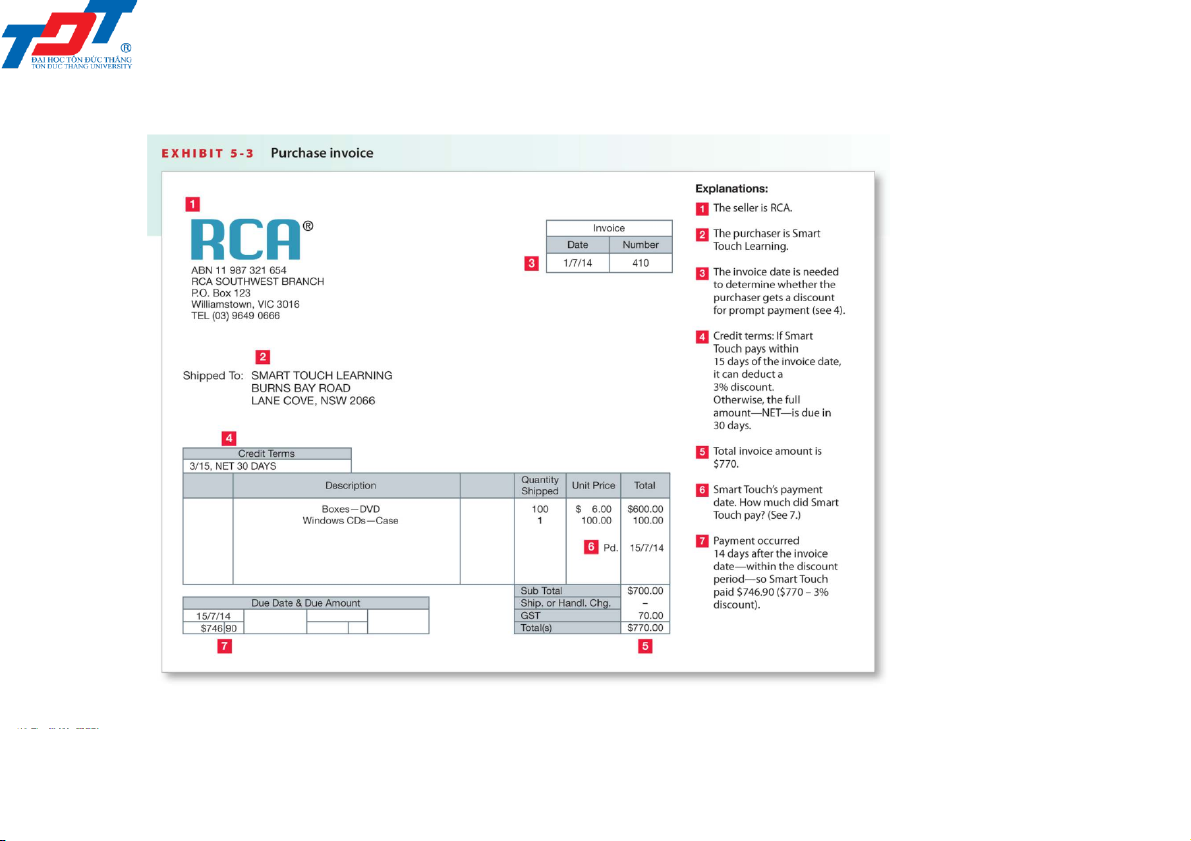
5.2. Accounting for inventory in the perpetual system Purchase of Inventory
• The inventory account is increased with each purchase
• The vendor submits an invoice for payment
• The inventory account is used for goods purchased
• The method of payment is credited Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 3 Inventory (770/1.1) (A+) 700 GST clearing (770/11) (A+) 70 Accounts payable (L+) 770
Purchased inventory on credit. 201044 - Retailing operations 8 4/6/2022
5.2. Accounting for inventory in the perpetual system
• Many businesses offer customers a settlement discount for early payment
• RCA’s credit terms of ‘3/15, Net 30 days’ mean that Smart Touch
can deduct 3% from the total bill (excluding freight charges, if any) if
the business pays within 15 days of the invoice date 201044 - Retailing operations 9 4/6/2022
5.2. Accounting for inventory in the perpetual system Date Account title Dr Cr Jul Accounts payable (L–) 770 15 Cash ($770 × 0.97) (A–) 746.90 Inventory 21.00 ($770×0.03×10/11) (A–) GST clearing 2.10 ($770×0.03×1/11) (A–/L+)
Paid within discount period. 201044 - Retailing operations 10 4/6/2022
5.2. Accounting for inventory in the perpetual system
• Businesses allow customers to return goods that are
defective, damaged or otherwise unsuitable – purchase returns
• The seller may also deduct an allowance from the amount
the buyer owes – purchase allowances Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 4 Accounts payable (L–) 110 Inventory (110/1.1) (A+) 100
GST clearing (110/11) (A–/L+) 10
Returned inventory to seller. 201044 - Retailing operations 11 4/6/2022
5.2. Accounting for inventory in the perpetual system
• The purchase agreement specifies FOB (free on board) terms to
determine when title to the good transfers to the purchaser and who pays the freight
• FOB delivery point means the buyer takes ownership (title) to the goods at the delivery point
• FOB destination means the buyer takes ownership (title) to the
goods at the delivery destination point
• Freight in is the transportation cost to ship goods into the
purchaser’s warehouse (part of the cost of inventory)
• Freight out is the transportation cost to ship goods out of the
warehouse and to the customer (selling expense) 201044 - Retailing operations 12 4/6/2022 5.3. Sale of inventory
• After a business buys inventory, the next step is to sell the goods
• The amount a business earns from selling inventory is called Sales revenue (Sales)
• At the time of the sale, two entries must be recorded in the perpetual
system: one entry records the sale and the cash (or receivable) at
the time of the sale; the second entry records Cost of sales (debit
the expense) and reduces the Inventory (credit the asset)
• Cost of sales (COS) is the cost of inventory that has been sold to customers 201044 - Retailing operations 13 4/6/2022 5.3. Sale of inventory 201044 - Retailing operations 14 4/6/2022
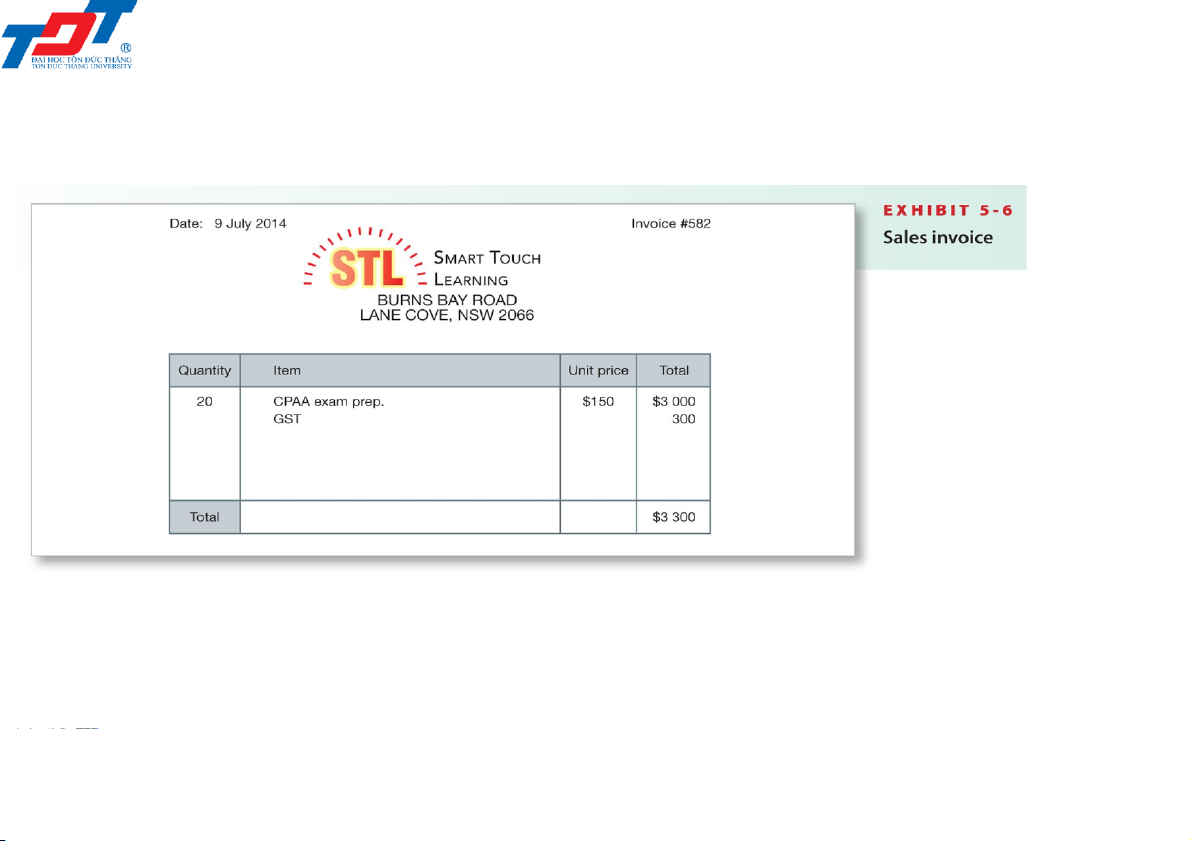
5.3. Sale of inventory: Cash sale Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 9 Cash (A+) 3 300 Sales revenue (3 300/1.1) (R+) 3 000
GST clearing (3 300/11) (A–/L+) 300 Cash sale. Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 9 Cost of sales (E+) 1 900 Inventory (A–) 1 900
Recorded the cost of goods sold. 201044 - Retailing operations 15 4/6/2022
5.3. Sale of inventory: Credit sale Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 11 Accounts receivable (A+) 5 500 Sales revenue (5 500/1.1) (R+) 5 000
GST clearing (5 500/11) (A–/L+) 500 Sale on credit. Jul 11 Cost of sales (E+) 2 900 Inventory (A–) 2 900 2 900
Recorded the cost of sales. Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 19 Cash (A+) 5 500 Accounts receivable (A–) 5 500 Collection on account. 201044 - Retailing operations 16 4/6/2022 5.3. Sale of inventory
• Sales returns and allowances and sales settlement discounts
decrease the net amount of revenue earned on sales
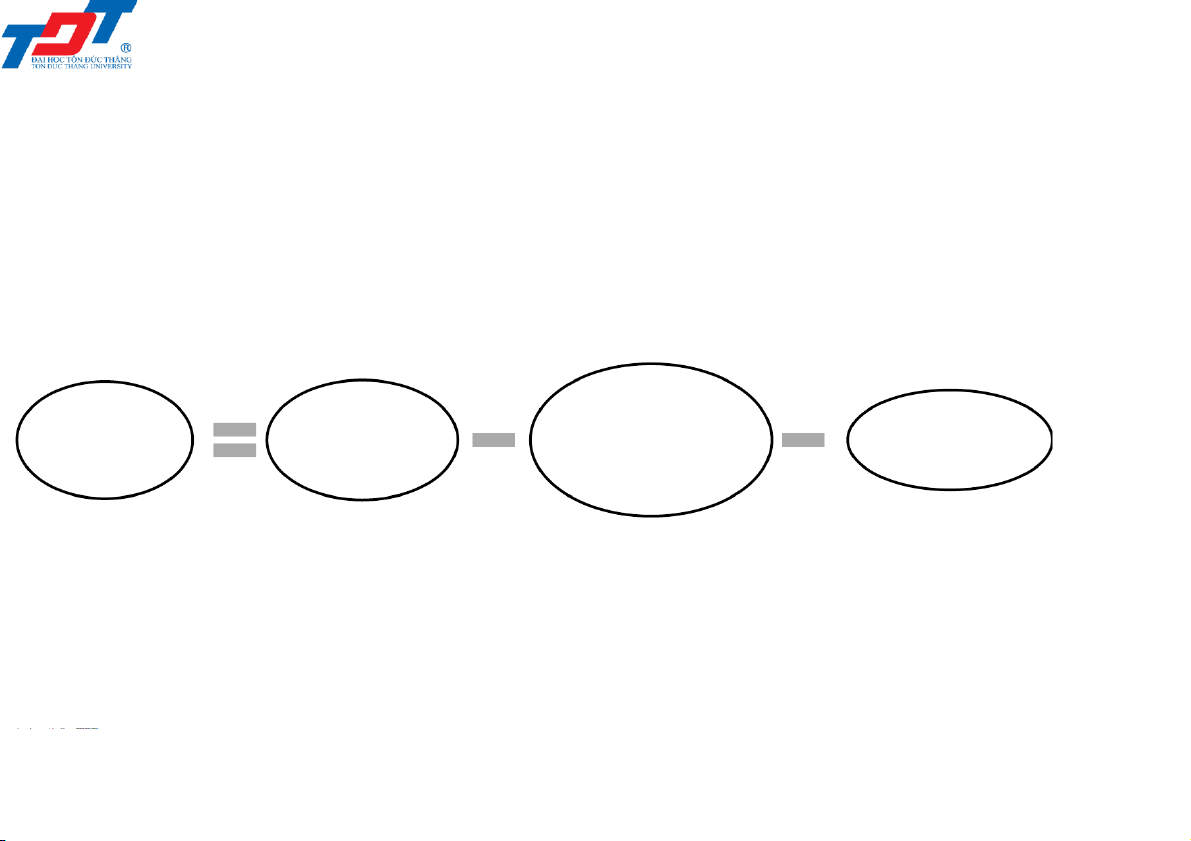
• Sales returns and allowances and Sales discounts are contra accounts to Sales revenue Net Sales Sales Sales sales returns and revenue discounts revenue allowances 201044 - Retailing operations 17 4/6/2022
5.3. Sale of inventory: Sales returns Date Account title Dr Cr
Jul 12 Sales returns and allowances 600 (660/1.1) (CR+)
GST clearing (660/11) (A+/L–) 60 Accounts receivable (A–) 660
Received returned goods. Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 12 Inventory (A+) 400 Cost of sales (E–) 400
Placed goods back in inventory. 201044 - Retailing operations 18 4/6/2022
5.3. Sale of inventory: Sales allowances Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 15 Sales returns and allowances 100 (110/1.1) (CR+)
GST clearing (110/11) (A+/L–) 10 Accounts receivable (A–) 110
Granted a sales allowance for damaged goods. 201044 - Retailing operations 19 4/6/2022
5.3. Sale of inventory: Sales discounts Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 17 Cash ($4 400 × 0.98) (A+) 4 312
Sales discounts ($4 400 × 0.02 × 10/11) 80 (CR+)
GST clearing ($4 400 × 0.02 × 1/11) 8 (A+/L–)
Accounts receivable (A–) 4 400 4 400
Cash collection within the discount period. Date Account title Dr Cr Jul 28 Cash ($7 150 – $4 400) (A+) 2 750 Accounts receivable (A–) 2 750
Cash collection after the discount period. 201044 - Retailing operations 20 4/6/2022




