



Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220 *Some definition:
+ Independent project: more than 1 promising project can be chosen; accepting or rejecting 1
project does not affect the decision of other projects
+ Mutually exclusive projects: only one of several potential projects can be chosen
+ Contingent project: acceptance of 1 project depends on the acceptance of other projects
Chap 5: Investment Decision Rules
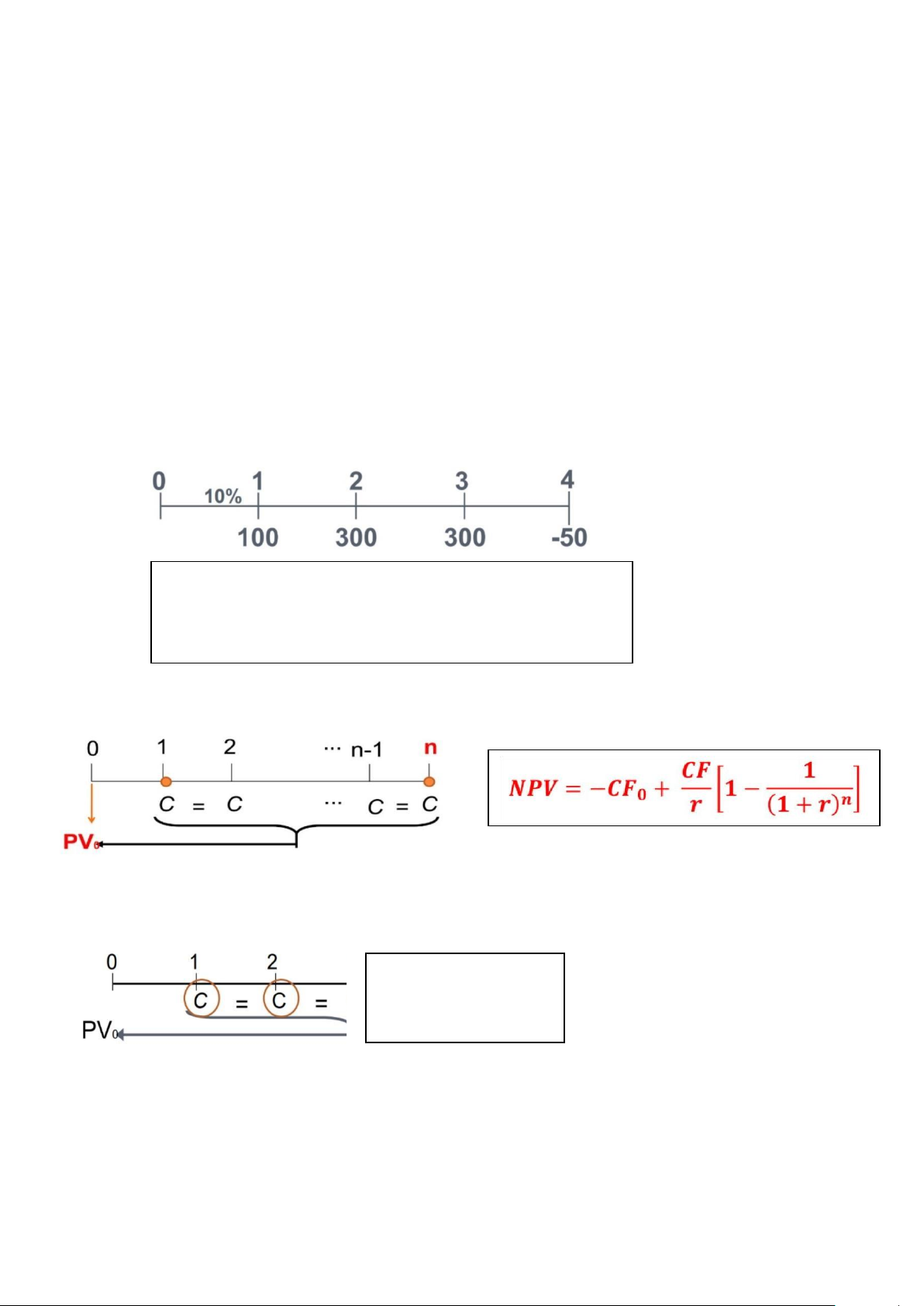
1. Net Present Value (NPV):
A goal of financial management is to create value for the stockholders. + If the cash flow uneven: 𝑪𝑭
NPV = -CF0 + 𝟏 + 𝑪𝑭𝟐𝟐 +…+ (𝟏𝑪𝑭+𝒓𝒏)𝒏 𝟏+𝒓 (𝟏+𝒓)
+ If all c ash flows are the same :
+ If the cash flow growing perpetuities: 𝑪𝑭
NPV = -CF0 + 𝟏 𝒓−𝒈
If the NPV is positive, accept the project lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220 #Note:
+ r : opportunity cost of capital, required rate of return, discount rate, WACC
+ Mutually exclusive projects: choose the highest NPV
+ If two projects have difference timeline Use EAA
2. Internal Rate of Return (IRR): is the return that makes the NPV = 0
Accept the project if IRR > Required of return (cost of capital) - Advantage:
+ Easy to know how much will receive (communication)
+ Marginal risk (high risk – high return) - Disavantage:
+ Financing project (the early CF is positive from raise capital)
+ IRR is just return don’t know whose belong to
+ Non-conventional cash flows (dòng tiền không quy tắc) => If the CFs changes sign,
will have more than once (IRR change overtime)
+ Mutually exclusive project (project with higher IRR may have lower NPV) NPV is more reliable
3. Payback Period: amount of time to recover initial investment - Disavantage:
+ Ignore TVM, remove CF after PP
+ Biased against long-term project
+ May note have positive in NPV
𝑹𝒆𝒎𝒂𝒊𝒏𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝒄𝒐𝒔𝒕 𝒕𝒐 𝒓𝒆𝒄𝒐𝒗𝒆𝒓
PB period = Years before cost recovery +
𝑪𝑭 𝒅𝒖𝒓𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒚𝒆𝒂𝒓
Accept if the payback period < a pre-specified length of time – maximum acceptable PB period (cut off point ( lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220
4. Profitability Index (PI): Measures value created per dollar invested #𝑵𝑷𝑽 PI =
𝑰𝒏𝒏𝒊𝒕𝒂𝒍 𝒊𝒏𝒗𝒆𝒔𝒕𝒎𝒆𝒏𝒕 •
Normally results in same accept-reject decisions as NPV (PI>1 NPV positive) •
When capital is scarce, accept projects with highest PI •
Cannot be used to rank mutually exclusive projects
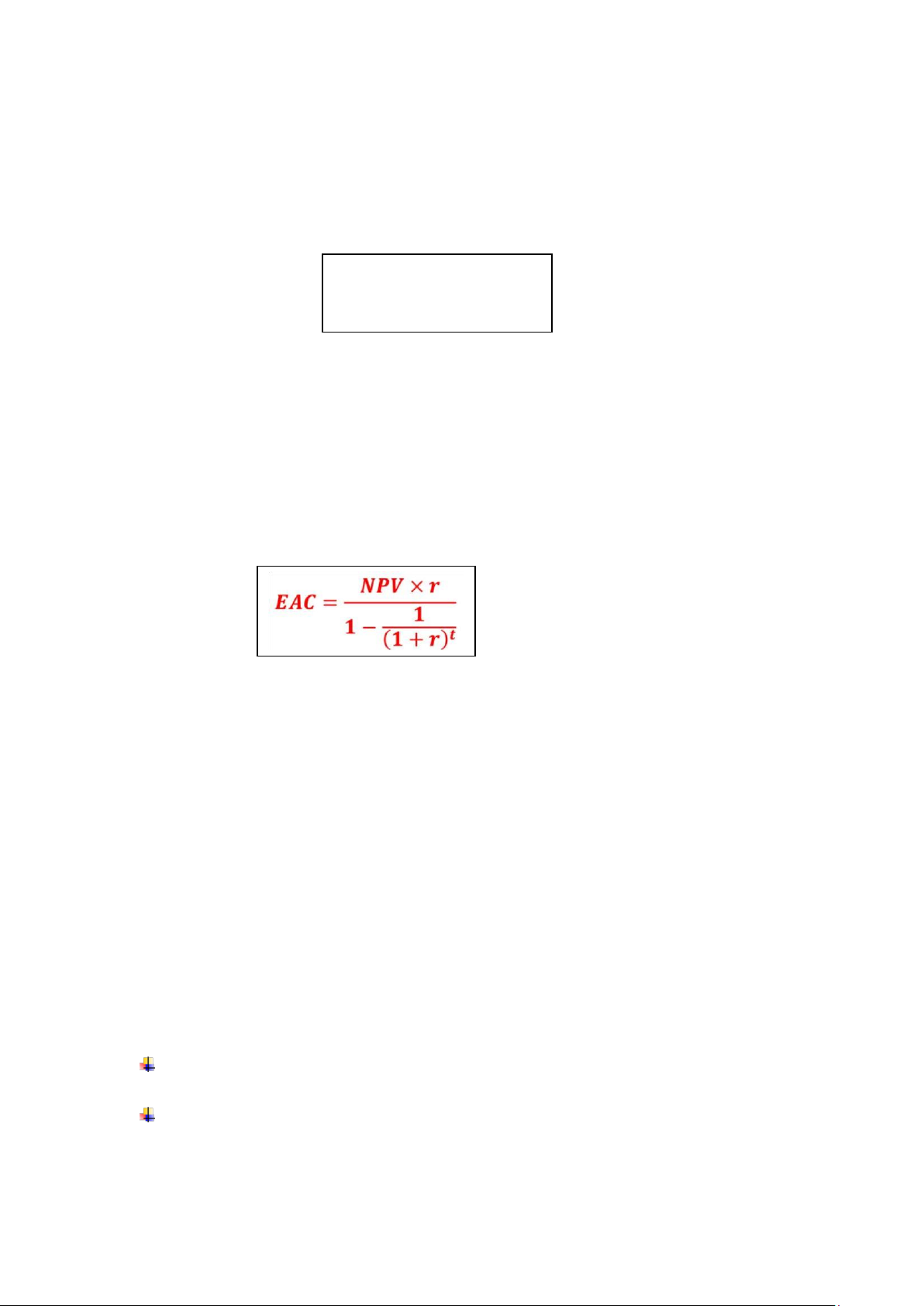
5. Equivalent Annual Cost/ Annuaity (EAC/EAA):
Compare when firm have 2 unequal projects (different time)
• Projects have negative CFs only (costs) and they are different projects lives.
• Replacement decisions (compute EAC for new equipment and compare it with
annual CFs from old equipment)
Revenue or profit (income): Choose highest EAA (NPV>0)
Cost: choose lowest EAC (NPV<0)
Chap 6: Capital Budgeting and Cash Flow Projection
*Incremental Cash Flow is the additional operating cash flow that an organization receives
from taking on a new project (difference between the cash flow with the project and the cash
flow without the project) included:
+ Initial investment: The total upfront cost to get the project going.
+ Opportunity cost: The value of the best alternative foregone.
+ Side-effects: The costs or revenues incurred due to the impact of the new project on existing projects.
Negative: For example, a new product causes customers to demand less of current products.
Positive: Resonance are created that increase demand for current products.
+ Operating cash flow: The cash related to directly operating the project. lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220
+ Change in working capital: The money the company invests to expand the project
(projected costs to run the project).
+ After-tax cash flow: Selling assets at their salvage value and incurring a gain/loss on assets
sold. This gain/loss creates a tax impact on the project's after-tax cash flow. Does not include:
+ Sunk costs: Costs that have already been incurred in the past and cannot be recovered
(market research costs, overhead costs like office rent…)
+ Interest expense or financing costs: These are separate expenses not directly related to the project's cash flow.
Step to calculate Cash Flow:
Step 1: Determine initial investment • Cost of new assets
• Machinery: included shipping cost, installation, modifying fee.. amum(không tính chi
&Nphếí thay mu đó là land thì pháy mới) ải lấy market value
• Opportunity cost: discount về present value hoặc làm cashflow của mỗi năm
If replacment machine (như bước 4) or sài tiếp máy cũ thì (machinery = book value)
Step 2: Determine operating cash flow (OCF) • Income method
+ Revenue – Cost (Fix & Variable) – Depreciation = EBIT (earning before interest and tax)
+ EBIT – TAX (EBITx%tax)= Net income OCF
= Net income + Depreciation t·ax shield • Depreciation method: + Straight line: Machinery -Book value Depreciation = Number of years + MARCRS:
Depreciation = Machinery x %depreciation (theo bảng)
Step 3: Determine Change in Working Capital
• Change in WC = New &OldWC requirement – NeweOld WC requirement
• WC năm cuối luôn bằng 0 (kết thúc project)
(Không phải bài nào WC cũng bắt đầu từ năm 0)
Step 4: Determine After Tax cash flow
• Book value: remaining value at the final of project lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220
+ Book value = Machinery – Total Depreciation
• Salvage value: selling price or market value
Taxes/Tax savings = (Selling price – Book value)*%Tax
+ Selling price > Book value (Gain)
After tax cash flow = Selling price – Taxes
+ Selling price < Book value (Loss)
After tax cash flow = Selling price + Tax savings Note:
+Nếu đề cho salvage nhưng không cho selling price Salvage value chính là selling price
+Nếu đề cho salvage value và selling price salvage value chính là book value
Step 5: Cash Flow for Project: cộng các dòng tiền ở các bước trên lại 1+2+3+4
Step 6: Decision criteria: Tính NPV, IRR, PI, PP, EAA theo yêu cầu của đề
Should or shouldn’t invest in the the project
Chap 7: Risk and Return 1. Rate of return: For bond: Coupon income + Price change Rate of return = For stock: Investment D1 + P1 - P0
Rate of return = Capital gains + Dividend yield = P0
2. Expected rate of return: based on the probability of possible outcomes. Note: R: possible return p: probability of the return
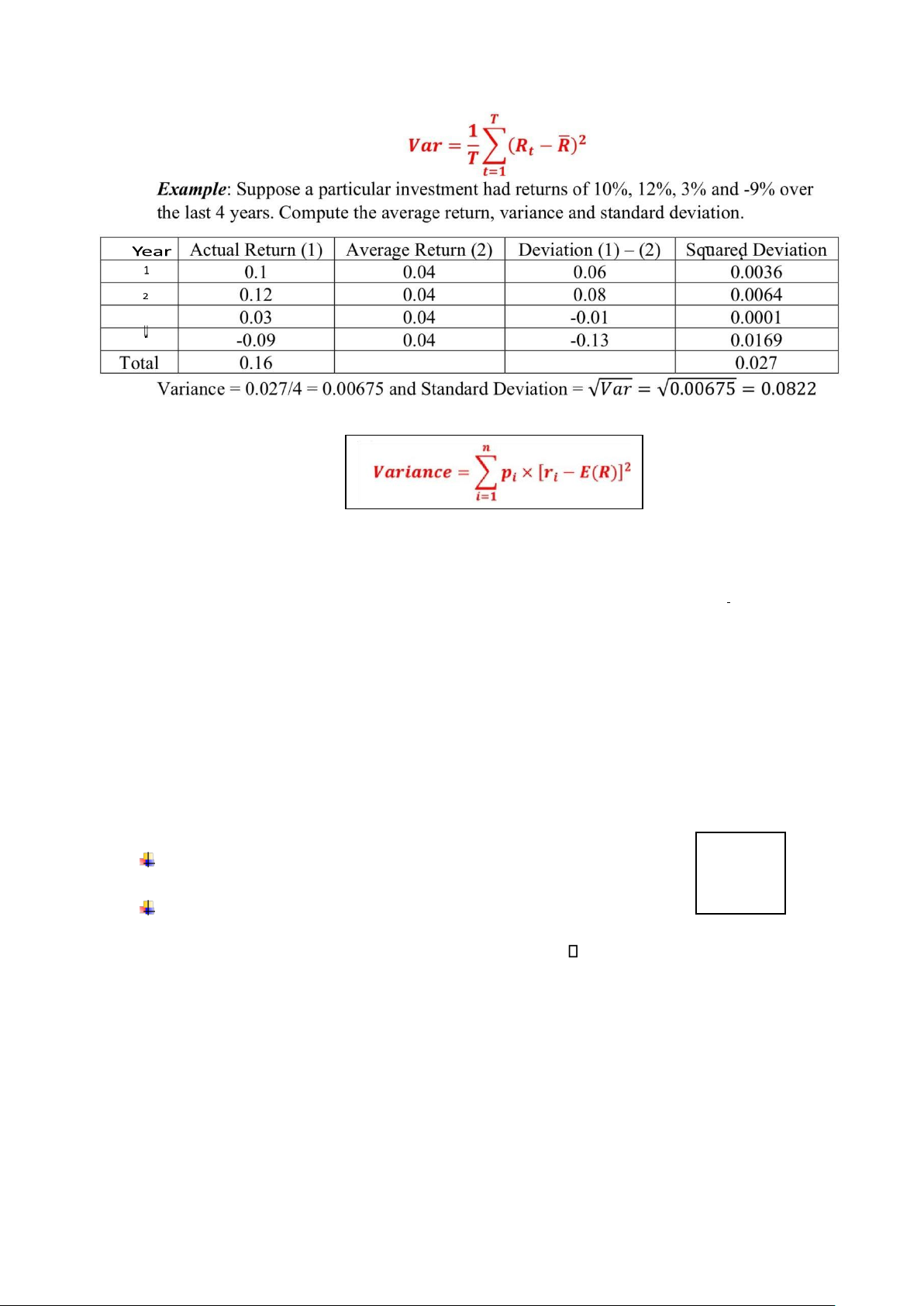
3. Measuring Risk: (standard deviation)
• Dạng 1: Đề không cho probability mà cho return theo các năm (có thể bấm máy): lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220
• Dạng 2: Cho probability (tính tay):
Example: You have been given the following probability distribution for the return on XYZ stock State of econoy Probability Return Boom 0.35 0.3 20% 2 Recovery 0.35 10% Recession -10%
What is the return standard deviation of XYZ stock?
Expected return = 0.35×20% + 0.3×10% + 0.35×(-10%) = 6.5%
Variance = 0.35×(0.2-0.065)2 + 0.3×(0.1-0.065)2 + 0.35×(-0.1- 0.065)2 = 0.016275
Standard deviation = √2 0.016275 = 12.76% 𝜎
Coeffcient of variation (CV): measure of the risk per unit of return CV =
So sánh các assets với nhau để xem nên invest vào asset nào r
• r bằng nhau, σ khác nhau: chọn lower σ (less risk)
• r khác nhau, σ bằng nhau: chọn higher r
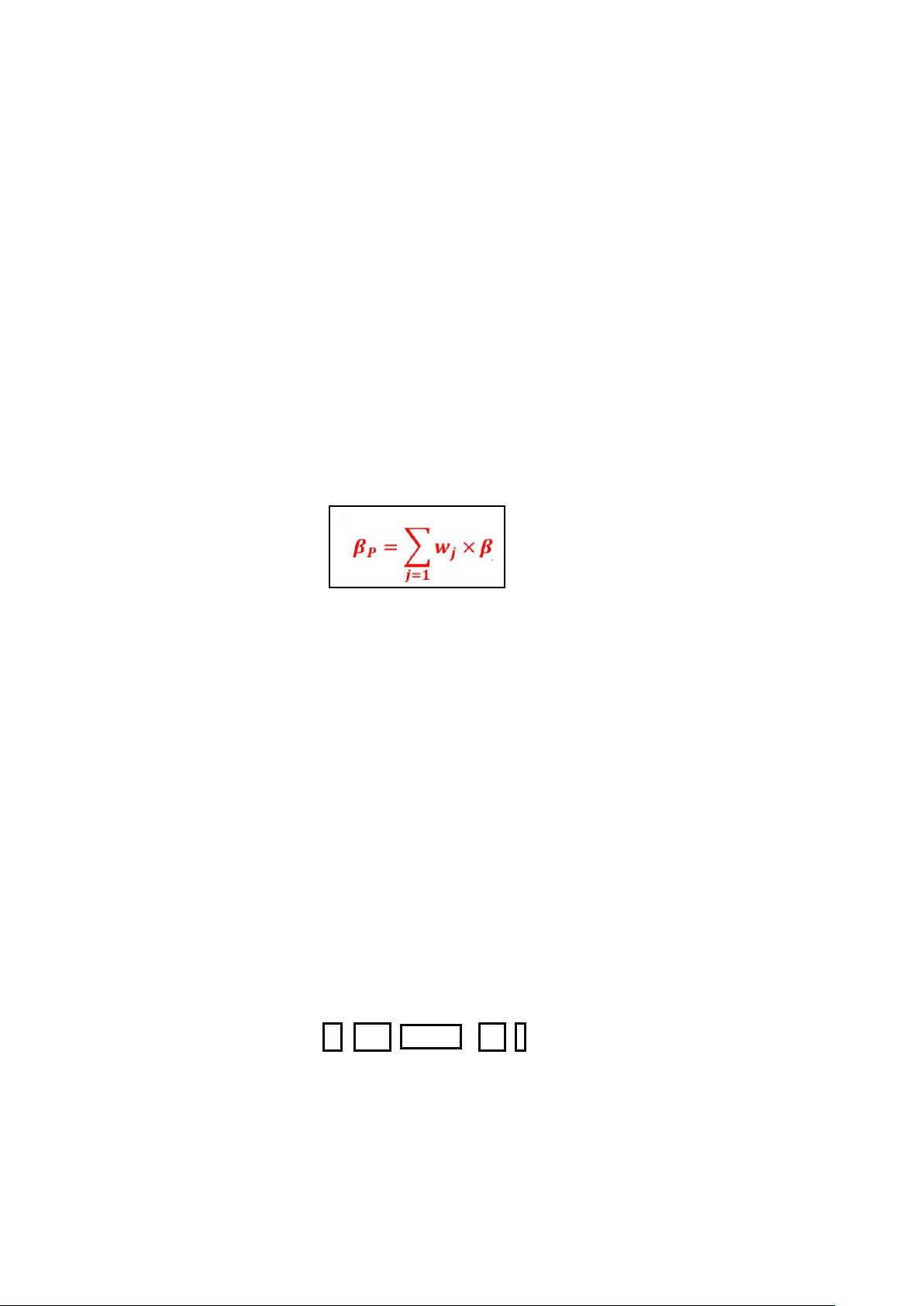
• r khác nhau, σ khác nhau: tính CV chọn lower CV (less risk per unit) 4. Portfolio
- The risk-return trade-off for a portfolio is measured by the portfolio expected
return and standard deviation.
- Portfolio weights: the proportion of the total investment in the portfolio invested in each asset. lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220 Example: State of econoy Probability Stock A Stock B Boom 0.4 20% 15% Recovery 0.3 10% 10% Recession 0.3 -10% 5%
What are the expected return and standard deviation for a portfolio with an investment of
$8,000 in stock A and $2,000 in stock B? & 5. Diversification:
Systematic Risk (market risk or non-diversifiable risk):
affect overall market and can not avoid
Mesure by Beta β độ risky của portfolio β < 1: less
market risk than the market (less-sensitve) β > 1: more
market risk than the market (more sensitve) β = 1:
market risk equal the market (market portfolio) β = 0:
no risk – risk free (How about β = -1?)
Unsystematic Risk (specific risk or diversifiable risk):
affect only that company and can avoid
6. CAPM (Capital Asset Pricing Model) Ri = RF + β(RM -RF) Note:
+ Ri: expected return on a security + RF: risk free + RM -RF: market risk premium lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220 + RM: market risk
Lưu ý: trong 1 portfolio tổng weight của 1 assets luôn bằng 1
RM=E(Rp) expected return on the market portfolio
Chap 8: Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)
1. Capital Struture and Cost of Capital:
• The mix of long-term debt and equity securities
• Leverage: the amount of debt used to finance a firm’s assets
• The return to an investor is the same as the cost to the company. 2. WACC
Capital Structure Market Value Cost of Equity Common stock Current price x Devidend growth model: number of stock 𝑫𝟏 outstanding + Re = + g 𝑷𝟎 + D1 = D0*(1+g)
CAPM: Ri = RF + β(RM -RF) Preferred stock Current price x 𝑫 number of stock R = outstanding 𝑷𝟎 Total fund Number outstanding = Par value Debt Bond
Market price x number Rb = YTM of bond outstanding
Selling at par: Rb = YTM= Coupon rate Bank Loan Book value Current interest rate on loan 𝑫 𝑬
WACC = x Rd x (1-T) + x Re 𝑽 𝑽 lOMoAR cPSD| 58562220 Note:
• E, D: Market value of Equity and Debt
• 𝑽 = 𝑬 + 𝑫 : Total market value of the firm
• 𝑅D, 𝑅E : Cost of Debt, Cost of Equity D E • Weights: WD = , WE = V V